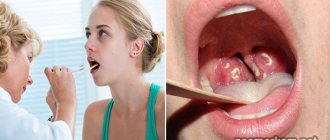
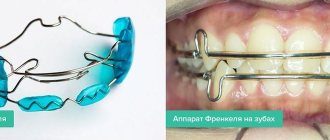
With a sore throat, a person complains of soreness, scratching, irritation, discomfort, and a burning sensation in the throat. The throat is sore, it is difficult to swallow food, drink, these sensations intensify when swallowing or talking.
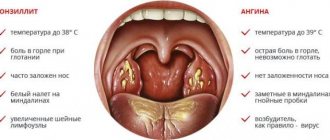
Sore throat may be accompanied by swelling of the throat mucosa, difficulty swallowing, soreness and enlargement of the cervical lymph nodes, the appearance of white or yellowish spots on the tonsils, coughing, sneezing, nasal congestion, runny nose, fever, chills, excessive salivation, muscle and joint pain, headache, nausea and vomiting, skin rash, loss of appetite, feeling of a lump in the throat, heartburn, hoarseness.
Causes of sore throat
Inflammatory. The most common cause of a sore throat and dry cough is acute respiratory diseases. These are infections caused by various pathogens:
- viruses (parainfluenza, influenza, respiratory syncytial virus, enterovirus);
- bacteria (streptococci, staphylococci);
- fungi (for example, yeast of the genus Candida).
Infections are transmitted mainly by airborne droplets, as well as by contact. Their maximum incidence is observed in the cold and damp seasons. An infectious agent, penetrating the body, is fixed on the mucous membranes of the respiratory tract, where, in response to its penetration, a protective reaction in the form of inflammation is triggered. Swelling and redness of the mucous membrane develop, leading to discomfort, pain and sore throat, causing coughing.
Non-inflammatory. A sore throat and dry cough can also occur with non-inflammatory damage to the mucous membranes of the upper respiratory tract:
- for allergic pharyngitis, laryngotracheitis, bronchitis;
- thermal irritation of the respiratory tract (inhalation of hot or cold air);
- irritation from chemical agents (ingress of particles and vapors of varnishes, paints, household chemicals, gasoline, etc.);
- strong vocal stress (“lecturer’s” laryngitis);
- smoking;
- injury or foreign body entering the lumen of the larynx, pharynx, trachea.
In addition to respiratory diseases, tickling and dry cough may occur:
- against the background of the use of certain medications (ACE inhibitors, diuretics);
- with heart failure;
- hypothyroidism and after surgery on the thyroid gland (damage to the laryngeal nerve leads to hoarseness, sore throat without coughing);
- diabetes mellitus;
- neuroses.
3. Symptoms and diagnosis
In addition to the actual pain that occurs or intensifies when swallowing, the clinical picture may include a huge number of concomitant, background, more pronounced or dominant symptoms: signs of infectious intoxication (malaise, fever, headache, etc.), plaque on the tonsils or the posterior wall of the nasopharynx , runny nose, psychopathological phenomena, signs of urogenital infection, foreign body sensation, pain and swelling of regional lymph nodes, symptoms of airway obstruction, painful changes in head position, dyspeptic symptoms, ear pain, skin rash, neurological disorders, etc. There are many cases where the apparent “understanding” of the causes, the habitual nature of pain when swallowing, or its moderate, tolerable intensity led to a delay in seeking help and the development of severe, sometimes fatal complications.
In this regard, the general principle of parental behavior should be emphasized if pain when swallowing is observed or suspected in children, especially infants, and quickly becomes worse accompanied by any “unusual” symptoms: in this situation, it is better to be safe a hundred times over by calling a pediatrician or going to an urgent medical facility at night than relying on your own medical knowledge, grandmother’s advice, online forums, folk wisdom, over-the-counter medications, or just “maybe.”
Diagnostics begins with the collection of available medical history and complaints, examination of the ENT organs, assessment of the patient’s general condition, and analysis of accompanying symptoms. As necessary, the otolaryngologist prescribes additional tests (X-rays, ultrasound, tomography, laboratory tests, etc.) and consultations with specialized specialists. In some cases, these steps must be taken on an urgent or emergency basis.
About our clinic Chistye Prudy metro station Medintercom page!
