March 31, 2020
Aphthous stomatitis is one of the most common inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity.
Aphthous stomatitis is one of the most common inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity. In this article we will tell you what additional examinations should be performed for recurrent stomatitis and how to treat this disease.
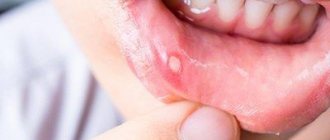
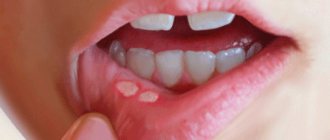
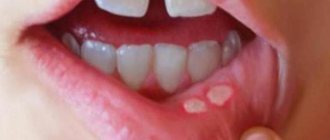
Stomatitis affects from 10 to 40% of the world's population. The diagnosis occurs with equal frequency in people in adulthood and childhood. Clinically, stomatitis manifests itself in the form of painful ulcers on the oral mucosa. Such formations are called aphthae. These pathological lesions are round, bright yellow formations with a bright red inflammatory rim in a circle. They can be located anywhere in the mouth, even on the tongue or gum. Sometimes there are multiple rashes.
The most common causes of stomatitis include viral or bacterial infections. Bacterial stomatitis is usually the result of dental problems and poor oral hygiene (for example, not brushing your teeth thoroughly enough). Sometimes aphthous stomatitis appears at the site of injury, burn or abrasion of the mucous membrane. Canker sores may also appear as a result of taking systemic antibacterial drugs.
What is stomatitis, symptoms, causes
Stomatitis
- an extremely unpleasant sore, and its unpleasantness lies in the fact that it is very painful. The pain is especially severe when eating or drinking drinks. Every piece of cake, every spoonful of porridge and every sip of juice will only cause discomfort and discomfort, let alone hot tea or cold ice cream. Remember, if you have stomatitis, you will remain without pleasure when eating for a long time.
In scientific terms, stomatitis is a lesion of the oral mucosa that occurs as a result of poor hygiene or trauma to the surface, which is accompanied by the appearance of white (often with pus) erosions or ulcers on the palate, tongue, under the tongue, on the inner surfaces of the cheeks and lips. The disease is accompanied by burning, itching, and painful sensations when eating and drinking.
It is very easy to recognize this disease, because its symptoms are quite specific.
So, the most popular symptoms of stomatitis:
- Uncomfortable dry mouth.
This symptom is the first and is often missed, as it can signal other problems, including thirst or a hangover.
- Whitish-gray coating.
It forms approximately three days after the body is infected. Places of dislocation are the tongue, the inner surfaces of the lips and cheeks, the tongue, and at the very end - the corners of the lips. This is already a sure sign of the disease, it is difficult to miss it, so it’s time to start treatment (which is best planned according to the doctor’s recommendations).
- Erosions, ulcers.
These are quite painful formations that appear at the site of the plaque if therapy is not started on time. They look like swellings covered with a whitish coating. In some cases, purulent deposits may form inside these sores.
- Malignant tumors.
A rather rare, but still occurring complication of stomatitis, which is better known to us under the terrible name cancer. If you do not want ordinary plaque to lead to such complications, monitor the condition of your oral cavity, thoroughly brush and rinse your teeth (and regularly, which is important) and respond in a timely manner to the slightest changes in the oral mucosa.
Once again, we emphasize that this disease is infectious, and therefore can be transmitted from carrier to carrier. Its causative agent is a microbe that can develop as a result of the following reasons:
- Insufficient or irregular oral hygiene.
- Injury to the mucous membrane (abrasions that sometimes occur due to using a toothbrush that is too hard, scratches, punctures, burns).
- Allergic reaction to food, medications and other substances.
- Immunodeficiency conditions, immune weakness.
- Wearing dentures or orthodontic appliances (common in older people and children).
- Contact with a sick person.
Prevention of stomatitis
This includes careful and regular oral hygiene, eating warm food and drinks, but not hot or too cold, using a suitable soft-fiber or medium-hard toothbrush, and proper care of dentures or orthodontic preparations. It is also necessary to avoid contact with carriers of the infection. This is especially true if you are susceptible to herpes. Stomatitis in combination with a herpes infection is a dangerous mixture that needs to be seriously dealt with under the guidance of a doctor.
