The most common periodontal diseases
The periodontium is an anatomical structure that unites the tissues surrounding the tooth and holding it in the socket.
This supporting-fixing function is provided by the gum with the periosteum, alveolar bone, periodontium, and tooth cement. It follows from this that periodontology is not only a science that deals with the treatment of gums. It covers a wider range of different pathological conditions. When exposed to negative factors and pathogens, the following periodontal diseases develop:
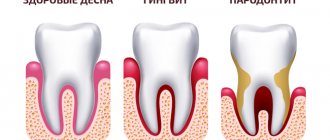
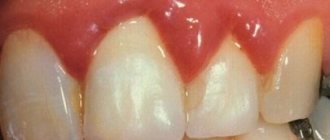
- Gingivitis is an inflammation of the gums that occurs without compromising the integrity of the periodontal junction. In terms of prevalence, the process can be localized, generalized, and in form - catarrhal, ulcerative, hypertrophic. Treatment tactics will also be determined by the severity of the disease.
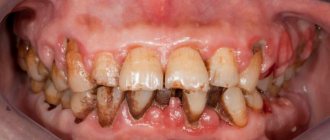
- Periodontitis is an inflammatory disease of periodontal tissues that occurs with damage to the dental-gingival junction and is a consequence of insufficiently effective treatment of gingivitis.
- Periodontal disease or (generalized form of periodontitis) is a non-inflammatory process characterized by dystrophic damage to periodontal tissue.
Much less frequently, periodontal damage can be caused by uncompensated diabetes mellitus and other somatic disorders. There are also cases of tumor growth of periodontal tissues.
Attention to periodontal problems is due not only to the widespread prevalence of pathology among diseases of the dentoalveolar region, but also to the fact that poor-quality treatment measures and their delay lead to a deterioration in the stability of teeth and subsequent loss.
In Moscow, specialists from the Dental Studio clinic are actively involved in the issues of periodontology and gum treatment. Periodontology is a complex science, so prices for the treatment of gums and other pathologies in this area are justified.
What are the possible complications?
Improper teething, accompanied by pericoronitis without treatment, can lead to the following serious complications:
- Formation of necrotic ulcers along the gingival margin. Subsequently, necrosis can spread to other tissues of the oral cavity;
- Damage to healthy neighboring teeth;
- Phlegmon of the perimaxillary spaces;
- Periostitis, which easily spreads to nearby areas;
- Osteomyelitis;
- Abscess formation.
Any of these pathologies can become life-threatening, so treatment of inflammation of the mucous membrane must be timely.
Treatment of pericoronitis is not difficult. A timely visit to the dentist and diagnostics will allow you to immediately carry out the correct treatment. For example, if a tooth initially erupts incorrectly, then removing it at the very beginning of the process will avoid further discomfort.
If for one reason or another it was not possible to visit a doctor on time, then you should come for a consultation when the first signs of inflammation appear. The purulent form is much more difficult to treat and causes more inconvenience. In addition, pus is the main cause of complications.
The post Treatment of pericoronitis appeared first on.
]]>
Treatment of periodontal disease, periodontitis, gingivitis
Therapeutic tactics in case of damage to periodontal tissues are determined by clinical symptoms, the extent of the process, and the severity of the disease. Since with gingivitis the tooth-gingival junction is not involved in the pathological process, the treatment provided will be simpler and limited to therapeutic measures. The features of conservative approaches in periodontology are such that with timely and well-structured dental care, you can count on the complete elimination of negative signs.
If the lesion progresses, such measures will not be possible. An integrated approach is taken as the basis, including both therapeutic measures and surgical intervention; various hardware techniques are also widely used. Modern periodontology also involves laser treatment of gums and other periodontal tissues, the use of innovative technologies, and Vector therapy. If the reason for the development of the lesion was injury to the gums by the edge of a crown or filling, then treatment should be supplemented by the elimination of these provoking factors.
Surgical periodontology: therapy and treatment of diseases
Surgical periodontology is a set of techniques that are relevant for deep and extensive pathological processes in periodontal tissues. However, even in severe situations, surgical treatment is not always taken as the basis when choosing treatment tactics. If measures such as oral hygiene procedures, anti-inflammatory therapy, and antibiotics are effective, then surgical intervention is not resorted to; conservative approaches are used.
