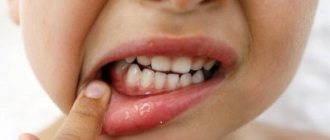
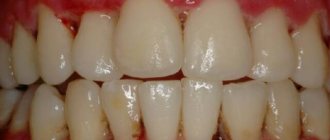
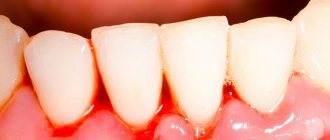
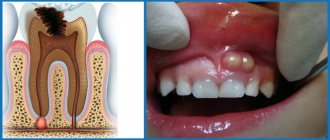
Healthy gums in a child have a pale pink color, but when inflamed they become bright red, swelling is observed, accompanied by pain and bleeding. With the development of gum disease, body temperature may rise and a strong bad breath may appear.
If you notice the appearance of these symptoms in your baby, try to seek help from specialists as soon as possible. An illness that is not treated in time can lead to the inflammatory process spreading to the bone tissue, causing more serious problems. In this case, as a rule, you have to say goodbye to one or more teeth.
Symptoms of gingivitis in babies
The course of the disease in children is most often observed in an acute form, which is easy to determine:
- When brushing your teeth, a lot of blood remains on the brush;
- soft tissues become bluish due to damage due to bacterial infection;
- painful sensations occur when biting food or drinking drinks;
- swelling, redness and discharge of serous contents.
If you have one or more symptoms, you should contact your dentist immediately. Only professional and high-quality treatment provided on time can prevent chronic inflammatory processes in the oral cavity.
In its extreme form, destruction of tooth enamel and damage to teeth by caries is possible, and, as a result, further complex therapy, up to extraction and prosthetics. Seeing a doctor as quickly as possible at the first symptoms of inflammation will help avoid complications.
Remember that mild gum disease responds quickly to treatment.
Treatment of gums in children and prevention of inflammation
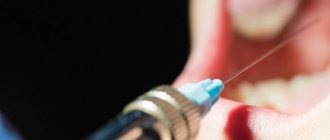
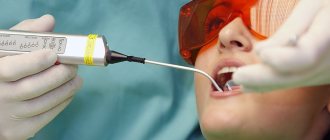
In general, experts recommend starting treatment by cleaning teeth from stone and removing plaque. For children, it is better to choose ultrasonic cleaning, which is absolutely painless and guarantees maximum effect.
After this, the doctor usually prescribes rinsing the gums with special solutions for 10 days. To consolidate the positive dynamics, children over 3 years old can be prescribed gels for the treatment of gums. Herbal infusions - chamomile, eucalyptus, sage, used as rinses, have proven themselves quite well in the treatment of gums in children.
Not least important is the sanitation of the oral cavity. Be sure to make sure that all carious teeth are treated, this will avoid gum infection in the future.
To ensure that your child’s gums do not become inflamed again, watch how he brushes his teeth and choose the right toothbrush and toothpaste. If you have problems with gums, it is better to choose a softer brush for your baby, and the toothpaste must be age-appropriate. It would not be amiss to use immunomodulators, for example, “Immunal”, “Amiksin” or “Sodium Nucleinate”. These drugs help improve immunity, which also has a beneficial effect on the condition of the teeth and oral cavity.
Prevention of the disease - careful care of teeth and oral cavity. Brush your baby’s teeth 2 times a day with Asepta toothpaste from the Baby, Kids or Teens series. These products clean teeth well, do not damage the enamel, saturate it with calcium, keeping your smile snow-white.
Types of gingivitis in children
So that the doctor can create the most complete picture, there are several classifications of the disease. Each type has its own clinical characteristics, methods of care and arises due to various factors. After treatment, strict monitoring is required to avoid relapse. This is especially true for children, because they are not able to carry out hygiene and other procedures on their own, so all the doctor’s recommendations fall on the parents.
