The emergence of antiseptics among medical drugs has made a real breakthrough in the treatment of infectious diseases. Local antiseptics have virtually no side effects and are effective against various types of microbes. However, bacteria do not develop resistance to such agents.
Chlorhexidine is often used as a rinse after tooth extraction and is one of the most well-known types of antiseptics, and has a history of use of more than 60 years. In dentistry, it is used in the form of a solution with a concentration of 0.05-0.1%. The solution contains: chlorhexidine biluconate and purified water. The drug has a pronounced antiseptic effect against a wide range of microbes, fungi and viruses. At the same time, chlorhexidine is powerless against microorganisms that are resistant to an acidic environment, and also has no effect on microbial spores and the herpes simplex virus. The product has a long-lasting effect, maintaining its antimicrobial effect for some time after treatment. The drug does not require surface sterility and is effective even in the presence of blood, purulent discharge, saliva and other organic liquids.
Important! Chlorhexidine is able to maintain its antiseptic effect in the oral cavity for 24 hours after treatment. This quality puts it in first place in terms of effectiveness among similar antimicrobial agents used for dental and oral hygiene. When using a solution of chlorhexidine in a concentration accepted in dental practice, it has an effect that depends on the duration of exposure to the drug. Antibacterial and antiviral effects are achieved within one minute. When the time is increased to 5 minutes, the medicine exhibits an antifungal effect. A more concentrated solution acts faster, but is unsafe for the mucous membrane, as it can cause burns. The solution does not have a mutagenic effect and does not have a carcinogenic effect. By interacting with certain types of antibiotics, the drug can enhance their effectiveness. At the same time, regular toothpaste contains components that weaken the effect of chlorhexidine.
Properties of the solution
Chlorhexidine is a broad-spectrum antiseptic that is effective against most pathogenic oral bacteria.
This drug is widely used in dentistry, is sold in pharmacies, and its purchase does not require a prescription. A solution consisting of only two components - chlorhexidine digluconate and prepared water - is effective against most microorganisms. Viruses, fungi and bacteria that are not resistant to an acidic environment die after treatment with this drug. Only the herpes virus, microbial spores and some other bacteria that are not sensitive to acids are resistant to the product. Dentists use chlorhexidine solution after tooth extraction, as well as when removing dental plaque and tartar. The superiority of the drug is its exceptional effectiveness, maintained for 24 hours. At the same time, it is not affected by the presence of bleeding wounds, pus, saliva and the general high humidity of the oral cavity. Taking drugs belonging to the category of antibiotics is more effective when used simultaneously with chlorhexidine. It should be taken into account that ordinary toothpaste used daily can significantly reduce the antiseptic effect of the drug.
Type of gum after removal (normal) –
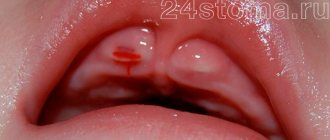
How can you determine that your gums are healing normally after tooth extraction? First, open your mouth wide in front of the mirror and see if the hole of the extracted tooth is covered with a blood clot. In the photo below you can see what the holes should look like immediately after removal and after different times.
Under no circumstances should the hole be empty. The latter may indicate that the blood clot has either already fallen out or has not formed at all (this is possible if the doctor used anesthetic solutions with a high vasoconstrictor content during anesthesia). In this case, you need to immediately consult a doctor again. Please note that normally the socket of each tooth will be covered with a dense blood clot (Fig. 5-6).
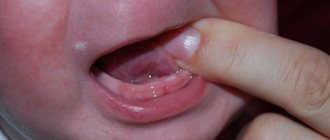
At first, the surface of the blood clot will be bright red, but within a few days it will become covered with a whitish or yellowish coating (this is fibrin). This is completely normal and does not indicate the development of inflammation. Next, gradual epithelization of the surface of the blood clot will occur (Fig. 7), until the usual gum mucosa appears on its surface. But if the hole is empty, there are food remains in it, there is pain and an unpleasant odor - these are signals of the development of inflammation. We hope that our article was useful to you!
Sources:
1. Higher prof. the author’s education in surgical dentistry, 2. Based on personal experience as a dental surgeon, 3. National Library of Medicine (USA), 4. “Outpatient surgical dentistry” (Bezrukov V.), 5. “Propaedeutics of surgical dentistry” (Soloviev M. .).
Instructions for using chlorhexidine after tooth extraction
Dentists often recommend rinsing with a solution of the drug after a tooth has been removed or a purulent inflammation in the oral cavity has been opened. For 3 days, peculiar baths with a 0.05% chlorhexidine solution lasting 20-30 seconds are prescribed. Baths are done three times a day. This method of application is preferable to active rinsing in the first days when the wound should heal. Careless rinsing movements during this period can cause bleeding or even tissue inflammation. Starting from day 4, you can move from baths to full rinsing for 1 minute. Procedures are carried out 2-3 times a day.
Attention! In addition to home use of chlorhexidine after tooth extraction, this substance is used by dental surgeons and directly in the dental office. Before removal, the oral cavity is treated with various preparations that contain the same chlorhexidine bigluconate.
This antiseptic is also used to prepare the surface before giving an anesthetic injection. Before the injection, many dentists apply icecoin to the mucous membrane and treat the area with a chlorhexidine-based solution. Thanks to this, the surface at the puncture site is cleared of bacteria that can infect the wound and cause inflammation of the deep mucosal tissues.
A chlorhexidine solution for rinsing the mouth and throat is used in a 0.05% concentration. The solution is sold ready for use, i.e. There is no need to dilute it with water.
Why are rinses dangerous?
