Insufficient oral care leads to the formation of soft plaque and stones on the teeth, resulting in inflammation. At first, its symptoms are quite harmless: slight bleeding of the gums, soreness, and sometimes swelling. But gradually tooth mobility and pus discharge from under the gums appear. At this stage, we can safely talk about advanced periodontitis, for the treatment of which curettage of periodontal pockets is used. What kind of procedure is this?
Closed curettage of periodontal pockets
Closed curettage or curettage is one of the few methods of treating periodontitis that allows you to eliminate granulations and various types of dental plaque from periodontal pockets. However, due to the lack of visual control, the doctor is not always able to completely eliminate these problems, which reduces the effectiveness of this method. That is why it is used for shallow periodontal pockets, which is typical for the earliest stages of the disease. With a more extensive lesion, the technique can only temporarily improve the patient’s health, but sooner or later periodontitis will begin to recur, which will require re-treatment.
Among the advantages of this type of surgical treatment are:
- Good aesthetic result.
- Rapid gum recovery.
- Minor blood loss.
Due to the features described above, closed curettage is not always used.
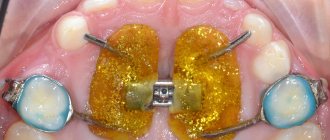
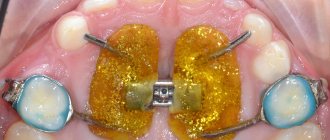
Treatment of reimplantitis with the vector device
Reimplantitis is a process that can occur in the dental tissues located next to the implant. Although the implant is not an organic structure, and the tooth is an organic structure, the nature of the occurrence of reimplantitis is similar to the nature of the occurrence of periodontitis.
The main “culprit” of reimplantitis is bacterial plaque, which accumulates on the part of the implant that rises above the bone. Plaque provokes inflammation of the tissues around the implant and can cause its rejection.
The occurrence or non-occurrence of plaque depends on the design of the implant, the volume of the gum, the quality of installation and the individual characteristics of the body. If plaque does occur, it must be removed.
The ultrasonic wave generated by the Vector device perfectly removes plaque, bacteria and biofilms from the surfaces of implants, stopping the development of peri-implantitis and without damaging the implants and superstructures themselves.
The success of periodontal treatment is due, among other things, to regular pocket cleanings and other measures that are repeated at certain intervals. This is especially important during maintenance therapy in the treatment of periodontitis.
Regular cleaning of pockets and removal of bacterial plaque from the roots of teeth or implants turns this procedure into an analogue of professional hygienic cleaning.
Open curettage of periodontal pockets
This type of operation does not have the disadvantages of the previous method. A good overview of the problem area allows the doctor to remove all granulation tissue and thereby prevent further progression of the disease. Open curettage is performed under local anesthesia and takes place in several stages:
- The surgeon makes an incision in the gum in the projection of the neck of the tooth.
- A certain area of the mucous membrane peels off.
- Granulations and deposits in periodontal pockets are eliminated.
- If necessary, plastic surgery of bone defects is performed.
- The flap is sutured, the surgical field is treated and protected with an aseptic dressing.
Due to the high traumatic nature of soft tissues, a limited area of gum can be treated in one operation, usually up to 8 teeth. After the wound has healed, repeated interventions are performed.
Why is curettage needed?
The process of development of periodontitis is slow and occurs in a certain sequence. First, due to poor oral hygiene, the active proliferation of microorganisms begins, which in the process of their vital activity release a large number of toxins. These toxins have a negative effect on the gums and cause inflammation.
If the patient does not seek medical help at this stage, the inflammation gradually leads to the detachment of the gum from the tooth and the formation of periodontal pockets. These pockets contain food debris and soft dental deposits, which over time mineralize and become hard. Ideal conditions are created for the proliferation of microorganisms that affect not only the gums, but also the bone structures. As a result, granulation tissue is formed, which contributes to the rapid destruction of bone and loosening of teeth. If it is not completely removed, periodontitis will progress further, leading to more severe consequences. In order to effectively clean periodontal pockets from dental plaque, hard deposits and granulations, curettage is used.
Indications and contraindications
Curettage of periodontal pockets is performed if the gum pockets (normally having a depth of no more than 2 mm) have deepened to 4 mm or more. In this case, other methods will no longer give the necessary effect and will not stop periodontal destruction and exposure of tooth roots.
Signs indicating the development of periodontitis and the need for this procedure can be considered:
- gum inflammation, bleeding,
- bad breath, discharge of pus from gum pockets,
- change in the appearance of the gums (swelling, darkening),
- tooth mobility.