Catarrhal
It is associated with age-related changes. Most often occurs during primary eruption or in the presence of a concomitant infectious disease. It can be recognized by pain when eating and bleeding when cleaning. An unpleasant odor and loss of taste sensitivity appear. The child may complain of burning and itching in the mouth. On examination, you can see redness.
Marginal
Most often observed in children with abnormal dentition and malocclusion. Because of this, it may be impossible to thoroughly clean all hard-to-reach places where plaque begins to accumulate and pathogenic microflora multiply. Bleeding is noticeable, and in the early stages there is virtually no pain or redness. The attachment of the gums to the teeth is not disturbed. In advanced cases it can become chronic.
Desquamative
The appearance is associated with hormonal disorders and most often occurs during puberty. May occur against the background of other diseases:
- lichen planus;
- pemphigus vulgaris;
- permanent infections.
In the early stages, other than bleeding during cleaning, no symptoms are observed. During the transition period, the gums swell greatly and acquire a bright shade and shine. In complex and advanced cases, purulent ulcers and erosion appear.
Hypertrophic
A complicated form that occurs against the background of a long-term inflammatory process that has entered the chronic stage. The redness will be pronounced, it is impossible to miss or not notice it during examination. The taste of food will be practically lost due to constant bleeding and the taste of blood in the mouth.
Ulcerative
Appears if there has already been primary inflammation in the oral cavity - stomatitis. Concomitant factors include severe hypothermia and decreased immunity. At the same time, the child’s condition worsens sharply; he feels pain in his gums and cannot swallow. Due to the inflammatory process, not only the gum tissue, but also the tonsils can swell. Upon examination, you can see ulcers with a serous putrefactive coating.
Atrophic
It often manifests itself as a medical error during poor-quality orthodontic treatment. An abnormal attachment of the frenulum may also be a provoking factor.
The child's condition will be stable, there are practically no signs of inflammation. You may notice only mild redness, exposed teeth and increased sensitivity to hot foods.
Causes of gum inflammation in children
The most common cause of gum disease in children, according to experts, is poor oral hygiene. Teach your baby to brush his teeth correctly and instill in him the habit of doing it regularly, and the likelihood of encountering inflammatory processes in the gums will become much lower.
If you are sure that everything is fine with the hygiene of your child’s teeth and gums, it makes sense to look for other reasons. It can be:
- insufficient intake of minerals and vitamins into the body;
- hormonal disorders;
- hereditary diseases and pathologies in the activity of other organs: the digestive system, cardiovascular system, etc.;
- malocclusion;
- wearing braces or other orthodontic devices;
- mouth breathing;
- damage to the gums by sharp edges of teeth with carious cavities;
- decreased immunity due to infectious diseases.
In any case, only a doctor can correctly understand the symptoms and prescribe treatment, so you should not put off visiting the dental clinic for too long.
Diagnosis of gingivitis
The diagnosis should be made by a doctor in a dental clinic; only through a visual examination will he be able to determine the status of the disease and differentiate it from many others, which at an early stage may manifest the same symptoms.
The main clinical signs by which a dentist can make a diagnosis are:
- the presence of erythematous formations at the gum edge;
- looseness, separation of soft tissues from the dentition, the appearance of pockets larger than 3 mm;
- when pressed with a dental spatula, exudative and bloody discharge is observed, in some cases with a putrid odor;
- obtaining the result of smears to determine the pathogen.
The last point is one of the most important in making a diagnosis and prescribing adequate procedures. Depending on the type of bacteria that caused the disease, various antibiotics and antiseptics can be used to speed up recovery. Also, after collecting an anamnesis, based on diagnostic results, the doctor needs to identify the root cause in order to further prevent the risk of relapse.
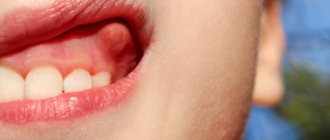
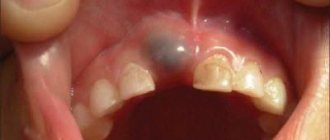
Symptoms accompanying the appearance of a fistula:
- pain, which, however, may not be present;
- mobility of the tooth next to which there is a hole;
- swelling and redness of the affected gum;
- purulent discharge from the hole.
