From this article you will learn:
- stages of caries,
- what are the signs of caries?
- how to identify caries yourself.
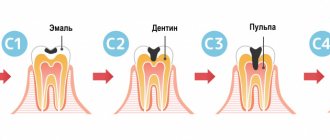
Caries is the process of destruction of hard tooth tissues with the active participation of cariogenic microorganisms of the oral cavity, such as streptococci, actinomycetes and lactobacilli. The main conditions for its development are irregular or insufficient oral hygiene, which leads to the accumulation of soft microbial plaque on the teeth, as well as food debris between the teeth. Depending on the depth of damage to the hard tissues of the tooth, caries is usually divided into several types, which, in fact, are successive stages of its development.
The initial stage is always spot-shaped caries (foci of demineralization in the form of white spots on the surface of tooth enamel), and if left untreated, it gradually goes through the stages of superficial, medium and deep caries. Symptoms of dental caries, where we include patient complaints and data from a visual examination of the carious cavity, will be slightly different at each stage, and below we will consider them in detail.
Causes of caries development
There can be many reasons for the appearance of caries, but the main one is a violation of the acid-base balance in the oral cavity, which leads to the formation of plaque. Gradually, plaque, if not removed, accumulates, penetrating the inner layers of enamel and destroying the tooth.
In turn, a violation of this balance may have the following reasons:
- poor hygiene;
- an excess of sweet and overly fatty foods in the daily diet;
- insufficient intake of vitamins (including from fresh fruits and vegetables);
- poor quality of drinking water;
- consequences of diseases suffered in childhood (for example, rickets);
- diabetes;
- dysfunction of the thyroid gland;
- gastrointestinal diseases;
- general decrease in immunity.
The answer to the question: “Is it worth treating caries?” - unambiguous. It doesn’t just need to be treated: you need to see a doctor at the first sign of its appearance. Otherwise, advanced caries can lead to severe pain and eventual tooth loss.
Complications
If deep caries is not cured in time, it turns into pulpitis - a disease in which the tooth pulp becomes inflamed. At this stage, patients complain of constant toothache. The inflamed pulp (nerve) must be removed.
Periodontitis is an even more advanced case when not only the pulp is affected, but also the bone around the tooth. The inflammatory process becomes dangerous: the patient’s temperature rises, chills appear, what’s left of the tooth festers and causes severe pain.
Complications of caries require removal of the pulp and thorough cleaning of the canals. It takes a doctor a lot of time to get to the most inaccessible branches and clean out all the infected tissue.
Factors provoking the development of caries
In addition to the above reasons, caries can be caused by:
- anatomical features of the structure of teeth (congenital dimples in the enamel in which plaque accumulates);
- malocclusion (crooked teeth lead to the fact that even good toothpaste and a high-quality brush are not able to fully cope with cleansing);
- increased viscosity of saliva (renewal of microflora does not occur properly due to this, resulting in various diseases);
- a state of constant stress and increased nervousness (this leads to a deterioration in the absorption of microelements from food).
Comments
[…] leads to diseases of the teeth and gums such as caries, gingivitis and periodontitis. But despite this [...]
Irrigator Aquajet LD-A8I, reasons why you should choose. (05/05/2018 at 09:00) Reply to comment
[…] tooth enamel and caries are two completely different diseases. However, thin and [...]
Enamel hypoplasia: 6 features of a dangerous disease (08/15/2018 at 12:00) Reply to comment
[…] But these two diseases are completely different. Firstly, caries is associated with the formation of a large number of bacteria, and [...]
Dental fluorosis: 5 facts about the problem that everyone needs to know (08/31/2018 at 09:00) Reply to comment
Write your comment Cancel reply
Treatment of dental caries and its features
The stage of development of carious formation directly affects the complexity of treatment.
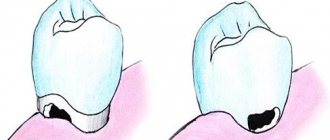
- Caries in the spot stage, when areas of white and less often dark color are noticeable on the enamel, but the enamel itself is not damaged. A change in color indicates a loss of calcium in the area where the stain appeared. This is the simplest form of carious formation, which does not even require drilling. To correct the situation, a remineralization procedure is necessary - sometimes the patient can do it on his own at home.
- Superficial caries, in which the defect is located within the enamel layer, without affecting deeper layers. Here you cannot do without standard filling.
