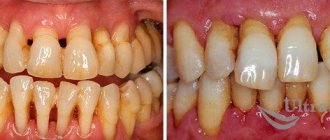
Periodontal disease is a term that reflects non-inflammatory systemic damage to the periodontal tissue (periodontal tissue) and this condition is very rare. Periodontium is the tissue that supports the tooth. These include bone, gums, mucous membrane and ligaments connecting these tissues. Periodontitis is an inflammatory process in the tissues surrounding the tooth. Periodontitis is the second most common disease of the dental system after caries.
Periodontitis is an inflammatory disease that causes destruction of the supporting apparatus of the tooth. With periodontitis, the infection enters the space between the tooth and the gum and begins to destroy the ligament of the tooth root with the bone. According to WHO experts, 100% of the adult population of the Earth and 80% of children show some signs of periodontitis. Periodontitis is one of the main causes of tooth loss in older age.
Causes of periodontal disease and periodontitis
The causes of periodontal disease are completely unknown. Hereditary predisposition plays a certain role. Local factors, such as the impact of microorganisms on the periodontium, can only aggravate the process.
Periodontitis can be a consequence of the action of pathogenic microorganisms that accumulate in dental plaque and tartar, tooth trauma, caries, poorly performed dental prosthetics or restoration, and violations of the integrity of the tooth. Significantly increase the likelihood of developing periodontitis, poor oral hygiene, crooked teeth and malocclusion, dietary habits, and a decrease in the general immune reactivity of the patient’s body.
The main cause of gum disease is bacterial plaque.
which is a sticky, colorless film that constantly forms on the teeth. If plaque is not removed, it hardens and forms a rough, porous build-up called tartar. As the disease progresses, toxins can lead to the destruction of the tissues that support teeth. A space is formed between the tooth and the gum - a periodontal pocket, which is filled with plaque. The bone that supports the teeth is subject to constant destruction. Periodontitis can develop after inflammation of gums and gingivitis.
How is recession treated?
Treatment of cervical exposure depends on the degree of development of the process, which our doctors determine during diagnosis and examination of the patient. There are two ways to correct the situation.
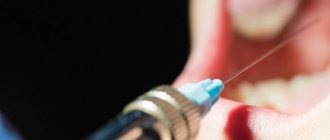
- Drug treatment (conservative) includes professional oral hygiene, local and general therapy with anti-inflammatory drugs, including injections. Our dentist will select gels for the treatment of inflammation and swelling of the gums, antiseptic rinsing solutions, and if there is pus, he will prescribe antibacterial medications.
- Surgical treatment: we can restore soft tissues using special membranes, which we install in the area where the cervix is exposed and cover with a bandage for a week. The gums return to their previous height and tissues become healthier. In addition to membranes, patient tissue can be used, for example, from the palate. The process goes like this:
- local anesthesia is administered;
- The implant surgeon implants tissue from the palate into the area of the tooth root or places a membrane in this area;
- applies stitches;
- schedules regular visits to monitor the progress of gum healing and restoration.
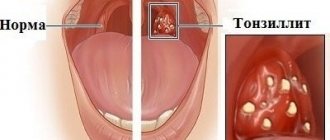
Symptoms characteristic of periodontal disease and periodontitis
Unfortunately, periodontitis tends to develop slowly.
. At the initial stage, periodontitis does not cause pain or other sensations. The disease develops asymptomatically, gradually destroying the periodontium. Therefore, patients, as a rule, are in no hurry to see a doctor. Periodontitis can manifest itself differently depending on the stage, and often begins with bleeding gums. At this stage, the process is still reversible; the periodontal ligament, which surrounds the tooth and connects it with its neighbors, is not affected, so that the chewing pressure is distributed evenly throughout the entire dentition and there is no overload in the periodontal tissues.
Without treatment, the process penetrates deeper
and destroys the periodontal ligament, a periodontal pocket appears, in which, in turn, plaque and stone are deposited and stimulates further progression of the process. Periodontal tissues (surrounding the tooth - gums, bone tissue) are destroyed, and the tooth begins to wobble, losing bone support in the jaw. At this stage, a change in the position of the teeth, their pathological mobility, the appearance of gaps between them, impaired chewing function, and traumatic occlusion may also be observed.
The initial period of the disease is characterized by itching, throbbing in the gums, mobility of teeth, discomfort when chewing, and bad breath. As the process progresses, the supporting apparatus of the tooth becomes looser, tooth mobility increases, the necks of the teeth become exposed and become more sensitive. The lack of adequate treatment measures at this stage leads to the loss of practically healthy teeth.
During an exacerbation, sharp throbbing pain, fever, malaise and weakness occur. There is marked redness and swelling of the gums, and pus is released from the periodontal pocket. Treatment is complex and aimed at stabilizing the pathological process.
