Basics of periodontal disease prevention
Basics of periodontal disease prevention
Primary prevention of periodontal diseases involves the following measures:
· rational and proper feeding of the child and his subsequent nutrition;
· training of the masticatory apparatus for the purpose of normal periodontal formation (compensation for insufficient chewing load);
· timely orthodontic treatment using multifunctional therapy (according to indications);
· training in the basics of rules and methods of individual oral hygiene;
· elimination of anomalies in the attachment of cords and frenulums of the lips, tongue, correction of the small vestibule of the oral cavity;
· maintaining the oral cavity in a sanitized condition;
· selective grinding of teeth to eliminate traumatic occlusion;
· timely and comprehensive orthopedic treatment.
Secondary prevention of periodontal diseases consists of treating early signs of emerging pathology of periodontal tissues in order to prevent their progression and the development of more severe conditions, namely:
· in eliminating local traumatic factors (tartar, overhanging edges of fillings, poor-quality dentures, malocclusions, etc.);
· improving methods of individual oral hygiene, monitoring the quality of its implementation during repeated visits to the doctor by determining digital indicators of hygiene indices;
· eliminating the precursors of diseases and treating their initial forms.
Tertiary prevention of periodontal diseases consists of complex treatment (conservative, surgical and orthopedic) aimed at relieving pathological conditions in periodontal tissues, preventing complications and restoring the physiological function of the periodontium and periodontium to the extent possible, which helps prevent their further destruction, the formation of periodontal pockets, resorption alveolar process and transforms an acute condition into a chronic, stabilized process [2, 3].
The main measures to prevent periodontal diseases include:
· elimination of pathogenic and conditionally pathogenic microflora;
· fight against plaque formation processes;
· elimination of oral dysbacteriosis;
· thorough and regular individual oral hygiene;
· sanitation of the oral cavity;
· sanitation of the gastrointestinal tract;
· elimination of factors that interfere with the normal functioning of the salivary glands and the performance of its functions by saliva, if necessary, the use of saliva substitutes;
· combating bad habits: smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, etc.;
· restoration of mineral balance and salt metabolism in general;
· elimination of local traumatic factors;
· elimination of anomalies in the attachment of cords and frenulums through surgical intervention;
· strengthening and maintaining general immunity by hardening the body and a healthy lifestyle;
· restoration of local immunity of the oral cavity by eliminating the causes causing disruption of its function;
· replenishment of deficiencies of vitamins, micro- and macroelements through their additional introduction into the body;
· the right combination of food products, leading to their proper absorption and replenishment of the lack of nutritional components;
· complete exclusion of sugars from intermediate snacks and reducing their amount during main meals.
Not missing the time for the most effective impact on the pathological process is the most important condition for any preventive and therapeutic measures.
Of great importance in the prevention of periodontal diseases, as well as other dental diseases, is the patient’s commitment to preventive and therapeutic measures. Fear of treatment, irregular visits to the doctor, failure to show up for follow-up visits, treatment only for acute pain, lack of a permanent attending dentist, ignorance of dental health - these are the reasons that lead to loss of time, complications of treatment and worsening of the disease.
Do not underestimate the negative role of stress factors in the development of both somatic and dental diseases. Each of us needs to strive to minimize the number of stressful situations, reduce the impact of stress on the body, maintain a work-rest schedule, alternate periods of intense work with periods of relaxation, giving the body the opportunity to rest and readjust.
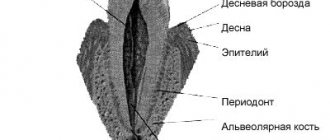
Individual oral hygiene as a method of preventing periodontal diseases should be given special attention. It is known that the main etiopathogenetic factor of inflammatory periodontal diseases are pathogenic and conditionally pathogenic microorganisms of dental plaque, capable of forming biofilms. They can also support and provoke the further development of many chronic general somatic diseases, and the risk of occurrence, development and further progression of inflammatory processes in the oral cavity and general somatic diseases directly correlates with the degree of microbial contamination of the oral cavity. That is why dentists attach great importance to the quality of hygiene procedures performed by the patient and the individual selection of personal oral hygiene products, their effectiveness and safety. Modern therapeutic and preventive oral hygiene products (toothpastes, rinses, balms, gels for gums), with proper selection and complex use, can have a pronounced anti-plaque, antiseptic, anti-inflammatory effect, and reduce gum bleeding due to the active components included in their composition.
In case of severe periodontal diseases, hygienic measures alone are no longer enough - they must be combined with complex treatment: conservative, surgical and orthopedic. However, without high-quality oral hygiene, any therapeutic measures and manipulations will be ineffective.
The above basic methods, methods and factors of preventive influence on the body as a whole, as well as periodontal organs and tissues, clearly demonstrate that the prevention of periodontal diseases is a complex task, the solution of which requires conditions of both local and general nature, including social issues and problems modern man.
