Ulcers with stomatitis
Stomatitis is a fairly common oral disease. He's pretty nasty. It begins with inflammation of the oral cavity. Sores appear, eating and drinking becomes much more difficult. Sometimes it even hurts to open your mouth.
Often the disease develops from an incorrect diagnosis. It is important to note that if stomatitis is not treated correctly, it can lead to chronic forms of the disease. What to do if a child’s gums bleed due to stomatitis or other unpleasant symptoms occur?
What is stomatitis
Viral stomatitis in children is a pathological process characterized by damage to the oral mucosa by a viral infection. In children, the pathology progresses rapidly. This disease is acute or chronic.
The pathogen is transmitted in the following ways:
- airborne;
- through contact with the patient’s blood;
- contact-household.
The main source of infection is a sick person or animal. The baby becomes infected quite easily. Most often this happens in kindergartens and medical institutions.
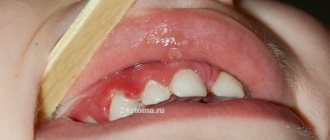
Stomatitis on the gum. Treatment
Causes of stomatitis
Is stomatitis contagious?
Treatment of stomatitis
Stomatitis is an inflammatory disease of the oral mucosa. Sores may appear in the gum area, tongue and throat. Due to painful sensations, people with stomatitis often refuse to eat, which leads to weakness and a deterioration in their general condition. In its acute form, the disease is accompanied by fever. How to treat stomatitis, whether it is contagious - we will tell you in the article.
Causes
Viral stomatitis in childhood develops due to various infections, since the baby has an underdeveloped immune system. He does not have time to recover from his previous illness. It also easily becomes infected from a patient with stomatitis. The situation is worsened by a lack of nutrients and vitamins in the body.
The disease in children is caused by the following pathogens:
- flu;
- HIV;
- mononucleosis;
- measles;
- papillomavirus;
- ARVI;
- enterovirus;
- chicken pox;
- herpes.
Most often, herpes is the causative agent of this disease; it accounts for up to 80% of all cases. Most of these viruses are persistent intracellular parasites. Therefore, this disease often becomes chronic. With this form, there is an alternation of exacerbations and remissions. The acute form can result in the formation of a carrier state, in which the pathogen remains in the cells, but there are no symptoms of the disease.
Most often, the infection affects children under four years of age. But it affects older children and teenagers.
The reasons why this happens are:
- undeveloped immune system;
- insufficient oral hygiene;
- weakness of local immunity;
- injuries to the gums and oral mucosa;
- general weakening of the body after an illness;
- long-term use of certain drugs (glucocorticoids, antibiotics, cytostatics).
Parallel inflammatory processes in other organs and systems also contribute to maintaining the infectious process in the mouth of children.
Main symptoms of stomatitis
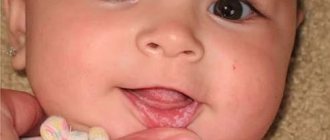
Stomatitis often appears in young children; more serious forms of the disease can occur in adulthood. There can be many causes of stomatitis. This includes poor nutrition, a complication from other diseases, metabolic disorders, and it can also be infectious. It often occurs against a background of reduced immunity.
Stomatitis can manifest itself in different ways. For example, a child changes his behavior. Irritated and capricious, seemingly for no reason. Parents need to be attentive to their child’s complaints. As a rule, with stomatitis, it is painful for children to eat, and sleep is often disturbed. Body temperature rises. Photos of the external manifestations of stomatitis can be viewed in this article.
Stomach upsets, such as bloating and diarrhea, also occur. This is a clear sign that you need to pay attention to the child's health. If stomatitis occurs not for the first time, then parents should be wary.
Typically, this occurs due to the child's weak immune system. Vitamin deficiency also affects the recurrence of the disease. In this case, you need to carefully monitor your diet and take appropriate measures for treatment.
Symptoms
At the beginning of the disease, stomatitis is confused with ARVI and sore throat, as the child’s body temperature rises and a sore throat bothers him. Then the baby refuses to eat. A little later, drooling begins.
Symptoms of viral stomatitis in children fully manifest themselves by the third day of illness.
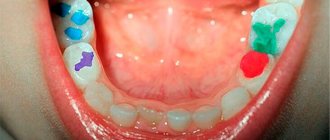
The following rashes appear in the oral cavity:
- erosions - these include areas of the mucosa devoid of surface epithelium, they are accompanied by severe burning and itching;
- bubbles - they are located on the inner surface of the cheeks, under the tongue, on the palate, a transparent secretion accumulates inside them;
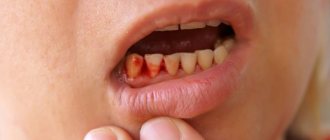
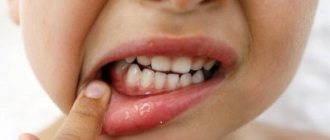
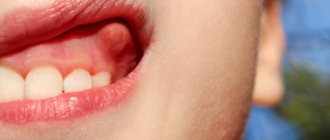
- ulcers are defects in the mucous membrane, covered with a gray coating or films, sometimes they bleed, and the mucous membrane around them is swollen.
In the mouth you can see a white-gray coating and swelling of the tongue. The mucous membrane is red and swollen.
The baby's general symptoms are increasing. He is worried about general malaise. He is whiny, restless, eats and sleeps poorly. The baby has bad breath. An increase in the submandibular and cervical lymph nodes is detected.
