Prerequisites for appointment
After tooth extraction, antibacterial drugs are not prescribed to all patients - only for serious indications. Amoxiclav after tooth extraction is often recommended for patients who have developed an acute purulent inflammatory process.
The prescribed therapy will help prevent the development of complications and stop further infection of tissues in the oral cavity. After surgical interventions, medication is prescribed without fail to prevent the development of an infectious process on the open wound surface.
For planned simple removal procedures, Amoxiclav is used when foci of caries are detected - as a means of preparation for the upcoming procedure. The main condition for this type of prevention is the absence of suppuration and inflammation.
Incorrectly grown teeth provoke a future inflammatory process in the gum tissue, which manipulation can lead to infection of the socket. The pharmacological agent is administered to the patient immediately before the medical procedure and after its completion.
The prescription of Amoxiclav in the postoperative period requires the presence of predisposing factors:
- prophylaxis to prevent the development of an abscess;
- complete suppression of the activity of pathogenic microorganisms;
- creating measures to prevent suppuration of the hole - after an extracted molar;
- protection of bone tissue health;
- a sharp drop in the functionality of the autoimmune system;
- traumatization of nearby tissues after extraction of a problematic tooth;
- inflammatory processes near the problem area;
- pathological abnormalities in the level of blood clotting;
- the appearance of a large hole.
Negative symptomatic manifestations provoke the formation of:
- sudden bursts of severe painful sensations;
- loss of appetite;
- a real threat of blood poisoning - up to the development of septic conditions.
Amoxiclav has valuable quality - its use is allowed at any age.
Allergic alveolitis
When compounds that cause a pathological reaction in the form of an allergy enter the human body, not only the respiratory tract and the mucous membrane of the eyes react - swelling and soreness of the dental alveoli with the subsequent formation of an inflammatory process can sometimes also be noted. Accordingly, all these changes can safely be called allergic alveolitis, because their pathogenesis is based on the same antigen-antibody reaction.
This type of pathology is manifested by constant aching pain, which intensifies significantly during food consumption. Quite rightly, allergic alveolitis is recognized as one of the “mildest” forms of this disease, because it is not accompanied by a pronounced clinical picture. Usually the patient's general condition is relatively satisfactory, there is no fever. Upon careful examination of the hole left after tooth extraction, one can note the almost complete absence or insufficient amount of a protective blood clot. Remnants of food are usually visible here. It may also be that allergic alveolitis forms after 2-3 days from the moment of tooth extraction. And if timely treatment is not started, the prognostically favorable form of the disease can lead to serious complications.
Dosage
The selection of the required amount of the drug is carried out on an individual basis and depends on the number of complications after the manipulation to remove problem teeth. The dentist prescribes the medication in optimal dosages to prevent the occurrence of negative reactions from the body and symptoms of overdose.
After complex surgical interventions involving large surgical fields, Amoxiclav 625 mg is prescribed for preventive purposes, one unit of the substance, up to two times a day. The drug is used after meals for five days.
With the development of an acute inflammatory process, the drug is recommended for use up to three times a day. The drug is used in the treatment of children of all ages:
- up to 10 years - in the form of suspensions;
- from 10 to 16 years - tablet form "Amoxiclav 375".
Individual dosage is calculated according to the child’s body weight, and not according to individual age groups.
Use during gestation and feeding
Any antibacterial agent affects the growth and development of the fetus - therefore, an antibiotic is prescribed during pregnancy if absolutely necessary, according to the decision of the attending dentist.
Changes in hormonal levels during pregnancy do not allow you to calculate the required dosage. Specialists use the drug in minimal quantities and in conditions where a woman’s health is at risk.
After removal of problematic molars, for women during lactation, dentists recommend the use of Amoxiclav in minimal doses, up to three times a day. If the mother has contraindications to the use of this substance, it is replaced with similar medications.
Are antibiotics needed after tooth implantation or extraction?
There are still many “blank spots” in modern Russian implantology and surgical dentistry.
Despite the fact that domestic dentistry is already catching up with the European level of implantology on many issues, there are some simple, in my opinion, issues that cause controversy and disagreement among Russian doctors.
One of them is the prescription of antibiotics after dental implantation or extraction.
In Europe and America there are clear indications when, in what cases and in what doses antibiotics should be prescribed. And no one doubts this. There are simply no other options other than the official protocol.