At the same time, there are often cases when the gum looks normal at first glance, but a deep pocket has formed under it, requiring mandatory intervention. In order to determine this, an X-ray of the tooth is taken, which shows the formed pockets and periodontal destruction. After a comprehensive examination and exhaustion of other treatment options, the doctor may decide to perform a curettage. Contraindications to curettage in dentistry are relative. These are, as a rule, inflammatory processes in the acute stage, accompanied by copious discharge of pus, fibrous formations (scars) inside the pocket, a very large pocket depth (more than 6 mm), and severe loosening of the teeth. Some of these problems can be solved - for example, suppressing severe inflammation, splinting mobile teeth, etc. And after this it becomes possible to carry out curettage.
Flap surgery for periodontitis
Flap surgery is indicated for patients with pronounced periodontal changes: pocket depths of more than 5 mm, active inflammation, etc. This technique allows not only to eliminate various types of deposits and granulations, but also to restore interdental defects and bone tissue defects. To form a flap, precise cuts are made in a specific direction:
- Horizontal cuts are always made. They can run either inside the gingival sulcus or parallel to the gum edge.
- Vertical incisions allow you to expand the surgical field, but lead to the formation of scar changes in the gums, so they are performed only when necessary.
Among the disadvantages of flap surgery, there is a possibility of flap displacement and exposure of the neck of the tooth. This complication worsens the aesthetics of the oral cavity, contributes to increased tooth sensitivity and the development of tooth root caries.
Methods for performing the procedure
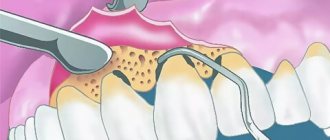
Curettage of gum pockets should not be confused with professional teeth cleaning, when the dentist removes tartar and plaque and polishes the surface of the teeth. Brushing removes deposits from the surface of the tooth, and curettage cleans the pockets between the gum and tooth. Depending on the depth of the pockets, closed and open curettage are distinguished.
Closed curettage: technique
If the depth of the gum pocket does not exceed 5 mm, closed curettage is performed. The procedure is less traumatic, but requires anesthesia. During the process, the doctor scrapes the gum surface adjacent to the tooth and removes dental deposits and damaged areas. Ultrasonic equipment can be used for this. Gum detachment is not performed here. By polishing the tooth surface, the likelihood of new deposits occurring is reduced. The only significant drawback of the method is that the doctor almost does not see the cavity of the gum pocket during manipulation. However, at the mild and moderate stages of periodontitis, closed curettage can improve the condition, stop the development of pathology, and then use conservative therapy.
Open curettage: indications for performance
For deep periodontal pockets (5-6 mm) and a large number of deposits, as well as signs of bone tissue damage, open curettage is performed. All procedures also require anesthesia. During this operation, a precise incision is made in the gum and it is separated, allowing the cavity of the deep gum pocket to be opened. Next, hard deposits are cleaned and the surface of the cavity is scraped. The wound is treated with an antiseptic, and if necessary, synthetic bone material is replanted. After this, stitches and a gum bandage are applied. After 10 days, the stitches can be removed. If all the requirements of the method are strictly followed, as well as the prescribed regimen during the rehabilitation period, recovery occurs quickly. The development of periodontitis stops.
Bone grafting
In severe periodontitis, there is a loss of bone tissue, which contributes to the loosening of teeth. In order to stop this process, bone grafting is used. The patient's own tissue, as well as artificial substitutes, can be used as a graft. In the first case, a section of bone can be taken from the chin, upper palate, or lower jaw. Since the patient’s own tissues are absolutely biocompatible, this method is the most effective, but requires two operations: tissue collection and transplantation.
Special bone substitutes do not have this disadvantage, so bone grafting in such cases is carried out in one stage. However, this method is characterized by a lower tissue survival rate, so it is not always possible to achieve the desired result with its help.
Plastic surgery of lip cords and frenulums
In the presence of pronounced strands of the mucous membrane, the risk of periodontal disease increases significantly. Massive folds that are fixed to the gingival papillae, when stretched, can displace them and lead to various problems. In order to prevent such conditions, band plasty is performed. Typically, the technique consists of excision of these folds and subsequent suturing of the resulting defect.
Lip frenuloplasty can be performed in the following cases:
- Pronounced tooth gap between the front incisors.
- Preparation for orthodontic treatment.
- Presence of gum recession.
- Before installing removable dentures.
- Incorrect sound pronunciation.
Surgical treatment can be performed in various ways. If the frenulum is very narrow, then it is cut transversely. If there is a wide frenulum, its excision is performed. In addition, individual sections can be moved to the desired position.
Among modern techniques, laser frenuloplasty is noted. The procedure is very quick, does not require stitches, has a short recovery period and rarely leads to complications.
After plastic surgery of the cords and labial frenulum, a period of rehabilitation begins. Typically, the patient is required to follow simple rules, which include careful oral hygiene and a certain diet. Typically, recovery takes about a week.
