12/21/2021
79 475
17 minutes
Co-author, editor and medical expert – Maksimov Alexander Alekseevich.
- Symptomatic treatment
- Rinsing
Many people are familiar with the diagnosis of tonsillitis. This unpleasant disease can take you by surprise and prevent you from leading a normal life. Tonsillitis is a pressing problem today, as it can occur at any age and with various diseases, such as herpes, diphtheria, streptococcal infections, scarlet fever and others. Often tonsillitis (or simply tonsillitis) acts as an independent disease. To understand the diagnosis and begin proper treatment, you need to consult a doctor. Remember that self-medication can lead to complications. What is tonsillitis? And how to cope with this disease? We will consider the answers to these questions below.
Up to contents
Forms of tonsillitis
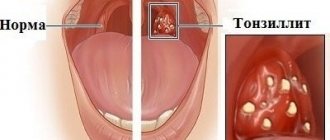
Tonsillitis (or sore throat) is an inflammation of the tonsils, often accompanies colds.
Types of sore throats
Sore throats are acute:
- Banal (vulgar or typical) tonsillitis: there are catarrhal, follicular, lacunar, mixed.
- Atypical tonsillitis: herpetic, Simanovsky-Plaut-Vincent's tonsillitis, phlegmonous, fungal and mixed forms. Usually they are severe, as they appear against the background of decreased immunity.
- Sore throats associated with infectious diseases (scarlet fever, diphtheria, sore throat due to HIV infection and others).
- Angina in blood diseases: monocytic, agranulocytic, tonsillitis in leukemia.
Tonsillitis can also be chronic (compensated and decompensated)1.
Interesting fact!
Our defense against infections is located in the pharynx - an anatomical structure consisting of lymphoid tissue. The lymphoid elements in the pharynx are located around the pharynx in the form of a ring, so it was called the “lymphadenoid pharyngeal ring” by Waldeyer-Pirogov. It is formed by two palatine tonsils (those that are sometimes called “tonsils”), one pharyngeal or nasopharyngeal (located on the back wall of the pharynx), one lingual (a collection of lymphoid follicles at the root of the tongue) and two tubal (located in the thickness of the mucous membrane of the nasopharynx near the openings eustachian tubes). Tubal tonsils are most pronounced in children under 5-7 years of age, and later undergo reverse development. In adults, due to their small size, they are almost invisible.
The pharyngeal ring is an additional barrier for bacteria between the external and internal environment of the body. These structures also produce antibodies and lymphocytes - immune response cells.
Acute tonsillitis
This is an acute inflammatory disease of the palatine tonsils. Their mucous membrane becomes swollen, hyperemic, and purulent deposits may appear in the crypts of the tonsils. But depending on the factors that caused the disease and the patient’s condition, the process is not limited to damage to the tonsils alone. A severe infection can take over the entire body. The most dangerous complications are rheumatic heart defects, joint damage, kidney damage (glomerulonephritis). Therefore, self-medication can be dangerous. For correct diagnosis and effective treatment, you need to consult a specialist.
Purulent tonsillitis is one of the forms of tonsillitis and can be a complication of acute or chronic tonsillitis. It is characterized by the presence of purulent discharge in the crypts of the palatine tonsils. Most often accompanies a bacterial infection. Improper treatment can lead to chronicity of the process.
Chronic tonsillitis is a persistent chronic inflammation of the tonsils, characterized by recurrent exacerbations in the form of tonsillitis, a sluggish course, and a decrease in the body's resistance to infection. Slight hypothermia or draft causes exacerbation of tonsillitis. Many factors play a role in the pathogenesis of chronic inflammatory process in the tonsils. Most often the disease occurs after repeated sore throats. Chronic tonsillitis is of two types: compensated and decompensated. This is important for further treatment tactics.