What it is?
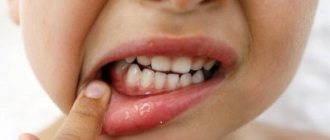
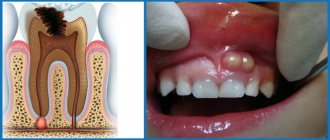
Gum recession is a process of soft tissue atrophy in which the gums recede, exposing the surfaces of the necks of the teeth. Visually, patients feel that their teeth have become longer, but thinner at the base, the spaces between them have increased, and the gums have become smaller. In addition to the loss of aesthetics, recession manifests itself with unpleasant symptoms:
- the gums are swollen, inflamed and bleeding;
- hypersensitivity appeared - pain when eating hot, cold, spicy and sour foods;
- discomfort when brushing teeth;
- when touching the tongue, a “step” is felt at the edge of the gum;
- bad breath.
All these signs indicate that the neck of the tooth is exposed. This requires immediate attention to the dentist, since if left unchecked, the recession will lead to very disastrous consequences. Because of it, the risk of developing caries increases, and it can affect the roots of the teeth. The gums peel off from the teeth, which leads to the formation of periodontal pockets where food debris, plaque, and pus accumulate. And this already leads to inflammation and gum disease, increased mobility and, ultimately, tooth loss.
Treatment of periodontitis
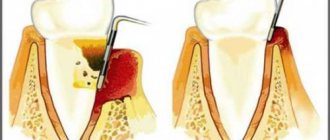
The disease requires urgent intervention by a dentist. Treatment of periodontitis includes non-surgical and surgical methods. The first (professional hygiene) is used in the early stages of the disease and for prevention. They consist of removing tartar (mechanically and ultrasound) and polishing the tooth surface, followed by treating the crown and root of the tooth with special brushes with fluoride-containing protective varnish.
There is a procedure for removing deep tartar called curettage: the doctor removes deposits using special hooks, excavators, curettes (closed curettage), or, if surgery is required, by cutting the gums (open curettage). The goal of surgical methods is to eliminate gum pockets (a consequence of bone tissue resorption) so that the tooth regains stability.
Why do my gums recede?
The reasons for receding gums are varied:
- atrophic gingivitis - a disease that causes bleeding, inflammation and swelling of the gums;
- periodontitis - destruction of soft tissues and ligaments that hold the tooth in the socket, resorption of bone tissue and receding gums;
- cervical caries - carious lesions of tooth tissue near the gums;
- bite defects - such features of the bite as crowding of teeth that were not corrected in time with the help of an orthodontist;
- incorrect home hygiene - including irregular cleaning, too much brushing, insufficient plaque removal, and so on;
- bruxism - grinding teeth during sleep;
- gastrointestinal diseases that lead to changes in the acidity of saliva;
- age-related changes.
What can a doctor do?
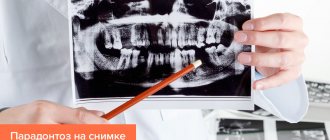
Only the dentist and hygienist with a simple examination
can determine the presence or absence of periodontal disease. The essence of the study is to measure the periodontal pocket (for periodontitis) using a special probe and an x-ray. This method allows the doctor to quickly and painlessly assess the condition of your gums, propose a treatment plan to prevent further development of the disease, and develop a special self-hygiene regimen that will suit your specific situation.
There are many options for straightening your teeth/bite at home:
- try to tie the teeth with a thread so that they come together (here most often we are talking about the upper central incisors. In adolescence, there is often a gap between them, called a gap among ordinary people, and in the dental community - a diastema).
It is absolutely forbidden to make such attempts to straighten your teeth! The thread can, in a completely incomprehensible way, “go” under the gum, from where it will have to be removed surgically. Not the most pleasant thing to do.
— Or here’s an option on how to straighten your teeth
at home: if you constantly press on the tooth with your finger (or tongue), you can correct it by placing it in the desired position. The exercise is questionable, because effective tooth movement most often requires constant pressure. And it is impossible to walk all day with a finger in your mouth or with an unnatural position of your tongue.
And it's not worth it. The orthodontist will still do it more effectively. Sometimes patients also say that they suspect (or already know that they have) an incorrect bite, and therefore they try to put the lower jaw themselves (since it is the only movable bone in the skull) in the correct position. Of course, this requires constant self-control, motivation and just patience. Probably funny. Not for those who put so much pressure on their jaw all day long and keep thinking endlessly: “Well, how else can I straighten my teeth? Damn, something isn't working! Well, HOW else?”
