Secondary caries is a new pathological process that occurs in the tissues of a tooth that has previously been subjected to dental treatment. Often, it appears due to insufficient antiseptic treatment of the carious cavity or poor-quality filling, but there may be other reasons, which we will discuss below.
Dental caries under a filling is characterized by a long asymptomatic course. The first symptoms may appear 2-3 years after the filling is installed: discoloration of the enamel and increased sensitivity of the tooth. In severe cases, pulpitis can develop, which can lead to serious consequences, including tooth loss and osteomyelitis of the jaw bone.
Causes of caries under fillings
As a rule, secondary caries is the result of a whole complex of different factors. Only a dentist can name the exact cause, based on medical history and examination of the unfilled tooth - after he sees what caries looks like under the filling and determines what factors could cause it.
Of particular importance in the formation of secondary pathology is the individual susceptibility of tooth tissue to caries, the composition of the filling material, as well as compliance with oral hygiene.
The main causes of caries under fillings:
- Application of high shrinkage fillings. Over time, such fillings reduce their volume in the carious cavity, which provokes detachment of the filling material from the edges of the hard tissues of the tooth. Bacteria penetrate into the spaces unfilled with a filling, provoking a new stage of caries development. Sometimes, caries damage can be seen with the naked eye along the edges of the filling, especially on the front teeth;
- Poor-quality cleaning of a carious cavity is a direct mistake by the doctor when filling: the affected tissue remains inside, in which bacteria are concentrated, continuing tooth destruction;
- Poor processing of the filling - rough grinding and polishing contribute to increased adhesion, which leads to accelerated plaque formation on the surface of hard tooth tissues, as well as the formation of chips of the filling material and microcracks.
Caries is a systemic disease that can occur not only due to the above reasons, but also due to general factors. For example, in regions of Russia with low fluoride content in the soil, more than 97% of the population (all age groups) suffer from primary and secondary caries. Also, the development of caries under a filling can be triggered by the patient’s refusal of immunomodulatory therapy during the treatment of concomitant diseases.
What determines the result of filling?
A tooth after filling can be destroyed by secondary caries for several reasons.
- When consuming cold and hot food and drinks at the same time (for example, cold ice cream and hot coffee or hot kebab and cold beer). In such cases, under the influence of a significant temperature difference, microcracks form in the tooth enamel and in the places of contact of dental tissues with the filling material.
- The seal may shift slightly when chewing on too hard, tough foods. This will be enough for a microcrack to appear.
- Malocclusion and pathology such as bruxism are accompanied by excessive friction of teeth against each other and cause accelerated abrasion of the filling composition and dental tissues.
- An insufficient level of hygiene leads to the settling of food particles and the formation of a significant amount of soft plaque in the fissures (tubercles on the chewing surface of the teeth) and in the interdental spaces. This accelerates the development of a bacterial infection.
Key differences between secondary caries and recurrent caries
Unlike secondary caries, recurrent caries occurs only at the site of treatment already performed. If lesions appear on the same tooth, but nearby, this is repeated caries. It is almost impossible to find out the cause of the development of recurrent or repeated caries. Only a doctor, based on examination data, can suggest why caries appeared under the fillings.
When diagnosing secondary and recurrent caries, the doctor must remember that both types can develop in combination due to a combination of various factors.
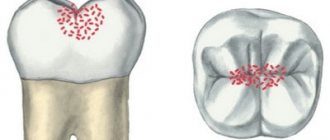
Description of the pathological process
The development of secondary (recurrent) caries is said to occur when the pathological process begins to develop under a recently fixed filling, inlay or crown. That is, after any treatment. As a result, the tooth gradually changes its color, and the most common reason for this is poor quality treatment. A relapse of the disease occurs, which in the vast majority of cases is the result of leaving a gap between the dental tissues and the filling material. Or poor quality cleaning of the cavity from inflamed tissues.
Secondary caries - how does it manifest?
Currently, high-quality modern materials are used in dentistry, but even they are characterized by limited strength indicators, which primarily concerns chewing teeth. Gradually, the material wears out, breaks down and falls out. Another common reason for the development of secondary caries is the abrasion of the filling - over time it decreases, exposing the walls of the carious cavity and provoking the re-development of inflammatory processes.
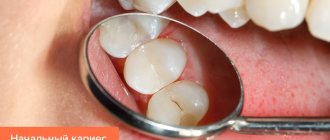
Symptoms of caries under a filling
In the vast majority of cases, secondary caries is asymptomatic. The first signs, with rapid development, may appear only 3-6 months after the filling is installed. If symptoms appear 2-4 weeks after filling, this is recurrent caries. It occurs due to improper treatment and can pose a serious threat to the tooth. To eliminate it, it is necessary to replace the old filling with repeated cleaning and disinfection of the carious cavity.
Classic symptoms of caries under a filling include:
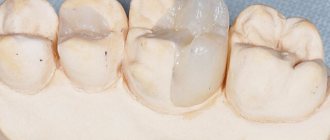
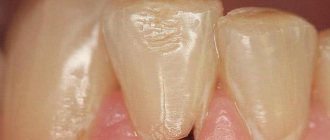
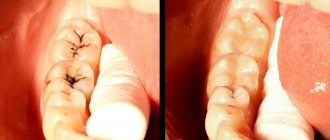
- Darkening of the enamel near the edge of the installed filling - pigmentation can be located either at one edge or along the entire rim of the filling;
- The causative tooth acquires a gray tint, through the enamel you can see what caries looks like under the filling - it will have a dark tint;
- Chips of the filling and tooth enamel appear, microcracks form (not always);
- The mobility of the filling increases. With prolonged development of caries, it may fall out;
- There is an unpleasant odor from the mouth, caused by the proliferation of bacteria in the formed microcracks;
- Increased sensitivity of teeth to cold, hot, sour and sweet;
- Aching pain appears, which intensifies during the process of biting;
- Acute tooth damage by secondary caries develops, accompanied by pain, swelling and bleeding.
