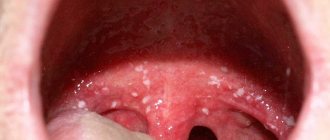
Chronic stomatitis is a disease that is accompanied by repeated inflammatory processes of the oral mucosa. Many patients want to know what causes the development of chronic stomatitis. In the vast majority of cases, the development of this pathological condition is associated with a whole complex of various factors - both internal and external.
The most common form today is chronic aphthous stomatitis, which is diagnosed in 5% of cases among all diseases of the oral mucosa.
In our clinic you can get a free dental consultation!
Our doctors
18 years of experience
Baghdasaryan
Armen Evgenievich
Chief physician, dentist-orthopedist-therapist
Graduated from VSMA named after. N.N. Burdenko. Internship on the basis of MGMSU named after. A.E. Evdokimov in “General Dentistry”.
Clinical residency at the Moscow State Medical University named after. A.E. Evdokimov in “Orthopedics”.
More about the doctor...
5 years experience
Sadina
Ekaterina Vladislavovna
Dental therapist, surgeon
Penza State University Medical Institute, specialty “Dentistry”.
In 2016, she underwent professional retraining in the specialty “Therapeutic Dentistry” at the Moscow State Medical and Dental University named after A.I. Evdokimov.
More about the doctor...
8 years of experience
Arzumanov
Andranik Arkadievich
Dentist-orthodontist
Graduated from Moscow State Medical University. Internship - Moscow State Medical University at the Department of Orthodontics and Children's Prosthetics.
Residency at Moscow State Medical University at the Department of Orthodontics and Children's Prosthetics. Member of the Professional Society of Orthodontists of Russia since 2010.
More about the doctor...
How to treat stomatitis
For any form of stomatitis, treatment begin with a visit to the doctor's office. The dentist must determine the form and severity of the disease in order to prescribe appropriate therapy. Self-medication may not bring results and thus aggravate the situation, allowing the disease to progress to a more severe stage.
The diagnosis of “stomatitis” is made by the doctor after an examination, and after that he can prescribe the patient to take an oral smear to find out the exact cause of the disease. PCR analysis of the biomaterial will show the presence or absence of a pathogen, for example a Candida fungus or a herpes virus. If the cause is not the pathogen, an additional visit to another doctor may be required. Thus, if allergic stomatitis is suspected, the patient will be referred to an allergist, and if immunity or metabolic disorders are suspected, the patient will be referred to an immunologist or gastroenterologist.
In addition to establishing the cause of the disease, the patient receives recommendations on how to treat stomatitis in his case , including:
- ✔️ Bringing oral hygiene back to normal and further supporting it;
- ✔️ Treatment of ulcers with special means, depending on the diagnosis - antiseptic, antiviral or antifungal;
- ✔️ Pain relief with anesthetics;
- ✔️ Use of products that eliminate inflammation and swelling;
- ✔️ Following a diet to restore the mucous membrane.
Although stomatitis is treated with drugs , the patient needs to adhere to a diet so that food does not cause mechanical damage to the already inflamed mucosa. You will have to exclude hard, sour, spicy and overly salty foods from your diet. The menu will be similar to what is prescribed for gastrointestinal diseases: boiled products crushed to a puree state, liquid porridges and broths, fermented milk products. Everything is warm temperature, nothing hot or cold. Even soft bread will have to be removed, as it can scratch irritated areas in the mouth. For children, the doctor gives recommendations depending on their age.
Causes
It is customary to identify various causes of chronic stomatitis in adults. They determine the form of the disease:
- The aphthous form can be caused by E. coli, streptococci, or a bacterial allergic reaction. There is a connection with autoimmune pathologies, as well as disruptions in the gastrointestinal tract and endocrine system;
- The candidiasis form develops with long-term use of antibacterial agents when infected with fungi of the genus Candida;
- The herpes form occurs due to the presence of the herpes simplex virus in the body with decreased immunity;
- Prosthetic chronic stomatitis in adults can be caused by various factors: an allergic reaction to the components from which the prosthesis is made; insufficiently good hygiene of dentures; frequent damage to the mucous membrane due to improperly fitted, installed or faulty dentures;
- Vincent's stomatitis can be provoked by spindle-shaped bacillus and Vincent's spirochete against the background of decreased immunity.
We cannot ignore the factors that provoke the development of chronic recurrent stomatitis. These include:
- unbalanced diet;
- taking medications;
- frequent stress;
- acute respiratory diseases;
- hypothermia;
- vitamin deficiency;
- irregular and insufficiently good oral hygiene;
- advanced stages of caries;
- ear, nose and throat infections.