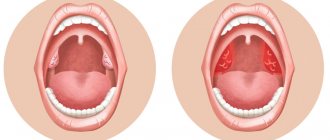
With compensated chronic tonsillitis, examination reveals some looseness of the tonsils, hyperemia, swelling, purulent plugs or plaque in the crypts of the tonsils, but this process is limited to the tonsils and does not spread beyond its boundaries. This precarious balance between local immunity and the body’s resistance on the one hand, and the presence of pathogenic organisms in the inflamed tonsils on the other, can shift towards decompensation if the course of the disease is unfavorable. With decompensated chronic damage to the lymphoid apparatus of the pharynx, local signs of chronic tonsillitis are usually clearly expressed. With this form, exacerbations often occur in the form of sore throats, peritonsillitis, peritonsillar abscesses, regional lymphadenitis, and in clinically advanced cases, disturbances in the functioning of other organs and systems (kidney pathology, formation of cardiac flow, articular syndrome, damage to the nervous system).
Up to contents
Classification B.S. Preobrazhensky
| Form of the inflammatory process | Distinctive manifestations |
| Simple (uncomplicated) form | Only local signs are present: Pus and dense plugs from it, closing the lumen of the lacunae, and the inflamed surface of the tonsils (they are loose, red, swollen). Inflamed edges of the arches of the palate (they are swollen, red, infiltrated). |
| Toxic-allergic tonsillitis 1st degree | Local manifestations of an uncomplicated form are superimposed by general symptoms of an allergic-toxic nature: Periodic low-grade fever (temperature readings up to 37.5°C). Tonsillogenic intoxication, present constantly or periodically - decreased performance, fatigue, poor appetite, general weakness, malaise, feeling of weakness throughout the body. Enlargement of the lymph nodes of the neck, their soreness. Periodically appearing joint pain. Changes in blood tests - increased leukocytes, accelerated ESR. |
| Toxic-allergic tonsillitis 2nd degree | Signs of the 1st degree are accompanied by severe manifestations of a toxic-allergic nature: Functional ECG changes. Heart pain. Heart rhythm disturbances. Long-lasting low-grade fever. Development of autoimmune complications of tonsillitis. |
Symptoms of tonsillitis
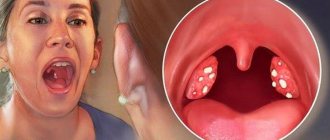
Clinical manifestations are quite varied and depend on the type of tonsillitis. The disease debuts acutely, against the background of hypothermia or stress. First there is a sore throat. It may intensify when swallowing, after smoking, or eating hard, dry foods. There is a cough, a feeling of a foreign body in the throat, rawness, soreness in the throat. The body temperature rises, the patient feels weak, tired, unwell, quickly gets tired, and there is pain in the joints and muscles. Upon examination, the doctor reveals enlarged and painful submandibular and cervical lymph nodes; the pharyngoscopic picture varies from hyperemia of the tonsils to friability, purulent changes (lacunae and follicles), and enlarged tonsils. The mucous membrane becomes swollen. In the presence of purulent plaque, a characteristic unpleasant odor from the mouth may appear.
Treatment for tonsillitis depends on its type and cause. Let's look at it in detail:
Etiotropic treatment (impact on the cause of the disease) depends on the causative agent of the disease. If a sore throat is bacterial in nature and if there are indications, antibiotics are used, which are prescribed by a doctor. Self-treatment of tonsillitis with antibiotics is not recommended, since an insufficient dose or the wrong choice of drug can lead to the development of resistance (persistence) in the microorganism, as well as to complications of angina (for example, peritonsillar, retropharyngeal abscess, diphtheria croup in children, acquired heart defects). For a viral infection, symptomatic therapy is prescribed, as the patient’s general condition remains satisfactory. Physiotherapy methods are also effective: ultraviolet irradiation increases the barrier function, the resistance of the tonsils, improves, stimulates local and general immunity, and has an antimicrobial effect. Laser treatment of tonsillitis in the submandibular area is carried out daily, in a course. The therapeutic effect is achieved by dilating small blood vessels and increasing blood circulation in the area of inflammation1.
Symptomatic treatment
Anti-inflammatory drugs (paracetamol, ibuprofen, aspirin) have proven themselves well in the treatment of tonsillitis. They reduce swelling, inflammation, and as a result, pain. Antihistamines (Zyrtec, Tavegil) and analgesics are also used. For the duration of treatment, smoking, drinking alcohol, and spicy and hot foods are excluded. A gentle diet and bed rest are prescribed for 5-7 days.
