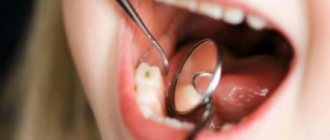
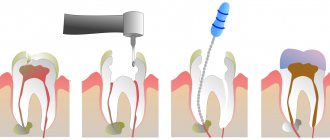
Cervical or basal caries is one of the most dangerous forms of the disease. With this diagnosis, the pathological focus is located in the area of the tooth adjacent to the edge of the gum. It is more difficult to treat due to the difficulty of accessing the carious cavity. The putrefactive process quickly spreads to the root and, faster than other forms, ends with a fracture of the base, that is, loss of the tooth.
Features of the disease
The cervical form of caries is particularly aggressive and inconspicuous in its early stages. Symptoms of this form of caries can appear when the tooth appears intact at first glance. According to statistics, more than 70% of cases of cervical caries are detected too late, when the root canals are damaged or the neck of the tooth is fractured.
Dentists call root caries the most aggressive form of the disease. This statement is based on three significant factors.
The first factor is specific localization
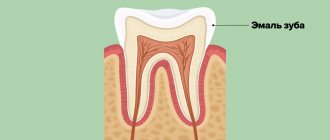
The neck of the tooth, connecting the root and crown, has the thinnest layer of enamel. In addition, this part is covered by the gingival margin, which is why more bacteria and substances that contribute to the destruction of the hard surface of the teeth accumulate on its surface.
Since the thickness of the enamel on the neck is not large enough, and the degree of its mineralization is lower than on the crown, destruction occurs faster. As a result, caries deepens into the dentin and pulp in a matter of weeks, that is, many times faster than when the crown is damaged.
The second factor is specific distribution
Cervical caries tends to spread the pathological process under the gingival margin. In this case, the lesion not only goes deeper inside the tooth, but also around its circumference. This leads to the breaking off of part of the crown at an early stage of the disease.
Important! When the carious lesion covers the entire surface of the cervix, we are talking about the transition of cervical caries to circular. In this case, it is almost impossible to save the tooth.
The third factor is a blow to aesthetics or the invisibility of caries
When located on the front teeth, cervical caries cannot be hidden: it is clearly visible when talking and especially when smiling. This has an extremely negative impact on the psychological state of the patient.
Cervical caries located on chewing teeth, on the contrary, is often ignored and left without treatment. Therefore, more than 80% of patients with this diagnosis turn to dentists when the disease is complicated by pulpitis and the spread of the inflammatory process to the periosteum.
Prices for treatment of caries of anterior teeth in Moscow
The price for treating caries of anterior teeth largely depends on the technique used. Standard therapy with the installation of a light filling will cost from 5,800 rubles. But prices for restoration start at 12,500 rubles. Treatment costs approximately the same without an Icon drill. Treatment of pulpitis on the front teeth involves cleaning the canals, which will add several thousand more to the total amount. If the tooth is seriously damaged and installing a filling is impossible, get ready for serious expenses. The average cost of a ceramic crown is from 25,000–30,000 rubles, and turnkey implantation will cost at least 55,000–100,000 rubles for the installation of one implant.
How does cervical caries develop?
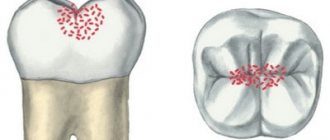
The beginning of cervical caries is the accumulation of plaque near the neck of the tooth.
Against the background of increased acidity and lack of oxygen, as well as under the action of enzymes secreted by bacteria, the enamel softens, opening the gates of infection.
The basal form of caries develops in 4 stages:
- in the first, known as the white spot stage, a dull white spot appears on the tooth at the level of the gum margin;
- at the second stage, a superficial carious lesion develops, which looks like darkening of the enamel;
- on the third, the carious cavity deepens through the enamel into the thickness of the dentin;
- at the fourth stage, deep caries develops, and a “hollow” forms in place of the spot.
The final stage of the disease is a fracture of the tooth in the neck area, pulpitis, accompanied by acute pain, and sometimes an abscess in the gum.
Caries between the front teeth, at the root and on the cutting surface
Caries between front teeth
Interdental caries of the anterior teeth is considered one of the most common. It, as the name suggests, affects the area between the teeth. In this place, the enamel is thinnest, and due to food debris, there is a high concentration of bacteria. Tooth decay on the lower front teeth is usually less common.
Root caries of anterior teeth
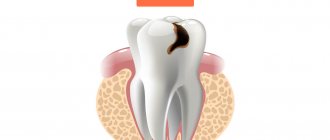
It is localized in the area of the neck of the tooth, hence the name. The lesion usually begins with a yellowish spot, which later turns brown. In the later stages, the disease significantly destroys tissue, so treatment of cervical caries of the anterior teeth must be timely.
