Published: 11/03/2021 10:00:00 Updated: 11/03/2021
Urticaria is an allergic disease, the causes of which in children and adults can be very different. The main symptom of the disease is the appearance of blistering rashes on the skin, which are very itchy and resemble a nettle burn.
According to statistics, 25% of the entire population of the planet has encountered this pathology at least once in their lives, mainly children and women under the age of 40. With constant contact with the allergen, the disease becomes chronic, and in half of all cases it is accompanied by Quincke's edema.
Reasons for the development of urticaria
Hives never develop on their own; there is always a reason for this.
In some cases, identifying it is not difficult, but sometimes it is difficult to do. Most often, urticaria in children appears after using certain medications or eating certain foods. The most allergenic foods for babies are honey, nuts, fish, food additives, spices, sausages, and processed foods. Therefore, they are not recommended for children under 3 years of age.
Also, provoking factors include:
- insect bites;
- the presence of parasites in the body;
- plant pollen;
- mold;
- chemicals, including household chemicals;
- latex;
- ultraviolet radiation;
- vibration.
However, it is not always possible to find out what exactly the patient developed allergic urticaria to. In about a third of all patients with this diagnosis, the causes of the disease, even after numerous tests and analyses, remain unknown.
Treatment
In the treatment of pimples on the tongue, regardless of the reasons that caused their appearance, there are common points:
- Mandatory thorough oral hygiene. After each meal, it is advisable to treat pimples with an antiseptic solution.
- Excluding any irritating factors from the child’s diet: spicy, hot or sour foods. It is desirable that the food is soft and does not cause additional injury to the mucous membrane.
- Under no circumstances should pimples be squeezed or opened; this can lead to the development of complications in the child and aggravation of his condition.
- Dr. Komarovsky recommends in such cases drinking a large amount of liquid, which will help remove toxins and allergens from the child’s body.
If pimples cause pain and discomfort in a child, then the doctor may prescribe products for topical use with an analgesic and anti-inflammatory effect (Solcoseryl, Metrogyl denta).
If the cause of pimples is a sore throat or stomatitis, then it may be recommended to take antibacterial agents in combination with antiseptics. Treatment of allergic manifestations consists of eliminating the action of the allergen and taking antiallergic medications. For herpetic lesions of the mucous membranes of the tongue, antiviral drugs have a good effect, and for candidiasis - drugs with antifungal action.
Before you begin to treat pimples that appear on the tongue, you need to find out the causes of their occurrence. It is from this moment that all further treatment measures will depend. In order to make a correct diagnosis, you need to visit a dentist. Self-medication can be dangerous for the child.
Symptoms of urticaria
The main manifestation is the appearance on the skin of red or pink spots of various shapes, and blisters, the size of which can reach several centimeters.
A slight swelling may appear, which gradually disappears over the course of a day, rarely two. If the swelling affects the deeper layers of the skin or mucous membranes, angioedema may result - a life-threatening condition that requires immediate medical intervention.
The rash of allergic urticaria is always accompanied by unbearable itching, and some patients describe it as an unbearable burning sensation. Violent scratching of such areas can lead to infection of the epidermis with further complications in the form of pustules and wounds.
Minor manifestations of urticaria include:
- headache;
- elevated temperature;
- sleep disorder;
- anxiety;
- loss of appetite.
According to the nature of the course, allergic diseases are divided into two types.
Acute urticaria is diagnosed most often. Blisters and swelling of the skin in this form appear completely suddenly, sometimes against the background of a person’s excellent health. Most often caused by some external reasons, food. It also happens after using medications, especially when self-medicating. Symptoms go away on their own within a few days to several weeks.
Chronic urticaria is a condition in which symptoms continue to persist for more than 6 weeks after the first rash on the skin. This variant is characterized by a wave-like course, when periods of complete absence of symptoms (recovery) are abruptly replaced by exacerbations with the appearance of a new portion of spots and blisters. This is accompanied by unbearable itching and rapid development of Quincke's edema. The emerging elements of the rash can merge with each other, covering more and more new areas of the skin.
Sometimes periods of complete well-being without symptoms can last for a long time - up to 10 years.
