12/21/2021
182 959
7 minutes
Author, editor and medical expert – Klimovich Elina Valerievna.
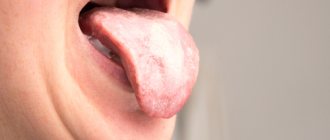
Fever with sore throat (acute tonsillitis) is the same characteristic symptom as a sore throat. But sometimes the temperature is high, and the sore throat is not very pronounced1. Because of this, people do not treat the disease, but simply try to “bring down” the temperature - this is unsafe1,3. What determines the temperature level during tonsillitis, and what needs to be done to alleviate the condition?
Before finding out what temperature happens with a sore throat, you need to figure out what is considered a normal temperature and what is not.
In children and adults, the morning temperature measured in the armpit should be less than 37.20C2. In the evening, the temperature is allowed to rise to 37.70C - this is normal, especially for children2. Anything higher is considered to be fever2.
Up to contents
Symptoms of pharyngitis.
Pharyngitis is not just a feeling of aching pain
inside it is also a whole “set” of additional symptoms that affect our body.
With viral pharyngitis, symptoms increase gradually (unlike symptoms with bacterial pharyngitis). Patients are accompanied by fever - usually not very high. In the case of bacterial infections, the temperature usually rises. Other symptoms include headache
, bone and muscle pain, and nasal congestion with mucus. There is also a cough - often caused by secretions running down the back of the throat.
Doctor examining throat with naked eye
, may notice deviations characteristic of its inflammation - redness, blisters, the presence of discharge or swelling.
Depending on the type of virus that causes pharyngitis, symptoms such
as conjunctivitis and skin rash may also appear.
“Throat and stomach hurt,” or what do you know about adenovirus
During seasonal ARVI, cough and sore throat are an “expected” phenomenon. But what if traditional respiratory symptoms are combined with diarrhea or vomiting? Perhaps it is an adenoviral infection.
Special signs
Adenovirus, unlike many respiratory viruses, affects not only the respiratory tract, but also the mucous membrane of the small intestine. In addition, the conjunctiva of the eye comes under attack.
It leads to:
- copious mucous discharge from the nose,
- sore and sore throat,
- cough (first dry, and later with sputum),
- symptoms of conjunctivitis, such as redness of the eyes, watery eyes, a feeling of dryness and “sand” in the eyes,
- as well as abdominal pain, diarrhea, vomiting
- and fever, the duration of which can reach 2 weeks.
Moreover, if intestinal symptoms may not develop during the entire infection, then the “characteristic” eyes are an important distinguishing feature of the adenovirus.
Where can you get infected?
Adenovirus is extremely infectious and resistant in the external environment. And the source of infection can be sick people or household items on which the virus remains active for up to 8 days.
You can become infected:
- when the patient coughs and sneezes,
- consuming food prepared without sanitary standards (thorough hand washing is required),
- and even through contact with the feces of an infected person (for example, when changing a diaper for an infected child).
You can “catch” the virus even in a swimming pool if the water is not properly disinfected. And, obviously, this viral infection is not uncommon in children's groups.
How dangerous is this?
Adenovirus infection, in most cases, does not pose a threat to health or life. And it usually ends without consequences after 7-14 days. Whereas in weakened patients, the infection can drag on and reach 6 weeks.
This same category of patients most often develop complications in the form of:
- pneumonia,
- otitis,
- bronchospasm
- severe keratoconjunctivitis.
However, Rospotrebnazor experts note that complications of adenoviral infection are always associated with the addition of pathogenic bacterial flora (staphylococci, streptococci and others).
How to identify adenovirus
The classic symptoms of adenoviral infection, as a rule, do not require additional tests. And the help of laboratory diagnostic methods is mainly resorted to at the earliest stage of the infectious process or in case of doubt about the diagnosis.
The most informative analysis in this case is PCR diagnostics of the material (throat swab or feces) for adenovirus.
The study can be ordered separately or immediately in combination with other ARVI viruses (for example, “ARVI-Screen”), which will allow you to immediately carry out a differential diagnosis. True, the PCR technique sharply loses its reliability if treatment, both local (rinses, sprays) and general, has already begun.
A blood test for IgA antibodies to adenovirus does not have these shortcomings.
They appear in the blood during the initial period of the disease, and continue to circulate for some time after recovery.
However, children, as you know, “don’t like” blood tests, so this examination format is more suitable for adults.