After removal within 1-2 minutes, a blood clot forms in the hole - this is a reliable biological protection of the wound, preventing bacteria from entering it and causing an inflammatory process. It is under no circumstances recommended to destroy, move or wash out this clot. However, during the rinsing process, patients often wash away the protective clot, leaving the socket “dry”. Dry socket is the main cause of alveolitis.
Today, dental surgeons are more inclined to believe that rinsing not only will not help the wound heal faster, but also increases the risk of secondary infection.
Chlorhexidine for oral diseases
The drug solution is often prescribed for certain dental diseases:
- stomatitis;
- gingivitis and periodontitis.
Stomatitis
For the aphthous form of the disease, rinsing with a chlorhexidine solution is effective. The product also helps with candidiasis of the oral cavity. Treatment usually does not take longer than 10 days.
Gingivitis and periodontitis
Diseases caused by the formation of accumulation of bacteria in subgingival pockets lead to bleeding gums and tooth mobility. In such a situation, rinsing alone is not sufficiently effective. Chlorhexidine is used comprehensively for the treatment of these diseases:
- treat the surface with the solution during cleaning;
- an antiseptic-based drug is placed in the pockets on the gums;
- rinsing with a chlorhexidine-based solution.
Two-week treatment allows you to relieve the main symptoms and reduce the concentration of microbes in the oral cavity several times. Chlorhexidine is also used as a prophylactic against gingivitis and periodontitis. This is especially true after oral surgery or when it is impossible to maintain proper hygiene. Removable prosthetic structures can be soaked in the drug solution to disinfect and prevent gum inflammation.
Chlorhexidine solution is the most effective antiseptic for the oral cavity; it has a unique property - when rinsing, a thin protective film is formed on the mucous membrane, which continues to act for several more hours after rinsing.
Contraindications
Important! Chronic use of the drug may cause the appearance of a yellow-brown tint to tooth enamel. To avoid this, during the period of use of chlorhexidine, it is necessary to refrain from eating food containing intensely coloring pigments (red wine, bright soda, beets, coffee, tea, etc.).
In order to clean the plaque that has already formed, you will have to carry out a professional hygiene procedure. There are other features of the use of this antiseptic. Solutions based on it are not used for longer than two weeks to avoid the development of dysbacteriosis of the oral mucosa. At the same time, you cannot use iodine-containing products. Wait a while before rinsing with chlorhexidine after brushing your teeth with toothpaste. After consultation with your doctor, and provided there are no open wounds in the mouth, the drug can be used by pregnant and lactating women. Chlorhexidine is not contraindicated in childhood, however, it should be used under adult supervision to avoid ingestion of the solution.
Tea, wine, coffee, as well as cigarettes, chocolate, colored vegetables and fruits, sweets should be avoided during the period of preventive actions using chlorgrexidine, because combinations of such products and medications can cause darkening of tooth enamel.
Side effects
Any drug has limitations in use and may have side effects. Chlorhexidine is a safe antiseptic; however, an allergic reaction to it is possible. In addition, it can stain the enamel yellowish, cause a burning sensation and temporary loss of taste. During use of the product, a slight feeling of numbness and a feeling of bitterness may occur. The listed side effects are minor and are fully compensated by the high efficiency and availability of chlorhexidine.
Helpful information
There are several points to consider when treating:
- When treating gum inflammation, chlorhexidine should be used in combination and only after removing plaque. You should not hope that rinsing with an antiseptic in this case will have a sufficient effect. The drug may partially relieve symptoms, but not completely eliminate inflammation. In advanced cases, teeth become mobile and are at risk of removal.
- The course of rinsing with the drug prescribed by the doctor should not last longer than 12 days. Otherwise, you can develop dysbiosis in the oral cavity, which, in turn, can provoke a fungal disease. To avoid candidiasis, after 10-12 days of treatment with chlorhexidine, it is necessary to switch to rinses with other auxiliary components.
Chlorhexidine kills microorganisms associated with various throat infections, as well as all general oral flora, including Candida Albicans, which causes thrush and oral infections, and bacteria that can cause mouth ulcers.
Why rinse your mouth after removal?
However, rinsing also has its advantages: it allows you to clear the mouth of blood, as well as clean it after each meal. Preventing food debris from getting into the hole. Often, tooth extraction is carried out without preliminary sanitation of the mouth, which means that there may be carious teeth around the hole. In this case, there is a high risk of infection entering the hole that is open after removal. In such a situation, rinsing with an antiseptic can minimize this possibility.
Use of the drug in children and pregnant women
Attention! If there are no wounds in the patient's mouth, chlorhexidine can be used by pregnant and lactating women. It does not penetrate into the blood or breast milk, but acts only on the surface. A 10-day course of treatment is safe for such patients, according to studies.
When treating children, the course of use of the drug should also not exceed 10 days. For the youngest patients, it is preferable to use chlorhexidine in the form of a spray, which does not require rinsing skills. The spray is easy to use and can be applied to any area of the oral mucosa. Children under 3 years of age should not use the drug to irrigate the tonsils. Despite the safety of the drug, if the drug is used by pregnant women or pediatric patients, it is recommended to first consult with your doctor.
Advantages and disadvantages of the drug
Positive properties of the drug:
- kills pathogenic microorganisms (antimicrobial activity is higher than that of Miramistin);
- maintains a long-lasting antiseptic effect even upon contact with bloody and purulent secretions;
- used in low concentrations, which protects the oral mucosa from irritation;
- impossibility of overdose;
- affordable price.
Negative points include:
- weak or zero effect in the treatment of viral diseases, especially like herpes;
- bitter, unpleasant taste causes discomfort;
- Regular use leads to darkening of the enamel and surface of the tongue.