What is gumboil of baby teeth?
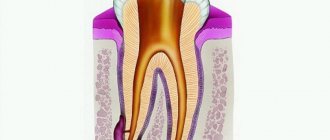
Flux is an inflammation of the tissues surrounding the bone (periosteum).
The pathology is acute and is often accompanied by a purulent process, which, in the absence of proper therapy, spreads to other tissues and parts of the face. In the medical literature, the periosteum is called the periosteum, so the disease is also called periostitis. Pathology often occurs in children due to the anatomical and physiological characteristics of the child’s body. So, unlike permanent teeth, a child’s baby teeth are more porous. The pulp of primary teeth is located closer to the gingival surface. In addition, the root canals for baby teeth are wider than for permanent teeth. All these circumstances contribute to the spread of the infectious and inflammatory process. Pyogenic bacteria multiply better in such conditions, which is why flux develops quickly in a child.
Treatment of abscesses and abscesses in a child
Depending on the nature and cause of the abscess, the doctor will choose the appropriate method of treating the lump on the gum. Most often this is:
- opening and cleaning of pus;
- treatment of caries or removal of a tooth if it is severely damaged and cannot be restored.
In this case, an abscess over a baby tooth can often be eliminated only with the removal of the tooth itself. This is an undesirable process, but it may turn out that it is impossible to fix the problem in any other way.
When treating ulcers in children, the doctor is always guided by the fact that soon the milk teeth will be replaced by molars. The formation of a cyst or abscess over a baby tooth can affect the future molar, so sometimes the decision to remove a tooth is actually advisable.
After the procedure, the child is prescribed antiseptics for home use.
Causes of gumboil in children
Inflammation of the periosteum in a child often develops against the background of pulpitis. This is an inflammatory pathology of the pulp - loose tissue that fills the dental cavity. The pulp also contains nerve fibers, blood and lymphatic vessels. Often pulpitis in children develops rapidly, after which it also affects the periosteum tissue.
Let's consider the main factors contributing to the appearance of flux in children:
- Poor oral hygiene . Children are unable to maintain proper dental and oral care. Food particles remain on the surface of the teeth and in the interdental space, which leads to the proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms.
- Weak immunity . The child’s immune system is just developing and is not able to cope with infectious agents that enter the body. For this reason, children often get colds and flu. But other infectious diseases, including flux, cannot be ruled out.
- Gum injuries . Children under 2-3 years old put various objects in their mouth. This often injures the gums, making them vulnerable to pathogenic microorganisms. In addition, sometimes the child brings the infection along with the object.
- Tooth extraction . There is a danger of a child developing gumboil when teeth are removed if there are infections in the oral cavity. For example, with gingivitis or tonsillitis, bacteria enter the site of an extracted tooth, which provokes the development of an infectious-inflammatory process in the periosteum. Therefore, pathologies such as tonsillitis, pharyngitis or adenoids should be considered as risk factors.
Reasons for appearance
The appearance of such a disease in childhood is most often associated with the penetration of infection into the tissue, which provokes the development of a purulent process. There may be several reasons for this:
- Deep caries. It is known that baby teeth are less dense than permanent teeth, so the occurrence of even a minor carious defect can cause deep penetration of infection in the shortest possible time.
- Young children have a habit of tasting almost everything around them. This causes injury to the mucous membranes of the gums. And if pathogenic microorganisms get into such a wound, then due to the characteristics of the child’s body’s immune response, the likelihood of periostitis occurring is very high.
- It is quite difficult for children aged 2-4 years to carefully maintain oral hygiene and brush their teeth correctly. The accumulation of plaque and food particles in the gum pockets can cause inflammation with subsequent spread deep into the tissue.
- Sometimes flux appears after tooth extraction in the presence of a source of infection in the mouth: carious cavities, purulent gingivitis, sore throat. Pathogenic microorganisms easily penetrate deep into the gums through an open wound and, against the background of reduced immunity, cause severe inflammation.
- It is extremely rare, but periostitis can occur as a complication of purulent inflammation in a different location, when the infection enters the periosteum with blood.
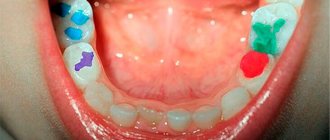
How to recognize flux in a child
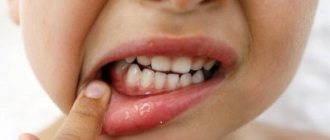
Flux is a lump that often appears on the gum. In most cases, the abscess comes out on the front of the jaw, since the bone wall in this area is thinned, and there is also a significant number of blood and lymphatic vessels there. Sometimes flux appears on the palate.