Treatment of viral pharyngitis.
As already mentioned, antibiotic therapy for viral pharyngitis will not be an effective treatment. Moreover, there is no so-called causal treatment. Viral pharyngitis is a disease that goes away on its own; treatment is symptomatic. The most widely used antipyretic drugs are those whose active ingredient is paracetamol. Antipyretic and anti-inflammatory drugs are also used
- these include, for example, compounds related to non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, the active ingredient of which is ibuprofen.
For nasal discharge, topical medications are used to relieve nasal congestion. Thanks to local action, active ingredients
almost immediately enter the infected area. In case of fever, it is also recommended to drink plenty of fluids to keep the body hydrated.
Many medications used to treat viral pharyngitis are available without a prescription. So you can buy them yourself without visiting a doctor. However, you should read these instructions carefully and adhere to the prescribed doses. In addition to symptomatic treatment
Rest and reduction in physical activity are also necessary.
Flu and ARVI are easier to prevent!
Currently, the most effective anti-influenza drugs recommended by the World Health Organization are blockers of viral proteins: oseltamivir and zanamivir, which suppress the activity of neuraminidase, as well as amantadine and rimantadine, which block the M2 protein, thanks to which the virus attaches to epithelial cells of the respiratory tract in order to penetrate them .
However, the processes of antigenic drift and antigenic shift lead to the emergence of influenza virus strains whose proteins are not affected by these drugs. Against such strains, some or all viral protein blockers become ineffective.
This deficiency is eliminated by drugs whose action is aimed at increasing the body’s own defenses, that is, immunomodulators. Their effect does not depend on the specific strain of the virus.
The effect of these medications is best seen if you start taking them immediately after the first flu symptoms appear - they alleviate the course of the disease at any stage.
In addition, immunomodulators have a pronounced preventive effect: if you mobilize the body’s defenses immediately when the epidemiological situation worsens, without waiting for infection, then if the virus enters, the disease will be mild or will not develop at all. This will allow you to maintain your ability to work and save money on treatment.
One of the immunomodulators that has demonstrated its anti-influenza activity over the years of use is the original domestic drug Cycloferon. Its active ingredient meglumine acridone acetate stimulates the production of special molecules in the body - interferons.
These molecules are released by the body's cells in response to the invasion of viruses and change the vital processes of the cell in such a way that it becomes immune to the virus and does not participate in its reproduction. In addition, interferons cause activation of immune cells - lymphocytes and macrophages.
Studies of Cycloferon have confirmed its effectiveness against influenza caused by various strains of the virus - the drug produces a pronounced preventive effect, and also significantly reduces the severity and duration of an existing disease.
How long does viral pharyngitis last?
The duration of viral pharyngitis varies - symptoms usually disappear within 10 days after the first symptoms appear. The disease resolves spontaneously
, only supportive symptomatic treatment is used.
Is viral pharyngitis dangerous?
Diseases caused by viral pharyngitis significantly limit daily life.
However, the symptoms themselves are not among the most serious consequences of contracting the virus. Unfortunately, even as a result of such a popular disease as viral pharyngitis, complications can arise - this is bacterial inflammation of the lungs, paranasal sinuses or middle ear. As already mentioned, complications have a bacterial etiology
, and the initial disease - pharyngitis - is of viral origin. It is also worth noting that the use of an antibiotic does not reduce the risk of bacterial complications.
Viral pharyngitis in children.
Anyone can get viral pharyngitis - both children and adults.
Throat infections in children occur all year round, although doctors observe the greatest intensity in the autumn-winter period. Viruses that cause pharyngitis in children are adenoviruses, rhinoviruses, Coxsackieviruses, EBV ( Epstein-Barr virus).
Bacterial pharyngitis.
Streptococcal pharyngitis is the most common form of bacterial disease.
Symptoms usually appear suddenly, with a high fever and a sharp sore throat that makes swallowing difficult. There are also plaques in the crypts of the tonsils
, and hyperemia of the pharyngeal mucosa is observed.
Often, nearby lymph nodes increase in size and become painful.
How to protect yourself from viral pharyngitis?
The key to disease prevention is proper hygiene to limit the transmission of viruses that cause viral pharyngitis.
Sick people should isolate themselves
- particularly the people they live or work with.
Why does the temperature rise
Fever accompanies most infectious diseases, including acute tonsillitis2,3. The processes that cause an increase in body temperature are quite well studied. They are triggered by special substances pyrogens, which can enter the body from the outside (exogenous pyrogens) or be synthesized inside it (endogenous pyrogens).