What lesions in the oral cavity can cause aphthous stomatitis?
The aphthous stage can be observed with lesions of the oral mucosa of a very different nature. Most often associated with the following.
Acute herpetic stomatitis (with primary infection with herpes viruses, primary). In many cases, in children, especially those with weakened immune systems, the first infection with the herpes virus leads to acute stomatitis, which develops into a very painful aphthous stage ( acute aphthous stomatitis ).
Recurrent herpetic stomatitis. Stomatitis caused by a herpes infection already present in the body, which is activated by a temporary weakening of the immune system. Usually manifests itself in the form of herpes on the lips or other local places. But in the chronic form, aphthous phases are also possible - chronic aphthous stomatitis.
Chronic recurrent aphthous stomatitis (abbreviated as CRAS). A disease whose causes have not yet been established (infection in combination with a vitamin imbalance and certain pathologies of the nervous system is assumed). The initial stage is characterized by the well-known symptoms of stomatitis and the appearance of one or several pink-white spots on the mucous membrane, which very quickly (1-2 hours) turn into aphthous formations. Relapses occur over periods of up to several months, and in the absence of systemic therapeutic treatment, the disease and lesions progress.
Clinical manifestations
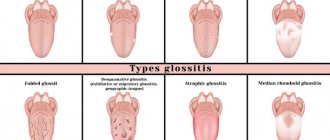
The symptoms of chronic stomatitis directly depend on the form of the disease
| Type of acute stomatitis | Clinical manifestations |
| Atrophic |
|
| Vincent |
|
| Herpetic |
|
| Prosthetic |
|
PREVENTION OF HERPETIC STOMATITIS
Prevention of herpetic stomatitis should be carried out not only after a person has had symptoms of herpes, but also before birth. That is, work should be carried out with parents both by an obstetrician-gynecologist and a dentist. The simplest rules for preventing herpetic stomatitis are:
- Use of masks;
- Careful hand hygiene;
- Use of personal hygiene products;
- Individual dishes, towels, etc.;
- Bans on kissing;
- Prohibition on tasting food;
- General cleaning of the premises;
- Ventilation;
- Hardening the body;
- Good nutrition;
- Physical activity;
- Timely treatment of common diseases.
But if you or your child come into contact with a person who suffers from herpetic stomatitis, it is recommended to lubricate the oral mucosa with antiviral ointments (for example, acyclovir) for 5 days, or prevention may involve taking interferon.
Diagnostics
The most important role in diagnosing a disease is to establish the causes of its development. It is they who determine the future tactics of treating inflammatory processes. In order to achieve the desired result, make a smear from the surface of the ulcer, and also carry out:
- study of ulcerative lesions;
- bacteriological examination;
- checking the plasma chain reaction of scrapings.
Symptoms
Manifestations of recurrent stomatitis are characterized by the following clinical signs and symptoms:
- At the very beginning of an exacerbation, the mucous membrane of the oral cavity swells, turns pale, the formation of pronounced red spots, as well as hyperemia of certain areas, is possible.
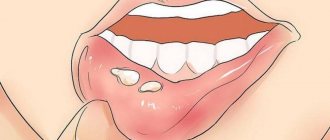
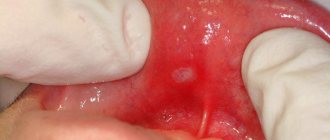
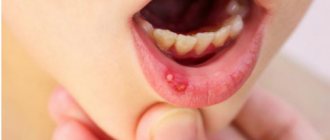
- A limited inflammatory process begins on the mucous membrane, resulting in the formation of an oval or round aphthae, reaching several millimeters in diameter. On top, the inflammation is covered with a grayish coating, difficult to separate from the aphthae. Most often, the inflammatory process occurs on the surface of the mucosa, but it can also penetrate deeper, causing tissue necrosis. In this case, an ulcerative inflammation forms at the site of aphthous inflammation, after healing of which a scar remains on the mucous membrane.
- Damage to the mucous membrane is painful, makes it difficult to eat and is accompanied by copious uncontrolled salivation.
- With each relapse, the cervical and submandibular lymph nodes become painful and increase in size. A slight increase in temperature, weakness, headaches and simultaneous aphthae rashes on the genital mucosa are possible.
- The disease can accompany a person throughout his life. At first, relapses have some kind of sequence, most often occurring in the spring and autumn seasons, but over time the frequency becomes confused, exacerbations occur more often, the periods between them can be shortened from several months to several weeks and even days.
- The duration of an exacerbation depends on the general condition of the body and can take up to ten days for one aphtha to heal. If they do not appear at the same time, then the relapse is prolonged until the last rash heals.