Contact
Most often occurs in children during the formation of baby teeth. In adults, this type of lesion occurs due to a genetic predisposition or a lack of minerals and other necessary components for the health of the enamel. Contact caries of the anterior teeth can appear when the process on the diseased tooth affects the neighboring one and “infects” it.
Symptoms
The appearance of cervical caries can be recognized visually, especially if the lesions are located on the front surface of the teeth on the smile line. When located on the lateral teeth, the disease may be indicated by:
- change in tooth texture at the base - roughness to which food sticks;
- when brushing your teeth and running a brush along the neck, acute short-term pain occurs (electric shock effect);
- acute painful reaction to cold and hot, sour and sweet foods.
Unpleasant sensations can appear even during a conversation on the street, when cold air enters the oral cavity.
Stages of cervical caries
Cervical caries develops gradually, the process of disease development includes the following stages:
- Superficial caries. Characterized by damage only to tooth enamel. The disease begins with the stage of a “chalk” stain - the appearance of a white mark on the surface of the tooth. In the affected area, the enamel softens and becomes matte. Pain is not typical for the initial stage of caries, however, as the enamel further deteriorates and a cavity forms, short-term discomfort or pain may be experienced associated with brushing teeth, eating cold or hot, sour or sweet foods.
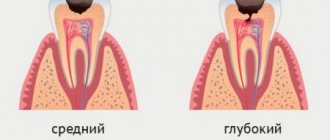
- Average caries. At this stage, dentin is involved in the pathological process. With caries in the middle stage, the pain is still associated with external influences, but lasts longer and becomes more intense.
- Deep caries. It is distinguished by deep penetration into the dentinal layer and severe pain. The reaction to external stimuli intensifies many times, the pain becomes unbearable.
Features of the flow
A distinctive feature of cervical caries is the extensive area of the carious cavity. Unlike other types of caries localization, the lesion quickly spreads not only in depth, but also in breadth. Cervical caries can be complicated by root caries when the cement covering the root of the tooth is involved in the pathological process.
The entire process from the beginning of demineralization of hard tooth tissues to the formation of a carious cavity can take from several weeks to several months (on average 3-6 months). Sometimes the progression of the disease stops - the growth of the stain stops, and the sensitivity of the teeth decreases. Suspended cervical caries is not a reason to refuse a visit to the dentist. It should also be treated, since the disease can become active at any time.
Causes
The main cause of the development of cervical caries is considered to be the bacterium Streptococcus mutans, which lives in dental plaque. Accumulating in gum pockets, it contributes to softening of the enamel and destruction of the tooth at the base.
Other factors can provoke the development of pathology:
- regular consumption of excessively acidic foods and drinks;
- improper brushing of teeth;
- long-term use of certain medications that weaken enamel;
- endocrine diseases;
- deficiency of vitamins and minerals;
- pregnancy.
According to statistics, cervical caries often develops in older patients with a history of periodontitis and bad habits (smoking).
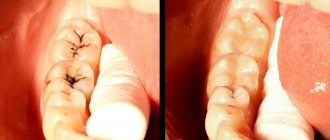
How is caries between teeth treated when molars and premolars are affected?
The algorithm is like this:
- First, anesthesia is performed. If the lesion is shallow, sometimes topical anesthesia is sufficient; for deeper stages, an anesthetic injection is given with a drug to which the patient is not allergic.
- The affected areas are cleaned of plaque and tartar, and a rubber dam is applied.
- Carious cavities are prepared; in most cases, not only the affected tissue is removed from the chewing teeth, but also some of the healthy tissue to provide the necessary access;
- The cavities are treated with disinfectants and treated with adhesives.
- The tooth is filled with modern photocomposite materials, which are illuminated with special lamps. To restore the side walls of the chewing teeth and ensure tight contact between them, the dentist uses special wedges and matrices.
- At the final stage, the restored surfaces are polished.
Diagnosis of the disease
Cervical caries can be diagnosed during a dental examination of the oral cavity. The specific location and rough structure of the carious spot make it possible to differentiate the pathology from a wedge-shaped defect and simple caries.
Additionally, instrumental diagnostic methods are used: dental radiography, radiovisiography, transillumination and others. They allow you to assess the degree of penetration of caries into the tooth cavity, see hidden lesions and predict the effectiveness of treatment.
Treatment Options
A variety of techniques are used to treat cervical caries. Their choice depends on the stage of development of the carious lesion.
Spot stage
At the spot stage, radical methods of therapy are not used. To restore the strength of the enamel, it is enough to carry out 3-4 courses of remineralizing treatment, which consist of several stages:
- Professional teeth cleaning.
- Application of a carious stain with fluoride-containing compounds.
- Systematic oral care with products containing a high fluoride content: mouth rinses, toothpastes.
- Including salt and water enriched with fluoride in the diet.
After just 1-2 courses of remineralization, the white spot will be eliminated, and the risk of recurrent caries will decrease.