Alas, this tactic is also ineffective, because in order to change the bite at home, most often it takes a long time to “retrain” the muscles to their new position and configuration, and for this to happen, you need to maintain them in the appropriate tone 24 hours a day
. Perhaps even the most disciplined patient cannot do this, because when we eat, talk, sleep, and finally, we are not able to control these moments 100%. Of course, this is not as dangerous and cartoonish as twisting threads around your teeth or constantly holding your finger in your mouth, but it doesn’t bring much benefit either. Contact an orthodontist - this is the best option of all of the above.
To understand the risk you are exposing your teeth to when trying to put them in order on your own, we bring to your attention a short but VERY interesting video - HOW TEETH MOVE. The truth is that only one tooth is not crooked; changes to one degree or another affect both the teeth adjacent to it and the entire dentition, and this can be very, very difficult for a non-specialist to understand.
Gum recession has many causes:
- Poor oral hygiene (read the article What does poor oral hygiene lead to and how to properly care for your teeth?)
- Improper hygiene (too vigorous brushing, incorrect brushing movements , hard brush, poorly selected toothpaste, etc.)
- Gingivitis and periodontitis ( about the causes , methods of prevention and treatment of these diseases in the article An effective method of treating periodontitis using a Doctor Smile diode laser)
- Periodontal disease ( non-inflammatory disease of the tissues surrounding the tooth, leading to their atrophy)
- Bad habits (biting seeds, nuts, etc.)
- Tissue injury from fillings and orthopedic structures
- Allergic reactions (for example: to the frame of metal-ceramic crowns )
- Cervical caries and the consequences of its unsuccessful treatment (when the edges of the filling lie on the gum)
- Orthodontic problems: shape and position of teeth, malocclusion, short frenulum of the lip (read more about this in the article Why frenuloplasty is needed)
- General condition of the body, chronic diseases (diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, diabetes, etc.)
- Age-related changes in the body
more about the causes of gum recession from the video “Gum Recession: Causes and Consequences.”
Poor oral can be either the sole cause of gum recession or aggravate other factors that cause the disease.
Therefore, professional and home oral hygiene is an integral part of the prevention and treatment of gum disease.
Watch the video “Gum Health Matters” about how oral hygiene affects gum health.
Unfortunately , it is impossible to completely avoid gum recession, since this is part of the age-related changes in the human body.
There is little chance of returning the gum “to its place.” Even a painful operation to close the recession using a mucosal graft may not be successful.
Prices for Prevention
| Name of service | Price |
| Professional oral hygiene Along with daily home hygiene, professional teeth cleaning is a mandatory procedure for the prevention of dental diseases. Find out what procedures professional oral hygiene includes | 6800 ₽ |
| Ultrasound removal of tartar (one tooth) Hard plaque is removed with an ultrasonic scaler. See how teeth are cleaned with ultrasound | 240 ₽ |
| Removal of soft dental plaque using the Air Flow device Soft pigmented dental plaque is removed by air-abrasive cleaning. See how plaque is removed with the AirFlow device | 3100 ₽ |
| Coating one tooth with fluoride varnish Bifluorid, Multifluorid After applying the varnish, a protective film is formed on the teeth, and the enamel is saturated with useful minerals. The procedure is effective for the prevention of caries and the treatment of dental hypersensitivity. | 280 ₽ |
| Coating one arch with fluoride varnish Bifluorid, Multifluorid | 2500 ₽ |
| Deep fluoridation (remotherapy) This procedure restores the natural structure of the enamel. Once saturated with essential minerals, the enamel regains its strength. Find out how remotherapy reduces tooth sensitivity and protects against caries | 3500 ₽ |
| Hygiene lesson with manual skills training During the lesson, the doctor will teach you how to properly care for your mouth to keep your teeth and gums healthy. See what poor oral hygiene can lead to and how to properly care for your teeth | 550 ₽ |
| Preventive examination once every 6 months If you regularly attend preventive examinations, the dentist-therapist will promptly recognize the first signs of caries and treat it at the initial stage, preventing the development of pulpitis and periodontitis. Sign up for a preventive examination | free for regular customers |
Share the link:
- Click here to share content on Facebook. (Opens in a new window)
- Click to share on WhatsApp (Opens in new window)
orthodontics, orthopedics, periodontology, prevention, articles, therapy, surgery topics: gingival margin, home dental hygiene, closed curettage, exposed roots, exposed cervixes, open curettage, professional teeth cleaning, remotherapy, gum recession, fluoridation
What can be done to prevent and prevent the development of gum disease:
- Visit the dentist regularly so as not to miss the first signs of the disease, and if detected, determine the true causes of gum recession and carry out the prescribed treatment.
- Take proper care of your teeth at home.
- As prescribed by your doctor, do professional hygiene and remineralizing therapy to strengthen your teeth enamel. Read more about these procedures in the articles Why do you need professional dental hygiene and What causes tooth sensitivity and will remotherapy help me?