Dentist-therapist (Head of RN No. 1) V.E. Gasyuk
Regular visits to the dentist as periodontal prevention
1. Examination of the oral cavity.
Even if you don’t have dental problems, you should visit the dentist at least once every six months. In this case, during the examination, the doctor can detect the earliest symptoms of pathology of teeth and gums, see overhanging and chipped fillings, determine errors in crowns and bridges, and assess the presence of tartar. The dentist may suggest a session of fissure sealing or tooth remineralization
2. Cleaning from tartar.
When visiting the dentist, you should periodically brush your teeth to remove tartar. In modern clinics, teeth are cleaned quickly and painlessly using ultrasound, so there is no need to be afraid of this procedure. After cleaning teeth from stones, doctors polish the teeth so that plaque does not linger on their surface.
3. Timely treatment by an orthodontist and orthopedist.
If the patient has an incorrect bite, then it is necessary to correct it, since the likelihood of developing periodontal disease or periodontitis in this case is especially high. In the case of occlusion pathology, the distribution of the functional load on the teeth and alveolar processes changes. Risk factors include abnormal attachment of the labial frenulum and shallow vestibule of the oral cavity.
In modern dentistry there are many different methods for correcting dental pathology - these are braces and splinting. Currently, doctors can offer clasp orthopedic structures to suit any budget. If the patient uses removable orthodontic or orthopedic structures, they must be looked after especially carefully. Removable dentures should be washed and brushed daily. You can purchase special tablets for washing and disinfecting such structures.
Prosthetics are also considered to prevent periodontitis.
4. Remineralization of teeth.
To increase the strength of the enamel, your doctor may suggest treating your teeth with calcium and fluoride. This process is called remineralization. At home, you can saturate your teeth enamel with fluoride using special toothpastes and identical rinses. But, of course, professional remineralization is much more effective. Using a brush, a varnish containing high concentrations of fluoride is applied to the dried and clean tooth enamel. This varnish forms a film that, when dissolved, combines with the calcium of the enamel and strengthens it. Dentists advise combining home remineralization with low doses of fluoride with sessions of professional applications.
Healthy eating as a preventive measure for periodontal disease
1. Take coarse “solid” food more often.
To prevent periodontitis and periodontal disease, you need to consume more vegetables and fruits. The menu should not systematically include pureed dishes with a very soft consistency. If there is no solid food in the diet, then the periodontium is deprived of the necessary load. Active chewing is very beneficial. It strengthens the gums, promotes the proper formation and development of the dentofacial apparatus.
2. Avoid eating very hot and very cold foods.
It is known that contrasting temperatures destroy enamel, promoting the formation of cracks. Moreover, very cold and very hot food in itself is also harmful to enamel.
3. Don't forget about vitamins.
Don’t forget about vitamins, preferably natural ones. Therefore, the menu must contain products containing vitamins A, C, B, E. If it is not possible to buy fruits and berries in sufficient quantities, then it is necessary to take vitamins from the pharmacy.
4. There should be no snacks between meals.
If you really want to snack on something, then it is better to stop at a green apple or raw carrots. Buns, sweets, cookies, that is, products containing sugary substances, are dangerous and very harmful to teeth and gums. Therefore, even after eating one toffee or piece of chocolate, it is necessary to brush your teeth and rinse your mouth within the first 5 minutes after the snack.
I. Conservative treatment
(all forms of gingivitis, initial stage of periodontitis)
— professional hygiene; - drug treatment; — training in personal hygiene.
Now let’s take a closer look at the treatment methods... Professional hygiene is a whole complex of measures based on 3 main stages:
- Removing dental plaque;
- Grinding and polishing;
- Fluorization is the strengthening of enamel.
Initially, stones and hard plaque are “beaten off” from the tooth and from under the gums using an ultrasonic nozzle (due to the vibration of thin metal plates when a low-voltage electrical signal is applied.) or special hand tools. This procedure, depending on the individual sensitivity of the patient, can be performed both under the influence of local anesthesia and without it. And it all ends with coating the teeth with fluoride varnish.
Prevention
- Primary: prevention of dental diseases by eliminating the causes and conditions of their occurrence, as well as increasing the body’s resistance to adverse factors.
- Secondary: a set of measures aimed at preventing relapses and complications of diseases.
- Tertiary: a system of measures aimed at the rehabilitation of dental status by preserving the functionality of organs and tissues of the maxillofacial area, mainly by replacement.
Preventive measures are beneficial to everyone without exception. They are especially needed by patients suffering from endocrine diseases, pregnant women, and people with bad habits.
Oral hygiene
Individual oral hygiene is the main method of primary prevention of periodontal diseases:
- regular and proper brushing of teeth (3 times a day);
- using high-quality toothbrushes and toothpastes;
- the use of additional means of prevention (flosses, interdental brushes, irrigators, devices for cleaning the tongue, etc.).
