Causes Types of prevention Hygiene Treatment in the stain stage How to avoid?
Caries is damage to hard dental tissues with the formation of cavity defects. First, the enamel is destroyed, then areas of dentin, pulp, periosteum and bone. It is the most common dental disease in the world and the leading cause of tooth loss. Comprehensive prevention of dental caries increases the resistance of the enamel layer to various cariogenic factors and prevents destruction of tooth structures.
Causes of the disease
The leading cause of caries is the activity of oral bacteria. The normal microflora of the mouth consists of many microorganisms. Among them there is a group of cariogenic bacteria that negatively affect the enamel. In the absence of factors that weaken the body’s defense response, the number of opportunistic microorganisms does not exceed the norm and the disease does not develop. But if there are too many bacteria, the organic acid they produce begins to gradually dissolve areas of the enamel layer. Primary prevention of caries is aimed at eliminating the causes and conditions that contribute to its occurrence.
The following factors contribute to the development of the carious process:
- disorders of mineral metabolism in the body;
- changes in the composition of saliva (increased viscosity);
- abnormal bite;
- crowded teeth;
- poor oral hygiene;
- addiction to sweet, sticky, viscous foods;
- cracks, chips of enamel;
- heredity;
- deficiency of fluorine, calcium, phosphorus in drinking water and food;
- reduced immunity.
The causes of caries are different, but the main mechanism of development is the same - lack or lack of oral hygiene. Primary prevention of dental diseases begins with regular removal of bacterial plaque, which creates a favorable environment for the proliferation of cariogenic microorganisms. This differs from secondary prevention, which consists of treating the disease and its complications.
Cost of treatment
| Inspection, general recommendations | For free |
| Anesthesia | |
| Appliqué | 200 |
| Injection | 550 |
| X-ray diagnostics (Visiograph “Satelek” Germany) | |
| Dental image without printing on a printer | 300 |
| Panoramic shot | 1000 |
| Dental filling (1-2 surfaces) | |
| Light-curing filling “Charisma” (Germany) | 2800 |
| Light-curing filling “Filtek” (USA) | 3970 |
| Restoration and cosmetic restoration of teeth (3 or more surfaces) | |
| Light-curing filling “Charisma” (Germany) | 3160 |
| Light-curing filling “Filtek” (USA) | 4260 |
| Veneering of anterior teeth | 6550 |
Payment by installments / Tax deduction
all prices
How to avoid caries?
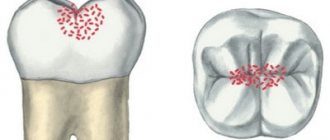
Depending on the depth of damage to hard tissues, there are 3 stages of caries - initial (spot stage), medium, deep. The rate of destruction of dental structures varies. In adults, the disease is predominantly sluggish and chronic. Children are more often diagnosed with an acute form of the disease with rapid destruction of dental structures. Inattention to the condition of teeth leads to progression of the disease. A carious lesion from the spot stage very quickly passes into the middle form, when dentin is destroyed and a visually noticeable defect is formed - a carious cavity.
How to avoid caries? Simple methods of primary prevention will help with this, most relevant when there is no visible damage to dental tissues.
Effect of fluoride preparations
The effectiveness of fluoride-containing drugs in strengthening tooth enamel and fighting caries is due to three facts:
- Fluoride compounds actively interact with dental tissues, significantly reduce the permeability of enamel, which blocks access to bacteria
- Fluoride helps reduce the growth of bacteria and pathogenic microflora
- Fluoride is involved in the formation of teeth and increased resistance to caries
The stronger the tooth enamel, the lower the risk of the appearance and development of caries, which is why it is so important to replenish the lack of fluoride. However, it is worth remembering that an excess of the element leads to fluorosis (the appearance of white spots on the teeth). Therefore, before using medications, you should consult your dentist regarding the duration of prophylaxis and the type of medication.
Types of prevention
Preventive measures are divided into primary and secondary. Primary prevention of caries is measures taken to prevent the disease, eliminate all provoking factors and causes of its development. It can be endogenous (general) and exogenous (local). The goal of the secondary set of preventive measures is to diagnose the disease at an early stage and prevent relapse.
Exogenous methods
Exogenous prevention of caries development includes methods that increase the resistance of the enamel layer to various cariogenic factors:
- Thorough
oral hygiene - Fluoridation
- the use of pastes, gels, solutions containing fluorine, calcium, phosphorus. Applications, physiotherapeutic procedures with remineralizing, fluoride compounds. Toothpaste for the prevention of caries, in addition to hygienic cleaning, provides additional mineralization of the enamel, increasing its protection, reducing the risk of disease. - Regular prof.
examinations - even in the absence of visible signs of carious lesions, you need to undergo a dental examination twice a year. This will help detect the problem at an early stage and quickly eliminate it without resorting to complex treatment or drastic measures. - Professional hygiene
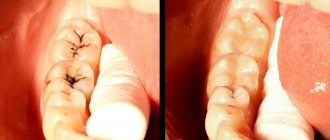
– removal of dental plaque (plaque, stone) in a dental office. - Sealing fissures
with polymer compounds.
Molars and premolars of both jaws are more susceptible to carious lesions, with the lesion predominantly localized on the chewing surface (in fissures, blind foramina, folds). Obturation (sealing) of fissures and other anatomical recesses of the tooth with adhesive materials creates a physical barrier that prevents the penetration of pathogenic microorganisms and organic acids that destroy dental structures into the retention areas of the enamel. The method is aimed at preventing caries of temporary and permanent teeth. The procedure is painless, the effect lasts 3-5 years
.
