Changing the color of tooth enamel is an alarming signal that cannot be ignored. Dark spots can be associated not only with the consumption of coloring foods and drinks, but also with the development of various pathological processes. If the tooth has turned black at the root, you should contact your dentist as soon as possible. Do not wait for pain and other symptoms to appear, as they indicate extensive damage to hard tissues or inflammation of the dental nerve. It is easier to treat any disease in the early stages, so do not delay visiting a doctor.
Chromogenic components (food, drinks, other products)
The food we eat and other substances we use contain coloring agents (coffee, tea, cola, wine, tobacco, etc.) that can cause yellow, brown or bright orange spots to appear on the skin. teeth In most cases, the discoloration of teeth is generalized, which means that stains tend to form with equal success both on the entire surface of the tooth and in individual areas. If stains appear, it is better to make an appointment with an inexpensive dentist near your place of residence.
Possible reasons
Has the tooth turned black near the root? There may be several reasons for this.
- Tartar. One of the most common problems. It is a hard brown coating. It is formed from food debris and soft plaque, which harden under the influence of saliva. Violation of the rules of oral hygiene is the main cause of the appearance of tartar. Most often it forms around the neck of the tooth. It can also be subgingival - adjacent to the root and covered by the gum.
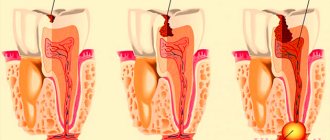
- Cervical caries. Dark spots at the root of the tooth may turn out to be carious cavities. They appear due to demineralization of enamel and destruction of dentin by pathogenic bacteria. As a rule, dental caries is preceded by tartar. The risk of developing the disease increases with insufficient oral hygiene, decreased immunity, and lack of calcium, phosphorus and vitamin D in the body.
- Dying of the pulp. Blackening of the tooth can also be a consequence of necrosis of the cells of the neurovascular bundle. Pulpitis occurs due to deep caries, burns during tooth treatment before prosthetics, or trauma. Pulp necrosis is manifested by prolonged pain when eating hot food and mechanical impact on the diseased tooth, but is often asymptomatic.
- Fluorosis. Darkening of teeth may be due to excess fluoride entering the body. This microelement is necessary for strong bones and teeth, but if the permissible concentration is exceeded, it leads to the development of fluorosis. This disease provokes destructive changes in the enamel and the formation of dark spots and stripes on the teeth.
Tooth decay
In the early stages of tooth decay, white spots or spots appear on the tooth enamel. The affected areas lose their natural shine and become dull. A thorough examination reveals the presence of damage to the enamel. If the process of tooth decay progresses, the affected area becomes brown or black, it is necessary to diagnose dental treatment. The damage is initially noticeable as a small dark spot or spots that gradually increase in size (over several months to several years) and often lead to actual tooth decay.
Why does the enamel color change?
Blackheads occur for many reasons, of which dentists identify the main ones:
- Presence of plaque if not cleaned regularly with a toothbrush.
- Hereditary factor.
- The presence of sealed teeth treated with metal fillings.
- Smoking and alcohol abuse.
- Long-term wearing of braces.
- Poor cleaning of dental canals due to caries.
- Erasure of enamel.
- Use of tetracycline antibiotics for treatment.
Additional symptoms
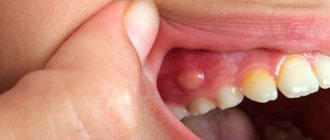
Typically, the appearance of secondary caries is accompanied not only by darkening, but also by a number of other symptoms that are difficult to miss. What should you pay attention to if your teeth turn black? Let's consider additional symptoms:
- change in enamel color, appearance of a black dot on the surface, darkening and other visual signs of destruction;
- bad breath, especially in the morning after waking up, is the result of the development of pathogens and tissue destruction;
- mobility of the filling, which may eventually partially crumble or fall out completely;
- pain, especially if the nerves are not removed;
- redness of the gums caused by the presence of an inflammatory process.
Even if the blackening of the filling is not accompanied by the additional symptoms described above, it is recommended to undergo a preventive examination so that a specialist can identify the causes of the problem and determine the tactics for further action.
How to treat caries in the form of spots on teeth?
Dental caries goes through several stages. First, a light spot appears on the enamel, which is sometimes even difficult to notice. Then it becomes rough and darkens. If the process is not stopped, the destruction continues further, and a cavity forms in the enamel. At the stage of medium and deep caries, the cavity affects the dentin and gradually expands.
Caries in the form of a dark spot is one of the early stages of carious lesions. Bacteria penetrate into areas of demineralized enamel, producing acid and gas, which stain the enamel dark. At this stage, you can still do without a drill if caries is diagnosed in time.
There are several methods for treating caries in the dark spot stage.
- Remotherapy.
Another name for the method is remineralization. Its essence is to restore the normal mineral composition of the enamel, saturating it with calcium and phosphorus ions. These minerals are delivered to the teeth using pastes, gels, and special compounds that are applied to the surface of the enamel.
- Fluoridation.
Another option for strengthening teeth at the stage of black carious spots is to saturate dental tissues with fluoride. The enamel is coated with gel or fluoride varnish. With simple fluoridation, the drug contains exclusively fluorides, with deep fluoridation - additional minerals, such as calcium.
