Diagnosis of maxillary sinusitis of odontogenic nature is an urgent problem in otorhinolaryngology, dentistry and maxillofacial surgery, since their occurrence is a consequence of the disease and treatment of the teeth and jaws [1]. In the structure of sinusitis, according to a number of researchers, the proportion of odontogenic sinusitis ranges from 14 to 24% [2, 3].
The prevalence of various forms of caries among the working population and the poor organization of dental services make this problem not only medical, but also economic and social.
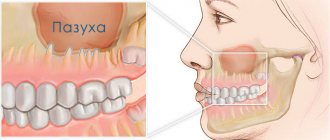
X-ray computed tomography (XCT) is the best option for studying the alveolar process, nasal cavity, paranasal sinuses and surrounding soft tissues if the odontogenic nature of sinusitis is suspected. Despite the high radiation exposure, X-ray CT allows one to immediately assess the condition of the bones of the facial zone and determine their anatomical features, identify the connection with the “causal” tooth, clarify the localization of the foreign inclusion and the degree of inflammatory changes in the mucosa. In cases of prolonged inflammation in combination with canal refilling, surgical removal of the material is the only effective treatment method, for planning of which it is necessary to know the spatial anatomy [4]. These data can be obtained by performing RCT.
As sinusitis progresses, depending on the nature of the inflammation, the thickness of the adjacent bone wall changes: in acute purulent processes, osteoporosis occurs, in chronic recurrent processes - osteosclerosis, in complicated forms - osteomyelitis and destruction of the bone wall [5].
Retromaxillary (retroantral) fiber also changes as a structure intimately located to the transformed bone wall. Anatomically, it is represented by most of the pterygopalatine process of the fatty body of the cheek, located in the infratemporal space and the pterygopalatine fossa. The fat body, which is adjacent to the upper and lower jaws, serves as a conductor of inflammatory processes of odontogenic origin, which primarily develop in the jaws [6].
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) can detect more “subtle” changes in soft tissues. If an early stage of fungal sinusitis is suspected, it is recommended to use MRI as the method most sensitive to bone wall invasion [7]. But this method has a number of disadvantages: “unreliability” of the spatial anatomy of bone structures, difficulties in identifying the bone walls of odontogenic cysts, filling material, artifacts from metal structures, as well as a high frequency of overdiagnosis, etc., which seriously limit its use [8].
The objectives of the study were to study the variations in the fatty tissue and posterolateral bone wall of the maxillary sinus and to determine the differential diagnostic value of changes in the retromaxillary fatty tissue and the posterior bone wall of the maxillary sinus in patients with odontogenic sinusitis according to CT and MRI data.
Why perforation occurs and how to avoid it
Such consequences can be avoided by properly planning removal using a CT scanner and following gentle removal protocols .
There is a group of patients with the anatomy of roots whose apices penetrate into the sinus, and if such patients are treated as a standard removal protocol, perforation and all associated complications will certainly occur. Only this is visible in the image created by a computer tomograph in a special ENT mode, and this is not possible in any clinic. In our Center this can be done with the latest SIRONA-SIEMENS equipment and the GALILEOS diagnostic software package.
Having studied the CT image, the surgeon must be prepared for an emergency situation. If perforation does occur, it is important to perform immediate microsurgical closure in a sterile operating room to avoid the development of an inflammatory process.
Even an experienced doctor without a good image on a modern expensive tomograph may not notice the details and skip the patient to a regular dental surgeon, not pay attention to the anatomical features and not carry out the necessary actions. The patient will find out about this later by the characteristic symptoms:
- passage of air, whistling and squelching in the socket of the extracted tooth;
- foamy, bloody or yellowish nasal discharge;
- strange, unreasonable organic odors in the nose and mouth,
- change in voice timbre (nasality).
If you do not carry out timely emergency closure of the anastomosis after tooth extraction, the hole itself may never heal . The gum tissues heal, epithelialize, and shrink, but the bones in the area of such a fistula between the nose and mouth never grow together due to the difference in the growth periods of the bone and gum, the gum will instantly take up all the free space, the slowly growing bone simply will not have time to fill the defect.
Within 2-3 weeks, a thin fistulous tract forms from the oral cavity to the sinus. In this case, the diameter of the hole is reduced naturally due to the formation of scar tissue; the symptoms of perforation may temporarily disappear or not appear. But this does not prevent infection from entering the sinus due to food entering the sinus.