Endogenous methods
Endogenous prevention of caries in adults can be medicinal (medicinal) and non-medicinal:
- Non-drug measures
involve dietary correction and a healthy lifestyle. Dental health is harmed by smoking, constant consumption of sweets, baked goods, and alcohol. It is recommended to give up bad habits and replace sweets and simple carbohydrates with berries and fruits. The diet should be balanced in the content of proteins, fats, carbohydrates, vitamins, essential minerals, and trace elements. - Drug prevention
includes taking fluoride-containing drugs, vitamin complexes, and nutritional supplements in age-specific dosages. The dentist selects medications for the prevention of caries individually, based on the condition of the teeth and general health.
Comprehensive prevention of dental caries includes a balanced diet, careful hygiene, and regular dental examinations. Even if a person brushes his teeth diligently, but abuses smoking or cannot go a day without sweets, he creates favorable conditions for the proliferation of cariogenic bacteria. Dental health needs to be taken care of as a whole. Can tooth decay be cured with toothpaste? No! But it is necessary to use it to prevent disease.
Prevention of caries of primary teeth in young children
You should take care of your baby’s dental health from a very early age, namely from the 5th week of your pregnancy. A method of antenatal prevention has been developed especially for expectant mothers and the following are recommended:
- a complete diet for a pregnant woman, including foods high in calcium and phosphorus - milk, cottage cheese, fish and seafood;
- taking vitamin preparations as prescribed by a doctor;
- sanitation of the oral cavity in the second trimester of pregnancy, timely elimination of foci of carious infection.
How to brush your baby's first teeth.
When the first teeth appear at the age of 5-7 months, it is necessary to clean the child’s oral cavity daily using rubber finger brushes. Hygienic procedures using toothpaste are carried out starting from 1.5-2 years.
Choosing a toothpaste
The first toothpaste should be fluoride-free, since young children swallow up to 30% of the product due to lack of teeth brushing skills, which threatens the development of fluorosis (damage to tooth enamel as a result of excess fluoride intake). Your dentist will give you more detailed advice after examining your baby’s teeth.
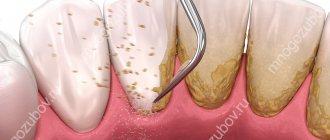
Professional hygiene
Modern methods of preventing dental caries involve in-office hygienic cleaning twice a year. Professional hygiene is aimed at removing bacterial plaque and mineralized formations (plaques, stones) from the supragingival and subgingival parts of the tooth. Hygienic cleaning includes the following steps:
- Removal of hard and soft deposits using the AIR-FLOW method or ultrasonic scaler.
- Polishing the surface of the teeth with an abrasive paste.
- Protection of enamel with fluorine varnish.
Hygienic procedures are painless and carried out quickly. Another plus is that the dentist gets the opportunity to accurately assess the condition of the oral cavity and detect pathology at the initial stage. Each stage can be carried out as an independent procedure. But it is a complete hygiene complex that will ensure effective prevention of diseases of the teeth and gums.
How to brush your teeth correctly?
It is impossible to thoroughly clean the entire surface of the teeth if the movements are directed only up and down or to the sides. You will also need to make diagonal or circular movements. It is desirable that the long bristles pick up plaque from under the gums. It is recommended to hold the brush at an angle of 45°C.
But all these rules have to be broken if brushing leads to bleeding gums. For those who have this predisposition, it is advisable to spend more time rinsing the mouth and use the brush as carefully as possible. Rinse aids must be antibacterial.
In general, it can be noted that in addition to good and constant oral care, it is important to see a dentist purely for preventive purposes, as well as for professional procedures that help maintain dental health.
Treatment methods for caries in the spot stage
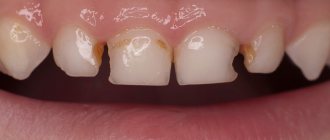
The appearance of a matte white smooth spot on the enamel is the first sign of a carious process. Such a stain means that the enamel in this place is demineralized and is more susceptible to destruction. Qualified therapy includes the following:
- professional hygiene;
- remineralization therapy, which uses drugs for the prevention of caries containing fluoride and calcium;
- regular dental examinations.
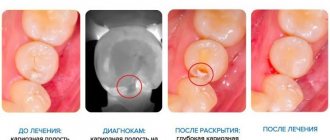
One of the latest innovations in drill-free treatment is Icon technology. After pre-treatment, a special infiltrate is applied to the affected area of enamel. The material penetrates deeply into the enamel structure, filling the defect. Excess material is removed, and the treated area is polymerized with a UV lamp. The defect is sealed, the carious process stops.
If the stain has reached the stage of pigmentation and a cavity defect has appeared on the enamel, then the affected tooth will require preparation followed by filling. The dentist selects the treatment method according to the clinical picture.
Preventive examinations with a dentist
Like any disease, caries is better, easier and cheaper to treat at the very initial stage. The initial stages of caries cannot always be diagnosed by a non-specialist: for example, white (or chalky) spots, which indicate the beginning of the carious process, are not always clearly visible, may be in places difficult to see, and may be covered with a layer of plaque. Regular preventive examination by a dentist, which is recommended once every six months, will help you begin timely treatment and get rid of unpleasant, often painful and expensive procedures in the future, and will help you maintain healthy teeth for a long time.