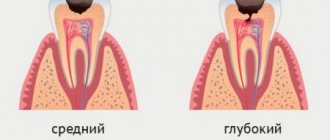
- Medium form, characterized by caries extending beyond the boundaries of the enamel and damage to the upper part of the dentin.
- Deep form , when the disease penetrates into the deep layers, sometimes involving the pulp. As a rule, it is accompanied by pain. This is the most advanced case, so a patient who did not go to the clinic on time and reached this stage will be forced to be treated in several stages. Treatment of deep caries requires separate consideration, as it is the most complex.
In addition, there is also bottle caries in children , the treatment of which has its own characteristics, since it affects only the upper incisors.
Why is caries dangerous if left untreated?
In this section we will talk about the complications of untreated dental caries in a timely manner, which without exception lead to the need to remove the nerve from the tooth and fill the root canals. And in case of purulent complications, in addition, contact a surgeon to make an incision on the swollen gum.
- Development of pulpitis - as the carious process spreads to the deep layers of dentin surrounding the tooth pulp, cariogenic microorganisms penetrate into the tooth pulp. The pulp is the neurovascular bundle of the tooth. As a result of infection, purulent inflammation of the pulp occurs - pulpitis. Pain due to pulpitis is usually acute and paroxysmal in nature. You can see schematically how pulpitis develops in the following pictures (Fig. 7-9) –
- Development of periodontitis – if pulpitis is also not treated in a timely manner, then pulp necrosis occurs, i.e. her death. This stage of inflammation is called periodontitis. In Fig. 11 you can see how the infection, spreading from the carious cavity through the root canals, penetrates beyond the tooth - into the periodontium and bone tissue. And as a result of this, a focus of purulent inflammation appears in the area of the apex of the tooth root (it can be designated by the term “periodontal abscess”).
On an x-ray, such an inflammatory focus looks like intense darkening around the apex of the tooth root. In addition, in Fig. 10 you can schematically see the differences between pulpitis and periodontitis. - Development of a cyst at the apex of the tooth root – as a result of infection of the near-apical tissues, their gradual destruction occurs: the bone tissue is resorbed, and in its place inflammatory granulation tissue is formed, and jaw cysts can also form. Such cysts are called radicular - from the Latin word Radix, which means “root” (24stoma.ru).
A radicular cyst is a cavity in the area of the apex of the tooth, the inner surface of which is lined with a membrane, and the cavity itself is filled with pus. Sometimes they can reach very large sizes. For example, I had to remove such cysts up to 5 cm in diameter. You can see what a radicular cyst looks like in the diagram of a section of the upper jaw (Fig. 12), as well as in the x-ray (Fig. 13), in which the cyst looks like an intense darkening at the root of the tooth.
- The development of gumboil is also a complication of pulpitis and periodontitis and includes a disease called “periostitis”, which is popularly called gumboil. Periostitis is always accompanied by severe swelling of the gums and/or cheeks. Inflammation and swelling in this case are a consequence of the spread of infection from the apex of the tooth root to the area of the periosteum, which covers the jaw from the outside. As a result, a purulent abscess occurs between the periosteum and the jaw (when the periosteum melts, pus breaks through under the mucous membrane of the oral cavity). Treatment of periostitis involves the need to make an incision in the projection of the swelling (to evacuate pus). After this, antibiotic therapy is prescribed. Before starting treatment, the issue of the need to remove or preserve the causative tooth that caused the inflammation is also decided. If it is decided to save the tooth, then after the acute symptoms have subsided, the dentist will need to treat this tooth appropriately so that it does not cause purulent inflammation next time.
How dental caries is treated with laser
In addition to the traditional treatment of caries, modern medicine offers an innovative method using a laser.
Using a laser you can:
- selectively remove affected tissue, preserving healthy tissue as much as possible;
- sterilize the canals, which is necessary in the treatment of pulpitis.
Among the advantages of the laser:
- high quality of treatment;
- no pain;
- longevity of the results obtained;
- complete safety for the patient;
- no discomfort during the treatment process.
The laser allows you to achieve the formation of a completely sterile cavity and avoid chips and cracks, which often happens when using a drill. The surface of the tooth becomes like pumice, which has a positive effect on the properties of the materials used for filling.
Signs of caries and pulpitis (differences in symptoms) –
Typical signs of caries are the infrequent occurrence of short-term painful attacks under the influence of various irritants:
- thermal irritants (cold water or cold air),
- chemical irritants (for example, sour, salty or sweet foods).