Therapeutic periodontology
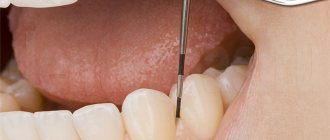
Therapeutic measures for damage to periodontal tissues begin with oral hygiene aimed at eliminating the main provoking factor in the development of pathology - hard dental plaque. These procedures are important not only for gingivitis. In case of periodontitis, by clearing the periodontal pockets of tartar, rinsing them and antiseptically treating them, it is possible to influence the causative factor and achieve a significant improvement in the situation. In modern clinics, ultrasonic teeth cleaning and an Air Flow device are used for this purpose.
The impact on pathogenic microorganisms and the inflammatory process is also achieved with the help of medications. Drug therapy at one stage or another may include:
- antiseptic solutions;
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs;
- in the presence of an infectious component - antibiotics;
- vitamins;
- biogenic stimulants, by introducing them into the gum tissue, experts try to improve local trophic processes;
- agents that promote healing and epithelization of the mucosa.
Conservative approaches also include laser action, the Vector apparatus, physiotherapeutic procedures, vacuum therapy, and ozone therapy.
Treatment methods for periodontal pathology directly depend on the clinical symptoms and severity of the process. It will be possible to achieve recovery only with the initial signs of the disease. The ineffectiveness of therapeutic approaches leads to the fact that the nature of treatment measures will be to stabilize the condition and prevent tooth loss.
Vector therapy
The operation of the Vector device is ensured by converting an electrical signal into an ultrasonic wave, with the help of which it is possible to thoroughly clean periodontal pockets, qualitatively eliminate dental deposits when they are localized subgingivally, and carry out prevention after completion of periodontal treatment. The technique is also effective in severe cases:
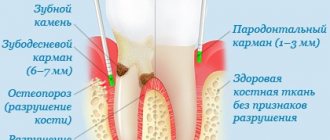
- deepening of periodontal pockets up to 11 mm;
- the presence of bleeding gums, suppuration from gum pockets.
During the procedure, there is no direct contact of the device head with the tissues of the oral cavity. At the same time, the simultaneous supply of a highly dispersed suspension ensures the washing out of dental plaque and polishing the tooth root.
Splinting teeth
Splinting is carried out to strengthen mobile teeth and prevent the progression of their loosening process. The desired result is achieved by using orthopedic techniques, crowns, clasp dentures, and fiberglass. Horizontal laying of a special thread connects the teeth to each other. The resulting strong contact increases the stability of the segment. As a result of the procedure, it is possible to prevent not only further loosening of the teeth, but also to fully restore their chewing function and appearance.
Indications for surgery
When deciding when an operation within the framework of surgical periodontology is indicated, specialists proceed from clinical signs. At the same time, doctors understand that this approach is less desirable compared to conservative treatment: it is associated with painful sensations, the need for sufficient anesthesia, and a recovery period. However, if conservative methods are ineffective, the pathological process will progress and bone tissue will be involved, which will worsen the further prognosis and the chances of saving natural teeth.
The indication for surgical intervention is the unfavorable course of the disease and the low effectiveness of therapeutic methods. For mild damage to periodontal tissue, one of the curettage methods is used; for moderate and severe damage, preference is given to flap surgery. X-ray diagnostics help in choosing the most correct tactics, allowing you to most accurately determine the depth of the periodontal pocket.
Surgical periodontology
For periodontal pathology, the following surgical techniques are most in demand:
- Open and closed curettage. The task facing these procedures is to cleanse periodontal pockets from tartar and granulation tissue. The choice of the most optimal technique is determined by their depth. Closed curettage is carried out somewhat simpler, without preliminary tissue incision, so it is used for slight deepening of periodontal pockets. The open curettage technique implies an extended scenario. It is used for more severe disease. In this case, an incision is made in the area of the interdental papillae, which guarantees convenience during cleansing procedures and increases the effectiveness of the procedure;
- Flap surgery allows you to relieve signs of inflammation, correct the gum edge, and restore bone tissue. The intervention is performed by peeling off the mucoperiosteal flap. This surgical approach allows you to eliminate granulations as efficiently as possible, clean and polish the roots of the teeth. Filling bone pockets with osteoplastic material makes it possible to speed up the process of tissue regeneration and restoration. The final stage of the operation is to return the flap to its original place and fix it with sutures in the interdental spaces;
- Autotransplantation. When bone tissue is involved in the pathological process, it is replaced by granulation tissue, the tooth root is exposed, which contributes to the aggravation of the situation, the development of an aesthetic defect, and also increased tooth instability. Gum transplantation is a common periodontal operation aimed at solving the problem of gum loss. If there is a shortage of soft tissues, they are taken from another part of the oral cavity, the palate.