Stage of superficial caries
When caries spreads superficially, the doctor removes tartar and plaque, and then grinds the surface of the pathological focus to healthy tissue. To strengthen the enamel and prevent repeated destruction, several courses of remineralization are carried out.
Stage of middle caries
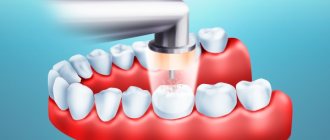
If enamel and dentin are damaged, preventive cleaning and fluoridation of tooth enamel is indispensable. To eliminate the pathology, the doctor will have to clean the carious cavity from putrefactive tissue, then literally saturate the dentin with drugs that suppress bacterial activity. Finally, the hole in the tooth is filled with polymer materials.
Stage of deep caries
With deep caries, treatment is extremely painful, so it is carried out only under local anesthesia. After the medicine takes effect, the doctor begins treatment:
- Pulls back the edge of the gum to have full access to the carious cavity.
- Cleans the carious cavity from necrotic tissue with dental instruments and a drill. If necessary, the pulp is removed and the dental nerve is extracted.
- The tooth cavity is isolated with special adhesive materials, and the equine canal is filled.
- Layer-by-layer filling is carried out with photopolymerization of each layer.
- The final grinding of the filling and tooth is performed.
This procedure takes several days or even weeks and costs several times more than treatment at the initial stage.
Can you take care of your dental health yourself?
Yes, sure. There are a number of rules that, if followed daily, will significantly reduce the risk of developing carious lesions:
- Brushing your teeth twice a day. Allows you to remove soft plaque in which bacteria multiply. To get rid of it reliably, you need to brush your teeth morning and evening with a brush that has medium-hard bristles. Each such procedure should last at least 3-4 minutes. A good solution would be to alternate fluoride-containing toothpaste (1 week) and fluoride-free toothpaste (3-4 weeks). This periodicity is due to the fact that enamel has a saturation limit with fluoride. A week of using fluoride-containing paste will provide the enamel with a sufficient amount of this element, and then fluoride will simply be removed from the body. But after a month, its concentration will decrease and its influx will be required again.
- Supplement the procedure with dental floss at least once a day, since the brush is not able to fully clean the spaces between the teeth.
- Regular brushing after meals. Residues should be removed by normal rinsing. It should be done after every meal. And to get rid of food particles that linger in the interdental space, it is best to use dental floss.
- Be careful with sweets! Bacteria that cause caries multiply much more intensively in an environment rich in sugars and fats. Therefore, instead of another cake, it is better to eat an apple or carrot. On the one hand, you deprive the bacteria of additional nutrition, and on the other, the solid consistency of such products itself cleanses the teeth and removes soft plaque.
The above preventive measures can be carried out independently. However, you cannot do without periodic assistance from a dental specialist. Therefore, we recommend contacting our clinic to determine the risk level of caries for you and your family members. And then, based on these results, SM-Dentistry doctors will develop an individual plan for preventive oral examinations for you. Constant preventative care will ensure your dazzling smile and the health of your entire oral cavity.
And of course, if acute symptoms of the disease appear, you should never self-medicate! This will only worsen the situation and cause complications. If you experience pain, we invite you for a consultation with a specialist at the SM-Dentistry clinic, call tel. or fill out the feedback form on our website.
Prevention
Only careful oral hygiene can prevent the occurrence of cervical caries. In addition to brushing your teeth twice a day with toothpastes, it is recommended to use dental floss. To remove plaque from gum pockets and remove hard deposits, you need to visit the dentist twice a year and have your teeth professionally cleaned.
To maintain oral health, it is recommended to include fresh solid vegetables and fruits in your diet: apples, carrots, cabbage, etc. Dairy products as a source of calcium and phosphorus will be beneficial for your teeth.
When the first signs of cervical caries appear, you should make an appointment with a dentist and treat the disease before it becomes complicated by pulpitis.
Other
Complications and consequences of internal caries
The soft tissues surrounding the tooth may also become inflamed. Sometimes the patient notes a general deterioration of the condition against the background of progressive carious lesions. His body temperature may rise, problems with the digestive system, bad breath, etc. may appear. Due to the negative effects of bacteria, flux and suppuration, cysts, and ulcers may appear.
Due to pain in the tooth, it becomes impossible to chew food normally, and a reaction to the slightest irritants appears. If the disease is not treated in time, periodontitis and periodontitis develop, which can result in tooth loss. This, in turn, is a serious stress and requires a long recovery.
Unfortunately, not all patients' caries disappears without a trace; some may encounter unpleasant complications both in the first days after treatment and several months after it. The most common phenomenon is an allergy to the materials used in the work. Sometimes infectious lesions are diagnosed, the cause of which may be the unscrupulous work of the doctor or failure to comply with the rules of personal hygiene.
previous post
White caries
next entry