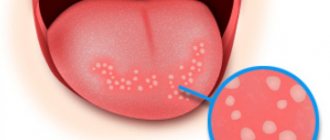
One of the most common diseases associated with damage to the mucous membrane in the human oral cavity is stomatitis, which occurs in approximately a quarter of the entire world population. Children are most susceptible to the disease, the development of stomatitis in the mouth is accompanied by severe symptoms and requires immediate medical attention. But even among adults, stomatitis is not such a rare occurrence.
Therefore, even if you have never encountered the formation of painful ulcers on the palate, mucous membrane, throat or tongue, it will still be useful for you to know what stomatitis is, how it manifests itself, and most importantly, how such a disease is treated with medications . Dentistry "LeaderStom" will tell you about this, as well as how to prevent the occurrence and development of the disease through preventive measures for the hygiene of the human oral mucosa.
Stomatitis: what kind of disease is it, the mechanism of appearance of stomatitis ulcers
Scientists have not yet fully studied the mechanism by which stomatitis occurs on the mucous membrane in a person’s mouth. The manifestation of symptoms of the disease is associated with the specific reaction of a person’s immune system, which he exhibits in relation to irritants present on the mucous membrane of the mouth.
Bacteria, fungi, viruses and other microorganisms act as irritants. Normally, they are always present on human mucous membranes in one quantity or another. But when a person’s immunity is weakened, or other reasons provoke an increase in the number of microorganisms and the development of infectious diseases in the mouth (staphylococcal, streptococcal, candidal, etc.), this fact can trigger a stomatitis reaction.
Ulcers on the human mucosa, which are stomatitis in nature, are formed as a result of the fact that lymphocytes (white blood cells of the human immune system) begin to attack molecules that they cannot recognize. This reaction of the body is similar to that which occurs in the case of organ transplantation. As a result of such a lymphatic attack, stomatitis ulcers are formed on the oral mucosa, which usually go away on their own in one to two weeks without scarring.
Types of stomatitis, causes and symptoms of the disease
Based on the peculiarities of the mechanism of occurrence, stomatitis manifests itself not only as a separate disease, but also as a concomitant sign of the presence of infection in the human body. Depending on what mechanisms provoked the appearance of stomatitis ulcers in the mouth of a child or an adult, various types of stomatitis disease are distinguished.
Types of stomatitis:
- Aphthous stomatitis.
This is a common form of the disease that occurs in humans at any age. It appears in the form of yellow-gray ulcers (ulcers) surrounded by a red halo. Oral ulcers occur in groups or singly; they hurt and cause discomfort to a person. - Herpetic form of the disease.
This stomatitis reaction develops against the background of a herpetic infection in the human body. Herpetic stomatitis appears in the form of painful small blisters on the oral mucosa, which are located in groups. Such bubbles burst after 3-4 days. The herpetic form of the disease in both children and adults is accompanied by fever, gingivitis develops on the mucous membrane in the mouth, and a person’s saliva becomes viscous. To treat the disease, the doctor usually prescribes the drug acyclovir to the patient. - Vesicular stomatitis.
In this case, a person with such a disease is contagious, since the causative agent of the disease is an RNA virus. In order to avoid infection, the patient’s personal belongings should be disinfected and separate utensils and personal hygiene products should be provided. - Allergic stomatitis reaction.
The disease occurs due to allergens entering the human body, to which it reacts by forming stomatitis ulcers. Allergic substances enter our body with food or drinks. Foods such as citrus fruits, red berries (strawberries, raspberries), tomatoes, peanuts, chocolate or cereals (since they contain gluten) can provoke an allergic reaction, the development of stomatitis and the formation of ulcers on the mucous membranes of a person’s mouth. - Traumatic stomatitis.
The occurrence of the disease is associated with injuries to the mucous membranes in the human mouth. They appear when a person eats rough food or drinks hot drinks. In addition, an adult or child can simply bite their tongue or scratch an area of the oral mucosa, and this will provoke a stomatitis disease. - Catarrhal stomatitis.
This form of the disease develops if a person does not follow the rules of oral hygiene: neglects daily brushing of teeth, rinsing, and flossing.
