Types of stomatitis
Damage to the oral mucosa can be caused by various factors, including viral, bacterial or fungal infection, allergies, mechanical damage, and poor oral hygiene. Depending on the nature, types of stomatitis are distinguished.
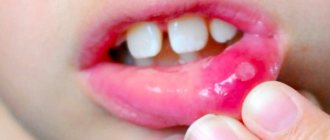
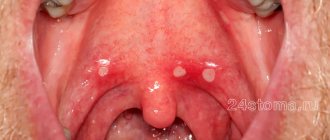
Treatment of herpetic stomatitis (viral)
– multiple blisters caused by the herpes simplex virus (HSV-1).
The lesion spreads both to the mucous membrane of the oral cavity and beyond – to the skin of the face (cheeks, chin, lips). Acute herpetic stomatitis most often occurs in young children under 5 years of age, but it also affects adult carriers of the herpes virus due to weakened immunity.
Herpetic stomatitis is contagious, so during an exacerbation, it is necessary to refrain from close contact with other people.
Treatment
: The patient is prescribed antiviral drugs (acyclovir) and drugs to relieve inflammation and pain.
Important!
In rare cases, the herpes simplex virus can cause complications in the eyes, the so-called herpetic keratoconjunctivitis. This complication can lead to blindness, so if you experience burning eyes and tearing during herpes stomatitis, consult a doctor immediately.
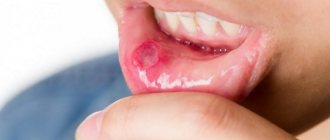
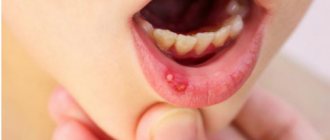
Treatment of Aphthous Stomatitis
– characterized by the appearance of wounds, usually white with pink edges. The disease is not contagious and is provoked by numerous factors, including:
- Increased sensitivity to certain foods;
- Mechanical damage caused by prosthetic and corrective systems in the mouth, biting soft tissues of the mucous membrane;
- Dehydration and mouth breathing during illness;
- Decreased immunity;
- Lack of certain vitamins and microelements in the body;
- Adverse reactions to medications, etc.
Treatment:
To eliminate ulcers, anti-inflammatory drugs and rinses with antiseptics are prescribed; it is important in this situation to correctly determine the cause of the disease.
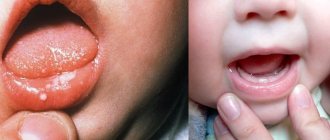
Treatment of fungal stomatitis
– damage to the oral mucosa by a fungus of the species Candida albicans, otherwise called oral candidiasis.
A doctor can diagnose a fungal infection by the characteristic white coating on the corners of the mouth, tongue, and tonsils. In mild cases, the lesions are focal in nature; in advanced forms, the fungal plaque spreads to the entire mucous membrane of the mouth.
Treatment:
local therapy, rinsing, wiping plaque; in difficult cases, systemic antifungal drugs are prescribed.
Treatment of allergic stomatitis
– one of the varieties of aphthous form of the disease.
It is the body's immune response to local and general irritants. Common irritants include food, medications, household chemicals; local irritants include components of prosthetic structures (prosthetic stomatitis). Treatment:
antihistamines, diet, eliminating the influence of the irritant.
Herpes stomatitis in children is a serious illness that requires immediate medical attention.
You probably know that more than 90% (and according to some sources, all 98%) of the population of our planet are carriers of the herpes virus. Most people live their lives and have no idea about it; for some, the presence of herpes manifests itself only as watery, quickly passing ulcers on the lips during a cold.
But for some, this harmful virus can bring a lot of trouble - genital herpes, herpes zoster, postherpetic neuralgia and herpes stomatitis, which also happens in children. Children under 3 years of age are more likely to get sick, and acute herpetic stomatitis in children . This is a rather serious disease that requires immediate medical intervention, as it has a complex course and is accompanied by a high fever - up to 40°, which is dangerous for young children due to possible seizures and other complications.