- ICON method.
This method of treating caries in the form of a black spot has appeared relatively recently. Its essence is that after preliminary treatment and preparation of the tooth, it is coated with a special sealant that seals the enamel pores, preventing bacteria from penetrating deep into the tooth and destroying dentin. The method is safe and painless, suitable for adults and children. But for such treatment it is important to sit for 20 minutes without moving. Therefore, ICON is not prescribed to children under three years of age who find it difficult to sit still for that long.
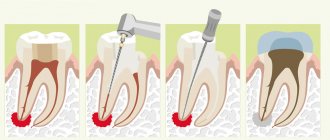
- Preparation and filling.
Sometimes a carious cavity is hidden behind a small black dot. If during diagnosis the dentist discovers a hole in the tooth, then it will have to be treated surgically using a drill. First, the tooth will be numbed with a modern anesthetic, then areas of dental tissue affected by caries will be removed, the cavity will be treated with antiseptic, medicinal solutions, and an adhesive composition will be applied to the walls for better attachment of the filling material. After this, the prepared cavity is filled with a special composite. Today, light-curing fillings are predominantly used, which harden under the influence of light, last for many years and do not shrink. At the final stage, the dentist will align the tooth according to the bite, grind and polish it.
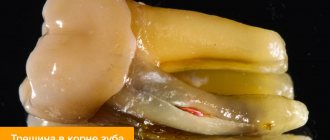
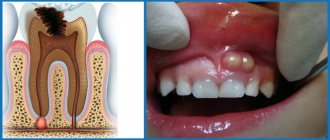
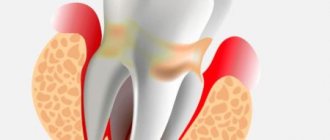
Surgical treatment of gum granuloma
Intervention is necessary in cases where conservative medicine has not had the desired effect. It is required when diagnosing destruction processes in the acute stage. Local or general anesthesia can be used for the operation. The simplest option is gingival excision to expose the purulent sac. The pus flows out, the cavity formed is washed and medicine is placed into it for disinfection and pain relief.
Root resection
During the procedure, the dental surgeon acts as follows:
- The gum tissue is peeled away to gain access to the top of the root system.
- The dental canals are opened and cleaned.
- The formed passages are filled with drugs.
- The granuloma is excised along with the upper part of the tooth.
- The place where the inflamed node used to be is filled with a special bone substitute.
- Filling is being done.
Interradicular hemisection of the root
It is necessary in case of severe damage, when it is no longer possible to cut off only the top while maintaining the main size. Key steps of the operation:
- Removal of the area located inside the alveolus, while the plate itself can be saved.
- Cleaning of periodontal tissues.
- Filling the cavity with a special compound.
- Implant installation.
For preventive purposes, it is necessary to monitor the operated area by regularly taking x-rays. This is an effective and fairly simple method that allows you to preserve a living dental plate, and a neat crown can be installed on the remaining areas in the future.
How to cure granuloma on the root of a tooth with cystotomy
This is a gradual elimination of a large focus of inflammation. To remove all the purulent exudate, an artificial canal is created that connects the inflamed node directly to the oral cavity. After removing the infected fluid, the area is treated with antibiotics and the wound is sutured. The resulting holes can be filled with artificial biomaterial - bone cells. This is a long operation, but it is usually performed without complications.
Removal
It is prescribed as a last resort if other procedures have shown to be ineffective, for example, when:
- Complications arise, an advanced stage.
- An external purulent pocket began to form on the gum.
- A longitudinal crack is formed - the dental plate simply splits into two parts.
- Bone tissue is destroyed (the tooth crumbles).
- Origin of root perforation.
- The canals are destroyed.
During the operation, the root system is completely removed, leaving a hole in the periodontium. It is filled with pus that needs to be washed out. 2-3 months after surgery, a pin can be placed on the healed area to place the implant. Additionally, the doctor prescribes rinsing solutions (for example, Chlorhexidine), gels for local anesthesia and disinfection (Cholisal), as well as antibiotics against bacterial infections and painkillers in tablets or injections.
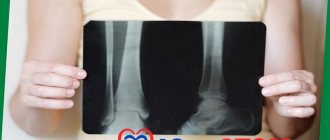
Diagnostics
The task of diagnosis is to determine why the filling material and the dental elements underneath have turned black. Professional techniques will help identify the presence of caries and the extent of damage in order to make a final decision on removal or treatment.
Diagnosis consists of a visual examination, as well as an x-ray examination. If concomitant diseases of the oral cavity are suspected, additional diagnostic methods can be used.
Therapy
If the filling on the front tooth or on any other tooth has darkened, there are three possible solutions to the problem, the choice of which should be determined by the diagnostic results:
- Removal: performed if the tooth is so damaged that it cannot be cured;
- Removing an old filling, treating caries and installing a new filling material;
- Installation of a dental crown after complete elimination of the pathology.
If complications develop and other diseases occur, additional therapeutic measures may be required to eliminate the source of infection and restore the tooth.