As a result, the sinus becomes inflamed, signs of unilateral sinusitis appear, which should confuse a thinking patient (sometimes there are coincidences, but sinusitis-sinusitis, which comes as an accompaniment of the flu or a cold, is always bilateral).
Other causes of perforation
The remaining 5% of clinical cases of sinus perforation injuries occur for the following reasons::
- Not ideal endodontic treatment of tooth canals - the therapist treated the canals, was in a hurry, used excessive force when filling the canal, and under the influence of a rotating canal filler with pressure, the filling material fell beyond the tooth root. We often encounter cases where even fragments of endodontic instruments are sometimes found in the thickness of the filling material, which jam in the canal and tear into pieces, leaving metal fragments in different places of the tooth root;
- Punitive sinus lifting - an inexperienced or rude doctor does not feel the density of the tissues, breaks through the Schneiderian membrane, the bone material is forced into the gap and enters the sinus;
- Author's implantation - it happens that due to the lack of skills in performing a sinus lift and the desire to restore the missing bone, a decision is made - the implant is placed in the residual bone that exists, without bone grafting. Result: the implant completely fails or partially comes out into the sinus.
A fragment of an endodontic instrument in a tooth canal
results
The results of RCT and MRI of 70 men and 54 women aged from 12 to 75 years were studied. Odontogenic maxillary sinusitis was detected on the right in 73 cases, on the left in 47 patients, and bilateral localization of the process was found in 4 patients.
In 72 (63.2%) patients, RCT revealed compaction (asymmetric increase in densitometric density) of retromaxillary tissue. X-ray manifestations of odontogenic sinusitis were in the form of: destruction of the alveolar process ( n
=14), fungal lesions (
n
=10), odontogenic cysts (
n
=6), in 6 cases the filling material was determined. Moreover, in 2 patients, changes were found on the contralateral side of the odontogenic lesion (in one patient, a biopsy confirmed cancer of the alveolar process, in the other - fibro-edematous polyps). Asymmetric thickening of the bone wall in the bone window of the viewing program was present in 22 (19.3%) cases, in the soft tissue - in 30 (26.3%) cases.
In 16 (14%) patients, RCT showed thinning (reduction in thickness) of the retromaxillary tissue, and odontogenic maxillary sinusitis in this case was detected in the form of: odontogenic cysts ( n
=6) and fungal sinusitis (
n
=2). Thickening of the bone wall in the bone window was detected in 1 case, in the soft tissue window - in 3 cases.
In 10 (8.8%) patients, RCT showed a combination of thinning and thickening of adipose tissue. The causes of sinusitis in 8 cases were destruction of the alveolar process and in 2 cases - odontogenic cysts. Thickening of the bone wall in the bone window was detected in 1 case, in the soft tissue window - in 2 cases.
In 1 (0.8%) patient, RCT revealed expansion of the adjacent fatty tissue (odontogenic intraosseous cyst extended into the anterior wall and did not come into contact with the posterior wall of the maxillary sinus). The thickness of the walls when viewed in soft tissue and bone modes is symmetrical.
An MRI examination revealed an asymmetric decrease in signal intensity in T1 mode from the retromaxillary tissue in 8 (80%) patients, and its thinning was detected in 3 (30%) cases. No changes in the bone wall were detected in these patients.
Why you should entrust your treatment to the ENT Department of Dentistry
ENT dentistry combines two areas of medical services and treatment options - otolaryngology and dentistry . This is a modern format for the clinic’s work on comprehensive rehabilitation in the treatment of traumatic and inflammatory processes in the upper jaw, penetrating into the maxillary sinus or passing along its borders.
The Center for Private Dentistry “Doctor Levin” has been specializing in providing care to patients with combined ENT and dental pathology for many years. Medical and surgical treatment programs are carried out by candidates of medical sciences, maxillofacial surgeons with ENT training.
Statistics for the 20 years of work of the Center and for the last 10 years of work of the Department, unfortunately, are inexorable. The main providers of patients with complications are our colleagues who are caught in the dead end of an unsuccessful treatment plan. We are grateful to our colleagues who do not hesitate to send us patients with ENT complications, despite the reputational damage. It is always possible to avoid a dramatic outcome if you stop treatment in time.