Symptoms
- redness of a local area of the mucosa (at the very beginning of the inflammatory process);
- swelling of the reddened area, burning and itching;
- the appearance of a round ulcer in the bacterial form (occurs within a day), the formation of a white coating in the fungal form or small blisters in the case of a viral infection;
- salivation gradually increases;
- the appearance of bleeding gums;
- unpleasant odor;
- increased discomfort, pain or burning sensation;
- Without treatment, your health may deteriorate and your temperature may rise.
If these symptoms appear, doctors at the Dentospas clinic recommend planning a visit to the dentist.
Types of stomatitis
There are several types of stomatitis, the symptoms and treatment of which depend on the characteristics of the disease. The most popular in our country are the following three varieties:
- Catarrhal stomatitis
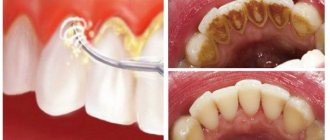
- the mildest form of the disease. Symptoms are limited to dry mouth and increased sensitivity of surfaces. If this form is not treated in time, it can lead to the formation of small ulcers on the gums, palate, and tongue. Wearers of dentures and orthodontic appliances are most susceptible to this type of stomatitis. The reason for the appearance is the poor quality work of the dentist, who did not make the prosthesis well enough, used unsuitable materials, or simply poorly adjusted the device to the jaw. Also susceptible to catarrhal stomatitis are smokers with plaque and who do not care for their oral cavity conscientiously or regularly.
- Aphthous stomatitis
. A chronic form of stomatitis, which manifests itself as a rash on the internal oral surfaces, weakness, and high fever. The rash is a collection of large numbers of small ulcers that are very painful and slow to heal. The healing period may take more than two weeks. A common symptom of this type of stomatitis is gastrointestinal upset. The cause of the disease is weakened immunity, vitamin deficiency. Let us remember that this is a chronic form that will return even with slight hypothermia.
- Herpetic stomatitis
. From the name it is clear that this form of the disease is associated with herpes and 90% of people with stomatitis suffer from this type. The activator is the herpes virus. Some people may get sick once, but in a dormant state the virus will remain in them forever and will not manifest itself. But most often this virus makes itself felt at the slightest weakening of the immune system. Well, stomatitis joins it if oral hygiene is not observed or performed irregularly, the mucous membrane has been injured, or there has been contact with an infected person. It manifests itself in the formation of blisters, which burst and become extremely painful ulcers, high temperature (up to fever).
Stomatitis is often accompanied by fever and painful swallowing. Remember that if you have had stomatitis once, it is very likely that you will have it again. Therefore, your first aid kit should always have medications and folk remedies for this disease.
Diagnostics
Most often, the diagnosis is made by a dentist after examining the oral cavity. In some cases, the doctor may prescribe additional examinations (bacterial culture, PCR smear, etc.) to detect candidiasis or the herpes virus. In case of massive damage to the oral cavity (severe forms of stomatitis), it is necessary to conduct a blood test and seek advice from a therapist. During diagnosis, it is important to distinguish between herpetic and aphthous forms of stomatitis, since different special therapy is chosen for them.
Stomatitis - treatment in adults and children
If we talk about drug treatment of stomatitis in adults, it should be clarified that there are several categories of drugs that, together, are effective against infection.
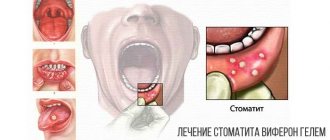
- Antiviral attack - Famciclovir (Famvir, Minaker), Valacyclovir (Valtrex, Valavir), MIRAMISTIN, VIFERON-gel, Acyclovir.
- Immunostimulants - AMIXIN 0.125, IMUDON, vitamins.
- Symptomatic drugs are antipyretics, but they should be used only at high temperatures.
- The fight against herpes rashes - products based on Famciclovir and Valacyclovir, for example, Acyclovir.
Let us remind you once again that taking medications must be approved by your doctor. Do not self-medicate.
Treatment of stomatitis in children is more complicated, since children are more sensitive to antibiotics and other drugs and in many cases their use is prohibited. Parents of a sick child should give him more drinks (water, fruit drinks, compotes). In order for a small patient to be able to eat, the oral cavity should be anesthetized. Teething products (Dentinox-gel or Kamistad) or other drugs containing choline salicylate or lidocaine can help with this.
At the same time, brush your baby’s teeth and rinse the mouth. Folk remedies will help with this, we’ll talk further.