It is difficult and excruciating for children to endure pain, so if these signs are detected, you should seek medical help immediately. Doctors at Family Dentistry know how to work with young patients, and many years of experience guarantee a correct and painless solution to the problem.
At the clinic, the doctor will first identify the cause of the disease. They may be:
- Insufficient oral care. The consequences are caries, and in the absence of proper treatment - pulpitis on one or more teeth. Later, the inflammation descends into the ligamentous tissue of the tooth, where a cavity with pus is formed;
- inflammation of the gums;
Diseases in which the gums become loose
Looseness is a characteristic symptom of gum tissue diseases. They can be recognized by the presence of other signs.
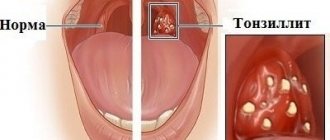
| Disease | Features of the flow | Characteristic signs |
| Gingivitis | Only the gums become inflamed. Teeth and periodontal tissues are not affected. The disease is often diagnosed in children, pregnant women and adolescents | • soreness in the gums; • bleeding; • swelling and change in color of the mucous membrane; • appearance of ulcers (with ulcerative form). |
| Periodontitis | The supporting apparatus of the tooth, the ligament between its root and bone, is destroyed. The disease is more often diagnosed in adults | • exposure of the cervical area of the teeth; • inflammation of the lymph nodes; • the appearance of periodontal pockets and pus in them; • change in position and loosening of teeth. |
Treatment methods
How to treat loose gums? To cope with the problem, an integrated approach is needed. Often the scheme for eliminating the disease consists of the following actions:
- Professional teeth cleaning, during which the doctor will remove dental plaque. He will also teach hygiene rules.
- Antiseptic treatment of the oral cavity. The doctor will prescribe solutions based on substances that have an antimicrobial effect - chlorhexidine, hydrogen peroxide, furatsilin, etc.
- Use of local agents. As prescribed by the doctor, ointment or gel is applied to the gums. Effective agents are, for example, Metrogyl Denta, Solcoseryl, Tantum Verde, Miramistin.
If the patient experiences pain, it can be relieved with the help of Analgin, Nimesil or Ibuprofen.
Separately, they also determine what to do to eliminate the cause of inflammation. For example, if the prosthesis is not installed correctly, it is removed and anti-inflammatory therapy is carried out. Next, a new structure is installed, which is made taking into account the characteristics of the patient’s jaw.
How is fistula treated?
If the tooth is milky, the fistula indicates the development of periodontitis and often the doctor will suggest removing the tooth. However, removal is not the only option. In some cases, it is possible to save the tooth - it all depends on the stage of the inflammatory process and the location of the source of inflammation.
If the inflammatory process is advanced, immediately after tooth extraction, the doctor will prescribe antibiotics. Under no circumstances should you deviate from the medication regimen prescribed by your doctor. To avoid causing problems with the gastrointestinal tract, you should ask a specialist what medications your child can take to support intestinal microflora. Medicines "Linex" or "Hilak Forte" may be prescribed.
With permanent teeth everything is more complicated. The Family Dentistry doctor will definitely try to save the tooth, using treatment and restoration methods that correspond to the cause of the disease. You will have to undergo several procedures in the dental chair.
There are doctors who, as an alternative to extraction and “in order to preserve the dentition,” offer the silvering method. But this method of treatment is ineffective for fistula. The specialists at Family Dentistry are against this method of “treatment” and will never prescribe procedures that are dangerous for a small patient.
Possible complications
Have you noticed that your gums have become loose? Make an appointment with your doctor. A prolonged inflammatory process provokes exposure of the neck of the tooth. This often entails the development of cervical or subgingival caries.
Lack of proper treatment increases the risk of inflammation of periodontal tissue. If left untreated, periodontitis may develop. As a result of this disease, not only the gums, but also the alveolar process, which holds the tooth root, decreases. Teeth become mobile, lose their functionality and may fall out.