Only a doctor can diagnose one or another form of stomatitis disease in an adult or child. Do not try to do this yourself at home, studying photos from the Internet, and prescribe treatment for yourself. Each case is individual, so if you suspect stomatitis in the mouth, you should seek advice from a dentist or therapist. Competent doctors from the LeaderStom network of dental clinics will help you cope with the disease and cure wounds on the oral mucosa, palate, throat and tongue.
Prevention
To avoid consequences, you should regularly visit a dentist, observe the rules of oral hygiene, do fluorography in a timely manner, avoid mechanical and chemical injuries to the tongue, avoid alcohol and smoking, and adhere to a diet.
Nutrition should be balanced, rich in microelements and B vitamins. A mandatory condition for maintaining health is taking medications that stimulate the body’s protective functions.
Sores under the tongue can be a signal of a serious disease, therefore, if discomfort and pain appear in the oral cavity, as well as in the presence of lumps and small wounds, the patient should consult a doctor in order to begin timely treatment and avoid negative consequences.
Stomatitis in a child: symptoms, causes
The description of stomatitis in a child deserves special attention. The specificity of stomatitis that occurs in the mouth of a young child is that the disease is a consequence of a weakened or not fully formed immune system. Therefore, the stomatitis reaction manifests itself clearly and the course of the disease is accompanied by severe symptoms.
Symptoms of stomatitis in a child:
- The oral mucosa turns red and swelling appears.
- Characteristic stomatitis ulcers form in the mouth, which are located either singly or in groups. The localization of ulcerative formations during stomatitis in a child is different: wounds and blisters appear on the tongue, on the palate, mucous membrane or in the throat. The nature of the lesions depends on the form of the disease and on what factors triggered the reaction (infections, allergies, vitamin deficiency, etc.).
- The development of stomatitis in the baby’s oral cavity is accompanied by an increase in the child’s body temperature (up to 38-39 degrees).
- The baby’s submandibular lymph nodes increase in volume and become painful on palpation.
- The child becomes lethargic, drowsy, capricious and whiny.
The baby has a hard time suffering from stomatitis in the mouth, and this is a lot of stress for the young body, not to mention the fact that the disease worsens the child’s appetite and disrupts the child’s sleep pattern. Therefore, if you notice the formation of ulcers in the mouth of your daughter or son or identify other symptoms of stomatitis, immediately show your child to a doctor (dentist or therapist).
Studying pictures and photographs of other children with oral stomatitis on the Internet is pointless; you will only waste your time and may come to the wrong conclusions. The doctor will help you understand the reasons that provoked the development of stomatitis in the child’s mouth and prescribe effective treatment for stomatitis.
Symptoms and signs
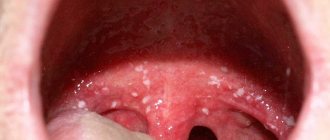
The most common cause of sores and ulcers is sublingual stomatitis, which is characterized by the following symptoms:
- the appearance of a whitish or yellowish coating on the tongue;
- swelling;
- ulcers and abscesses in the sublingual area.
In especially severe cases, ulcerations heal poorly, fester, and subsequently leave a scar.
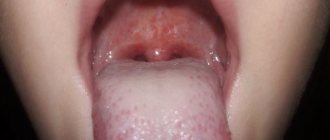
With herpetiform stomatitis, the ulcers are located at the bottom of the tongue. In appearance, they resemble herpes - small blisters filled with liquid.
With tuberculosis of the oral cavity, the sores initially look like small tubercles, the ulcers are round, their edges are undermined. Often the formations may bleed. Over time, they become very painful, the patient's condition worsens sharply, and pain occurs when eating and talking.
Why can our articles be trusted?
We make health information clear, accessible and relevant.
- All articles are checked by practicing doctors.
- We take scientific literature and the latest research as a basis.
- We publish detailed articles that answer all questions.
With tongue cancer, the patient observes lumps. Mouth ulcers are a sign of metastatic disease. They can reach from 1 to 4 cm. The color of the affected area can vary from dark red to dark gray or yellow.
Tongue cyst is a rare disease. A small, painful white growth forms under the tongue. The patient has difficulty breathing and swallowing.
Which people are at risk for stomatitis?