Patients and methods
We analyzed the results of 114 RCT and 10 MRI patients with odontogenic maxillary sinusitis. The X-ray CT study took place in the computed tomography department of the Kursk Regional Clinical Hospital (KOKB) using X-ray computed tomographs (USA) NXI and VCT models in axial and coronal projections. MRI examination - on tomographs of the SIGNA PROFILE 0.2 T and SIGNA OVATION 0.35 T models in axial, sagittal and coronal projections. Measurements were made using the RadiAnt DICOM Viewer diagnostic image viewing program using line and ellipse tools.
How we treat
Treatment is carried out only comprehensively and strives to be carried out in one visit , simultaneously:
- Hygienic cleaning and dental treatment We prepare the oral cavity for sterile surgical work. We treat compromised roots. Operations are performed only in a sanitized oral cavity to avoid re-infection.
- The operation is carried out in the surgical department, subject to all conditions of sterile operating rooms. Ultrasound removes inflammatory processes, removes roots that provoked or supported inflammation, eliminates all inflammatory elements, removes cysts, polyps, mucoceles, and foreign bodies.
- Orthopedics Temporary crowns or any other orthopedic elements are fixed to mask the work performed. We do everything to avoid sending the patient home without teeth!
We do not welcome radical and punitive surgery!
Rest assured that after surgery we will never keep you in the hospital unless absolutely necessary.
Levin Dmitry Valerievich Chief physician and founder of the Doctor Levin center
Classification and complications of perforations of the maxillary cavities
Depending on the diameter of the hole, it is customary to distinguish:
- Small perforations - from five millimeters;
- Medium perforations - from six to seven millimeters;
- Large perforations - more than eight millimeters.
Depending on the period of development, the process proceeds:
- In acute form - it is detected either during the procedure or immediately after it;
- In its chronic form, it is detected only a few days after dental treatment.
Localization determines the presence of the following types of perforations:
- Palato-sinus - located on the palatal side;
- Alveolar sinus - located on the alveolar process;
- Vestibulosinus - located in the vestibule of the oral cavity.
Perforations that were not diagnosed on time always provoke infection and the development of inflammatory processes in the form of perforated sinusitis. The patient suffers from a feeling of nasal congestion and intense purulent discharge mixed with blood. Due to the entry of liquid food from the mouth into the sinus, infectious and inflammatory processes of the periosteum of the alveolar process and purulent lesions of the jaw bone develop.
Hospitalization
The day hospital at our Center is a post-operative support service for patients. Necessary if the patient has concomitant cardiac issues, such as hypertension, arrhythmia, AOS, etc.
Gentle ultrasound surgical protocols for low-impact PiezoSurgery operations in combination with microscopic surgery performed by operating teams consisting of pairs of the most experienced surgeons at our Center allow you to carry out treatment so delicately that you will not need mandatory hospitalization, which is so popular in Moscow hospitals.
All operations are performed only in medicated sleep, without pain or nervous overload.
The treatment will be carried out with respect for your personal time, in a short time and at a comfortable time, the operating teams and anesthesiology department work seven days a week and holidays.
Perforation of the maxillary sinus: diagnosis
In order to accurately make a diagnosis, CELT dental surgeons:
- Anamnesis is collected, which includes the removal of an upper jaw tooth or endodontic treatment, surgery to replenish bone volume or implantation of an implant;
- An examination is carried out to identify the cause of the perforation, the hole is probed, and the patient is asked to exhale by opening his mouth and closing his nose;
- The patient is prescribed an X-ray examination of the maxillary cavities and orthopantomography;
- The patient is prescribed an endoscopic examination of the nasal cavities.
What can be included in therapy during treatment?
Don’t know how to treat maxillary sinusitis besides pills? You need herbal preparations. They are good both in the treatment of existing inflammatory processes and as a preventive measure. Their effectiveness is explained by the special composition of active components. As a rule, these are herbal extracts.
Each capsule of this product contains a whole set, including up to 10 or more medicinal plants. It is this composition that helps to quickly eliminate the causes of the disease - any viruses and bacteria in the body, and also helps to cure sinusitis or sinusitis at an early stage.
Just one capsule a day - and your sinuses breathe freely, and your health remains normal even during seasonal colds!
Paranasal sinus cyst - symptoms and treatment
Treatment depends on the type of cyst, its location and size. If it is less than 1 cm and there is no discharge, then the doctor suggests conservative methods: regular examination, tablets, sprays and drops. If the cyst is large or there is purulent discharge, then surgery will be required.