In Russia, to my surprise, antibiotics are prescribed at random after implantation or tooth extraction. This may depend on many factors: on what university the doctor studied at, in what region he works, whether he sees a doctor in a private or public clinic. That is, the prescription of antibiotics after implantation or tooth extraction may actually depend on the doctor’s mood. Or from his knowledge. And even more often, unfortunately, from lack of knowledge.
If you don’t believe me, ask any Russian dentist who places implants or removes teeth, in what cases does he prescribe antibiotics?
You will be very surprised, but in 90% of cases the answer will be the same: if it’s a mild case, then we don’t prescribe it, if it’s a complex case, then we prescribe it just in case.
If you continue to ask: how many days should you take antibiotics? The answers will surprise you even more with their differences.
By the way, this is why this article will be useful not only to patients, but also to many implantologists.
So in what cases do we still prescribe antibiotics? The answer is very simple. There are 5 groups of surgical interventions, each of which involves the use of certain dosages of antibiotics, and for a certain number of days.
In words and terms understandable not only for professional doctors, but also for ordinary patients, I will briefly talk about these 5 groups.
1 group
Involves removing teeth without infection. Installation of single implants without flap formation.
In such cases, we do not prescribe antibiotics at all.
2nd group
Tooth extraction multiple or traumatic tooth extraction. Installation of several implants with the formation of a flap. Augmentation of sockets (plantation of artificial bone tissue).
In this case, we prescribe 1 gram of Amoxycillin an hour before the procedure, and 500 mg (1 tablet) after taking it 6 hours later. One time.
3 group
Ridge augmentation with the presence of a membrane and the use of grafts, all except autogenous ones. I translate it into simple human language (for patients): working with bone tissue, including artificial, without transplanting bone from another place.
Multiple implants with the formation of a full flap. Multiple simultaneous implantation.
In such cases, we prescribe 1 gram of Amoxycillin an hour before the procedure, then 500 mg (1 tablet) 3 times a day for 3 days.
4 group
Ridge augmentation (autogenous bone). I translate for patients: this is a bone block transplant from one place to another. For example, from the chin or ilium to a place where there is not enough bone tissue for implantation. Sinus lifting (closed). This is work in the maxillary sinus, without open access to it. Multiple implantation, when 8–10 implants are installed simultaneously.
In this case, we prescribe 1 gram of Amoxycillin an hour before the procedure, then 500 mg (1 tablet) 3 times a day for 5 days.
5 group
Open sinus lift. This is an operation to plant artificial bone tissue in the maxillary sinus, during which the surgeon makes a “window” in the bone tissue, thereby opening the maxillary sinus.
1 hour before open sinus lift we prescribe 1.5 g of Aygmentin, then 875 mg 2 times a day for 5 days.
And another very simple but useful tip. It will help to significantly reduce the number of microorganisms before any operation.
Not only before implantation or tooth extraction, but also before any dental procedure, rinse your mouth with a 0.2% chlorhexidine solution.
This will surprise many, but even rinsing the mouth with plain water reduces the number of microorganisms by 60-70%.
And in the end, I simply have to remind you that each case of implantation is unique in its own way, and the human body very often behaves completely differently from what is written in the books. But I am sure that this information will greatly help many of you to avoid complications after implantation or tooth extraction.
Remember that it is easier to prevent any problem than to treat it later!
Prohibitions on use
The main range of contraindications for dental therapy includes a number of conditions:
- spontaneous allergic reactions to a subgroup of penicillins and their analogues - the condition is an absolute prohibition, in which a more suitable remedy is selected;
- with insufficient functionality of the liver and kidneys or disturbances in their performance;
- in case of lymphocytic leukemia – neoplasms in the area of red bone marrow (lymphatic sprout);
- for certain types of viral lesions - infectious mononucleosis.
Any non-standard reactions of the body of allergic etiology when using a medicinal product are the basis for a ban on use.
Negative reactions
When using the medicine, the body may experience adverse reactions:
Hematopoiesis department:
- anemic conditions;
- eosinophilia – increased number of eosinophils in laboratory parameters;
- thrombocytopenia – decreased platelet count;
- agranulocytosis – decrease in leukocyte counts;
- leukopenia - a decrease in leukocytes in the blood count.
Digestive department:
- increased gas formation;
- gastroduodenitis;
- dyspeptic disorders – diarrhea;
- nausea leading to vomiting;
- glossitis - inflammation of the tissues of the tongue;
- stomatitis;
- anorexia;
- enterocolitis is a simultaneous inflammatory process in the small and large intestines.