Treatment options
To effectively treat dryness, sore throat and cough, it is necessary first of all to act on the cause of their occurrence - inflammation. To make an accurate diagnosis, you should consult a doctor who, depending on the anamnesis (history of the development of the disease), complaints and examination, will immediately suggest a particular disease or prescribe additional examinations and consultations. Since dryness, tickling and cough are not a diagnosis, but only one of the symptoms of the disease, it is necessary to carry out comprehensive treatment, and not limit ourselves to just eliminating unpleasant symptoms. Elimination of pathogens.
In case of infectious origin of tickling and cough, therapy is prescribed that acts on the pathogen - antiviral, antibacterial or antifungal drugs for systemic use (orally or by injection, in the form of rectal suppositories). The selection of an antibiotic or antiviral agent is carried out by a doctor. Under no circumstances should you independently cancel and replace one drug with another or stop taking it earlier - this can lead to the progression of the process or its transition to a chronic stage.
Pain relief
. However, cough and severe sore throat, as a rule, are subjectively difficult for patients to tolerate, causing severe discomfort and disrupting their usual way of life. Therefore, it is difficult to do without the use of symptomatic medications to reduce the severity of complaints. For this purpose, a variety of local remedies are used: tablets and lozenges, sprays, rinsing solutions. If your throat is very sore, frequent warm drinks, warming and distracting procedures can help soothe the irritation of the mucous membranes. If you have a painful, obsessive, prolonged non-productive cough, you may need to prescribe antitussive drugs.
1.General information
“It hurts to swallow” is one of the most common complaints that not only an otolaryngologist, but also a pediatrician, general practitioner, district physician, surgeon, infectious disease specialist and many other specialists have to deal with.
The wide prevalence of pain during the act of swallowing is partly due to the anatomical complexity, intensive innervation and vasculature (blood supply) of the ENT organs and the initial parts of the digestive tract: with these structural features, even a minor problem can be accompanied by severe pain. But it is also important that the range of such “problems” is very wide – from really minor to very serious and even life-threatening. Therefore, enduring pain when swallowing (in the hope that “this often happens to everyone and goes away on its own”) is not only unwise, but often dangerous, since some of the processes underlying this phenomenon develop fulminantly (lightning fast), and treatment seeking help may be too late.
A must read! Help with treatment and hospitalization!
Doctor MOM® for the treatment of cough and sore throat
In the complex treatment of cough and sore throat, the use of herbal medicines from the Doctor MOM® line - syrup and herbal cough lozenges - is indicated. Thanks to the unique1 “FITO BRONHO formula”2 based on medicinal plant extracts, the products in the Doctor MOM® line have a complex effect, helping to both relieve unpleasant symptoms and eliminate their cause - inflammation.
The main actions of Doctor MOM® syrup and herbal cough lozenges are:
- Eliminating the cause of cough – inflammation;
- Removing infection from the body3;
- Combating unproductive and unproductive cough.
Acute and chronic laryngitis
What can you do if you have a sore throat and lost your voice?
Acute and chronic laryngitis: symptoms and treatment in adults and children
Laryngitis is “ubiquitous.” It affects teachers and students, lecturers and students, singers, announcers and those whose profession is not associated with vocal strain. It appears in the cold season, when, having frozen or wet feet, the next morning you feel a telltale sore throat. Again, laryngitis and its symptoms interfere with life. Or in the summer you enjoy the coolness of the air conditioner, drink cold water and then wonder why your throat hurts and your voice has disappeared. More than 2,000,000 residents of Russia, according to official statistics, get sick every year. And almost half of them are children, in whom acute laryngitis often causes serious complications.
When to see a doctor? And when will it “go away on its own”?
Many people ignore the symptoms. Just think, your throat is sore, your voice has sunk and it’s painful to swallow. Just something to do. Type “laryngitis symptoms and treatment” into a search engine, a couple of tablets, at best, gargle, drink hot tea, and go to work.
However, with laryngitis, everything can go according to a different “scenario”. For example, when the infection spreads down the mucous membrane of the respiratory tract, tracheitis begins, then bronchitis. And they take much longer and are more expensive to cure. Therefore, if your condition does not improve or worsens within a few days, consult a doctor.
