Frenuloplasty of the frenulum of the tongue and lips
Skip to main content
- home
- Specialists
- Price-list
- Stock
- Contacts Ask a question
- Vacancies
| MOSCOW ST. CHASOVAYA, no. 24 09:00 - 20:00, Mon-Fri 09:00 - 18:00, Sat-Sun 8 8 | MOSCOW ST. MARIA ULYANOVA, 8 09:00 - 20:00, Mon-Fri 09:00 - 18:00, Sat-Sun 8 | DUTY NUMBER 08:00 - 20:00, DAILY 8 (926) 617-16-59 |
Clinic opening hours during the New Year holidays
Holidays: December 31, January 1, 2, 3, 4, 7 and 8
Open: January 5, 6 and 9
Happy New Year!)))
Features of frenuloplasty
Plastic surgery of the frenulum of the penis is aimed at restoring the normal functioning of the organ. Performed for medical or reconstructive plastic purposes. During the surgical procedure, the doctor makes a transverse incision and then sutures the edges of the wound. The procedure lasts approximately 30 minutes and is often performed under local anesthesia. If the pathology is accompanied by phimosis, flesh circumcision is performed in parallel with frenuloplasty.
If sexual intercourse is accompanied by discomfort or unpleasant sensations in the frenulum area, a consultation with a urologist is recommended. Don't wait for the rupture to happen - it's painful and dangerous!
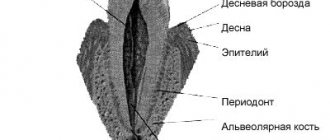
Symptoms of improper attachment of the frenulum
You can understand that there are problems by the following signs:
- The tip of the tongue moves down and takes a flat shape. Normally, it should be sharp and stay straight.
- There is difficulty pronouncing vowel sounds and a lisp.
- Infants have difficulty taking milk due to impaired sucking and swallowing function.
- The endings of words are swallowed.
- Slow speech development in children.
- Malocclusion.
- Periodontal diseases.
Indications and contraindications for frenuloplasty
Indications for frenulotomy may include:
- Curvature of the erect organ. During an erection, the head bends downwards.
- Difficulty retracting the skin fold, an unpleasant feeling of tightness.
- Painful frictions.
- Microtears of the frenulum, which are accompanied by bleeding.
- Phimosis, paraphimosis.
- Early ejaculation in men can also be associated with a short frenulum.
60% of men with the problem of early ejaculation note excessive tension on the frenulum during sex. Frenuloplasty solves this problem.
The manipulation is not classified as complex, but requires sophistication and skill from the surgeon - many receptors are concentrated in this area.
Consequences of pathology
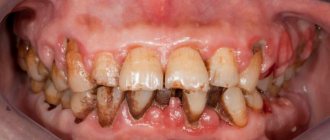
The formation of a short frenulum is associated with various factors. In almost all cases, this is a congenital pathology detected in early childhood, but some parents do not attach importance to the problem, as a result of which various complications arise.
First of all, babies with a short frenulum of the tongue find it difficult to suck. They begin to smack their lips and are unable to grasp the breast or pacifier. If the problem is not corrected within the first few months, the child may have trouble pronouncing certain sounds in the future, such as “r”, “l”, or “u”. In addition, a short frenulum contributes to malocclusion of permanent teeth.
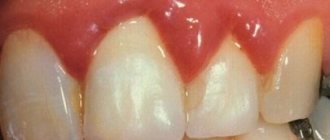
It is also important to note that with this pathology the blood circulation process in the periodontium is disrupted. This may cause him to become ill. Also, problems such as deposition of stones on teeth, trauma to the mucous membrane, displacement or subsidence of the gingival margin cannot be excluded. A short frenulum of the lip can provoke displacement of teeth with the formation of trema and diastemas. In order to prevent this, it is important to perform frenuloplasty . The operation allows you to change the length of the frenulum that attaches the lip or tongue to the periodontium. In parallel, vestibuloplasty is sometimes prescribed. It allows dentists to increase the height of the gums to reduce tension.