Factors in choosing personal hygiene products
- age;
- the presence of dental diseases or a predisposition to them;
- individual characteristics of the oral cavity (atypical structure of the dentition and shape of the teeth, the presence of orthopedic or orthodontic structures in the oral cavity, etc.).
Prevention of hypersensitivity of dental tissues
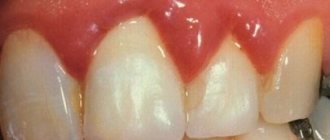
About 62% of the adult population in Russia suffers from painful tooth sensitivity. Most often, increased sensitivity occurs when the necks of teeth are exposed due to periodontal disease. In addition, it can cause the development of periodontal diseases due to unsatisfactory tooth brushing due to the pain of its implementation. Special toothpastes, rinses, flosses and gels are used as therapeutic and prophylactic agents for increased dental hypersensitivity.
Elimination of local factors
A number of local factors contribute to increased accumulation of dental plaque. There are a number of such factors: cervical carious cavities; unrestored interdental contacts; overhanging edges of fillings; edges of artificial crowns deeply advanced under the gum; foci of demineralization of gingival surfaces; lack of equator of tooth crowns; wide and attached close to the gingival edge of the frenulum and strands of the mucous membrane; availability of orthodontic devices; close arrangement of teeth, etc. Therefore, timely elimination of the listed factors is a necessary component of the prevention of inflammatory periodontal lesions.
Elimination of supercontacts and functional selective grinding
The traumatic factor is one of the most significant. In the absence of physiological abrasion of the enamel tubercles, which is observed in 20-22% of the population, in order to prevent increased and uneven load on the periodontium, functional selective grinding is carried out.
Surgical elimination of deformation of the soft tissues of the oral vestibule
Correction of pulling cords, frenulums, and small vestibule of the oral cavity should be carried out before they have time to lead to destructive lesions. The optimal period is the school period, after the completion of the formation of the alveolar process.
Bite correction
Malocclusion affects the condition of the periodontium, usually due to uneven mechanical load on the periodontium. Therefore, correcting malocclusion in childhood has a significant preventive effect.
Prophylactic use of antiseptic drugs
When carrying out preventive measures, it is necessary to use antimicrobial drugs that affect periodontal pathogenic microflora. Some of the most effective agents are chlorhexidine and triclosan. The use of products containing these substances should be supervised by specialists.
Professional oral hygiene
Professional oral hygiene is an important point in the system of preventing inflammatory periodontal diseases. We use the following tools: scalers, air-abrasive systems (handy blasters), such as Air-Flow (EMS); abrasive polishing pastes.
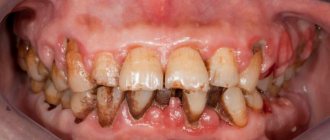
Types of periodontitis
Depending on the extent of inflammation of the periodontal tissue, periodontitis can be:
- focal - pathology is concentrated on one or several adjacent teeth;
- generalized – characterized by damage to all or most teeth. This type of periodontitis is included in the list of the most complex and unresolved problems in the field of dental services.
According to the nature of the course, acute, chronic and aggravated periodontitis is distinguished.
Spicy
This type of periodontitis occurs mainly in a focal form. The disease can begin suddenly with damage to 1-3 adjacent teeth.
Chronic
In the chronic form of the pathology, progressive cyclic gum damage is observed. They periodically bleed or make themselves felt by a feeling of itching. Chronic periodontitis is accompanied by increased mobility and displacement of teeth.
Aggravated
The symptoms are similar to acute periodontitis. According to statistics, it is the most frequently diagnosed type of periodontal inflammation in children aged 4-13 years.
The benefits of our preventative procedures
- special attention to the condition of the oral cavity during pregnancy;
- strengthening gums with the help of professional procedures: therapeutic dressings, applications, coatings.
- individual selection of hygiene products;
- timely detection of the development of gum disease at an early stage, which facilitates the treatment process.
We hope that preventative measures will help you never experience gum disease. However, gum inflammation can occur against the background of certain body conditions:
- stress;
- hormonal changes: puberty, pregnancy, diseases of the internal secretion organs;
- diseases of the endocrine system - high levels of glucose in the blood (diabetes of any type); vascular diseases; gastrointestinal tract;
- problems with the absorption of certain vitamins and microelements;
- the presence of pathogenic microflora in the oral cavity.
In case of suspicion of serious disorders that played a role in the development of gum disease, Kuntsevo specialists give a referral for examination by doctors in other departments. A multidisciplinary approach to each patient allows not only to cope with the symptoms, but also to eliminate the underlying causes.
Kuntsevo dentists guarantee high quality of services provided. We not only relieve our patients of discomfort and relieve inflammation, but also fight the underlying causes that led to the development of the disease, which ensures lasting results and prevention of relapses.