Moreover, rush to talk to your doctor if a rash appears due to laryngitis, pain radiates to the ear, a severe cough bothers you and it is difficult to breathe.
If complications arise, such as false croup or laryngeal stenosis, minutes count. This often happens in children under 8 years of age. Even in the evening, the symptoms of laryngitis in children are minor, and at night patients begin to cough, turn blue and choke. You need to call an ambulance, go to the hospital to relieve the attack, treat inflammation of the larynx.
The course of the disease during a viral and bacterial process is rarely limited to the larynx. Neighboring areas are involved and pharyngitis, tracheitis, and bronchitis begin.
How to recognize acute laryngitis? Symptoms in adults and children
If:
- My throat is sore, burning, something is bothering me.
- My throat is dry.
- It became painful to swallow.
- The cough bothers me - first dry, then with phlegm.
- The voice is hoarse or has disappeared altogether.
- The temperature increased to 37.5-38°C.
- If you feel weak or have a headache, call a doctor and get treatment. “Feat of labor” and going to work in this state can cost you dearly.
Call immediately if it is very painful and difficult to swallow, or if you are coughing up blood.
Laryngitis in children, especially young children, develops faster, the temperature is higher, and the condition is more severe. And if difficulty wheezing or a “barking” cough develops, false croup may develop, and you must urgently go to the hospital.
What are the causes of acute laryngitis symptoms?
Due to the introduction of infection, swelling and inflammation of the larynx appears. The following are “to blame” for the disease:
- Influenza viruses, parainfluenza, adenovirus.
- The causative agents of “childhood” infections are measles, diphtheria, whooping cough.
- Bacteria - strepto- and staphylococci. They occur against the background of acute respiratory viral infections or chronic infections, such as tonsillitis.
Chronic laryngitis: symptoms in adults. How to understand why your voice is hoarse
If episodes of acute inflammation are repeated frequently, the process becomes chronic.
The temperature is normal, when there is no exacerbation, the general condition does not change. Patients are concerned about dryness, sore throat, hoarse voice, deep throat, and constantly want to clear their throat. When an exacerbation occurs, the symptoms of chronic laryngitis intensify.
Inflammation of the larynx rarely occurs as an independent disease. More often it accompanies other conditions. For example, it is a concern for chronic tonsillitis, sinusitis, bronchitis, reflux disease - the reflux of acidic stomach contents into the esophagus.
Other causes of chronic laryngitis:
- smoking and alcohol,
- air polluted with dust, smoke, industrial emissions,
- allergens,
- increased vocal load on the voice,
- specific infection - syphilis, tuberculosis.
- chronic diseases (diabetes mellitus, circulatory failure, etc.)
The reasons are different, the symptoms are similar. Therefore, without eliminating the cause, searching for “how to treat chronic laryngitis at home” and then gargling with “herbs” and dissolving lozenges is, at a minimum, ineffective.
Who treats - which doctors should I contact?
First of all, if you have a sore throat, lost your voice, have a dry cough, or have other unpleasant sensations, you should make an appointment with an otolaryngologist
. However, there are situations when the participation of other specialists, for example, a gastroenterologist, is necessary in diagnosis and treatment.
How to diagnose laryngitis?
Survey
First, the specialist asks what is bothering you. Tell us in detail about your sore throat, cough, and other uncomfortable sensations. Be sure to report if you have a fever, muscle pain, weakness, or headache.
Next, the otolaryngologist will ask you how long you have had these symptoms and what you did, what medications you took to get rid of them. Be sure to let us know if you smoke, breathe dry, dusty air, have a strained voice, or have allergies.
If you have already had laryngitis, the treatment of which did not give the desired result, you have been tested - take the card and test results with you. Doctors at the Energo clinic with many years of experience take into account all the details in order to make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe adequate treatment.
Initial examination
During a general examination, it is noticeable that the patient’s voice has changed.
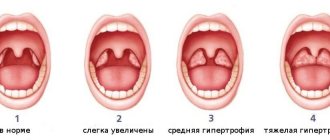
During an ENT examination of the larynx (laryngoscopy), the doctor sees redness of the laryngeal mucosa throughout, or only in the area of the vocal folds. It is not difficult for an experienced doctor to diagnose laryngitis, the signs of which are thickening, swelling and incomplete closure of the vocal folds.
