A fistula on the gum (also called a fistula) is an opening in the gum from which pus is released, often with blood. A fistula appears against the background of caries, periodontitis, and also due to poor-quality dental services. Over a long period, the fistula develops asymptomatically, but subsequently can lead to severe complications. Therefore, if a purulent formation appears on the gum, you should immediately contact your dentist.
Fistula on the gum: causes
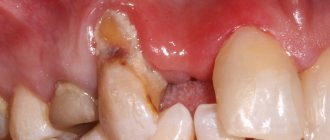
A fistula on the gum is a hole that forms as a complication after inflammatory pathologies, including untreated ones. It can also occur after dental intervention (poorly provided services). Very often, a fistula is formed as a complication of long-term chronic periodontitis.
Also, the reasons for its appearance may be:
- damage to the tooth root;
- advanced caries;
- pulpitis;
- inflammatory processes of the cyst;
- problems with the growth of wisdom teeth;
- improper teething in children;
- granuloma - inflammatory processes in the tissues of the periosteum and the apical region of the tooth root (accompanied by an increase in temperature, enlarged lymph nodes and other signs).
What happens if the fistula is not treated?
If the fistula is not treated, then nothing good will end. The tooth will need to be removed, and what’s more, the bone surrounding the tooth suffers greatly, and the vestibular cortical plate suffers. When the tooth is not treated, when the cause of the fistula is not dealt with, the cortical plate is quite destroyed. Large cavities are formed in the bone, as exudate is formed, all this rots and the bone decomposes, softens and becomes infected, lyses, and exits through the fistulous tract.
Therefore, in addition to, as I said earlier, there is a fairly strong load on the body, since a fistula is a constant open source of infection in the oral cavity.
How a fistula is formed
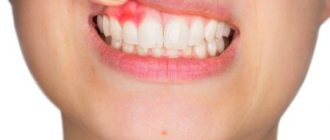
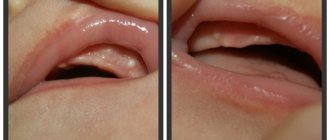
The process of fistula formation looks like this. A small hole appears in the gum near the base of the tooth. Its color stands out a little against the background of healthy tissues - the color is rich pink or red. At the same time, the remaining teeth remain healthy and do not hurt.
At first, the fistula looks like a small swelling, then it grows and resembles a pimple or an abscess. The last stage - the seal opens, after which mucus or pus comes out of it. Then the wound becomes covered with a scar, but does not disappear. In the future, the development of the fistula can become chronic - it will open several times a year and exude pus. During exacerbations, mild pain will be felt.
What is epulis
A tumor on the gum is characterized by a benign nature. It is classified as a group of periodontal diseases. Epulis is also called “giant cell granuloma” or “supragingival”. Epulis looks like a lump that is attached to the gum in the area of the interdental space on a stalk. A formation is formed from the epithelium of the alveolar process.
In diameter, an epithelial tumor of the gums can reach a size of more than 3 cm. The shade of a giant cell granuloma can be different: bluish, brown, red-brown, or the color of the gums. Ulcers may appear in the affected area.
If the epulis on the gum has a diameter of up to 2 cm, does not cause pronounced symptoms and progresses slowly, then the pathology is classified as a benign form. With rapid growth of the supragingival tissue, severe pain, inflammation and swelling of the gums, there is a risk of developing a malignant tumor.
According to statistics, the pathology is most often diagnosed in pregnant women, but supragingival formation also occurs in women who are not pregnant. Less commonly, the disease occurs in men and young children when replacing milk teeth with permanent ones.
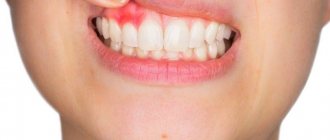
Symptoms of a fistula: how dangerous is it?
Fistula manifests itself with a number of symptoms:
- unpleasant odor from the mouth;
- tooth mobility;
- feeling of foreign taste;
- mucous membrane is bluish or, conversely, pale in color;
- discharge of purulent mucus, often with blood;
- painful sensations during mechanical contact (chewing food, drinking hot drinks, brushing teeth).
