October 24, 2017
Periodontitis and periodontal disease are diseases of the periodontium - the complex of tissues around the tooth and the ligaments that hold it in the alveolus or socket. Despite the fact that these problems are fundamentally different both in clinical manifestations and in terms of treatment, many patients often confuse them. Moreover, often even doctors pass off one disease as another.
It is noteworthy that periodontitis occurs in 95% of the adult population, and periodontal disease occurs in only 2%. The first occurs most often due to dishonest or insufficient oral hygiene, but the second is usually associated with general diseases of the body.
UltraSmile.ru offers to understand what “periodontitis” and “periodontal disease” are, and what is the difference between the two diseases.
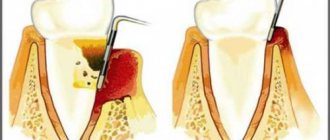
Periodontal disease (photo on the left) and periodontitis (photo on the right)
Periodontitis is an inflammatory disease of the periodontium1, simply an inflammation of the gums, as well as the ligaments that hold the tooth in the socket. Periodontal disease is a systemic periodontal disease, that is, it occurs without inflammatory processes and is characterized by progressive gum atrophy. But in order to see the full picture of the differences, let's look at the comparison table.
| Periodontitis | Periodontal disease | |
| Gum condition | The gums become inflamed, become scarlet, bleed, swell and noticeably increase in size. | There are no inflammatory processes - the gums become white-pink and shrink in volume |
| Presence of bleeding gums | At first it occurs due to mechanical impact (food, brush), over time it becomes permanent | Absent |
| Swelling of the gums | Present | Absent |
| Presence of gum pockets | Present. Their depth varies up to 3.5 mm in the initial stage and up to 5-6 mm in severe form | None |
| Tooth mobility | Appears as the disease progresses, occurs due to inflammation of the ligamentous apparatus | Missing for a long time, but if the disease is not treated, the tooth can still be lost |
| Exposing teeth | Only in severe forms, when voluminous periodontal pockets are formed | Present – due to the reduction in gum volume, the necks and roots of the teeth are exposed, the teeth visually lengthen |
| Bad breath | Present, caused by the process of decay of food debris in the gum pockets | Absent |
| Main causes of the disease | Neglect of good oral hygiene, advanced gingivitis | Age-related changes, cardiovascular diseases, diabetes mellitus |
| Main consequences of the disease | Rapid loosening of the tooth, its loss, bone tissue atrophy and difficulties during implantation. The disease cannot be cured completely; it often recurs if it has reached a chronic generalized stage, when all teeth on one or both jaws are affected | Violation of the aesthetics of a smile, since the teeth are exposed and gaps between them are visible in the gum area. Teeth can also be lost, but the process of gum atrophy is slower than with periodontitis. In addition, teeth quickly decay, since the exposed parts have thin enamel that is not able to protect them from external influences |
| Features of treatment | Removal of dental plaque, anti-inflammatory therapy, cleansing and removal of gum pockets, treatment with ultrasound and Vector, Varius devices, platelet injections, splinting of teeth using thread or clasp dentures (in the absence of some elements of the dentition) | Physiotherapy to restore nutrition to the gums, treatment of the underlying disease that caused periodontal disease, surgery to correct the position of the gums |
Among other things, in both cases it is important for the patient to prepare for long-term treatment, which may not be limited to one month. You will also have to maintain strict control on your part, taking an active part in getting rid of the problem: strengthen oral hygiene, follow all doctor’s recommendations, purchase floss, rinses and irrigator, take medications, make applications from gels and medications.
Features of periodontitis treatment
Treatment of periodontitis directly depends on the degree of tissue inflammation - the more advanced the disease, the more complications, the more difficult and lengthy the treatment. Doctors strongly recommend starting the fight against periodontitis in the early stages, when the damage is localized and affects only a few teeth. Then the problem can actually be eliminated without further consequences.