Drug treatment of cysts
The method allows you to eliminate unpleasant symptoms and causes of cyst formation: swelling, inflammation and blockage of the sinus anastomosis. Drug treatment is effective and can alleviate the patient's condition in the early stages of the disease. However, it will not help when the fibrous membrane of the cyst has become too dense.
Drugs used:
- vasoconstrictor drops - quickly reduce swelling in the anastomosis area and normalize ventilation of the sinuses of the nasal cavity; medications in this group are addictive and can be safely used for no more than 5 days in a row;
- antihistamines - will help if the cyst is caused by allergies;
- mucolytics - normalize the outflow of mucus;
- antiseptics - help fight inflammation and cleanse the surface of the nasal mucosa;
- topical glucocorticosteroids are most effective in the treatment of allergic rhinosinusopathy, prolonged sinusitis, hyperplasia of the mucous membrane in the area of the anastomosis and ostiomeatal complex;
- painkillers - reduce pain caused by the pressure of the cyst on surrounding tissues [6];
- probiotics - normalize the microflora of the nasal cavity and nasopharynx, which is important in the treatment of chronic inflammation of the upper respiratory tract.
Surgery
Indications:
- cyst more than 8 mm;
- ineffectiveness of conservative treatment;
- signs of suppuration inside the cyst [7].
The most popular method of treating cysts is puncture or puncture. The surgeon pierces the wall of the cyst with a thin needle and pumps out the purulent discharge [1]. However, this method only has a temporary effect. Piercing the cyst, as well as spontaneous leakage of its contents, relieves pain for a while. But gradually the cyst grows together again and begins to accumulate purulent fluid. To remove it completely, more serious surgery will be required [8].
Maxillary sinusotomy according to Caldwell-Luke
It is performed through an incision under the upper lip in the mouth. This is a classic method for removing sinus cysts, but now it is practically not used due to its high morbidity: after the operation, scars, adhesions can form and the functioning of the sinuses can be disrupted.
Microsinusrotomy
A minimally invasive surgical technique that is performed through the anterior wall of the maxillary sinus. A 4–8 mm hole is formed in the bone, and the cyst is removed with special instruments. Performed under general anesthesia. The disadvantage is the risk of damage to the branches of the trigeminal nerve and the formation of persistent facial neuralgia.
Functional Endoscopic Sinus Surgery (FESS surgery)
This method is considered the most gentle and effective: during the procedure, unnecessary incisions and punctures are not made on the patient’s face. It is performed through the nasal cavity under endoscopic control. Allows you to reach all paranasal sinuses, including the sphenoid, frontal sinuses and cells of the ethmoid labyrinth. The operation is performed under local and general anesthesia [17].
Additional benefits:
- can be used to treat children;
- reduce the likelihood of cyst recurrence;
- you need to stay in the hospital for no more than two days;
- the incision heals quickly;
- the operation leaves no scars;
- there is no risk that adhesions will appear [18].
Relative disadvantages: trained specialists and special equipment are required, which makes the operation expensive.
Prevention is the best remedy for sinus inflammation
Of course, no one can be 100% insured against sinusitis and more severe inflammatory processes. Prevention will help strengthen the immune system and build a protective barrier against viruses, bacteria and infections. To prevent sinusitis without symptoms in an adult or child, you should follow simple rules:
- Avoid hypothermia. Yes, low temperature in itself does not provoke colds and runny nose. But it causes a narrowing of blood vessels and makes the mucous membranes more vulnerable to viruses and infections. In cold, rainy and windy weather, it is important to properly insulate - and you will not face chronic inflammation of the sinuses.
- Rinse your nose more often. This should be done in the fall during epidemics of colds and flu, as well as in the spring during the flowering of trees and shrubs. For rinsing, ordinary saline solutions are suitable, which effectively remove bacteria and allergens.
- Eat properly. The immune system weakens due to lack of nutrients. Include more natural products in your diet - fresh meat and fish, grains and slow carbohydrates, vegetables and fruits. It’s better to avoid processed foods and fast food, or at least reduce their consumption to a minimum.
- Drink vitamins. Nowadays there are many special vitamin complexes and supplements with herbal active ingredients. They work gently but effectively: the result is noticeable within 1-2 weeks. And most importantly, they are completely safe, non-addictive and have no side effects.