As already noted, children are primarily susceptible to stomatitis, since their immune system is just learning to fight infections and diseases and respond to irritants appropriately. Therefore, if, with timely consultation with a doctor and proper treatment, your baby still chronically develops stomatitis in the mouth, then perhaps the reason is due to age, and over time these problems will disappear.
But besides age, there are other factors that increase the risk of stomatitis ulcers in a person’s mouth. They are associated with various reasons, some of which we have already named when characterizing the types of stomatitis, but now we will try to specify each factor separately.
Those at risk for possible development of stomatitis include:
- People with a hereditary predisposition to the disease. Scientists have proven that the likelihood that stomatitis will develop in a person’s mouth (on the palate, mucous membrane, throat or tongue) increases if one or both parents have ever encountered similar problems. The best way out in this situation is to follow the rules of oral hygiene and take vitamin and immunomodulatory complexes as prescribed by your doctor.
- People with current somatic diseases. Quite often situations arise when stomatitis chronically develops in a person’s mouth without any obvious reason. During a complete examination of the body of such a person, any diseases are usually revealed, in particular, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (giardiasis or helminthic infestations). Parasites, while in the body, may not manifest themselves in any way and not bother a person for years, but they reduce his immunity and prevent resistance to infections and other diseases. In this case, in order to get rid of stomatitis in the oral cavity, a person should undergo a course of treatment that will allow him to get rid of other concomitant diseases.
- People with reduced immunity. Human immunity is reduced not only by somatic diseases, but also, for example, by factors such as stress. Therefore, if you have a hard job or tense family relationships, this can cause chronic stomatitis, localized on the oral mucosa. In addition, frequent occurrence of ulcers in a person's mouth may indicate more serious problems with the immune system caused by a disease such as AIDS. Therefore, in this situation, a person is recommended to get tested, undergo a full examination of the body and get plenty of rest.
- People with bad habits. Bad habits such as alcohol, smoking and drug use can cause stomatitis and the formation of painful ulcers in the mouth. The fact is that such a lifestyle weakens the immune system and undermines human health. In addition, cigarette smoke and alcohol create favorable conditions in the oral cavity for the development of bacteria, viruses and fungal infections, which provoke the appearance of stomatitis ulcers on the human mucosa.
If you have seen photographs of people with stomatitis in the mouth, then you have probably noticed how unattractive this disease looks, not to mention how much discomfort it causes to a person. Therefore, if you are at risk for the possibility of developing stomatitis ulcers on the mucous membrane, palate, throat or tongue, then you should take measures to reduce the chances of getting stomatitis: quit bad habits, undergo a course of treatment for somatic diseases, increase your immunity and take vitamin complexes. But these measures should be taken only after consulting a doctor.
Which doctor should I contact?
If a lump appears under the tongue on the frenulum, you need to find out what factors provoked its formation. Only a doctor can correctly determine the cause. After all, the ball can be filled with liquid or consist of epithelial cells. The degree of discomfort depends on the size of the formation. When papillomas are soft, the patient may not feel them, but large inflammatory growths interfere and begin to hurt. Contact your doctor if you experience any of the following symptoms:
- The mucous tissues of the oral cavity constantly dry out;
- The deficiency of saliva and its composition is clearly expressed;
- The taste sensations have changed a lot;
- Increasing pain appeared;
- Swelling on the face increases;
The affected tissue around the lesion may become red and begin to bleed. First of all, you should consult with your local therapist. To confirm the suspected diagnosis, it is most often necessary to visit a dermatologist, dentist, otolaryngologist, venereologist, or gastroenterologist. If the need arises, the patient is referred to a surgeon or oncologist. During the examination, the doctor collects anamnesis, conducts a thorough examination, and performs laboratory diagnostics and histology. In complex cases with abscesses, patients are referred for ultrasound examination, as well as computed tomography. The pathogen is detected using a cytological analysis of saliva.
Treatment methods for stomatitis
Local treatment of stomatitis involves treating ulcers on the palate, tongue, or other areas of the oral mucosa with antiseptic agents. If stomatitis ulcers appear in the throat, the patient is prescribed gargling with an antiseptic solution or medicinal herbs.