Nervous system:
- unreasonable anxiety;
- non-standard behavior;
- increased arousal;
- convulsive conditions;
- impaired clarity of consciousness;
- hyperactivity;
- periodic dizziness;
- sudden attacks of headache.
Skin:
- swelling;
- rashes on the dermis;
- hives;
- exfoliative dermatitis;
- epidermal necrolysis of toxic origin;
- erythema multiforme;
- acute toxic-allergic lesions - Stevens-Johnson syndrome.
Urinary department:
- hematuria;
- interstitial nephritis.
In some cases, superinfection may occur, including candidiasis. Negative reactions of the body due to the use of the drug are mild and temporary.
Exogenous alveolitis
A persistent febrile condition is characteristic; throughout the entire disease there is pronounced pallor of the skin. The patient's quality of life deteriorates significantly - he cannot eat properly, because it becomes very difficult to eat.
Lymphangitis and lymphadenitis are characteristic signs of exogenous alveolitis, because the infection quickly spreads to nearby areas. Upon visual examination, a gray coating and severe hyperemia are noted, and upon palpation the patient notes sharp pain.
Overdose
Accidental or intentional excess of the recommended volumes of the drug cannot cause death or serious life-threatening side effects.
The main symptomatic manifestations of overdose are:
- changes in water and electrolyte balance indicators;
- disturbances in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract - pain in the epigastric region, diarrhea and vomiting;
- development of crystalluria with a gradual transition to insufficient renal functionality;
- convulsive phenomena suggest the use of a pharmacological agent in increased dosages or in cases of impaired renal function.
An overdose requires contacting a medical facility for symptomatic drug therapy. If the drug was used less than four hours ago, the patient is prescribed gastric lavage and activated charcoal. In more serious cases, cleansing the body is carried out by hemodialysis.
Features of use
The use of medication for dental therapy is carried out after the appointment of the attending physician. The patient must read the instructions provided, paying attention to the following special instructions:
- Before first use, you must make sure that there are no allergic reactions to the components included in the drug. It is advisable to conduct a preliminary allergy test.
- The product is used in the formation of a bacterial type of infectious process caused by pathogenic microflora that is sensitive to the active ingredient. Amoxiclav has no effect on viral infections. Before therapy, it is necessary to carry out bacteriological culture to determine the type of pathogen and its resistance to the drug.
- If there is a lack of the required effectiveness of the drug within two days, then the drug is replaced with a similar substance or a change in treatment tactics is necessary.
- The medication is prescribed with extreme caution to persons with impaired renal or liver function, and at the same time, constant monitoring of their performance is carried out.
All recommended features must be taken into account when drawing up the necessary therapy regimen.
Post-extraction alveolitis
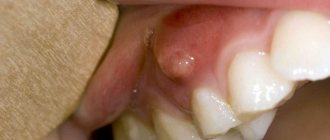
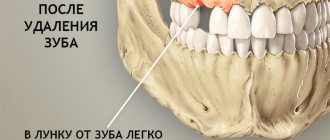
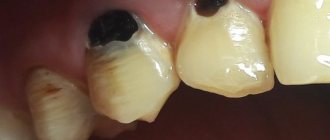
In this case, the name of the pathology indicates its direct origin - it is easy to guess that post-extraction alveolitis develops as a result of unsuccessful (complicated) tooth extraction. This variant of alveolitis involves inflammatory tissue damage not only to the socket itself, but also to the adjacent gum. The statistics of complications is impressive - even taking into account the potential of modern medicine, the incidence of post-extraction alveolitis is about 40% of cases, and most of them are associated with interventions performed on the lower molars.
The clinical picture of post-extraction alveolitis occurs 2-3 days after tooth extraction. Symptoms can be conditionally classified into two variants of manifestations - symptoms of general and local significance. Alveolitis necessarily has symptoms from both the first and second categories.
The first category includes:
- Low-grade or febrile fever.
- Lymphangitis and lymphadenitis (regional);
- Halitosis.
Manifestations related to the second category are:
- Local hyperemia and swelling.
- Lack of protective blood clot.
- The presence of a gray coating on the hole.
- Separation of pus.
- Local pain syndrome.
In this case, alveolitis treatment requires primarily symptomatic treatment.
An important point that must be taken into account when diagnosing post-extraction alveolitis - for the reason that the possibility of provoking the development of the disease by the remaining piece of tooth cannot be excluded, the patient must be referred for an x-ray. It may be that even if alveolitis develops, the symptoms of this disease do not indicate the presence of pathology for a certain period of time.