At the same time, caries is characterized by the absence of spontaneous pain, i.e. pain during caries occurs only under the influence of irritants. And as soon as the irritant is eliminated, the pain should immediately disappear. The presence of spontaneous pain not associated with exposure to irritants indicates that the process from caries has already passed into pulpitis.
With deep caries (plus the above), pain may also occur when mechanical pressure is applied to the thinned bottom of the carious cavity. This can occur, for example, while eating - in the process of biting or chewing hard food. In this case, food enters the carious cavity and presses on its bottom, causing compression of the dental pulp (neurovascular bundle inside the tooth). In this case, removing food debris from the carious cavity usually relieves pain.
How to distinguish caries from pulpitis: differences in symptoms
- With caries, pain occurs only in the presence of irritants (thermal, chemical). When the irritant is removed, the pain immediately disappears.
- In acute pulpitis, pain is usually acute, spontaneous and not associated with any irritants.
- But with chronic pulpitis, pain can still be provoked by thermal irritants - cold or hot water. But the difference between caries and chronic pulpitis is that with caries the pain goes away immediately after the irritant disappears, and with chronic pulpitis the pain does not go away immediately, but only after 10-15 or more minutes.
How caries is treated with the ICON system
This is another modern technology that allows minimal use of medical instruments: in rare cases, the doctor uses a drill, but in most situations it is possible to use a hand instrument, which preserves the maximum possible volume of natural tooth tissue.
In addition, the ICON system has the following advantages:
- no need for pain relief;
- healthy dentin is not damaged during treatment;
- the procedure lasts no more than 45 minutes, there are no age restrictions.
How to treat dental caries using the ICON system:
- soft tissues are isolated with a rubber dam;
- the affected area is treated with a special gel;
- the carious area is cleaned with a medical instrument;
- a gel is applied, popularly called a “liquid filling”;
- the composition is fixed using ultraviolet light;
- The surface of the tooth is polished.
But the procedure also has a minus, otherwise it would be used everywhere: this method can only be used at the initial stage of caries development, but for deeper lesions you cannot do without a drill.
Causes of dental diseases in humans
The main cause of dental diseases is the activity of bacteria, which results in caries. But there are other factors that affect oral health:
- heredity and genetic pathologies;
- quality of drinking water;
- ecology of the urban environment;
- nutritional features;
- professional activity.
In most cases, it is impossible to change anything from this list. Therefore, it is important to at least be able to promptly recognize the symptoms of dental disease and consult a doctor as soon as possible to avoid complications.
Treatment of caries on baby teeth
Many parents, having noticed caries on their child’s baby teeth, believe that nothing needs to be done - these teeth will fall out anyway. However, such a decision is explained by ignorance: not every person knows what kind of caries is treated in modern dental clinics.
When visiting a doctor, a child undergoes:
- ozone therapy is a modern method using a powerful jet of ozone used for antibacterial treatment;
- infiltration is a method in many ways similar to ICON, but a filling is not installed (the doctor is limited to isolating the cavity);
- abrasive cleaning - the method is suitable for the initial stage of caries, has many similarities with professional cleaning of the oral cavity;
- silvering - the enamel is coated with a solution of silver diamine, which disinfects the surface. The method is rarely used due to its low aesthetic appeal - teeth remain black until they fall out;
- Conservative treatment for more serious lesions, accompanied by pain relief.
Treatment of average caries in stages
Step-by-step treatment of caries includes the following steps:
- Cleaning the surface from plaque . How are caries treated in dentistry? First, be sure to clean the damaged tooth and the teeth adjacent to it. To remove plaque, the dentist can use an abrasive brush or floss; to remove the stone, ultrasonic attachments will be required.
- Drilling out affected tissues . Since enamel is hard and durable, it is destroyed less than dentin. It is for this reason that the entrance hole of the cavity may be small, expanding as it deepens. If cervical caries occurs, how to treat it? The doctor drills the edges of the enamel and removes dentin affected by caries. If even a small area of affected tissue remains, on top of which a filling is placed, this is fraught with problems in the very near future, because caries will begin to develop rapidly, which can ultimately lead to pulpitis.