Symptoms accompanying flux include:
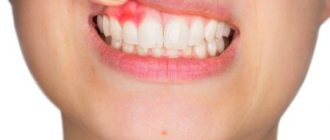
- the appearance of an abscess on the gum;
- aching pain in the affected area;
- swelling of the cheek (it noticeably increases in size);
- increased body temperature;
- enlargement of lymph nodes located near the inflammatory process.
Young children who cannot yet talk (or talk about their symptoms) experience restlessness, tearfulness, and decreased appetite. Carefully examine your baby's mouth. It is quite possible that the cause is gumboil gumboil, which requires medical intervention.
Main symptoms and manifestations
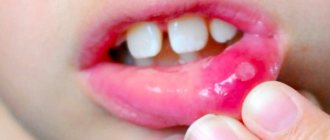
In the first days of development of the inflammatory process, the child complains of moderate pain in the mouth. The gums at the site of inflammation swell slightly and become hyperemic. Children under 3 years of age may become capricious and refuse to eat. Most often, this stage of the disease goes unnoticed, and parents attribute its first manifestations to the child’s bad behavior.
As the purulent process develops, the child’s condition becomes more severe. The pain becomes intense and pulsating. A purulent focus forms on the gum in the form of a small whitish formation on a red, swollen background. Due to active inflammation, significant swelling of the soft tissues of the face develops. If flux appears on the upper jaw, then such swelling can be located not only on the cheek, but also spreads to the parotid region and the eye. If the flux is localized in the lower jaw, then tissue swelling may also affect the cervical region.
The baby’s general condition suffers and the temperature rises (sometimes to quite high numbers), the child complains of weakness and lack of appetite.
Complications of flux in children
Periostitis in a child does not require delay in treatment. Naturally, the acute course of the pathology cannot be ignored, and usually parents immediately seek help from a doctor. At the same time, chronic flux is often not noticed.
Doctors at the Israeli Dental Center in Kyiv strongly recommend not to delay your visit to the doctor. Otherwise, flux leads to a number of consequences that are much more difficult to treat. Some of the consequences of flux are completely irreversible. Let's take a closer look at the complications that arise if this pathology in a child is not treated:
- Acute purulent process . Do not allow large abscesses to develop. They are dangerous, especially for a child. With the development of a large abscess, purulent masses affect not only the gingival tissue and periosteum, but also other facial tissues. In severe cases, an abscess may break through on the outside of the cheek. In this way, a fistula (hole) is formed, from which purulent masses flow.
- Edentia . The purulent masses during gumboil sometimes reach the rudiments of permanent teeth, destroying them. This means that after the baby teeth, the molar will no longer appear.
- Sinusitis . If there is no treatment, the gum gum gum sometimes spreads to the maxillary sinuses. This is how purulent sinusitis develops - a difficult treatment that often requires hospital treatment.
- Phlegmon . If the abscess that develops against the background of flux in children is limited in nature, then phlegmon has no boundaries. This is a serious complication that affects different parts of the face - muscles, bones, blood vessels and other elements. Phlegmon is characterized by a rapid increase in body temperature up to 42 degrees, which threatens the life of the child.
- Sepsis . When pathogenic microorganisms that provoke flux in a child enter the bloodstream, the risk of developing sepsis increases. This is a blood infection in which the inflammatory process becomes generalized - it covers various organs and parts of the body.
- Osteomyelitis . This is a purulent-necrotic process occurring in the jaw bones. This complication is extremely rare and develops against the background of long-term flux in a child, when the pathological process from the periosteum passes into the bone tissue.
Treatment
Treatment of flux in children should be carried out strictly under the supervision of a doctor. At the same time, treatment tactics for a one-year-old baby and a 7-year-old child may differ due to the fact that before the natural change of the primary bite, it is possible to remove a temporary tooth, which is extremely undesirable before the age of 5-6 years.
In such cases, it is rarely possible to do without surgery. Quite often it is necessary to resort to a surgical method of treatment - opening the flux with complete removal of all purulent masses and drainage of the resulting cavity. This allows you to both relieve acute pain and prevent the re-formation of gumboil.