If the patient’s general condition does not suffer, we can limit ourselves to the use of local means of treating tonsillitis.
Local treatment consists of prescribing medications that have an antiseptic, anti-inflammatory, and analgesic effect2. Drugs for local therapy should not only relieve sore throat, but also have a wide spectrum of antibacterial activity, low allergenicity, and be non-toxic.
Hexoral ® has all these properties. The drug is active against a wide range of gram-positive bacteria, as well as pathogenic fungi of the genus Candida; the drug Hexoral ® can have its effect in the treatment of infections caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Proteus. At a concentration of 100 mg/ml, the drug inhibits the growth of most bacterial strains. Hexetidine, being the active ingredient of the drug Hexoral ®, also has an anesthetic effect on the mucous membrane3. The variety of dosage forms of Hexoral ® makes its use accessible to the whole family. Hexoral ® spray is a convenient, effective and proven form for the treatment of tonsillitis in adults and children from 3 years of age. The Hexoral® line also includes a rinse solution (from 3 years old), Hexoral® tabs tablets (from 4 years old), Hexoral® tabs Classic (from 6 years old), Hexoral® tabs Extra (from 12 years old) years). In the form of a rinse solution, lozenges and sprays, the medicine is convenient to use, which makes patient adherence to treatment high.
In all cases of tonsillitis, it is necessary to consult a doctor, so that only a specialist can prescribe adequate treatment and prevent complications.
Surgery
Tonsillectomy is the removal of tonsil tissue and the underlying capsule. It is used in cases of unsuccessful conservative therapy, in the presence of a focus of chronic infection in the tonsils. A tonsillectomy is performed by an ENT doctor. Before the operation, you should consult with a therapist, do blood and urine tests, perform an ECG, and a chest x-ray. If there are concomitant diseases, undergo additional examination by specialized specialists.
Tonsillectomy is usually performed under local anesthesia with the patient sitting. Local anesthesia is performed, and then the tonsils are removed along with the capsule. The operation does not last long, about 10 minutes, complications are quite rare. Indications for surgical treatment are chronic persistent inflammation of the palatine tonsils in the stage of decompensation, frequent exacerbations of chronic tonsillitis, purulent complications in the form of abscesses and phlegmon.
Contraindications for tonsillectomy are: blood diseases (hemorrhagic diathesis), neuropsychiatric diseases in the stage of decompensation, which can interfere with the course of the operation and compliance with the postoperative regimen, open form of respiratory tuberculosis, cardiac, renal failure, severe diabetes mellitus. In each specific case, the issue of performing an operation is decided individually1.
Cryotherapy is a gentle method of semi-surgical treatment. Cryotonsillotomy - exposure to the tonsils with a special applicator (cryoprobe), in a closed system of which liquid nitrogen circulates at a temperature of -196 °C4. Areas of chronic inflammation where the tonsil no longer performs its functions are removed. Since cryotherapy is painless and bloodless, it is the method of choice for weakened patients, patients with blood diseases and those for whom surgical treatment is contraindicated (allergy to novocaine, severe diabetes mellitus, uncontrolled hypertension, severe heart failure, renal failure, hemophilia) and also in children. After cryodestruction, the body recovers more quickly and the patient returns to normal life. However, along with the advantages, the cryosurgical method has a number of disadvantages: several stages are assumed over 1.5 months, but in some cases it is not possible to achieve complete removal of tonsil tissue.
Contraindications to cryotherapy: decompensation of diabetes mellitus, some oncological diseases, acute myocardial infarction, high-grade heart failure, severe hypertension.
Up to contents
Diagnosis of the disease
A diagnostic search for chronic tonsillitis is not only making a diagnosis, but also determining the form of the disease. Therefore, the examination is always comprehensive, which includes:
- Objective examination data (redness, swelling, injection of blood vessels on the tonsil mucosa, etc.);
- Survey – assessment of complaints, the history of their occurrence and other anamnestic information;
- Microbiological examination (seeding pathological secretions taken from lacunae on special media to determine the causative microbe, as well as its sensitivity to antimicrobial drugs);
- Laboratory tests (blood, urine);
- Instrumental examinations (ECG, ultrasound of the heart and lymph nodes).