- Isolating the tooth from moisture and saliva . Unfortunately, some dentists (in fact, most of them) neglect this point and skip it. When carious tissue is eliminated, the doctor, in preparation for filling, must isolate the tooth from contact with saliva. It might seem like a small thing, but it affects how long the filling will last. For a long time, ordinary cotton wool or gauze was used for isolation, which was used to cover the tooth, but this method was found to be ineffective. Modern dentistry recommends the use of rubber dam - a thin latex material in which holes are made. Its installation is quite labor-intensive, so dentists avoid this procedure in order to save their own time. The use of a rubber dam by a doctor is a sign that the dentist is conscientious about his work, putting the patient’s health above the profit received.
- Treatment of the cavity with antiseptics.
- Recreating the side wall . How is caries treated if it has affected the surface of the tooth in contact with another tooth nearby? Then you will need to install matrices and wedges to restore the side wall. The procedure cannot be called simple.
- Using acid to condition enamel . To ensure that the adhesive material applied to dentin penetrates into the deep tissues, phosphoric acid is used. At the end of the procedure, the gel must be completely washed off and the surface dried.
- Treatment of enamel with adhesive . In order to ensure ideal fastening of the filling, the enamel is thoroughly impregnated with adhesive material, and after its absorption, it is illuminated with a polymerization lamp.
- Installing a gasket for a seal . A gasket made of a special material is placed at the bottom of the drilled cavity. The need for this action is explained by the peculiarity of the shrinkage mechanisms of the filling material.
- Direct filling , restoring chewing function and aesthetic appearance. To do this, photopolymer materials are laid layer by layer, with each layer illuminated by a lamp, which gives greater strength.
- Surface grinding and polishing . Immediately after installation, the filling is uneven, as a result of which it not only causes a feeling of discomfort, but can even damage the tongue. Polishing will make the tooth smooth.
For many people, it is important not only to undergo caries treatment in Krasnodar, getting rid of pain and discomfort, but also to look attractive. Therefore, the dentist selects the filling material by color, trying to achieve 100% shade similarity with the natural tissue of neighboring teeth. The doctor’s task is to make sure that the filling does not stand out from the rest of the teeth, which is especially important when smiling.
Is it possible to treat caries on the front teeth without pain? Absolutely yes. Long gone are the days when going to the dentist and the treatment process was accompanied by physical suffering. Modern means of anesthesia make it possible for the patient to feel nothing at all. The anesthesiologist is able to select the concentration of the anesthetic so that it will act for several hours. The only unpleasant moment is the insertion of a needle into the gum: the faster the drug enters the tissue, the more painful it is for the patient. Although much here depends on the characteristics of the nervous system of each individual person. For people with a high pain threshold, going to the dentist can be an enjoyable experience.
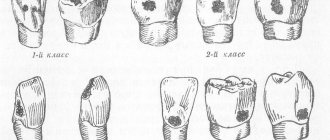
Classification of caries by place of formation
Cervical - the most common type, occurs near the gums - where the enamel is thinnest. Plaque accumulates more actively near the gums. An infection settles in it, which provokes the destruction of enamel and dentin. In advanced cases, cervical caries leads to caries of the tooth roots.
Fissure - damage to the cavities on the chewing surface of the teeth. It is not always possible to remove plaque from the cavities with a brush, so microbes also actively multiply there.
Contact (interdental) - appears on the lateral surfaces of adjacent teeth, affecting two teeth at once. The root cause is still the same - the accumulation of plaque between the teeth. Diagnosis of such caries is difficult. Most often, the patient comes to the clinic only when pain occurs.
Preventive measures against caries
Any disease is easier to prevent than to treat, and caries is no exception in this regard.
To avoid its appearance, you need to:
- brush your teeth twice a day for 2 minutes;
- do not use toothpicks - special dental floss is more suitable for high-quality cleaning;
- use an irrigator or mouthwash;
- get rid of bad habits (smoking and drinking alcohol provoke deterioration of the oral cavity);
- eat more calcium in food;
- Get checked by a dentist at least once a year, but it’s better to do it more often.
| We must not forget that the main reason for the formation and development of caries is lack of hygiene. Therefore, prevention is extremely important, which consists of regular high-quality brushing of teeth after each meal. |
Classification
There are several layers of this degree of caries:
- surface
. The amount of fluoride decreases, minor areas are affected;
- subsurface.
Calcium levels decrease, enamel permeability increases;
- central.
The calcium level decreases significantly, the enamel quickly loses strength;
- intermediate.
There are some changes, the microspace has a volume of 15-17%;
- area of shiny enamel.
Relatively normal condition.