Endogenous pyrogens are substances that enter the bloodstream during the destruction of immune cells and cells of the inflamed mucous membrane of the throat2,3.
Exogenous pyrogens in the case of tonsillitis can be various microorganisms: viruses, bacteria, fungi3. In children aged 3 months to 3 years, tonsillitis most often develops with mixed herpesvirus infections3. When a child reaches the age of 3-7 years, viruses give way to bacteria, and in 30% of cases the disease is caused by group A3 beta-hemolytic streptococcus. In addition, the tonsils are often affected by streptococci of other groups, staphylococci, etc.1 In adults, acute tonsillitis is often viral and accompanies ARVI1.
Exogenous and endogenous pyrogens affect the thermoregulation center located in the brain2,3. As a result, he begins to perceive normal body temperature as lower and increases the level of heat production, which leads to an increase in body temperature2,3.
Up to contents
Forms of sore throat and symptoms of the disease in adults
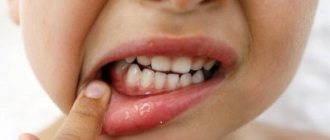
Each form of sore throat manifests itself differently. It is important to find out which pathogenic microorganism caused the disease. But it is impossible to determine this at home. Only a qualified doctor can accurately identify the nature of the pathogen and prescribe adequate treatment for sore throat, promoting a speedy and complete recovery.
Catarrhal sore throat
Acquired through contact with an infected person, it begins acutely, with a slight increase in body temperature and a feeling of weakness. The tonsils and submandibular lymph nodes are slightly enlarged. Dryness in the mouth and throat is accompanied by a sore sensation; swallowing is painful and difficult. If not stopped in time, the disease can develop into a severe form with subsequent complications.
Lacunar tonsillitis
The purulent form of tonsillitis is characterized by a very rapid onset of symptoms. The lymph nodes become enlarged and swollen, the tonsils are markedly swollen and covered with a white-yellow purulent coating. The throat with lacunar sore throat hurts especially badly.
An increase in temperature to 40 degrees is accompanied by headache, muscle and joint pain, sometimes radiating to the heart. Fever may cause seizures, vomiting, and confusion.
In the absence of proper treatment, lacunar tonsillitis can develop into fibrinous tonsillitis, when severe purulent intoxication of the body begins, in some cases causing brain damage.
Follicular tonsillitis
The purulent form has symptoms similar to lacunar angina. The tonsils are covered with many purulent follicles. Sometimes the patient complains of pain in the lower back, joints ache, like with the flu. Unbearable pain in the throat radiates to the ear.
This form of purulent tonsillitis is dangerous due to a wide range of complications, as well as rupture of the follicles inward, followed by a purulent abscess.
Herpangina
A dangerous viral form acquired by using a shared toilet, shaking hands and any type of tactile contact with a carrier of the disease - a person or animal. Small serous blisters appear on the tonsils, throat and palate. The throat hurts unbearably, the cervical lymph nodes are swollen and painful to the touch.
At the same time, all the symptoms characteristic of influenza appear: fever, chills, headache, nausea, diarrhea.
Confirming the diagnosis of “herpetic sore throat” is only possible by consulting a doctor. A qualified specialist will first of all direct the patient to undergo tests for serological testing and virology, after which he will prescribe a course of necessary antibiotics.
Otherwise, improper treatment can have serious consequences: encephalitis, meningitis, and myocarditis.
Phlegmonous sore throat in adults
This is a purulent form of the disease, typical for the age group of 20-40 years. The causative agent is streptococci, and the cause is not long-standing catarrhal or follicular tonsillitis. With this form of sore throat, redness is observed not only of the palate and tonsils, but also of the peri-almond space.
The throat hurts on one side, the focus of suppuration does not have clear boundaries and requires surgical intervention.
The patient has chills and fever, the voice is hoarse or disappears completely. As a result of purulent melting of the tonsil, a characteristic, unpleasant odor comes from the mouth.
Treatment of phlegmonous sore throat cannot be delayed. In the absence of timely assistance from specialists, in most cases, cervical or brain abscesses, purulent meningitis, and general blood poisoning occur.
Treatment of angina should occur under the strict supervision of a doctor, who will be able to notice in time and prevent the development of complications that are of the most unexpected nature.