Manifestation of herpes stomatitis
Parents are interested in how herpes manifests itself in the mouth, how to distinguish it from other inflammatory diseases and how to treat viral stomatitis . The disease begins with a catarrhal period, when bright red spots appear on the gums, inside the cheeks and lips, causing obvious discomfort to the child because they itch and tingle. If older children immediately draw the attention of their parents to this pathology, then the children simply become irritable, whiny, and stop eating. In children, the temperature rises almost immediately, so the onset of herpes stomatitis is often mistaken for a sore throat or acute respiratory viral infection and the moment of starting treatment for stomatitis is missed. A day later, whitish bubbles appear in place of the spots, which burst and turn into ulcers, which are very painful for the baby. At the same time, enlargement of the lymph nodes is often observed, there may be vomiting, dyspeptic symptoms - diarrhea, rumbling in the abdomen.
Treatment of herpes stomatitis
In acute cases of herpes stomatitis, hospitalization of the child is almost always indicated. If the course of the disease is mild and is not accompanied by fever or other complications that can only be determined by a doctor, treatment at home is possible. In this case, the sick child should be isolated as much as possible from other family members so as not to infect them too. If a diagnosis of herpetic stomatitis in children is established, treatment has some features than for other types of stomatitis. Firstly, this is a local treatment - rinsing with antiseptic solutions (to prevent secondary infection of erosions) using a solution of pimafucin, sage or chamomile decoctions. Children over 1 year old can treat their mouths with propolis, which gives very good results.
How to quickly cure stomatitis in a child under 1 year old - in the article “Treatment of stomatitis in infants. In any case, a course of acyclovir (Zovirax) will be prescribed to lubricate the gums and tongue, for older children - in the form of tablets, after which keratoplasty is prescribed - substances that actively restore damaged oral mucosa - vitamin A, sea buckthorn or rosehip oil, Vinylin ointment . So that the baby can eat - before eating, you can lubricate the painful areas with Baby Doctor ointment, Kalgel, etc. as prescribed by the doctor. At the same time, a course of vitamins and immunomodulators is prescribed to improve immunity. If herpes stomatitis is detected on time and appropriate treatment is prescribed, it is completely cured (but the herpes virus remains in the body forever).
Professional approach to treatment
Stomatitis is not an independent disease; rather, it is a symptom of deeper problems with the body. Therefore, a competent doctor approaches treatment comprehensively, drawing up an individual treatment plan for each patient.
Treatment of stomatitis in dentistry is carried out according to the following scheme:
- Inspection and diagnostics
. The doctor examines the patient and makes a diagnosis based on the nature of the wounds and other symptoms, medical history, and the patient’s complaints. To identify the cause, in some cases an examination is prescribed (biochemical blood test, including for bacterial infection, allergens). - Symptomatic treatment
. To alleviate the course of the disease and speed up recovery, the patient is prescribed: anti-inflammatory and wound-healing drugs, antiseptics for mouth rinsing, ointments based on analgesics.In some cases, antibiotics, antiviral or antifungal agents of local or systemic action are necessary.
- Eliminating the cause of the disease
. Based on a visual examination and diagnosis, the doctor tries to understand what caused the disease. Sometimes it is necessary to correct braces and other orthopedic structures, fill teeth, and sanitize the oral cavity.
If the problem is allergic in nature, antihistamine therapy and nutritional correction help; if there is a lack of certain substances in the body, taking vitamin complexes and measures to strengthen the immune system.
Can folk remedies help?
Some believe that stomatitis can be eliminated at home and it is not necessary to visit a dentist. It is enough to rinse your mouth with herbal decoctions, hydrogen peroxide, treat wounds with blue or other compounds.
However, herbal rinses have limited effectiveness. They can be used as part of complex therapy as an adjunct and only after consultation with a doctor. This is due to the fact that herbal infusions can complicate the course of the disease if there is an allergic component.
Remember, self-medication is in many cases useless and even dangerous. Only a doctor can correctly determine the cause of stomatitis and prescribe adequate treatment.