Treatment Basics
If an adult has a swollen tongue, the surface is covered with plaque, or has severe hypothermia, you should consult a dentist. Even in the absence of neoplasms in the oral cavity in the form of papules, ulcers or erosions, a specialist will be able to determine the development of the inflammatory process. With timely treatment, the risk of pathology becoming chronic is minimal.
Treatment of stomatitis on the tongue in adults is carried out exclusively conservatively. Depending on the causes of the disease and the clinical picture, the doctor will determine a treatment regimen and prescribe effective drugs of systemic and local action.
The dentist’s task is not only to eliminate symptoms and inflammation, but also to identify the cause. If the provoking factor has a constant impact, then stomatitis under the tongue will constantly recur.
Treatment of stomatitis on the tongue in adults begins with the relief of concomitant diseases - the root causes.
Folk remedies for stomatitis
For stomatitis, you can rinse your mouth with decoctions or extracts of chamomile, sage, linden blossom, onion peels, carrot juice diluted with warm water, white cabbage or horseradish juice, kombucha infusion, etc.
You can also prepare ointments from garlic with milk (three drops per spoon), honey with olive oil, novocaine and protein (dissolve a spoonful of honey in a water bath, add a spoonful of oil, protein and 0.5% novocaine solution), grated potatoes with olive oil oil, crushed aloe with olive oil, burdock with hot sunflower oil (need to cool before use), etc.
But remember that traditional treatment will be much more effective if it is used together with traditional treatment prescribed by a doctor.
How to treat stomatitis during pregnancy
During pregnancy, a weakened immune system coupled with hormonal changes can lead to the formation of ulcers or white plaque in the mouth. This fate awaits almost every second expectant mother.
Major stomatitis can be cured during pregnancy only under the supervision of a specialist. Rinsing your mouth with folk remedies with an antiseptic and anti-inflammatory effect will help cure a fungal infection. Regular chamomile gives a good result (it is enough to infuse one spoonful of the herb in a glass of boiling water).
Do not thoughtlessly use rinsing for healing. It is also important to establish the root cause of the disease and, if possible, eliminate it.
How to cure tooth decay without a dentist
It is believed that it is impossible to cure a tooth affected by caries without visiting a dentist. But only if it is not caries at the chalk spot stage - this is the initial stage of caries, when calcium is washed out of the tooth enamel. At this moment, the tooth is most susceptible to attack by cariogenic bacteria. But the damage can still be stopped without visiting the dentist.
For example, using remineralizing gels. They contain all the necessary minerals that fill the washed areas: for example, in Tooth Mousse, casein performs this function. This way the tooth regains its original appearance and receives additional protection from carious formations.
Even if a child, at first glance, does not have caries, the gel can be used for prevention.
Gel for strengthening teeth ROCS (ROCS) Medical Minerals with tuber flavor…
Gel for strengthening teeth ROCS (ROCS) Medical Minerals with fruit flavor…
Tooth gel GC Tooth Mousse Strawberry
Tooth gel GC Tooth Mousse Multifruit
Literature:
- Fungal, viral and traumatic stomatitis in a therapeutic dentistry clinic. Tutorial. Edited by Dr.Med.Sc. K.G. Karakova - Stavropol. Publishing and information, 2013. – 100 p.
- Pankrusheva T.A., Maravina I.N., Chekmareva M.S. Research on the development of the composition and technology of tablets for the treatment of stomatitis // Scientific result. Medicine and pharmacy. – T.4, No. 1, 2022, pp. 78-88.
- Tilis S.Yu. Stomatitis. Nurse, 2010, No. 2.
- Glukhmanyuk D.S., Malinovsky V.A. Aphthous stomatitis. Proceedings of the scientific and practical conference “Modern problems of pharmacology, cosmetology and aromology.” International Humanitarian University, Odessa Medical Institute, 2015. (Current problems of pharmacology, cosmetology and aromology: Materials of the scientific and practical conference dedicated to the 160th birthday of a prominent Ukrainian pathologist, endocrinologist, immunologist , microbiologist, professor Volodymyr Valerianovich Pidvysotsky and Pharmacist Day. m. Odessa, June 15, 2022 – Odessa: International Humanitarian University, 2015. – 48 p.)
- Volkova, M.N. Diseases of the oral mucosa: educational and methodological manual / M.N. Volkova, Yu.P. Chernyavsky, N.A. Sakharuk, Yu.R. Elenskaya. – Vitebsk: VSMU, 2016. – 236 p.
- Therapeutic dentistry: textbook: in 3 hours / ed. G.M. Barera. - M. : GEOTAR-Media, 2005. - Part 3. - 288 p.