Is it always possible to replace an old filling with a new one?
Depending on the degree of tooth decay and aesthetic requirements, restoration can be done:
1. Filling made of composite material. As a rule, if the tooth decay is less than 50%
2. Veneer or componir in case of restoration of the anterior group of teeth - Veneer - the thinnest porcelain plate made in a dental laboratory using an individual impression - Componir - a budget analogue of a veneer, made in a factory from composite materials
3. Inlay made of composite material or ceramics. In case the tooth is destroyed by more than 50%. An inlay is a “large” filling that is made in a dental laboratory. It is much stronger than a filling and better conveys the anatomical features of the teeth and matches the color
4. A crown made of metal ceramics or zirconium dioxide. A crown is installed in case of significant tooth decay
If the crown part of a tooth is completely destroyed, then a crown will be the best solution to preserve it, since under heavy chewing load the wall of a tooth covered with a filling may break off, and if the crack goes under the gum, then the tooth will have to be parted with.
Consequences of secondary caries
The lack of timely diagnosis and proper treatment leads to the development of complications in the form of acute or chronic tooth pulpitis with aching pain and all the ensuing consequences. At this stage, replacing the old filling with a new one, while simultaneously cleaning the carious cavity, will not help - preliminary treatment of pulpitis is necessary.
Delaying the treatment of pulpitis under a filling leads to partial or complete destruction of the hard tissues of the tooth. It is accompanied by the development of infection affecting the periodontal tissues with subsequent progression to periodontitis. In particularly severe cases, periodontitis affects the jaw bone - this can result in osteomyelitis of the jaw bone.
Symptoms and signs
Recognizing signs of tooth decay by caries is not so easy; a filling and the inconvenience of self-examination do not allow one to detect darkening of the enamel or the beginning destruction of bone tissue. However, there are symptoms by which you can recognize the presence of the disease:
- pain on individual teeth and the lower part of the jaw;
- inflammation of the gums in the area of the filled tooth, swelling;
- an unpleasant odor emanates from the mouth (if the tooth is rotting under a filling);
- the appearance of blood on the gums when brushing the mouth or as a result of a minor collision with blunt objects.
Bleeding from the gums of the affected tooth and aching in the jaw area are often observed. Carious lesions of bone tissue can also be detected visually. It is worth paying attention to the seal. Often it changes color or a dark brown rim appears along its edges. The formation of cracks and chips of tooth enamel is also observed.
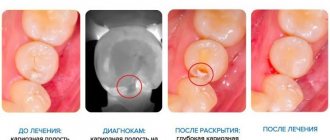
Methods for diagnosing and treating caries under fillings
It is quite difficult to determine the presence of secondary caries in the initial stages, due to the absence of symptomatic and visual manifestations. The disease is diagnosed during a follow-up appointment using diagnostic equipment (hardware diagnostics).
Diagnostics includes two stages:
- Anamnesis and initial examination of the causative tooth in order to detect visible structural changes in hard tissues;
- Hardware diagnostics (physiography) is aimed at detecting hidden changes in the structure of dental tissues.
If a pathology is detected, treatment is prescribed taking into account the individual characteristics of the patient.
Prevention
For daily care, we recommend using certified toothpastes with fluoride and calcium and rinsing your mouth with antiseptic liquids (Glister, Splat, Lacalut).
Don’t forget to get examined by a dentist once every six months in order to detect a relapse in time. A method of preventive filling will also not hurt - covering the fissures with a sealant or liquid composite.
Remember that the doctor is obliged to give you a guarantee for the filling. During the warranty period (6-12 months), you have the right to undergo free re-treatment in case of caries recurrence.
Do you have a toothache after endodontic treatment? Find out what pain signals after root canal filling.
Features of treatment of secondary caries
The use of one or another treatment regimen for secondary caries directly depends on the location of the lesion, its depth and the condition of the causative tooth. Treatment may include two options for developing the situation:
- Re-filling or replacing part of the filling in the affected area is performed only after treating the tooth and eliminating the carious lesion. In some cases, it may be necessary to remove the nerve and fill the canals.
- Surgical tooth extraction is used in extreme cases when the damage is too large and the doctor cannot save the affected tooth.
Types of ceramic inlays
- inlay tab - restores the “cavities” of the tooth crown
- onlay tab - restores most of the chewing surface of the tooth crown
- overlay tab - restores the chewing surface and side walls of the tooth crown
The service life of the inlays is more than 10 years, while the filling will require replacement after an average of 5 years.
Now, when a dentist suggests restoring a tooth with an inlay, you know what benefits this will provide in the future.
Methods for preventing caries under a filling
High-quality prevention of secondary caries involves the elimination of complications at the stage of initial installation of a filling - the doctor must ensure the correct method of caries treatment, antiseptic treatment of the hole for the filling and installation of the filling.
On the patient’s side, the most effective prevention of secondary caries under a filling is maintaining proper oral hygiene, as well as systematic examinations in a dental clinic: a month after the filling is installed and at least 2 times a year thereafter.
Preventive measures
Regular visits to the doctor will greatly help in assessing whether a filled tooth may have caries. It is important to have your teeth professionally cleaned twice a year and to ensure proper hygiene yourself - floss, brush your teeth twice a day, and use mouth rinses after meals. An early visit to the dentist will allow you to promptly detect the onset of the disease and take action - the doctor will promptly replace the old filling, preserving the maximum amount of living tooth tissue.
Category Caries Published by Mister stomatologist