Many patients consider the occurrence of alveolitis to be solely the fault of the doctor, because there are articles that write that the socket can become inflamed as a result of improperly carried out preventive measures after tooth extraction. Yes, such cases happen, but not in the Academy Dent clinic - the use of modern techniques, coupled with the highest professionalism of our doctors, allows pain relief and removal without any consequences for the patient.
The worst option is when the tooth is not completely removed and some part of its root remains in the socket. This situation, without a doubt, is the fault of the doctor, because he was not convinced that the intervention was performed correctly and did not study the anatomy of the root system of the tooth using an x-ray. Severe purulent inflammation develops - body temperature rises, purulent discharge with an unpleasant odor is noted. The patient complains of a specific sensation of something sweet in the mouth - but in fact, the inflammatory process is to blame. Therefore, it is very important to ensure that after tooth extraction there are no foreign bodies left in the socket - in this case, their imperceptible resorption by cells of the immune system is a priori impossible.
The process in question, which occurs in one place, can easily inflame several adjacent holes, as a result of which eliminating the problem will become much more difficult. It will be necessary to drain the purulent lesion and use strong antibiotics administered orally. Alveolitis often requires surgical treatment, with dissection of the adjacent subcutaneous fat.
Requirements for the use of antibiotics
Antibacterial drugs should be used in strict accordance with the dentist's prescriptions. Medicines lose their effectiveness with the following deviations:
- with independent dosage changes;
- missing time to take medications;
- spontaneous change in the entire treatment regimen.
Specialists require all patients to know the rules for taking Amoxiclav.
Duration of use
No change in accuracy and time of application - the recommended intermediate time must be maintained between two applications. Precise timing of use will allow you to maintain the concentration of the active component at the proper level:
- in the case of a three-time daily appointment, the interval is at least eight hours;
- with a double dose, treatment is carried out every 12 hours.
Antibiotics should be taken at the same hours, regardless of the form of manufacture.
Duration of therapeutic effect - the average duration of treatment is one calendar week; if necessary, the process can be extended to two weeks. The treating specialist is responsible for adjusting the timing of the appointment.
Changing dosage
Prohibition on independent changes in dosage - individual patients reduce the prescribed volume of medication spontaneously. The main goal of the change is to take care of your own health. In reality, these actions can lead to the ineffectiveness of the drug and the emergence of microflora resistance to the active ingredient.
An unauthorized increase in dosage often provokes the formation of overdoses and the development of severe side effects.
Discontinuation
Discontinuation of treatment – it is prohibited to stop prescribed therapy in the middle of the process. Some patients, feeling better, believe that the treatment can be considered complete. Experts recommend continuing therapy for another three days from the moment your health returns to its previous limits.
Dentists ask patients to report the lack of effectiveness of the treatment if no visible improvements occur within three days. Low efficiency indicates resistance of pathogenic microflora and the need to replace the drug.
Admission rules
Rules for administration - the instructions supplied with the medication clearly state the requirement for use - before, during or after eating. Doctors advise patients to drink the pharmacological drug with clean drinking water, without gases.
Using any other drinks may render the medicine ineffective or reduce its effectiveness. It is forbidden to take medications with juices, coffee, tea, fermented milk and dairy products (unless specifically stated in the instructions).
Diet food
Dietary nutrition - all antibacterial agents are a serious burden for the patient’s body. Their main active components can have a depressing effect on the functionality of the digestive tract. Experts advise following the required diet during the treatment period.
When using Amoxiclav, you need to exclude from the daily menu:
- fried;
- fat;
- canned food;
- sour fruits;
- alcoholic and low-alcohol drinks.
You need to include in your diet:
- fresh vegetables;
- sweet fruits;
- clean drinking water.
On the nuances of diet, the dentist will provide comprehensive information suitable for each individual case.
Treatment of the intestinal tract
Additional treatment of the intestinal tract - antibiotic therapy involuntarily leads to suppression of the activity of standard intestinal microflora. Changes in the digestive tract can provoke the development of the following symptomatic abnormalities:
- bloating;
- constant heartburn;
- dyspeptic disorders - constipation and diarrhea;
- painful sensations in the gastrointestinal tract.
To prevent further death of microflora and return it to its original values, doctors recommend taking special medications and fermented milk products. Therapy is carried out during breaks between courses of antibiotic treatment.
Ignoring supportive treatment can provoke the development of pathologies of the stomach and intestines.
Important nuances - at the time of prescribing any type of antibacterial medication, the patient must pay attention and take it seriously:
- use in other pathological processes;
- prohibitions on use;
- negative responses of the body;
- permission for use with age restrictions.