Important! No matter how bitter the truth is, it is almost impossible to get rid of diseases in the chronic stage, this applies to both periodontitis and periodontal disease, forever; you can only temporarily bring the patient’s condition into remission. In most cases, loose teeth will have to be removed and ways to restore them will have to be found. Today it is not difficult to do this - it is possible to acquire a new smile in 3 days, even in conditions of acute bone atrophy, with the help of progressive implantation methods that allow you to restore teeth for a long time (one might even say lifelong) in just a couple of days.
Treatment consists of mandatory cleaning of teeth in periodontal pockets - bacteria and plaque accumulate in them, which provoke tissue inflammation. For these purposes, ultrasound and hand instruments are used; gum curettage can also be performed - this is a surgical operation in which the gum is cut, peeled off from the surface of the tooth, and all foci of inflammation are cleaned out from under it. Next, the mucosal flap is returned to its place, and the gum is sutured. This procedure is necessary in case of large periodontal pockets formation, if they cannot be cleaned in any other way.
Cleaning periodontal pockets
With an integrated approach, splinting of mobile teeth can also be carried out - a thin fiberglass splint is placed on them, as well as healthy neighboring ones on the inside. It unites teeth into groups and allows you to fix loose ones in a motionless state. At the same time, anti-inflammatory therapy, rinsing and physiotherapy are prescribed. If several teeth are missing in the oral cavity, clasp removable dentures can serve as a splint - their design contains a metal base and hooks, so the denture is quite solid and reliably keeps the teeth from loosening. And at the same time it allows you to close the “holes” in the row.
Photo: splinting teeth
Patients should remember that it is impossible to cure periodontitis - you can only delay the process of tooth extraction and temporarily relieve tissue inflammation. If your teeth are very loose, the best option would be to remove them and replace them with implants - this will achieve a more lasting treatment result.
Splinting teeth for periodontitis
Stomatitis
This is a group of diseases characterized by inflammation of the oral mucosa with hyperemia, swelling, and an increase in the amount of mucus in the oral cavity.
Depending on the severity and depth of the lesion, even ulcers or foci of necrosis may form in the oral cavity, sharply disrupting the general condition - fever, weakness, anxiety, refusal to eat. There are many causes of the disease: mechanical, chemical, thermal, bacterial factors. Often the cause of the disease in infancy is contaminated nipples, toys and other objects that fall into the child’s mouth. Stomatitis often develops as a result of infectious diseases (measles, scarlet fever, influenza, whooping cough, etc.). The mucous membrane of the oral cavity acquires a bright red color, becomes swollen, and tooth marks are visible on the mucous membrane of the cheeks and tongue. Saliva becomes viscous and viscous. The mucous membrane is covered with a whitish coating. The tongue is dry, swollen, often with a brown tint, chewing is painful. The duration of the disease is from 1 to 3 weeks, the prognosis is favorable.
A general preventive rule for children and adults is to maintain good oral hygiene.
Features of periodontal disease treatment
But the treatment of periodontal disease is fundamentally different from the treatment of periodontitis. This is due to the absence of gum pockets, tissue inflammation and tooth mobility. With periodontal disease, the gums, on the contrary, are reduced in volume due to metabolic disorders, so all efforts should be aimed at improving the nutrition of the mucous membranes.
For this purpose, a whole range of measures is used aimed at stabilizing the physiological parameters of not only the periodontium, but also the entire organism as a whole. Massages and physiotherapy are performed to stimulate local blood circulation, the patient is prescribed vitamin complexes (including in the form of injections into the gums). It is also recommended to periodically apply protective compounds to exposed areas of the teeth, which will strengthen the enamel and reduce susceptibility to bacteria.
Massage gums using an irrigator
The editors of the portal strongly recommend that you sound the alarm already when you encounter a symptom of bleeding gums. Otherwise, get ready for a long treatment, or better yet, opt for implantation, because in most cases with periodontal disease, this is the only option that will help you return to a healthy and happy life.
Periodontitis and periodontitis: are they the same thing or not?
Despite sounding similar, periodontitis and periodontitis are two completely different diseases. They are provoked by various factors and differ in symptoms, consequences for the body, and approach to treatment.