Treatment
In order to eliminate chronic stomatitis, professional oral hygiene, sanitation of infectious foci and local applications are carried out. As for the specific tactics used for one form or another of the disease, they are presented in the table below
| Type of acute stomatitis | Treatment options |
| Vincent |
|
| Herpetic |
|
| Traumatic |
|
Prognosis for aphthous stomatitis
In the most typical cases, aphthae disappear without a trace after 7-14 days. But in certain cases, relapses are possible (diagnosed as chronic aphthous stomatitis or as a specific disease - chronic recurrent aphthous stomatitis ). Treatment of such chronic diseases is extremely difficult, there are no standard methods, only an individual approach is possible depending on the reasons causing the recurrent course.
Our dental clinics “TAVI” and “Veronica” provide high-quality and safe treatment of aphthous stomatitis of any stage and complexity.
Request a consultation
Where to contact?
You can get treatment for chronic stomatitis at the Good Hands dental clinic. Our specialists are well aware that frequent relapses of the disease can reduce the patient’s quality of life and can provoke the development of periodontitis and benign and malignant oral tumors. They use individual treatment tactics that allow you to achieve good results, make the treatment effective and painless. You can schedule a free consultation with us and find out all the necessary information right now by filling out an application on our website or calling us by phone.
Causes of aphthous stomatitis (stages of the appearance of aphthous stomatitis in the mouth)
The mechanisms leading to the appearance of such specific formations in the oral cavity are still not clear. Undoubtedly, the appearance of aphthous stages is facilitated by various negative effects on the body: stress, depression, overwork, various internal diseases, common infectious diseases, mechanical damage to the oral mucosa, etc. Among the mechanisms that directly lead to the formation of aphthae, the following are most often considered.
Autoimmune reactions. The components of the immune defense attack not only foreign bodies and cells, but also cells of the body’s own (for example, cells of the oral mucosa). It has been noted that in some autoimmune pathologies, aphthous stomatitis .
Allergic reactions. There is evidence that patients suffering from food allergies, especially to citrus fruits and gluten, have an increased risk of aphthous stomatitis.
Viral infection of unknown origin. It is well known that herpes simplex viruses cause herpetic stomatitis. But some studies suggest that the aphthous stage, including that of herpetic stomatitis, is initiated by another virus of unknown nature.
Damage to nerve endings. Healing of tissue lesions is always difficult when blood circulation is obstructed in these areas. Therefore, it is assumed that the formation of aphthae can be initiated by local lesions of nerve endings that take part in the regulation of local blood circulation.
Deficiencies of nutritional components. It is assumed that the appearance of aphthous lesions may be due to a deficiency of vitamin B12 and folic acid (necessary for cell division), and iron.
Some substances and components. It is believed that aphthous lesions can be initiated by components of toothpastes such as sodium lauryl sulfate, sodium dodecylpolyoxoethylene sulfate, triclosan, as well as some food additives (food colorings) and some drug components.
Some diseases. It has been noticed that some diseases are sometimes accompanied by the appearance of aphthae in the oral cavity. Among them: rheumatoid arthritis, inflammation of the iris (iritis), erythema nodosum, joint pain (arthralgia), and some pathologies of the intestinal mucosa.
Stomatitis and treatment at home
Treatment of stomatitis at home primarily involves the use of various herbal decoctions and infusions with antiseptic, anti-inflammatory and immunostimulating effects. For example, even doctors recommend rinsing with calendula - it has a strong antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory effect and promotes healing. Chamomile is an excellent antiseptic - it is one of the most popular remedies that is widely used in folk and official medicine.
Stomatitis is treated using folk remedies not only for rinsing, but also for oral administration. For example, rosehip decoction is a real storehouse of vitamins and other substances necessary for the human body. It improves immunity, prevents the development of inflammatory processes, and also helps destroy harmful bacteria. Despite the miraculous power of herbs, it should be remembered that candida and herpetic stomatitis will not be eliminated by such folk treatment, since fungi and viruses are not affected by antiseptic, anti-inflammatory and immune-modifying agents.
Prognosis and prevention
Provided the cause of the disease is identified and timely adequate treatment, the prognosis for stomatitis is favorable - the disease goes away without a trace. If treatment is insufficient or started late, the process may become chronic, exacerbations of which will periodically cause discomfort to the patient. In severe cases, systemic complications of the disease may develop - the prognosis is unfavorable.
To prevent the development of stomatitis, you should provide proper oral care, lead a healthy lifestyle, avoid stress and regularly undergo preventive examinations with a therapist and dentist - this will allow you to diagnose diseases at an early stage and take measures to eliminate them.