Diagnostics
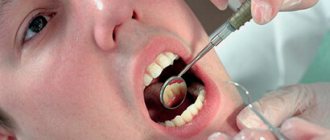
If there is a suspicion of damage to the mucous membrane in the mouth, only a doctor, pediatrician or pediatric dentist should make a diagnosis and examine a child. It is important to identify the cause of the disease in order to prescribe effective treatment. Identifying the cause of the disease does not present any difficulties. This pathology is detected during examination due to the characteristic clinical picture, the presence of rashes, and signs of inflammation in the mouth. In addition to an examination to clarify the nature of the disease, the doctor prescribes a general blood and urine test. In severe cases, tissues of the affected mucous membrane are examined to identify the type of pathogen. For this purpose, washouts and scrapings from erosions and ulcers are taken.
The following methods are used to identify the type of virus:
- immunofluorescence method;
- PCR;
- RSK;
- ELISA.
In order to prescribe effective therapy, especially in severe cases, identification of the type of pathogen is required.
Treatment
Treatment of viral stomatitis in children is carried out under the mandatory supervision of a doctor. Mild forms can be treated at home; in severe cases, the baby is admitted to a hospital. Children are prescribed bed rest and a diet. Food should be pureed, warm, and not irritate the affected mucous membrane. The patient is advised to drink more fluids.
The disease requires complex therapy. For this disease, local and general treatment methods are used.
The following medications are indicated for the child:
- antiviral drugs (Panavir, Acyclovir) - taken strictly according to the regimen prescribed by the doctor; if you do not follow his instructions, a relapse of the disease is possible;
- antihistamines (Suprastin, Citrine, Loratadine) - reduce swelling and reduce pain;
- immunomodulators (Imunofan, Timalin) – strengthen the baby’s immune system;
- antipyretics (Panadol, Nurofen) are used at high temperatures.
Local remedies are used to treat infectious stomatitis. They relieve inflammation and swelling.
For this purpose the following are used:
- antiseptic solutions (Panavir, Miramistin) - the oral cavity is rinsed every hour with a soda solution or Furacilin, and then treated with antiseptics;
- dental gels (Kamistad, Dentinox), which have an anti-inflammatory, analgesic, disinfecting effect, are used thirty minutes before meals;
- antiviral ointments (Acyclovir, Oxolinic) - penetrate the virus and destroy it, the oral cavity is lubricated up to five times a day for two weeks.
Mouth rinses with herbal infusions are used. Herbs are used to relieve irritation and pain (chamomile, calendula, sage).
Physiotherapeutic methods are used: tube quartz, devices with infrared irradiation.
How does the treatment work?
If a child has stomatitis or bleeding gums, you should immediately consult a doctor. You should not contact your pediatrician. They cannot always determine the form of stomatitis.
The further success of the treatment process depends on a correct diagnosis. It is important to strictly follow all doctor's instructions. Incorrect treatment can cause complications.
Pediatric herpetic stomatitis
There are different types of stomatitis, so it can be difficult to make a diagnosis on your own. Some symptoms can only be seen by a professional.
Depending on the type of stomatitis, the doctor prescribes different medications. Their price depends on the type of treatment and the degree of the disease. To avoid significant expenses on medications, you need to diagnose the disease as early as possible.
Mild forms of stomatitis can be treated quickly and rarely lead to complications. For more information, you can watch the video in this article.
Prevention
It is not possible to completely prevent the development of this infection in a child. Most people are already infected with viruses at birth, but it is quite possible to reduce the incidence of the disease.
To do this, the following measures are used:
- if one of the adults is infected, they should not be allowed to contact the child;
- choose a group in kindergarten with a small number of children;
- If possible, do not attend mass events during epidemics;
- it is necessary to harden the child (walk barefoot at home, go to the pool);
- stop bad habits (sucking fingers, toys, other objects);
- thoroughly wash and treat the child’s toys and dishes;
- treatment of all surfaces in the apartment using antiseptics.
Infectious stomatitis in children is a rather unpleasant disease. If you follow all the doctor’s recommendations and preventive measures, you can minimize the occurrence of this disease in your baby.
Nutrition and other factors
Child nutrition becomes a big problem. This process is accompanied by unpleasant and painful sensations. These can be reduced by using painkillers prescribed by your doctor.
As for the food itself, you can give your child dairy products. They should be low-fat. This is due to the fact that fat may not be absorbed and cause digestive problems. You can give your child soft-boiled eggs, omelettes, and liquid porridge. Decoctions of vegetables and fruits are also good.
It will be useful to include various soups and purees in your diet. If fish and meat are present in the diet, they should be well boiled and ground.
What should be excluded?
It is also important not to give your child very cold or hot food. It should be warm to reduce discomfort. It is imperative to remove salty and sour foods. Spicy foods are also excluded.
You also need to reduce the amount of sweets. This will speed up the healing process and help the medications work properly. You should not feed your baby more than four times a day. Eating in between is excluded.
Stomatitis in a baby
The general recommendation would be to structure the diet in such a way as to reduce the impact on the oral mucosa and not injure it further. Honey is also excluded.
Doctors say that it can provoke the appearance of a fungus, which leads to the onset of the disease. It’s also a good idea to give your child juices and rosehip infusion.
It is important to note that citrus juices can negatively affect the healing process. Therefore, the best solution would be carrot juice. Decoctions of sage, chamomile, oak bark, calendula and eucalyptus will be useful. It is also important to drink plenty of water. It should be warm. Rinsing your mouth also helps.
How else can you speed up the healing process?
To prevent the disease from progressing, the child must remain at home. Therefore, parents need to make sure that he does not go to school or kindergarten.
You need to provide him with a separate towel and dishes. The room in which the child is located must be frequently ventilated and wet cleaned.
If a child has stomatitis on the gum, then the teeth should be brushed with a synthetic brush. This will reduce the traumatic effect on the gums and oral cavity in general. Under no circumstances should this be done with someone else’s brush, because the likelihood of spreading the disease is high.
Stomatitis on a child's gum