Children's urticaria is an allergic skin disease, which most often develops against the background of an existing exudative diathesis and appears due to food products introduced as complementary foods.
It has been noticed that this type of allergy mainly develops in babies who are bottle-fed or eat foods that are not appropriate for their age.
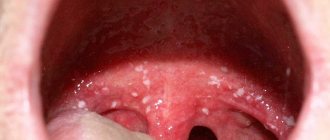
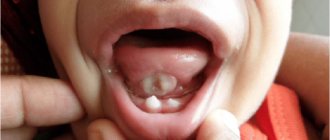
Pimples on the tongue - what are they?
The mucous membrane in the mouth and tongue does not have sebaceous glands, so typical pimples cannot form on it. Such formations have two formation mechanisms:
- Under the influence of damaging factors, viruses or bacteria, the mucous membrane stratifies, under the top layer of which liquid accumulates and small bubbles form. If such a formation is not infected, then its contents will be transparent, but if infection has penetrated into its cavity, then suppuration is possible - the vesicle will turn white. If blood gets into the liquid, then this formation takes on a red or dark tint. The blisters may burst and painful ulcers form in their place.
- Sometimes, in response to inflammation, cells on the surface of the tongue begin to actively divide and slough off. Whitish or red formations form that resemble ordinary pimples, but at the same time they are only enlarged papillae.
Complications of urticaria
It is important to know what hives look like and to be able to provide first aid correctly.
This will help prevent the development of severe complications that can lead to death. Often urticaria is accompanied by Quincke's edema, which is also called angioedema. Its development in the larynx area is especially dangerous, as it can compress the trachea and impair breathing.
Another serious complication is anaphylactic shock. This is a life-threatening immediate allergic reaction that occurs when the human body is hypersensitive to a particular allergen. Usually develops upon repeated contact with the allergen and requires immediate medical attention.
4.How to treat urticaria and Quincke's edema?
The easiest way to deal with urticaria and angioedema is if you can identify and eliminate the factor that caused the problem. But this is not always possible. Typically, antihistamines are used to treat hives. They will help relieve the symptoms of the disease. Sometimes antihistamine medications need to be taken regularly to prevent the rash and associated swelling.
Chronic urticaria is treated with antihistamines or a combination of them. But if this does not give the desired result, sometimes the doctor prescribes corticosteroids.
In severe cases of urticaria and angioedema, an injection of adrenaline or steroid medications may be necessary.
What else can be done to treat hives?
While the course of treatment is ongoing and you are waiting for the redness and swelling to disappear, follow these simple recommendations.
- Do not use hot water. Let it just be warm.
- Wash with mild soap.
- You can apply cold compresses or apply a damp cloth to the affected areas.
- Be in a cool room.
- Wear loose, lightweight clothing.
Diagnosis of urticaria
Before starting treatment, it is important to understand what exactly a person has such a strong allergic reaction to.
Only by removing this provoking factor from your usual life can you not be afraid that the symptoms of urticaria will appear again, and this is possible even after proper therapy. Most often, this type of allergy appears to food. It is possible to determine what exactly caused the rash by a blood test: the level of IgE antibodies to a mixture of food allergens is detected. First of all, you need to diagnose the presence of an allergic reaction to:
- nuts;
- vegetables and legumes;
- citrus fruits and fruits;
- seafood;
- cereal and sesame flour;
- fruits and melons;
- baby formula;
- fish;
- meat;
- mushrooms;
- loose leaf tea;
- goat milk.
In addition to food, allergic manifestations can also occur to other substances that surround us almost everywhere in life:
- mold fungi;
- pollen from early flowering trees;
- pollen of late-flowering trees;
- weed pollen;
- epithelium of domestic animals;
- house dust;
- house dust mite;
- poultry feather.
To identify the exact type of allergen, allergy tests are performed on certain foods.
It often happens that rashes appear due to seasonings and herbs used in cooking: paprika, cumin, cloves, basil, ginger, tarragon, thyme, marjoram, dill, bay leaf, black pepper, vanilla. Some types of fish may also be allergenic: cod, halibut, mackerel, and squid meat. But sometimes an allergic reaction in the form of urticaria develops to such familiar products as:
- cucumber;
- apricot;
- cherry;
- tomato;
- plum;
- grape;
- persimmon;
- carrot;
- beet;
- watermelon.