But surgical treatment is one of the stages of therapy. After visiting the dentist, the child’s parents should continue treatment at home, which will include taking an antibiotic prescribed by a doctor, rinsing the mouth with antiseptic solutions and using traditional medicine.
Treatment at home
In the first few days after visiting the dentist, when pain may still bother the baby, it is necessary to take anti-inflammatory drugs (paracetamol, ibufen), which help both relieve pain and help the inflammatory process subside as quickly as possible.
An important point in home treatment is the use of antiseptic solutions for treating the oral cavity. The dentist will tell you what exactly to rinse the child’s mouth with, but we will only present possible treatment options that can be used even in a small child.
- Aqueous solution of chlorhexidine. A ready-made pharmaceutical preparation is used, which is used to rinse the mouth 3-4 times a day (after meals and before bedtime). It has a powerful antiseptic effect, but does not irritate the mucous membranes of the mouth.
- Furacillin solution. You can prepare it at home (1 tablet per 0.5 liters of water) or buy a ready-made product. Rinse your mouth up to 5 times a day (it is advisable to do this after eating).
- Miramistin is destructive to microorganisms and relieves inflammation well. It is recommended to rinse your mouth with 10 ml of solution 3-4 times a day. However, the drug cannot be used before the age of three.
A child should rinse his mouth with any of the above products strictly under the supervision of adults in order to avoid accidents. The course of treatment should continue until all manifestations completely subside and the purulent cavity heals.
Treatment with folk remedies
Traditional medicine recipes complement traditional treatment well. However, you need to be careful with such methods in very young children, and for treating children under 2 years of age it is better not to use them at all.
- Soda solution. This remedy has a good anti-inflammatory effect. A teaspoon of dry baking soda powder is dissolved in a large cup of warm boiled water and allowed to rinse the child’s mouth 3-4 times a day after eating. The effect of treatment can be enhanced with iodine by adding a few drops to the rinse solution.
- Propolis tincture also perfectly relieves inflammation and has an antiseptic effect. To treat the oral cavity, dissolve 5 drops of tincture in 200 ml of warm water and rinse the mouth 2-3 times a day.
- Herbal decoctions. Medicinal plants such as chamomile, calendula, and string are natural antiseptics and quickly relieve even severe inflammation. They allow both to cure the disease itself and to prevent the development of its complications. Decoctions are prepared daily, for which 2 tablespoons of a mixture of herbs are infused in half a liter of boiling water. Rinse your mouth with the resulting decoctions 4-5 times a day until complete recovery.
Homeopathy treatment
Homeopathic medicines can also be used in addition to primary treatment. You cannot try to cure gumboil in a child using homeopathy alone, since such remedies only play a supporting role. All prescriptions should be made only by a homeopathic doctor.
First aid for flux: what can and should be done at home
Let’s make a reservation right away: treatment of this pathology should only be carried out by a doctor. Non-traditional home therapy methods are unacceptable in this case. Not only are they ineffective, but they can also harm the child. But the most dangerous thing is that by giving preference to home treatment methods, precious time is lost, which increases the risk of complications.
Home treatment methods are relevant while waiting for a visit to the doctor. For example, if you are unable to see a dentist immediately, then before visiting the clinic, use the following recommendations:
- Antiseptic drugs . Contact your doctor and find out which medications should be used to rinse your mouth. The doctor will recommend antiseptic solutions such as chlorhexidine, furatsilin and others.
- Soda and salt . If antiseptic drugs are not available, you can rinse your mouth with a solution of soda and salt. It is not difficult to prepare such a solution. For 250 ml of boiled warm water, take one teaspoon of salt and soda. You should rinse every 30-40 minutes.
- Medicinal herbs . A number of medicinal plants have pronounced anti-inflammatory, antibacterial and sedative effects. Such herbs include chamomile, sage, lemon balm, St. John's wort and oak bark. The mentioned medicinal herbs are used both individually and in the form of collections.
Treatment of flux in a child at the CIS
At the Center of Israeli Dentistry on the Left Bank of Kyiv, a team of pediatric dentists performs the full range of treatment measures for diseases of the teeth, gums and oral cavity. We have a special approach to small patients that allows us to get rid of fears and anxiety before medical procedures.