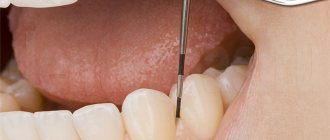
Progress of the operation
Plastic surgery for truncation of the frenulum of the penis takes place without hospitalization. The procedure takes half an hour, and after 1-2 hours the man can return home.
If the operation is performed under local anesthesia, the doctor will give a pain-relieving injection under the frenulum and wait until the target area is completely numb. In a classic frenulotomy, the doctor performs a transverse dissection with a scalpel and stretches the edges into a diamond shape. After adjusting the tension, the specialist applies sutures. If there are scars or tissue growths, they are also removed.
Laser plastic surgery is characterized by the absence of blood and an almost zero chance of infection. The tissues are burned out with a laser, and the vessels are sealed. There are no scars left.
Modern dentists more often use the following techniques:
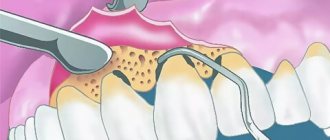
- The Glickman method involves fixing tissue with a clamp deep in the oral cavity. Next, using instruments, the frenulum is excised into the shape of an angle. In this case, the incision is made first from the side of the lip, and then from the side of the teeth. After this, sutures are applied and treatment is carried out.
- Vinogradova’s technique consists of creating two incisions from the transitional fold to the periodontal margin. The flap peels off and the edges of the wound tighten. After this, the triangle is sewn to the wound.
In addition, there are features of the excision itself. The shape of the cut can be Z or Y shaped. In the first case, an incision is created in the middle of the frenulum. Next, two cuts are made from the edge of the first in different directions. After this, the formed flaps are laid so that the first cut becomes horizontal. Next, sutures are applied, with the obligatory capture of bone tissue for reliable fixation.
By creating a Y-shaped cut, a diamond shape is formed. Triangles of mucous membrane are placed in the submucosal layer using instruments, after which the wound is sutured with tissue fixation to the periosteum.
After surgery, it is important to maintain oral hygiene. When excision of the frenulum in newborn babies, it is enough to treat the wound at the dentist with an antiseptic solution, after which it is allowed to feed the child with breast milk, but not formula. Older patients should refrain from eating for two hours. As a rule, the wound heals quickly and does not cause any discomfort.
Frenuloplasty according to Limberg (Z-shaped)
Technique of operation. After anesthesia (Fig. 85), a vertical incision is made in the middle of the frenulum. Two oblique cuts are made from opposite ends in different directions from the first cut at an angle of 60-85° (Fig. 86). The formed triangular flaps are mobilized (Fig. 87) and fixed so that the central incision is horizontal.
An important point is the preparation of the receiving bed, since simply suturing the edges of the incisions together within the mucous membrane will only lead to
Rice. 89. Condition on the 7th day after surgery
Rice. 90. 14th day after the intervention
also tightly, but without fixing the flaps to the periosteum (Fig. 89, 90).
Vestibuloplasty
- manipulation aimed at increasing the width of the attached gum in order to eliminate mechanical trauma to the marginal periodontium by muscle cords of the muscles of the perioral area (lip, chin, cheek, lingual and facial muscles) and, as a result of this, to prevent the development of destructive processes in the periodontium.
One of the main indications is to prevent gum recession or stop their progression.
This intervention is also carried out as the first stage before flap operations, if the bottom of the pockets is located below the transitional fold.
Quite often, vestibuloplasty is performed for orthopedic indications - to improve the fixation of removable dentures, and in some cases - before orthodontic treatment.
The main disadvantage of the operation is the formation of a postoperative scar. This causes a rather unpleasant feeling of tightness for 3-9 months. (depending on the individual speed of scar resorption).
To avoid or minimize this, the patient should be carefully questioned before surgery to see if he has a tendency to form rough and severe postoperative or post-traumatic scars. This feature may in some cases be a contraindication to vestibuloplasty or may require the use of significant modifications of accepted techniques.
Passing and less significant deficiencies include sensory disturbances of varying duration and severity in the area of the intervention performed.
The most common techniques are: vestibuloplasty according to Edlan-Meicher and according to Clark. Our department has developed and patented tunnel vestibuloplasty, which differs from basic techniques in being less traumatic, virtually absent postoperative pain, and therefore more comfortable for patients, as well as a higher healing rate.
