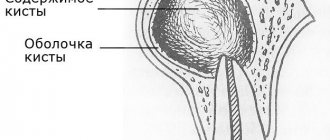
Patients with chronic periodontitis often encounter a situation where a cyst forms at the apex of the root - a cavity in the bone tissue filled with pus. Most often, a cyst develops due to infection in the root canals; sometimes the cause of a cyst is trauma, inflammatory processes in the periodontium (gums) and adjacent areas. It can also occur due to undetected caries, pulpitis or periodontitis, as well as due to poorly filled root canals.
Such a neoplasm may not bother a person for a long time. As a rule, a cyst makes itself felt during periods of weakened immunity, against the background of a cold. In such cases, the infectious process in the cyst cavity worsens, which leads to abundant pus formation. The patient feels acute pain, swelling and swelling of the gums appears, and a fever may appear. The main thing is to seek dental care on time. In these cases, resection of the apex of the tooth root and dental surgery to remove the cyst are used. However, you can often get by with therapeutic treatment.
Treatment of dental cyst: methods
Most often, treatment of dental cysts is carried out jointly by dentists - a therapist and a surgeon.
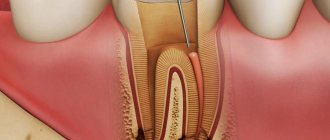
Therapeutic treatment of a dental cyst is aimed at sanitation, or cleaning of the root canals - it is necessary to remove the source of infection and the cause of the cyst. First, the dentist-therapist processes the root canals and fills them with antiseptic paste for a period of 1 week to 1 month, as in the treatment of periodontitis. Then he fills the root canals with gutta-percha and sealer. Sometimes, especially in young patients, therapeutic treatment of the cyst is quite sufficient.
Surgical treatment is an operation to remove a cyst from bone tissue, sometimes this operation is accompanied by resection of the apex of the tooth root. The technique of apex resection is generally simple, but the operation is a complex surgical procedure and, like any operation, it must be taken seriously.
If resection is not done in time, the infection will spread upward through the root canals and can spread to the entire jaw. The consequence is that you may have to schedule the removal of all inflamed teeth. Therefore, you should not joke with such inflammations!
Clinic doctors
A jaw cyst is an inflammation characterized by the formation of capsules with a dense shell. Dental cyst removal is carried out in our clinic. The reason for the appearance of a cyst is the penetration of pathogenic microorganisms into the tissue. For a long time, the disease can be asymptomatic, but in an advanced state it can lead to serious complications (fistula in the gums, etc.). Previously, to get rid of a cyst, it was necessary to remove a tooth. Today, tooth-preserving operations are carried out to completely get rid of the disease.
What is a dental cyst (granuloma). Types of cysts?
Granuloma, cystogranuloma and dental cyst are successive stages in the development of the inflammatory process:
- Granuloma consists of granulation tissue, which is enclosed in a capsule. It forms around the apex of the root and looks like a sac with a diameter of about 0.5 cm.
- Cystogranuloma is slightly larger. It forms when inflammatory fluid (exudate) begins to accumulate inside the granuloma.
- A dental cyst is a tumor-like formation, a kind of chamber filled with exudate, which contains toxins produced by microbes.
Depending on the etiology and location, two types of cysts are distinguished: radicular (formed near the root of the tooth) and follicular (appears near the developing tooth).
What are the indications for removing a tooth cyst (granuloma)?
The cyst must be removed if it has reached a large size, since over time the entire tooth may fall into its cavity, and then it will have to be removed. Also, an indication for cyst removal is its presence on baby teeth.
What are the contraindications?
The patient has cardiovascular diseases, mental disorders, blood diseases, acute infectious diseases, as well as malignant tumors. In addition, pregnancy at 1, 2 and 9 months is a contraindication.
How is diagnosis carried out before surgery?
Before an operation to remove a dental cyst, the question arises not only about preserving the causative tooth, but also about whether the apex of the root of an adjacent tooth with a healthy pulp enters the cystic cavity. It should also be taken into account that during surgery, nerves and blood vessels in the periapical region of adjacent teeth can be damaged. If this happens, death of their pulp will follow after the operation. X-rays do not always provide a reliable answer to these questions, so you have to resort to computed tomography.