With chronic inflammation, changes are of a different kind. Depending on the form of chronic laryngitis, the mucous membrane may be reddened and thickened, covered with viscous mucus, and the vocal folds may not close completely. Patients complain of soreness and discomfort in the throat, cough with sputum that is difficult to cough up. Chronic laryngitis in children, the treatment of which is a task for an experienced doctor, manifests itself in exactly this way.
In another form, the mucous membrane grows excessively, and singing “nodules” form on the vocal folds. The main complaint is loss of voice. With atrophy, the mucous membrane becomes thin, covered with crusts, and patients are bothered by a dry, painful cough.
What methods are used for diagnosis?
In most cases, a simple laryngoscopy is sufficient. If there is a suspicion of a bacterial or fungal cause of laryngitis, a smear and bacteriological culture are done.
How to treat laryngitis?
At the first stage of treatment, the doctor decides on the tactics. For acute process and chronic inflammation, treatment is different. This depends on many factors - the form of the disease, the severity of general symptoms, concomitant pathology. The doctor prescribes drugs for the treatment of laryngitis in adults: anti-inflammatory, antiviral, antiseptics, immunomodulators, physiotherapy, according to the form of the disease and concomitant pathology. For a dry, obsessive cough, medications that suppress the cough reflex are prescribed for a short course. You shouldn't prescribe them to yourself. Do you want to know how to quickly cure laryngitis? Follow these rules. During the acute period:
What to do
- Take your medications as prescribed by your doctor.
- Do alkaline (soda solution) inhalations for laryngitis.
- Avoid spicy, sour, hot foods.
- Drink enough fluids.
- Humidify the indoor air.
What not to do
- Don't talk, even in a whisper.
- Do not smoke.
- Don't drink alcohol.
In case of exacerbation of a chronic process, treatment is carried out depending on the form of the disease.
For mucosal atrophy, these are things that improve blood circulation and metabolism: physical procedures, vitamins, biostimulants. If the process is accompanied by thickening of the mucosa, anti-inflammatory drugs are needed.
For catarrhal form, antiallergic and decongestant drugs, expectorants, antiseptics, anti-inflammatory drugs and alkaline inhalations are used.
Plus, gentle mode.
If you are looking for how to treat laryngitis in children, remember: the main thing is not to waste time. All processes in a child’s body proceed much faster, and complications may arise.
At the second stage of treatment, the doctor evaluates the effect of the treatment. With a chronic process, it takes time to get the effect. Be patient and follow your doctor's recommendations.
At the third stage of treatment, after there is a positive result from the treatment, the doctor prescribes a set of measures to prevent exacerbation. Necessary:
- Treat diseases that support laryngitis: pharyngitis, tonsillitis, bronchitis, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, diabetes, etc.
- Eliminate factors that provoke exacerbation - stop smoking, reduce contact with ARVI patients if possible, humidify the air.
- Take medications prescribed by your doctor: vitamins and medications to increase general and local immunity.
At the fourth stage of treatment, the doctor determines the frequency of follow-up examinations and studies in order to monitor your condition and notice a relapse in time.
What results can be expected from laryngitis treatment?
- Itching and dryness disappear
- Voice is restored
- The cough stops
- The general condition is normalized.
Prevention of laryngitis
Spicy
- Adhere to a healthy lifestyle - eat right, don’t get nervous, get enough rest, walk in the fresh air, humidify the indoor air.
- Treat acute respiratory viral infections in a timely and correct manner, do not endure them “on your feet,” and do not allow the process to become chronic.
- Strengthen the immune system: hardening, courses of vitamins, herbal remedies.
- Eliminate factors that have a harmful effect on the mucous membrane of the respiratory tract - smoking, alcohol, dust, allergens.
Chronic
- Eliminate factors causing exacerbation.
- Don't get too cold.
- Try to eliminate foci of chronic infection - treat teeth, sinusitis, tonsillitis, bronchitis in a timely manner.
If your throat is sore, hoarse, or your voice has disappeared or you have a cough, you should not wait for laryngitis to “go away on its own.”
The inflammation often spreads further, and more serious diseases will need to be treated. Making an appointment with a doctor and being treated by a specialist is easier than eliminating a chronic process or its complications. Call and schedule a visit. Or make an appointment with our otorhinolaryngologists online on the website.