Without prior consultation with a dentist, antibiotic therapy is strictly prohibited for a certain category of people:
- when the body is weakened;
- in childhood;
- during pregnancy and breastfeeding.
Treatment of alveolitis
Treatment of alveolitis, regardless of its etiology, is a very difficult task, the solution of which clearly requires professional medical care. In no case should you act independently and at home, because with an illiterate approach there is a high chance of causing significant harm.
Conditionally, the treatment of alveolitis can be classified into stages - depending on how timely the alveolitis was diagnosed, the treatment and general management tactics are determined.
Early treatment
If alveolitis was diagnosed in the initial stages, then to get rid of the disease it is sufficient to perform the following measures:
- The implementation of drug anesthesia is primarily because, despite its relative simplicity, the process of getting rid of alveolitis is quite painful.
- Treatment of the hole in which there is an inflammatory process is washed with an antiseptic solution.
- Removing necrotic debris from the socket.
- Repeated treatment of the hole with an antiseptic followed by drying with gauze.
- Placement on top of fabric soaked in antiseptic and drugs that provide an anesthetic effect.
- Apply applications with antiseptics daily (for a week) in order to eliminate the possibility of a relapse of the inflammatory reaction.
Possible interaction
Simultaneous use of Amoxiclav with other bactericidal antibiotics increases the effectiveness of the main drug.
A decrease in the desired result is observed when using an antibiotic with certain medications:
- macrolides;
- tetracyclines;
- sulfonamides.
Sharing the medicine with hormonal contraceptives weakens the functionality of the latter.
When using the drug and alcoholic (low-alcohol) drinks, a decrease in the effectiveness of the drug and a possible negative effect on the liver are observed.
Combined treatment with anticoagulants can increase prothrombin time - if necessary, extreme caution should be used.
Specifics of flux therapy
Self-exposure to the affected area with antibiotics does not make logical sense - in one case out of a hundred, the patient correctly guesses the required drug. When visiting a medical facility, the patient undergoes a full diagnostic examination, which allows one to determine the type of pathogen that has penetrated and its level of resistance to medications.
During the examination, the dentist will accurately determine the problem tooth that caused the formation of the inflammatory process, the need for sanitation of the oral cavity (treatment of carious surfaces) and only after all the procedures will he prescribe a treatment regimen.
Purulent lesions that form near the apex of the tooth root are most often caused by staphylococcal or streptococcal infections. Even without carrying out the necessary diagnostics, experienced specialists will recommend that the patient adhere to the following rules:
- the total time of therapeutic effect cannot exceed two weeks, a smaller number of days is determined by the severity of the pathological process;
- flux detected in the initial stages can be treated conservatively with medications;
- pathology recorded in advanced stages requires surgical intervention.
The presence of constant toothache indicates the development of pathological abnormalities that cannot be cured on your own. In any scenario, a visit to a dentist will take place. Experts recommend avoiding self-medication with the “best” antibiotics recommended by neighbors and work colleagues.
The drug Amoxiclav is one of the most commonly used drugs in the practical work of surgical dentists. The positive quality of the medication is its tolerability and the minimum number of adverse reactions of the body.
Use during pregnancy and lactation is not prohibited by the manufacturer; there is only a limitation on permissible dosages. If the requirements of the instructions attached to the pharmacological substance and the advice of the attending physician are correctly followed, the drug will act in a short time. The high effectiveness of the drug allows it to be considered one of the main drugs for the treatment of inflammatory and other pathological processes in the oral cavity.
Sources used:
- Medicines in dentistry. Directory / L.N. Maksimovskaya, P.I. Roshchina. — M.: Medicine
- Rational pharmacotherapy in dentistry. — M.: Litterra
- National Library of Medicine (USA)
- The use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for the treatment of dental diseases / S.T. Sokhov et al. - M.: MEDpress-inform, 2011.
Fibrosing alveolitis
This type of pathology is notable for the fact that connective tissue develops to replace the necrotic residue of the hole left after tooth extraction. In principle, many dentists propose to consider fibrosing alveolitis not as a separate type of this nosology, but as one of the stages of its course, which is characterized by a slight decrease in the intensity of the manifestations of the inflammatory reaction and partial stabilization of the general condition of the patient. If you take a closer look at the condition of the oral cavity, you will notice a slight proliferation of soft tissues adjacent to the hole in which the pathological process occurs. The formation of a gap between the soft tissues and the hard, bone wall is also typical in this situation.