What difficulties hinder the operation?
Removal of granulomas and cysts on the upper jaw is difficult due to the proximity of the maxillary sinus. Because of this, a complication such as perforation of the maxillary cavity may arise during the operation. Surgical intervention on the lower jaw is complicated by the proximity of the mandibular canal, which contains blood vessels and nerves. The slightest damage to them can cause pain and loss of sensitivity in the gums, lips, cheeks or tongue.
What is the surgical procedure for removing a dental cyst? Types of operations.
The cyst can be removed using different surgical methods:
- Cystotomy. The purpose of the operation is to remove large cysts. The essence of the operation is to remove fluid or pus from the neoplasm, treat the cyst and use antibacterial agents to break down its membrane. This method implies that if the cyst gradually decreases in size, the growing bone tissue will fill the vacant space.
- Cystectomy. Complete removal of the cyst with resection of the tooth root. The gum is cut, the apex of the root is cut off with a drill, the resulting cavity is filled with bone-forming material, after which the wound is sutured.
- Hemisection. The operation is performed on multi-rooted teeth. In this case, not only the cyst or granuloma is removed, but also one of the roots - partially or together with the coronal part.
What are the possible complications?
When removing the apex of a tooth root that has fallen into a cystic cavity, trauma to the tooth may occur, which can lead to its loss. During curettage, damage to the vessels leading to the pulp of a healthy tooth located next to the cyst is possible - this will lead to the death of the pulp.
What are the recommendations in the postoperative period?
Immediately after the operation, you must refrain from hot and cold foods, smoking, and alcohol. For fever and severe pain, antibiotics and analgesics are recommended. To speed up healing, you need to rinse your mouth with antiseptic solutions. If fever and pain persist for a long time, you should definitely consult a doctor.
What are the quality criteria for removing a dental cyst?
In most cases, after surgery, the patient can forget about the cyst forever. Confirmation of quality will be the absence of a tumor on an x-ray. However, in some cases, the cyst may reappear - if such relapses occur, you must regularly visit the dentist for a follow-up examination.
How much does it cost to remove a dental cyst?
The cost of such an operation depends on the size of the cyst, the chosen technique and the complexity of the case. The sooner the patient sees a doctor, the cheaper the operation will cost him. A detailed calculation is possible only after a doctor’s examination and x-ray examination.
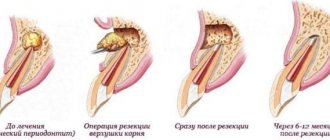
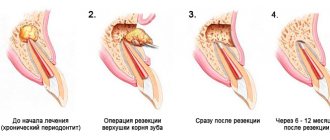
How is tooth root apex resection and cyst removal performed?
Typically, the entire procedure takes about an hour. In this case, the position of the tooth is important: surgery on distant teeth requires more skill and time.
During the operation, which is performed under local anesthesia, an incision is made in the gum near the diseased tooth to peel it away to expose the bone tissue. A small hole is then made in the bone using a special bur. Through it, the doctor should see the apex of the tooth root and the cyst attached to it.
Using a drill, the tip of the root is cut off and then removed from the wound along with the cyst attached to it. After the cyst is removed, synthetic bone is placed into the empty space to restore jaw bone tissue. At the end of the procedure, the mucous membrane of the gums at the incision site is sutured, sometimes a drainage is inserted between the sutures to drain the ichor from the operation site for several days.
When performing a tooth resection, only the inflamed and infected part of the root is removed, healthy tissue is not affected.
Symptoms of anterior tooth cyst
This disease is especially dangerous due to its practically asymptomatic course at the initial stage - few people will worry if they notice a slight change in the color of the enamel or a slight displacement of the tooth. But a front tooth cyst is much more likely to be noticed than other types, since the frontal units have to “work” more often, because they are located only on one side of the jaw. However, other types of formations can go unnoticed for years, for example, if the patient is used to chewing on only one side. A cyst on the front upper or lower tooth is noticed much earlier, because pain is immediately felt.