All tests are carried out only by a specialist laboratory technician. You cannot independently determine the presence of an allergy in the form of urticaria to a particular food product or substance. This can be life-threatening, since it is possible to develop not only Quincke's edema, but also anaphylactic shock.
3.Diagnosis of the disease
The diagnosis of urticaria or Quincke's edema is made after examination. Your doctor will ask you a few questions to find out the possible cause of your hives or angioedema and examine your skin. Depending on your health condition, you may need to consult an allergist, immunologist or dermatologist.
Skin tests may be done to determine which substance is causing your allergy. And routine blood tests are needed to determine the presence of some systemic disease.
About our clinic Chistye Prudy metro station Medintercom page!
First aid for hives
It is important that you always have allergy medications in your home medicine cabinet, since urticaria in adults, and in children too, can appear at any time.
Allergy medications can be in the form of drops or tablets. Modern remedies do not cause drowsiness and have virtually no side effects. Doctors recommend having in your home medicine cabinet to eliminate urticaria and itching, Fenistil drops, which can be used from childhood, Erius tablets, which have a long-lasting antihistamine effect after administration, Loratadine, which helps cope with Quincke's edema, which often accompanies urticaria.
It is important to take the medicine at the first symptoms, without waiting for the general condition to worsen. If after 20 minutes from the moment of administration there is no improvement, you should call an ambulance.
How is diagnosis and treatment carried out?
To cure a rash on a child’s tongue, it is dangerous to self-medicate - after all, you first need to identify the true cause of the disease. Therefore, the first thing you should do is contact a pediatric dentist or pediatrician (if the child is very small) and undergo the appropriate tests - PCR blood diagnostics or tongue scraping.
Next, the drug is prescribed in accordance with the goal that needs to be achieved during treatment:
- for pain relief: for example, ibuprofen-based drugs,
- to relieve swelling and allergic manifestations: antihistamines are shown here - “Suprastin” or “Zodak”,
- to neutralize the pathogen: antibiotics are prescribed for bacterial inflammation. If the herpes virus is “to blame,” then antiviral drugs (“Acyclovir”) are used; in case of fungal infection, “Nystatin” or “Fluconazole” are used.
- Regenerative drugs are prescribed for tissue restoration.
To strengthen the body, a course of fortification and proper nutrition are prescribed. Until the negative symptoms are completely relieved, the child should not eat dry, hard, sour or spicy foods. You should also exclude very hot and cold foods. Food should be warm and soft (can be mashed with a fork or blender) so as not to further injure the inflamed areas in the mouth.
Treatment of urticaria
The only way to get rid of the disease is to avoid contact with the allergen, which is previously detected by laboratory tests.
If testing does not reveal a provoking factor, and the urticaria is episodic, then taking antihistamines will quickly eliminate the symptoms. During treatment, it is recommended to follow a diet that, in case of urticaria, will help prevent the recurrence of the disease. The menu should include only hypoallergenic products: lean boiled meat, soups with recycled meat broth or vegetarian. It is better to choose rice, buckwheat, and oatmeal from cereals. Low-fat cottage cheese, natural yogurt, apples, dried fruit compote, excluding raisins, and whole grain bread are recommended.
Citrus fruits, nuts, fish and all seafood, chocolate products, smoked meats, coffee, eggs, honey, and store-bought baked goods should be excluded from the menu during treatment.
Treatment is carried out by a dermatologist and an allergist-immunologist. For topical application, ointments for urticaria are effective; they not only relieve itching, but also eliminate swelling, redness and a burning sensation on the skin. One of the most effective is Dimetinden gel, which must be applied in a thin layer to the affected area of the skin up to 4 times a day.
A course of antihistamines is prescribed in the form of tablets. Your doctor may also prescribe calcium gluconate or calcium chloride for urticaria. They help reduce the symptoms of allergies, but they should only be administered under the supervision of a doctor in the treatment room.
If antihistamines do not provide the desired effect quickly, or for severe forms of hives, corticosteroids are used, which can be applied to the skin or taken in the form of tablets or injections.