- Galizina O.A. Main aspects of the occurrence, clinical manifestations, treatment and prevention of chronic recurrent aphthous stomatitis. Russian Dental Journal, 2014, No. 6, pp. 39-43.
- Instructions for the medical use of the drug Metrogyl Denta® Dental gel // Registration number P N015982/01 // State Register of the Russian Federation. – URL: https://grls.rosminzdrav.ru/Grls_View_v2.aspx?routingGuid=9bc9a05c-d28b-…
- Dental gel for gums Metrogyl Denta® in the treatment of periodontal diseases and oral mucosa. Practical medicine, No. 1(33), March, 2009, pp. 105-106.
- Strakhova S.Yu., Drobotko L.N. Chronic recurrent aphthous stomatitis (lecture). RMZh, No. 29 from December 27, 2006, p. 2096
When to wean off a pacifier to avoid problems with bite
The habit of putting everything in the mouth can lead to poor articulation of the tongue, lips and jaw when swallowing, as well as an open bite. Studies have shown that a child can be weaned off the habit of sucking a pacifier up to three or four years of age. But since such a habit has biomechanical reasons, it can be difficult to wean a child - in this case, the help of a psychotherapist is necessary.
To avoid problems with bite, it is important to give up the pacifier in time. By 8–9 months, if complementary foods are introduced in a timely manner, the sucking reflex is gradually replaced by a chewing reflex. It is from this age that it is recommended to start giving the baby a pacifier less - it will be psychologically and physiologically easier for him to wean himself off the habit.
What kind of pasta should a child under 3 years old have?
If we look at clinical studies that were conducted on the principles of evidence-based medicine, the main component in children's toothpastes is fluoride. Only they confirm their effectiveness in preventing caries.
However, it is widely believed that children under 3 years old should not brush their teeth with fluoride toothpaste. This position is due to the risk of developing fluorosis due to an excess of fluoride in the body - destruction and darkening of the enamel. But an excess of this substance is possible only in areas with a high fluoride content in water, and is also due to genetics.
The fluorine content in water can be checked on the Russian water map. And the genetic predisposition can be determined by the attending physician after passing tests. If the quality of drinking water is normal and tests are normal, dentists usually recommend using a toothpaste with a low concentration of fluoride (up to 500 ppm) at an early age.
In addition to fluorides, it is recommended to look at the abrasiveness of the paste (up to 50 RDA), as well as the presence of therapeutic and preventive additives in the composition: enzymes, xylitol, herbal extracts.
What to look for in the composition when choosing a paste:
- Abrasives - An alternative, non-traumatic but effective abrasive is silica. It is worth giving preference to toothpastes containing this substance.
- Fluorides - Organic fluorine contains compounds such as amino fluoride (olaflur).
- Dairy enzymes - lactoferrin, glucose oxide, lysozyme, lactoperoxidase. All of them stimulate the development of beneficial microflora, strengthen local immunity and restore the acid-base balance of the oral cavity.
- Xylitol is a natural sugar substitute with properties beneficial for teeth and gums. It prevents the growth of bacteria and reduces the risk of caries.
Biorepair Kids toothpaste with strawberry flavor (from 0 to 6 years)
Apadent Kids toothpaste with strawberry and grape flavor (from 0 years old)
Toothpaste Brush-Baby Apple-mint (from 0 to 3 years)
Toothpaste Mamiae Strawberry up to 6 years
Features of the disease
Currently, dental stomatitis is one of the most common diseases of the oral cavity. If a person discovers an ulcer in his mouth, he needs to see a doctor as soon as possible and identify the causative agent of the disease. Only then can appropriate treatment be prescribed to help prevent future complications.
What are the causes of stomatitis? There may be several of them at once. The main source of the problem is viral, bacterial and fungal infections. Stomatitis can also develop after a serious injury or accident, with constant mechanical damage to the mucous membrane, frequent stressful situations, the presence of chronic diseases, poor nutrition, HIV infection, etc.
Insufficient hand hygiene can cause harmful bacteria to enter your mouth. This usually occurs upon contact with contaminated surfaces and even unwashed vegetables or fruits. Another cause of stomatitis may be the use of certain medications, for example, antibiotics, which tend to disrupt the normal microflora of the oral cavity. The presence of problems with the digestive system, allergies, hormonal disorders, bad habits and much more - all of these are provoking factors.