Dangerous symptoms!
When the size of the granule with pus begins to exceed 10 mm, pronounced symptoms of a front tooth cyst arise:
- constant nagging pain with a feeling of fullness
- high fever and painful condition, which sometimes continue after the procedure for removing the cyst of the front tooth has already been completed
- swelling of the gingival tissue at the location of the granule, in severe pathologies it spreads to the face
- protrusion of a tubercle in the affected area
- enlarged lymph nodes - occurs if bacteria from the granule with pus begin to spread through the blood
Cystectomy / root apex resection: indications, contraindications and causes
- The appearance of any neoplasm, for example, fibroma or other, larger than 1 cm.
- Incomplete or poor-quality root canal filling in the treatment of pulpitis, for example;
- Stump tab or pin in the dental canal;
- Damage to the root walls during tooth filling;
- Periodontitis, granulomas, cysts, fibromas;
- Perforation of the tooth root, fracture of the root or its apex;
- Curvature of the root canals or the apex of the tooth root;
- Presence of a foreign body;
- Inflammation near the site where the denture is installed;
- A fragment of a dental instrument in the canal;
Contraindications include periodontal disease, periodontitis, and the presence of a tumor at the location of the tooth.
Why do cysts form on teeth?
Dental cysts are a polyetiological disease. Slow inflammatory reactions around the apical zone of the root can cause the development of radicular tumors. A follicular dental cyst is formed due to a disruption in the development of the dental germ of a permanent tooth from the dental sac.
The reason for the disruption of the development of the tooth germ is chronic periodontitis of temporary teeth, due to which the division of epithelial cells occurs around the crown of the unerupted segment. The pathogenesis of a retromolar cyst involves the formation of a bone pocket. Due to inflammation, it closes to form a cavity.
Provoking factors leading to the formation of a cyst under a tooth:
- complicated course of caries, pulpitis, periodontitis;
- incorrectly installed orthopedic design;
- maxillofacial injuries;
- tooth root fracture;
- complicated infections of ENT organs;
- pathology of teething, etc.
Possible complications after cyst removal
Removing a cyst is a necessary procedure; the longer the treatment of a cyst is delayed, the more likely complications are to develop. There is no need to be afraid of removing a cyst; according to statistics, the percentage of possible adverse consequences is immeasurably less than complications from an unoperated cyst (abscess, phlegmon, sepsis).
After cystectomy, the service life of the tooth is not reduced. Both after therapeutic and surgical treatment of cysts, dynamic monitoring of the condition of the bone tissue is required.
To avoid complications, it is important to maintain oral hygiene, follow your dentist's recommendations, as well as eat a healthy diet and avoid alcohol, smoking, carbonated drinks and solid foods in the first days after surgery.
What happens if you don't treat a dental cyst?
The formation does not manifest itself clinically for a long time. The progression of the disease leads to discomfort in the pathological area (especially when chewing food). Over time, a tubercle forms on the surface of the gum near the root area, which gradually increases. The mucous membrane changes color and swelling appears.
When the process suppurates, a person experiences symptoms of inflammation and intoxication: hyperthermia, headache, toothache, chills, tachycardia. A fistula may form in the middle of the protrusion, from which the contents of the cavity are released.
If you do not start treating cystic formation in a timely manner, serious complications may develop:
- phlegmon;
- lymphadenitis of nearby lymph nodes;
- inflammation of the maxillary sinuses;
- periostitis (spread of infection to the periosteum);
- osteomyelitis;
- abscess;
- deformation of the dentition;
- blood poisoning.
What do patients say about apex resection? Reviews are usually only positive!
“Resection of the top of the tooth took about an hour, the operation was performed under pain relief. It didn’t hurt very much near the tooth for about a month. A few months later I had to take an x-ray, the doctor showed that all the tissues had been restored."
“The cyst grew, they told me to remove it, it was a little unpleasant, but quite tolerable - the doctor quickly and accurately carried out the procedure. Everything was restored soon, now it’s completely unnoticeable that there was anything there.”