Surgical treatment of periodontitis
Treatment of periodontitis takes place in several stages
. If therapeutic approaches, hygiene procedures, and local use of medications do not give the desired effect, proceed to surgical periodontology methods. The task facing them is the removal of dental plaque in the area of periodontal pockets and subsequent sanitation. The result is achieved by performing closed or open curettage. If lost bone tissue needs to be restored, targeted tissue regeneration is provided. The technique of such an operation is the simultaneous use of osteoplastic materials, membranes and grafts, which can significantly improve the process of osteogenesis. In this case, the positive effect of treatment is observed at any degree of damage.
Surgical periodontology in Moscow
widely represented in the Dental Studio clinic. Treatment of these diseases is carried out by specialists with specialized education and extensive experience in using both conservative and surgical techniques. An individual approach is applied to each patient, taking into account the entire range of associated factors. Properly prescribed and carried out therapeutic measures provide a positive prognosis for the disease. This area of activity of our doctors finds a positive response among patients.
Possible signs
Based on the nature of the flow, the following options are distinguished:
Acute catarrhal pericoronitis
During the process of teething, the patient experiences unpleasant sensations, which intensify when eating. The mucous membrane in the affected area will be red, swollen and painful when touched. Regional lymph nodes increase in size. Their palpation becomes painful.
Acute purulent pericoronitis
With this form of the disease, pain increases. Purulent discharge appears from under the hood. Pain when eating is accompanied by discomfort when swallowing. Mouth opening is limited.
The patient's general condition changes. There is an increase in body temperature to 37.5-38 degrees. Sleep is also disturbed and appetite is lost.
Chronic pericoronitis
The chronic course of the disease occurs if the necessary treatment is not carried out in a timely manner. Painful sensations decrease in intensity and appear only periodically. Since the hood remains, food continues to get trapped under it. This leads to bad breath. Regional lymph nodes are slightly enlarged and painful only on palpation. Swallowing and mouth opening are not impaired.
Kinds
Surgical intervention is divided into two main groups:
- cleaning gum pockets;
- correction of various defects.
The first group includes the following types of surgical intervention:
- curettage using special instruments, carried out when gum pockets are exposed, provides for complete cleaning, removal of all foreign matter and infected tissue;
- gingivotomy is carried out in the form of cleaning, for which the doctor makes a vertical measurement, followed by open curettage with removal of infected areas;
- gingivectomy is performed with horizontal removal along the gum contour; the operation can be performed on the lingual or vestibular side;
- gingivoplasty - edge modeling in order to recreate the natural contour and remove affected areas, can be combined with bone augmentation or curettage;
- The flap technique is performed with excision of lesions and fixation of the flap in the spaces between the teeth;
- bone grafting compensates for the lack of volume and is indicated as one of the preparation stages for installing implants;
- electrosurgery involves the use of a special electrocoagulator, which eliminates infection and allows you to quickly simulate the edge, accelerating the healing period.
The second group of interventions includes the following types of operations;
- vestibuloplasty to deepen the vestibule of the oral cavity, expanding, deepening the area between the teeth and lips;
- plastic surgery of cords and frenulums is usually performed in childhood; it eliminates a number of problems in the future; if it has not been performed in a child, it is recommended for adults at any age;
- closing the recession to reduce soft tissue volume.
Indications
The main indications for surgical intervention are:
- pocket depth from 5 millimeters;
- proliferation of granulomas;
- enlargement, deformation of interdental papillae;
- lag of the edge of the tissue from the surface of the tooth;
- abscesses, discharge of pus from the pockets appears;
- to form the correct gum edge;
- Conservative treatment methods have not given the expected result or cannot be used for a number of reasons.