Understanding the difference between periodontal and periodontal disease will help to understand the nature of these diseases.
- Periodontium is a complex of soft and hard tissues that hold the tooth in the alveolus (tooth socket). It includes the gums, tooth cement, periodontal ligaments, periosteum, and bone tissue of the alveolar process.
- The periodontium is a layer of connective tissue that is located between the cement of the tooth root and the bone layer of the alveolar ridge.
That is, the periodontium is the entire supporting and retaining apparatus of the teeth, while the periodontium is one of its components.
Periodontal diseases. What gum diseases are there?
Notice
: Undefined variable: post_id in
/home/c/ch75405/public_html/wp-content/themes/UltraSmile/single-item.php
on line
45 Notice
: Undefined variable: full in
/home/c/ch75405/public_html/wp-content /themes/UltraSmile/single-item.php
on line
46
Rate this article:
( 2 ratings, average: 3.00 out of 5)
gum disease
1 Beloklitskaya G.F. Clinical forms of generalized periodontitis and their significance for its differentiated therapy.
Gingivitis
An inflammatory process that causes swelling and tenderness of the soft tissues. If not treated in a timely manner, the problem worsens and becomes chronic.
The main causes of gingivitis:
- insufficient oral hygiene;
- thermal or chemical burns;
- use of certain medications;
- unbalanced diet (insufficient amount of vitamins in food)
- smoking;
- some infectious diseases;
- gastritis;
- ulcerative processes in the digestive system;
- caries.
Forms and types of gingivitis
Depending on the clinical situation and the nature of the development of the disease, acute and chronic gingivitis are distinguished. Acute gingivitis
manifests itself in the form of classic signs of the disease: redness, swelling and bleeding of the gums.
Chronic gingivitis
develops more quietly, without pronounced signs, but gradually leads to the growth of gum tissue (hyperplasia), which entails partial and complete coverage of the surface of the tooth crown by the gum.
Prevention measures
By following simple rules you can reduce the likelihood of serious oral diseases:
- Brushing your teeth at least 2 times a day after eating;
- Using dental floss and mouthwash;
- Balanced diet;
- Rejection of bad habits;
- Visit the dentist at least once every six months.
A few words about the importance of periodontitis prevention
Treatment of periodontitis is a complex and lengthy process, sometimes it can last for several years. And naturally, carrying out the necessary procedures will require you not only time, but also significant financial expenses. Both time and money costs can be avoided if you prevent the development of periodontitis.
To effectively prevent the development of periodontitis, dentists advise following the following simple recommendations:
1. Regularly carry out high-quality dental and oral hygiene at home and from time to time - professional teeth cleaning in dentistry.
2. Contact the dental clinic at the first signs of not only periodontitis, but also caries, and undergo treatment on time.
3. Monitor your diet: it must be balanced and your menu must contain foods containing vitamins and minerals.
4. If you lose even one tooth, do not postpone the prosthetic procedure.
5. Regularly undergo preventive examinations at the dentist.
Also, for effective prevention of periodontitis, you should avoid stressful conditions, strengthen the body’s immune system, and protect your gums from injury. Follow these simple rules, and then you won’t have to waste time and money on periodontitis treatment.
Calculate the cost of treatment by taking a short test in 20 seconds!
Do not delay your treatment, because in this matter time plays against us.
Prosthetics for periodontitis
Prosthetics for periodontitis are necessary in cases where a person has no dental units in his rows. Carrying out prosthetics allows you to prevent the displacement of teeth in rows and completely restore the correct chewing load in the oral cavity. Prosthetics is the final stage in the conservative treatment of periodontitis and must be carried out before surgery (if the operation is planned in the general treatment plan).
For prosthetics in the treatment of periodontitis, it is extremely important to choose the right prosthesis. It must be of high quality and modern, otherwise it will not be possible to stop the process of bone atrophy.
Diagnostics
- Taking anamnesis;
- dental examination with measurement of the depth of periodontal pockets (periodontogram);
- orthopantomogram (OPTG), CT;
- rheoparodontography (assess the tone of blood vessels);
- Schiller-Pisarev test;
- microbiological studies (PCR);
- blood tests (general, sugar).