Increased salivation in women during pregnancy
A common cause of hypersalivation in women is pregnancy. When a woman is preparing to become a mother, the hormonal background of the body changes greatly, and with it many processes: blood circulation, digestion.
Pregnancy affects all systems at once:
● endocrine;
● nervous;
● digestive.
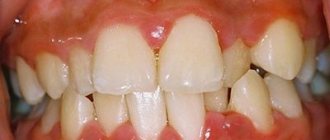
Often, expectant mothers experience problems with their teeth and gums, such as gingivitis. This disease also affects the amount of saliva produced.
Healthy and inflamed gums
How to understand that salivation is increased: symptoms and signs of failure
Saliva is involved in many important processes occurring in the human body. When everything is normal, we do not notice that saliva:
● helps to pronounce words and sounds clearly and correctly;
● enhances the perception of the taste of food and drinks;
● participates in digestion - helps to chew food and also swallow it.
When salivation is increased, several processes are disrupted at once:
● the taste of food changes - salty food becomes too pronounced, and subtle nuances are not felt;
● problems with diction appear – pronouncing some sounds is problematic;
● it becomes painful to swallow food.
Location of glands
In addition to indirect signs, there are also clear, measurable criteria. If more than two milliliters of saliva is released within five minutes, the patient is diagnosed with increased salivation. The normal value is 2 ml.
Sometimes patients complain of false profuse salivation. This happens when there is injury or inflammation in the mouth and it may seem that there is more saliva than there should be, although the levels are normal: 2 ml in 5 minutes or 2 liters per day.
Diagnostics
With the problem of drooling, patients turn to a dentist, or less often to a therapist. Given the variety of causes of pathology, the doctor is required to take a detailed medical history and clarify related complaints. The diagnostic search begins with an examination of the oral cavity to identify signs of inflammation or caries. To establish the causes of drooling, the following instrumental and laboratory diagnostic methods are used:
- Biochemical analysis of saliva.
The study evaluates the amount of fatty acid metabolites formed during the life of bacterial flora. Based on the results of the analysis, it is possible to determine the presence of dysbacteriosis and determine the level of damage to the digestive tract. - General clinical studies.
Patients with drooling undergo a general blood test, changes in which indicate the presence of an inflammatory or infectious process. To exclude helminthic infestations, a coprogram is prescribed, a fecal examination for helminth eggs. According to indications, a clinical urine test and studies according to Nechiporenko and Zimnitsky are performed. - Instrumental techniques.
If a patient suffering from drooling has complaints about the functioning of the digestive system, an ultrasound of the abdominal organs and plain radiography are necessary. To exclude neurological diseases, CT or MRI of the brain is recommended. Electroneuromyography is effective for assessing the functions of peripheral nerves.
Causes of increased salivation in men and women
The volume of saliva secreted is controlled by the nervous system. When everything is in order with health, it happens naturally and unnoticed by a person. But when problems arise or diseases appear, the process is disrupted. A variety of factors can influence, but most often the cause of increased salivation in adult men and women is one of six factors.
- Oral diseases - gum inflammation, periodontitis, stomatitis, as well as cuts and burns. When bacteria enter the glandular tubules, the body begins to produce more saliva to get rid of them. This is a natural reaction.
- Digestive system problems - abnormal stomach acidity, pancreatic and liver diseases.
- CNS diseases - Parkinson's disease, trigeminal nerve damage, bulbar syndrome, migraine. With these diseases, the natural process of salivation is disrupted. Short-term impairment may occur due to air sickness, seasickness, or problems with the vestibular apparatus.
- Hormones - failures of the hormonal system, in particular the thyroid gland, menopause, diabetes mellitus lead to excessive salivation. Sometimes this is observed in adolescents during the restructuring of the body.
- Smoking and removable dentures can also affect it. Both of these phenomena irritate the mucous membrane, stimulating the overactive functioning of the glands.
- Taking medications - some medications have side effects of increased salivation or, as it is also called, hypersalivation. Most often these are those medications that contain iodine or mercury. For example: lithium, physostigmine, muscarine.
Pilocarpine, nitrazepam also lead to hyperactivity of the glands
What to do with increased salivation depends on the factors that caused it. In some cases, for example, when taking medications, the disease will go away without the intervention of a doctor.