Herpetic stomatitis - symptoms and treatment
Treatment of patients with mild and moderate forms of the disease is carried out on an outpatient basis, i.e. at home, but with regular visits to the doctor. Patients with severe forms of stomatitis, complications and generalized forms of the disease - when the virus affects the entire body - are subject to hospitalization. Treatment includes adherence to the regimen, diet, local and general therapy [5].
All patients require gentle treatment . If the child is lying down, he needs to be provided with fresh air and regular changes of linen. If he plays and refuses to go to bed, there is no need to put him to bed by force - it is better to occupy him with quiet games, reading, etc. You should not go with a sick child to kindergarten, school, shops, shopping centers, cinemas, playgrounds. It must be remembered that the disease is very contagious, and other children can become infected. But during the recovery period, walks in the fresh air separately from other children are possible.
The room where the child is located must be ventilated 3-4 times a day, daily wet cleaning is necessary. The child also needs more sleep. But if he sleeps almost all day and has difficulty waking up or, on the contrary, hardly sleeps, then an additional examination by a doctor is required.
But refusing to eat is not so bad. Eating becomes very painful, so you should not insist, much less force-feed the child. It is worth offering liquid food, porridge, jelly, pureed soups.
It is important to prevent dehydration . Small febrile children become dehydrated very quickly, this increases intoxication and aggravates the condition. Therefore, it is necessary to give the child plenty of water. It is worth offering any liquids: water, compote, tea, diluted juices without sugar. The amount of liquid you drink should be at least 1.5-2 liters. If there is vomiting or the child refuses to drink, you need to give him a teaspoon every 5-7 minutes.
Pain relief also plays an important role . At the height of the disease, patients experience severe headaches and mouth pain. For pain relief, paracetamol and ibuprofen are most often used. The dose is calculated depending on body weight, drugs can be alternated.
Fever above 38.5℃ in young children, in children with a history of febrile seizures or with poor tolerance should be brought down. Fever above 39.5℃ should be reduced in all patients. If, when taking an antipyretic drug, the temperature drops by at least a degree, this is good, but if it does not decrease or rises even higher, then an additional examination by a doctor is required.
With mild severity, it is quite possible to get by with local treatment . This requires careful oral hygiene, rinsing or treatment with antiseptic solutions that do not contain alcohol: furatsilin 1:5000, 2% aqueous solution of chlorhexidine, etc. Acyclovir ointment is used to treat aphthae - 3% for mucous membranes, 5% for skin . From about the third day of illness, healing agents based on an oil solution of vitamin A, sea buckthorn oil, aekol, and solcoseryl are added. Local treatment is carried out 5-6 times a day until the lesions are completely healed.
IMPORTANT : the use of local anesthetics based on lidocaine is not recommended for children under 12 years of age [5]. The use of local aerosol antiseptics for acute herpetic stomatitis is also undesirable.
For moderate forms, local treatment alone is not enough. General antiviral treatment is added . For this purpose, acyclovir and valacyclovir (Valtrex) are used in children. The first drug is used in an age-specific dosage 5 times a day - this is important . Valtrex is used 2 times a day, which is more convenient.
IMPORTANT : interferon preparations (viferon, genferon, cycloferon), as well as homeopathic antiviral agents (anaferon, aflubin) and immunomodulators (imudon, thymogen, lykopid) are not indicated, since their effectiveness and safety in the treatment of infections caused by herpes viruses has not been proven .
Recurrent forms require additional examination by a doctor and the appointment of a prolonged course of antiviral treatment.
Severe and complicated forms of the disease are treated in a specialized hospital, since outpatient treatment will be ineffective [1][2]. It involves taking antiviral drugs in the form of tablets and injections, detoxification therapy, replenishment of lost fluid and electrolytes, and intravenous supply of necessary solutions [11].
It is worth remembering that acute herpetic stomatitis is a disease caused by a virus. Therefore, in routine cases, antibiotics are not required , even if the fever lasts more than three days - this is a typical condition for the disease.