At Ritsa Dentistry, cyst removal operations are performed by experienced surgeons with extensive experience in performing such procedures. Therefore, you can rely on our professionalism and entrust the treatment of the cyst to our doctors.
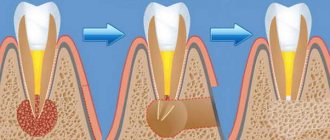
The mechanism of formation and growth of a dental cyst
The cystic cavity, located in the jaw, has external resistance from the surrounding jaw bone. But the epithelial cells of the lining begin to produce fluid, which gradually fills the cavity, creating excess pressure.
This pressure acts on the surrounding bone tissue, causing its gradual peripheral resorption, giving the cyst the opportunity to grow even larger, increase fluid secretion, and therefore put even more pressure on the walls. This is why cysts can grow to very large sizes, sometimes asymptomatically, if not accompanied by periodic inflammation. This may be due to the patient’s good immune status, low pathogenicity of the microflora in the lesion and other factors.
Causes of the disease
Other diseases and bad habits can lead to the development of this disease, such as:
- viral and bacterial infections;
- nicotine abuse;
- weakened immune system;
- sinusitis and tonsillitis;
- ARVI;
- dental diseases.
Risk factors are:
- hypothermia;
- increased mental and physical stress;
- frequent stress.
The influence of factors often leads to accelerated tumor growth. Teeth that were previously filled or reconstructed are most susceptible to this disease.
Risks of immediate implantation immediately after removal of a tooth with a cyst
The one-stage protocol involves implanting a titanium root immediately after tooth extraction, into the hole left after it. This method eliminates the need for the patient to wait for tissue restoration. But removal of a tooth with a cyst is carried out when there is inflammation in the surrounding tissues. Therefore, the risk of installing a sterile implant in pus is almost one hundred percent.
I advise patients who have read marketing articles on the Internet about the benefits of instant removal and instant installation of dental implants directly into the sockets using special computer templates to be more relaxed about such offers from surgeons. Taking antibiotics for a month and being afraid is worse than taking a break for a month, recovering and performing a sterile operation without risk.
The root cyst is combined with a jaw bone defect. Under such conditions, it is impossible to ensure the stability of the implant. The probability of developing peri-implantitis with titanium root rejection is close to 100%. The risk of inflammation spreading beyond the primary focus increases.
Don't let your fears of doctors get the better of your common sense.
Patients, due to their disapproval of dental procedures, are ready to make not entirely correct, but quick, express decisions. Please take the time to carefully study the guarantees section in the contract before deciding to carry out such procedures.
Levin Dmitry Valerievich
Chief physician, Ph.D.
Clinical cases that served as the prototype for this experimental treatment were demonstrated at several surgical conferences. But with a detailed analysis of information and a request for facts of “ideal results” of long-term observation of patients, external information independently received and processed by us cannot be considered reliably confirmed by us.
Undoubtedly, this technique is an interesting new technology that requires additional monitoring for several more years.
In cases of surgery with a lifetime guarantee, these scientific experiments are unacceptable when providing medical care on the principles of high-quality paid medicine.
The method of installing an implant immediately after removing a tooth with a cyst at the Dr. Levin Center for Private Dentistry is not used until successful and confirmed results of such treatment are obtained.
What is the “insidiousness” of pathology?
The tumor develops slowly. The cavity gradually increases under the pressure of the produced pus. In the early stages it is difficult to diagnose, since the symptoms are not clearly expressed and occur periodically (with exacerbation). Signs of pathology:
- pain when biting;
- discomfort when palpating the gums;
- swelling of the gums and face;
- increase in body temperature.
If the tumor grows, bone deformation is possible. The bone tissue of the upper jaw is porous, so resorption occurs quickly, with pronounced deformations. Large cysts of the molars and premolars of the upper jaw often occupy the entire volume of the maxillary sinus.
Formation on the root of the tooth complicates subsequent implantation:
- During removal, there is a risk of damage to the tumor membrane. Then its contents spill out onto the surrounding tissues, and the infection spreads.
- For large cystic tumors, osteoplasty is required before implantation to restore bone deficiency and ensure reliable fixation of the artificial root.