Assessment of these parameters allows you to correctly determine the stage of the inflammatory process and optimally select treatment.
| Examination method | Signs | What does the examination give? |
| Collection of anamnesis and complaints | Pain and discomfort in the throat, sensation of a lump or foreign body, heart and joint pain, general weakness, malaise. Single or multiple exacerbations of tonsillitis throughout the year. | Allows you to suspect chronic tonsillitis and the stage of the process, and evaluate the effectiveness of the treatment. |
| Pharyngoscopy | Pus or purulent plugs on the surface of the tonsils (pathological secretion fills the lacunae). Redness, infiltration and swelling of the arches of the palate, their cicatricial fusion with the tonsil. | Confirms the diagnosis of chronic tonsillitis, but does not allow assessing the stage of the process. Allows you to evaluate the effectiveness of conservative treatment. |
| Bacteriological examination | Identification of the microorganism and its sensitivity to antibacterial therapy. | Allows you to identify the causative microorganism and select the necessary treatment. Assess the effectiveness of conservative treatment. |
| Laboratory diagnostics | Clinical blood test, biochemical blood test (urea, creatinine, ALT, AST), C-reactive protein, ASLO, rheumatoid factor, IgE, total blood IgA. | Allows you to determine the activity of inflammation, identify the risk of development or the presence of concomitant diseases (rheumatism, glomerulonephritis, polyarthritis, infective endocarditis, etc.) Helps choose treatment tactics, evaluate the effectiveness of treatment. |
| Functional diagnostics | ECG (electrocardiogram) Echo-CG (ultrasound of the heart) Ultrasound of the kidneys Ultrasound of the lymph nodes of the neck. | Helps determine the stage of chronic tonsillitis, identify the presence of associated diseases (rheumatism, glomerulonephritis, polyarthritis, infective endocarditis, etc.) Helps choose treatment tactics. |
Treatment at home
To determine the diagnosis and begin treatment, contact your doctor. If you are diagnosed with acute tonsillitis, you must observe strict bed rest in the first days of the disease, then limit physical and psycho-emotional stress, which will help get rid of complications, among other things. The patient is given a personal plate, spoon, mug and, if possible, isolated. Prescribe non-irritating, soft foods, mainly plant-based, dairy, vitamin C, and plenty of warm drinks. Symptomatic therapy is also carried out: taking antipyretic, anti-inflammatory, painkillers.
Rinsing
Special attention should be paid to local therapy. Gargling with antiseptic solutions (Hexoral ® gargling solution) is useful for tonsillitis. The drug Hexoral ® has broad antibacterial activity, including against gram-positive microbes, is also active against the pathogenic genus of fungi Candida, and has an effect in the treatment of infections caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Proteus. The antimicrobial effect of the drug is associated with the suppression of metabolism in bacteria, their oxidative reactions, without which the latter cannot exist (thiamine antagonist). At a concentration of 100 mg/ml, the drug inhibits the growth of most bacterial strains. The development of resistance to Hexoral ® is not observed. The active substance hexethidine has a mild analgesic effect on the mucous membrane of the pharynx and tonsils, can linger on it for a long time and is practically not absorbed. Therefore, it does not have a systemic effect. When using the drug Hexoral ®, regression of inflammatory changes in the pharynx may be observed5. It is recommended to use 15 ml of undiluted solution 2 times a day after meals, unless otherwise prescribed by a doctor. Before use, consult a specialist.
Rinsing is an effective method and an important component of the fight against tonsillitis, which can be successfully used in home treatment. Rinsing with a salt solution, irrigating the oropharynx with sprays with sea water, a decoction of chamomile, sage, chlorhexidine and other antiseptics help well. Rinsing with solutions at body temperature (36-37 degrees) reduces inflammation, mechanically cleanses the mucous membrane of the oropharynx from viruses, bacteria, pus, helps relieve swelling, and as a result, reduce sore throat. Rinsing is completely safe for children, pregnant women and nursing mothers.