When treating flux in a child, the first thing the doctor does is diagnose it. This includes an examination of the oral cavity, interviews with parents and the child, and an x-ray examination. An x-ray shows the extent of damage to teeth and tissues. Only after diagnostic procedures does the doctor decide on the patient’s treatment tactics.
Flux on the gums: surgical treatment
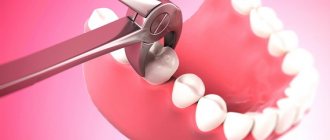
Flux in children and adults is mainly treated surgically, like all purulent formations. The abscess needs to be opened and the wound cleaned. Surgical operation to remove flux consists of the following steps:
- Pain relief . First of all, the doctor administers local anesthesia so that the child does not feel pain or discomfort.
- Removing flux . After administering the anesthetic, an incision is made with a scalpel. The doctor removes the pus, after which a drainage is placed - a small rubber strip. This is necessary so that the wound does not heal prematurely, since within 3-4 days the remains of purulent masses still flow out of the wound.
- Tooth extraction . Typically, teeth in the area of purulent lesions should be removed. Removal of teeth due to gumboil is practiced more often in pediatric dentistry, since children's milk teeth will be replaced by permanent teeth. In some cases, the doctor decides to save a baby tooth if this will have a positive effect on the formation of the child’s bite.
Flux on a child’s gums: what to do after surgery
Therapeutic measures for flux are not limited to surgical intervention. No less important is the postoperative period, during which the small patient is prescribed antibiotics and antiseptics for rinsing the mouth. Even if the child feels well, be sure to take the prescribed medications, adhering to the dosage and regimen.
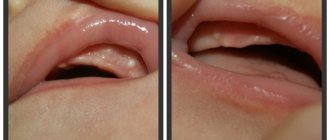
These treatment measures usually end successfully. Symptoms that bother a child with flux disappear (fever, pain). Within a few weeks, the lump also resolves, since there is no longer an abscess in it.
Prevention measures
It's no secret that it is easier to prevent any disease than to treat it later. The same is true with periostitis. To reduce the risk of developing the disease described, it is very important:
- control how thoroughly the child brushes his teeth;
- take him to the pediatric dentist every six months for a preventive examination;
- competently treat all emerging infectious pathologies;
- follow the recommendations given by the doctor after tooth extraction.
These simple rules allow you to keep baby teeth healthy until permanent teeth begin to emerge in their place.
What NOT to do with flux
Let's look at some things and procedures that absolutely cannot be done when dealing with flux, as this will only worsen the situation:
- Do not use warm compresses or heat the affected area. This will only stimulate the growth of bacteria.
- You should not self-prescribe medications, especially antibiotics. Uncontrolled use of antibiotics is fraught with serious side effects, in particular, the development of bacterial resistance to the drugs.
- Do not take aspirin until the wound has healed from treatment. Aspirin is a blood thinner that can slow the healing process and promote bleeding.
Consult a doctor if, after removing the gum gum, your child still has intense pain 6-8 hours later.
Consequences of untreated flux:
- abscess (abscess) - the formation of a purulent sac;
- phlegmon - an extensive inflammatory process after the rupture of an abscess;
- osteomyelitis of the jaw - inflammation of the tissues of the jaw bone;
- inflammation of the sinuses of the skull - the sphenoid, maxillary and frontal sinuses are involved in the pathological process. Sometimes the infection penetrates into the brain tissue.
Important: specialists from the “Smile” clinic network recommend starting treatment as early as possible. The faster the inflammation is stopped, the less effort will be required to eliminate the problem and restore the patient’s health.
Flux prevention
Flux on the gums is easier to prevent than to treat. Unfortunately, it is impossible to insure against the disease, but following some recommendations will reduce the likelihood of developing gumboil:
- Teach your child to maintain oral hygiene.
- Visit your dentist twice a year for a checkup.
- Monitor the condition of your teeth: prevent the development of caries and other dental pathologies. At the first symptoms, consult a doctor.
- Choose a toothbrush with soft or medium bristles.
- Limit your consumption of sweets - the main cause of tooth decay.
In the clinics of the Center of Israeli Dentistry in the Dnieper (metro station Livoberezhnaya) and Darnitsky (metro station Osokorki, Poznyaki) areas, your child will be provided with all the necessary services for the treatment, diagnosis and prevention of dental diseases. Dentistry has long been painless, and we follow modern standards of treatment. Your child will feel at ease and comfortable with our doctors.