Indications for treatment with the Vector device
- Periodontitis of varying degrees.
- Periodontal disease (as determined by the doctor).
- Gingivitis, including in pregnant women.
- Prevention and treatment of peri-implantitis.
- Installed braces.
- Supportive treatment for periodontal diseases concomitant with systemic diseases (endocrine, cardiovascular pathologies).
- Planned hygienic oral care for the prevention of periodontal diseases.
- Sanitation of the oral cavity before dental treatment, implantation, in women - when planning pregnancy.
If Vector Fluid Abrasive with abrasive particles of silicon carbide is used instead of Vector Fluid Polish, the Vector device is used for minimally invasive preparation of carious cavities and treatment of artificial teeth.
Closing gum recessions
Closing gum recessions is carried out only by surgical methods, which involve moving donor flaps to the recession zone and plastic surgery of the existing defect. You can receive a transplant in several ways:
- Pedicled flap. In this case, the donor tissue is a nearby area of the mucous membrane. The technique is used in the presence of localized defects.
- Gingival flap. It is taken from the gum area, provided that the volume of tissue in the selected area is sufficient.
- A scrap from the sky. In this case, the donor fragment is taken from a specific area of the hard palate
To close recession zones, the method of directed tissue regeneration can be used. In this case, special membranes are used as donor tissue, which can be absorbable or non-absorbable. These membranes promote the migration of cells from natural tissues and subsequent regeneration of the damaged area.
This method does not require the formation of a donor wound, but is not suitable for all patients. To obtain a successful result, the membrane must be covered with a layer of mucous membrane, which will provide the necessary nutrition, which is not always possible. In addition, due to the long process of formation of new tissue, it is necessary to observe certain rules of oral hygiene, therefore this method requires the active and conscientious participation of the patient in the treatment process.
Alternative methods of performing the procedure
Removal of hard dental deposits in the pocket cavity can be done in various ways. A significant part of them can be classified as a closed type of operation, because their use does not involve any incisions in the gums.
Vacuum curettage in dentistry
The periodontal cavity is cleaned here with special curettes, which are connected to a vacuum suction device for separated particles from the treatment area. Fewer injuries and instant removal of tissue particles and plaque reduce the risk of complications and shorten the rehabilitation period.
Chemical
This technique uses various chemicals (particularly citric acid) to soften and then remove hard plaque particles. The solution has not only a cleansing and softening effect, but also an antiseptic, making it easier and with less damage to remove all excess from the gum pocket, while simultaneously disinfecting the cavity and reducing the likelihood of infection.
Ultrasonic
The method of destroying hard dental deposits using ultrasound requires the use of special equipment, for example, the Vector apparatus. Using ultrasound, as well as a water-air jet under pressure, it allows you to successfully remove hard plaque, although ordinary hand tools are also used for curettage.
Cryo method
The use of liquid nitrogen to remove various deposits and affected tissues is also practiced when treating periodontal pockets. Freezing also kills pathogens, reduces the risk of complications and makes the entire operation completely bloodless.
Laser
The most frequently asked question from patients is what is laser curettage of periodontal pockets? We answer: laser curettage is one of the most modern methods of cleaning gum pockets, its essence is that the laser beam heats the area of action to a high temperature, instantly burning out foreign inclusions and bacteria, while simultaneously closing the blood capillaries, preventing bleeding. This method causes less tissue trauma, does not require sutures, and shortens the recovery period.
Transplantation of a flap from the palate
Recession flaps are usually taken from the hard palate. In this case, the graft can consist only of connective tissue, or be epithelialized. The thickness of the flap depends on the tasks and the result that needs to be achieved. Direct closure of gingival recessions requires thick flaps, while restoration of visible gingival areas is carried out using thin and epithelialized fragments.
The graft is usually taken from the area of the hard palate, which borders the canines and premolars. In this case, it is necessary to retreat 2 mm from the edge of the gum. These rules allow you to avoid crossing the palatine artery and the development of bleeding. The thickness of the mucous membrane from the donor area should not be less than three millimeters, so probing is carried out first. After obtaining a flap, the defect is sutured
Cost of gum treatment with the Vector device
The cost of the procedure depends on the number of teeth being treated. The price list identifies the following areas for teeth (implants): segment, one jaw, oral cavity.
The duration of the procedure depends on the number of teeth being treated and the condition of the periodontium and takes from thirty minutes to two hours.
The greatest contribution to the cost of the procedure is made by: preparation for the procedure - 30 minutes; consumables , polishing fluid ; procedure - 30-120 minutes; instrument sterilization - 30 min. Therefore, the price difference between treating one tooth and the entire oral cavity is only 50%.
Below is the cost of the Vector procedure in Dental World dentistry.