The appearance of a pimple on the tongue: diseases and treatment
The most harmless reason for the appearance of a pimple on the tip of the tongue is mechanical damage. Regular antiseptic treatment is enough to get rid of the problem. To relieve inflammation, you can use decoctions of sage and chamomile. A prerequisite is not to touch the wound with your hands, as you risk causing a more serious infection.
Allergy
It usually manifests itself as a scattering of small pimples throughout the tongue plate; if treatment is not addressed immediately, the pathology penetrates the root of the tongue, the frenulum and affects the larynx.
How long does it take to cure hives?
Within 4-6 weeks, acute urticaria resolves in almost all patients with this diagnosis.
However, sometimes the acute form can become chronic, and then the disease becomes incurable, with periods of exacerbation and complete remission with the absence of symptoms, which alternate with each other. To deal with this allergic reaction as quickly as possible, it is recommended:
- Immediately consult a doctor at the clinic or call an ambulance.
- Follow a hypoallergenic diet for several months.
- Follow all doctor's orders and recommendations regarding treatment. Do not stop taking allergy medications at the first signs of improvement, but complete the full course.
- Be sure to have modern antihistamines recommended by an allergist in your home medicine cabinet.
Author:
Pugonina Tatyana Alekseevna, Therapist
When and which doctor to contact
Usually a doctor is consulted:
- if the rash spreads over a large area;
- when symptoms increase;
- when signs of general intoxication occur;
- if the urticaria does not go away on its own after eliminating the factor that caused it;
- if the disease becomes chronic or often recurs,
It is advisable not to delay your visit to the doctor and come when the first manifestations of the disease occur. Then it will be easier to establish the cause, and treatment will take less time. In addition, the doctor will recommend what to do to prevent hives.
A therapist or pediatrician, a dermatologist can provide assistance with urticaria, and an allergist is involved in targeted diagnosis and treatment.
Possible reasons
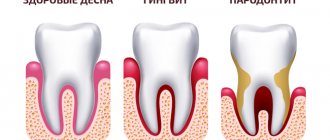
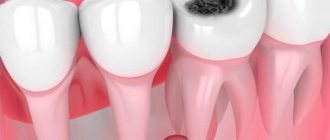
- Mycoses. Most often, red dots in the mouth are symptoms of oral candidiasis. Fungi of the genus Candida are considered opportunistic. They live in the intestines and do not cause harm to the body. However, when they enter the oral cavity, they quickly multiply and provoke inflammation of the mucous membrane. Spots of different shades of red can form on the gums, palate, cheeks, tongue, and tonsils.
- Bacterial infections. One of the main pathogens is streptococci. They change the structure of the mucous membrane and lead to inflammation of the soft tissues. They provoke the development of pharyngitis and tonsillitis.
- Viral diseases. Acute respiratory viral infections can also be accompanied by the formation of red spots on the oral mucosa. Pathogens enter the oral cavity through the nose. The gums and palate become inflamed, local hyperemia appears. If the spots become covered with a white coating, we can talk about a fungal or bacterial infection.
- Neoplasms. Suspicious spots on the gums may turn out to be benign tumors. The most common include papillomas and granulomas. Also, the risk of malignant neoplasms cannot be excluded.
Location: on the base
Pimples at the base of the tongue interfere with swallowing and even speaking, they hurt and cause a lot of trouble. The reasons for their appearance can be very diverse. It could be stomatitis, a fungal infection, a sore throat or pharyngitis. Only an experienced doctor can make a correct diagnosis. We can only suggest what you should pay attention to.
If a pimple appears on the base of the tongue, you should carefully analyze other symptoms - fever, enlarged lymph nodes, the presence of allergic reactions. For example, with a sore throat, pimples form in the throat quite often. They are painful, make swallowing difficult and cause pain when talking. In this case, the patient also has enlarged tonsils and submandibular lymph nodes, and an elevated temperature. As a matter of fact, acne and fever almost always occur either with a sore throat, or with tonsillitis or pharyngitis.
It is undesirable to ignore pimples on the tongue near the throat, since in particularly advanced cases they can interfere with breathing, which can lead to suffocation. Therefore, having discovered them in yourself, you need to contact an ENT specialist for a diagnosis.