Vestibuloplasty according to Edlan-Meicher [1963]
Technique of operation. After infiltration anesthesia (Fig. 91) - preferably using the hydropreparation method for easier subsequent peeling of the mucous flap - a scalpel is used to make an incision in the mucous membrane parallel to the bend of the jaw (Fig. 92), retreating from the mucogingival border by 10-12 mm in the area from canine to canine and 7-10 mm in the area of premolars and molars (although in this area you should strictly focus on the exit point of the neurovascular bundle).
| Rice. 91. Condition of the vestibule of the oral cavity after infiltration anesthesia |
Using scissors, bluntly peel off the mucous flap from the incision line to the jaw (Fig. 93).
Rice. 92. Making an incision on the lip to form a mucous flap
Rice. 93. Peeling of the mucous flap from the submucosal tissue
Rice. 94. Displacement of submucosal tissues along the periosteum to the depth of the formed vestibule
Rice. 95. Removing muscle fibers with scissors
After this, the submucosal tissues (muscles, tendons) are moved along the periosteum to a depth of 10 mm in the frontal section and 6-7 mm in the lateral sections (Fig. 94). On the lower jaw, you should work extremely carefully in the area of the chin openings. A very important point is the removal of remaining muscle and fibrous fibers from the wound surfaces of the periosteum and mucous flap, since their presence usually leads to recurrence of the strands (Fig. 95).
The detached mucous flap is fixed to the periosteum with catgut sutures in the depths of the formed vestibule (Fig. 96).
Rice. 96. The mucous flap is fixed to the fixed periosteum with sutures
A protective bandage is applied to the remaining wound defect (Fig. 97). Previously, for this purpose, an iodoform turunda, a gauze swab impregnated with keratoplasty preparations, etc. were applied to the wound. Currently, the absolute priority remains with the Diplendent film with lidocaine and chlorhexidine: firstly, it reliably closes the wound surface until a protective fibrin film is formed; secondly, it eliminates pain sensitivity and prevents infection. As a result, all this significantly facilitates the patient’s condition in the postoperative period (Fig. 98).
Rice. 97. Condition of tissues on the 1st day after surgery
Rice. 98. Condition of tissues on the 14th day after surgery
The initial area of the wound defect is about 8-12 cm2. The healing period with this technique is 12-14 days.
Vestibuloplasty according to Clark [1976]
It should be noted right away that this technique is advisable to use mainly on the upper jaw.
Technique of operation. After anesthesia (Fig. 99), an incision is made with a scalpel along the transitional fold to the depth of the mucous membrane (Fig. 100).
Rice. 99. Condition of the vestibule before surgery. Positive sign of ischemia when retracting the lip
Using scissors, peel off the mucous flap from the incision line to the lip by approximately 10 mm (Fig. 101).
The complex of submucosal tissues - muscles, tendons - in the same way as according to the Edlan-Meicher method, is moved along the periosteum to a depth of 10 mm in the frontal section and 6-7 mm in the lateral sections (Fig. 102), and single fibers of the cords are also removed and muscles.
Rice. 100. After anesthesia, an incision is made along the transitional fold to the depth of the mucous membrane without affecting the periosteum
Rice. 101. Mobilization of the mucous flap with scissors to prevent narrowing of the red border of the lips
Rice. 102. Moving a complex of submucosal tissues along the periosteum to a new depth with a raspatory
Rice. 103. Fixation of the mucous flap to the periosteum with catgut sutures in the depths of the vestibule
The mucous flap is fixed to the periosteum with catgut sutures in the depths of the formed vestibule. In this case, a fairly extensive wound defect remains on the alveolar process (Fig. 103), which is covered with a protective bandage (Fig. 104), currently with a diplene film, as in the previous technique.
Rice. 104. Applying a protective film “Diplen-Denta” to the wound surface
The healing time with this technique is also about 14 days (Fig. 105 and 106). The wound defect is about 8-12 cm2. The operation is optimal for the upper jaw due to the fact that in the lower jaw powerful muscles and tendons can often subsequently significantly neutralize the initially obtained results.