Washing the lacunae of the tonsils with antiseptics is used for many types of both acute and chronic tonsillitis. The most common method of washing the lacunae of the tonsils is according to N.V. Belogolov. and Ermolaev V.G1. This effective procedure is performed by an otolaryngologist. Under the control of pharyngoscopy, the doctor sequentially inserts a thin cannula through each lacuna into the crypt of the tonsil, and with a syringe filled with an antiseptic, under pressure washes out everything unnecessary from the lacuna. As a rule, 2-3 crypts of the upper part of the tonsil are washed. All tonsil crypts are usually connected to each other, so the entire tonsil is washed and drained. After this, the treated mucous membrane is lubricated with Lugol’s solution, iodine, and 5% collargol. The positive effect of the procedure is achieved by mechanically flushing the lacunae from pus and restoring their drainage function. Treatment is carried out in a course of 10-15 washes, which are prescribed every other day.
The right approach
Sore throat, tonsillitis - treatment in children and adults is important to carry out immediately for all diseases of the oral cavity and nasopharynx that bother you. If breathing through the nose is impaired, and mucus or mucopurulent discharge flows down the back wall of the pharynx, then these symptoms should be given special attention.
Chronic tonsillitis - treatment (effective) can be conservative and surgical. Due to the fact that the removal of tonsils can cause serious harm to the defenses and immunity of the human body, otolaryngologists should try their best to preserve the tonsils and restore their functions without resorting to surgery to remove the tonsils. Modern methods of treating tonsillitis provide a greater chance of recovery without intervention.
Friends! Timely and correct treatment will ensure you a speedy recovery!
Chronic purulent tonsillitis - treatment of a conservative type must always be carried out in an ENT clinic, performing a complex, pathogenetically based course of treatment, as well as using a medicinal approach - medications prescribed by an ENT doctor.
Surgical removal of tonsils
If we talk about the removal of the tonsils, then the operation to completely remove the tonsil tissue is called a bilateral tonsillectomy.
Partial removal of the tonsils is called a bilateral tonsillotomy.
It is extremely rare that the palatine tonsil is removed routinely on one side. There is also a practice of a number of hospitals (they like to do this in the Pirogov City Clinical Hospital No. 1) of removing the palatine tonsil or tonsils in case of a paratosillar abscess. This operation is called abscessonsillectomy. But it must be remembered that against the background of severe pain caused by an abscess, removal of the tonsil is extremely painful. Due to the purulent process, it is impossible to provide adequate anesthesia. Therefore, it is necessary to anesthetize the peri-almond tissue only with strong anesthetics: Ultracaine and Ultracaine DS-forte.
Routinely, palatine tonsils can be removed under local anesthesia or general anesthesia. Previously, this operation was performed only under local anesthesia.
Fortunately, there is now modern equipment that allows removal of palatine tonsils under general anesthesia or under anesthesia using cold plasma coagulation - Coblator.
Why are tonsils needed?
The tonsils are an integral part of our immune system. And their main purpose is to protect the body from the penetration of pathogenic bacteria and viruses. In total, a person has six of them: palatine and tubal (paired), pharyngeal and lingual. By their names you can roughly understand in which part of the pharynx they are located. Their general arrangement resembles a ring. This ring acts as a kind of barrier for bacteria. When we talk about inflammation of the tonsils, we mean only the palatine tonsils (aka tonsils). Let's look at them in more detail.
If you open your mouth wide, then in the mirror you can easily see two formations that look like almonds - tonsils, these are tonsils. Each tonsil consists of small openings (lacunae) and winding canals (crypts).
Bacteria that enter the air, in contact with the tonsils, are rebuffed and are immediately disposed of, without having time to cause an outbreak of a particular disease. Normally, a healthy person does not even suspect that real fighting is taking place inside him. Now you understand the importance of the mission of the palatine tonsils. Therefore, a good otolaryngologist will never rush to recommend their removal. Although to hear from a doctor, speaking about tonsils: “They need to be removed!” - a common phenomenon in our time. Unfortunately, today not all clinics can offer high-quality treatment for tonsillitis, and sometimes the turnaround rate is off the charts. That is why it is sometimes easier for a doctor to brush it off and refer the patient for surgery.