Differential diagnosis of periodontitis is carried out with gingivitis, eosinophilic granuloma of the jaw, periodontal changes in Lefebvre-Papillon syndrome. What examination methods will be required depends on the form and severity of the disease.
Symptoms of periodontal disease depend on the stage and characteristics of the disease.
The first stage is characterized by a complete absence of complaints and symptoms, despite the fact that pathological changes are already slowly beginning to occur in the periodontal structure. The second stage is manifested by a decrease in the interdental septa. The patient complains of blood, itching and unpleasant pain, and possible food debris getting stuck between the teeth. The third stage is the complete and irreversible destruction of the periodontal space. The main complaints are severe bleeding even with minor mechanical impact, pain, the appearance of ulcers and erosions, pathological mobility of teeth progresses, and possible tooth loss.
Periodontitis: what is this disease?
Before moving on to considering treatment methods for periodontitis, it is worth finding out what kind of dental disease it is and why it appears. In dentistry, periodontal tissue is the tissue that tightly surrounds the roots of the teeth and holds the tooth itself in its socket. When an infection penetrates into the periodontium, an inflammatory process begins in the tissue, which leads to the occurrence of periodontitis. Treatment of periodontitis should be started immediately, however, the disease cannot always be recognized in a timely manner and independently, since it can develop completely asymptomatically. It is for this reason that it is recommended to undergo regular examinations by a dentist: a specialist will determine the signs of periodontitis and treatment of the disease will be as effective as possible.
Calculate the cost of treatment by taking a short test in 20 seconds!
Do not delay your treatment, because in this matter time plays against us.
The main cause of periodontitis is pathogenic microorganisms that penetrate into the deep layers of the periodontium, however, there are factors that contribute to the appearance of the disease and accelerate the process of its development. These factors include:
- Untreated or advanced gingivitis;
- Autoimmune diseases (diabetes mellitus, HIV);
- Bite defects;
- Increased tone of the jaw muscles;
- Injuries to soft tissues of the oral cavity;
- Poorly performed dental procedures: prosthetics, fillings;
- Stressful and depressive conditions, the presence of bad habits;
- Poor or irregular oral and dental hygiene;
- Some gastrointestinal pathologies.
The listed factors will complicate the treatment of periodontitis, and therefore it is recommended to eliminate them before starting a course of therapy, which means that for effective treatment of periodontitis you will need to visit not only the dentist, but also specialists in other areas of medicine.
Symptoms
- Inflammation of the gums;
- hyperemia (redness) of the mucous membrane, swelling, reaction to temperature stimuli;
- sore gums;
- discomfort, bleeding gums when chewing, oral hygiene;
- detachment of the gum from the tooth wall;
- formation of periodontal pockets;
- abundant plaque and tartar around the tooth;
- pus from the gums;
- loosening of the gum edge;
- exposure of tooth roots;
- tooth mobility;
- inflammation of the submandibular lymph nodes
Symptoms of periodontitis vary depending on the extent of the inflammatory process. The more severe the stage of the disease, the more pronounced the symptoms. The disease does not occur suddenly; the early stage of periodontitis is catarrhal gingivitis - inflammation of the gums, not accompanied by a violation of the integrity of the mucous membrane.
Nature of the disease
Periodontitis is an acute inflammatory reaction in the gum tissue, and periodontal disease is the internal depletion and thinning of the periodontium.
Causes of diseases
Periodontitis occurs due to the penetration of pathogenic microbes into the gum tissue. This can be caused by poor oral care, non-compliance with hygiene rules, mechanical damage to the jaw, teeth and gums, or incorrectly installed dentures and implants.
The causes of periodontal disease are more difficult to establish: it may be a hereditary predisposition, the consequences of trauma to the gums and teeth, vitamin deficiency, and impaired vascular function in the tissues surrounding the teeth. Periodontal disease also develops against the background of chronic diseases of the body (for example, diabetes, diseases of the digestive system, etc.), and also often appears during pregnancy.