General therapy for the disease includes drugs that are aimed at eliminating the causes of stomatitis in the mouth: antibiotics (for a bacterial infection), antiviral drugs (for example, acyclovir for herpetic stomatitis in the mouth), antifungals (if the cause of stomatitis is a fungus of the genus Candida or what -other), antihistamines (for allergic stomatitis or to relieve swelling during the inflammatory process), etc.
For prevention, increasing the defenses of the human body and in order to prevent complications and the development of chronic stomatitis, the patient is prescribed immunomodulatory agents and vitamin complexes. To relieve pain and reduce fever during stomatitis, doctors use painkillers.
The closure and disappearance of stomatitis ulcers with appropriate treatment of stomatitis disease and inflammation that occurs in the human mucosa usually occurs within 1-2 weeks, but you should take medications prescribed by your doctor strictly within the course. The fact that you felt better and stopped experiencing pain and discomfort due to stomatitis in the mouth does not yet indicate that the disease has been cured.
Strictly follow all the doctor’s recommendations and do not try to cure stomatitis yourself, using the advice of friends or photographs and recipes for preparing medicinal potions found on the Internet. At best, you simply will not achieve the desired effect, and at worst, you will increase the symptoms of the disease.
Treatment of ulcers under the tongue
If a parent discovers a sore in the child’s tongue area, he should immediately take him to a dentist for examination. This is the doctor who deals with such diseases. He will conduct an examination and, if necessary, ask the patient to see a doctor of another specialization.
Traumatic ulcer during teething
To make a diagnosis, the doctor must talk with the patient. This will allow us to understand the nature of the lesion in the oral area. A microscopic examination will also be required.
The easiest way to understand how to treat ulcers that appear as a result of mechanical damage. As a rule, they heal fairly quickly if the affected area is provided with suitable care. To quickly get rid of a sore that has formed under the tongue, you must immediately treat it with an antiseptic. Can be used:
- hydrogen peroxide;
- brilliant green;
- propolis spray;
- soda solution.
Propolis spray effectively heals wounds
This antiseptic treatment is usually prescribed for stomatitis. Additionally, vitamin complexes are prescribed.
Individual therapy must be selected for each patient. In addition to treatment with an antiseptic, the attending physician may prescribe:
Painkillers. They contain benzacaine or lidocaine. Ointments and gels based on corticosteroids. Flucinocide is especially in demand. In particularly severe cases, corticosteroid drugs are used. They are necessary for patients who suffer from recurrent aphthous stomatitis.
Squamous cell carcinoma at the bottom of the tongue
If the ulcers were caused by herpes, the patient is prescribed the use of local medications, this may be Acyclovir ointment. Candidal stomatitis cannot be defeated without antifungal drugs, which are used in local and internal treatment.
READ ALSO: How the laser resurfacing method works
When stomatitis is accompanied by deterioration in health, namely fever, inflammation of the lymph nodes and exacerbation of a number of diseases, then the patient is immediately sent to the hospital. It is very difficult to cure a patient, especially a child, at home in such a situation.
Tongue herpes in a child is very painful
Acute and chronic stomatitis, what is the difference?
There are two forms of stomatitis disease: acute and chronic. For the first time, stomatitis usually manifests itself in an acute form, characterized by the sudden appearance of ulcers on the palate, mucous membranes in the mouth, tongue or throat of a person. The ulcers hurt and cause discomfort when talking or eating.
Acute stomatitis goes away on its own after 7-10 days, even if it is not treated, but in most cases the disease returns in a chronic form. This means that a person develops stomatitis ulcers in the oral cavity from time to time throughout his life. In order to prevent the transition of stomatitis disease from an acute to a chronic form, a person should undergo a course of treatment for the disease at the initial stage. It is very important that a plan and methodology for combating stomatitis in the patient’s mouth is developed by a competent and competent doctor who could take into account all the factors that could provoke this disease and get rid of them.
The LeaderStom clinic invites you to diagnose stomatitis and undergo a course of effective treatment under the supervision of the institution’s experienced dentists. Our doctors know modern methods of combating this disease in patients of different ages and are able not only to solve the existing problem, but also to give valuable recommendations for further oral care in order to prevent the occurrence of stomatitis ulcers on the mucous membrane, palate, throat or tongue of a person again .