The disease may also be accompanied by symptoms not directly related to the oral cavity. It is manifested by such signs as apathy, general weakness, and fever.
Despite the small area affected, the fistula poses a certain health hazard. Thus, purulent discharge can penetrate the lymph or blood, which will lead to diseases of the internal organs, pathological processes in facial tissues and even loss of teeth. Therefore, even at the first relatively mild symptoms, it is important to consult a doctor.
It is worth keeping in mind that the disease is asymptomatic for a very long time. Moreover, if treatment is delayed, this can lead to partial death of the periosteum. And then the patient will have to remove not one, but several teeth at once.
What reasons can lead to its appearance?
The main cause of epulis on the gums is considered to be constant mechanical impact (rubbing) of soft tissues.
Injury to one area can cause gum swelling:
- poorly installed seal;
- uneven edges of the opposite tooth, which is destroyed or chipped;
- tartar;
- poor quality or incorrectly installed prosthesis;
- agonist tooth for malocclusion;
- adjacent teeth when teeth “pile up.”
Supragingival tissue occurs and, as a consequence, injury to epithelial tissue as a result of a burn, bruise or constant ingestion of irritating foods. In pregnant women, tumors occur due to hormonal imbalances. Epulis on a child’s gums can form due to general causes or disturbances in the eruption of permanent teeth.
Diagnosis and treatment of fistula
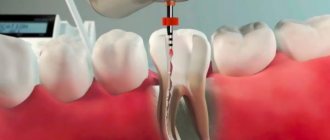
To carry out a diagnosis, you must contact your dentist. The doctor orders an x-ray and conducts a visual examination. Treatment is carried out in a clinical setting. Therapy depends on the cause of the fistula. For example, fillings are used to treat caries, and when an infection is detected, appropriate medications are used. The dentist can also perform treatment with ultrasonic waves or laser.
In some cases, a fistula appears due to poorly done filling of the canal. Then the patient is given an anesthetic, the filling is removed, the dental canal is cleaned and then a new high-quality filling is performed.
If the cause is a cyst, it is removed, which also requires the intervention of a dentist. For recovery, the use of antimicrobial agents, antibiotics, and antihistamines is indicated. If swelling occurs, the doctor may prescribe rinsing with a salt solution.
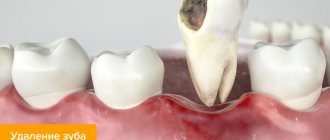
Fistula in the soft periodontal tissues after tooth extraction
The formation of a hole after tooth extraction is normal. As a rule, the hole heals within one to two weeks. If the operation was performed on wisdom teeth, the tightening process may take several weeks. Impaired socket tightening can occur due to infection or in case of injury to the area where the tooth was removed.
In a situation where the hole has tightened and a gap has formed in the periodontium, it may indicate that the tooth was not completely removed. Small fragments of the tooth gradually begin to decompose, forming a fistula.
Is treatment possible at home?
A fistula can only be treated in a clinic. But if it is impossible to urgently visit the dentist, for example, the pain occurred at night, it is recommended to rinse the mouth with the following means:
- infusion of chamomile;
- infusion of oak bark (dry raw materials can be purchased at a pharmacy);
- if there is purulent discharge, the mouth should be rinsed with a solution of salt and soda or antibacterial agents.
The described measures help relieve pain, but do not eliminate the cause of the disease. Therefore, in any case, you need to see a dentist.
Factors contributing to the appearance of a fistula tract
Among the provoking factors that are important to exclude:
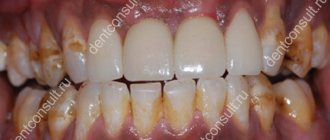
- poor oral hygiene;
- presence of untreated caries;
- pulpitis;
- malocclusion;
- frequent stress;
- unbalanced diet;
- physical fatigue;
- deficiency of vitamins and minerals;
- habit of eating a lot of sweets;
- smoking.
Prevention of fistulas
The main measure for preventing fistulas is maintaining oral hygiene. It is necessary to undergo an annual examination by a dentist and, if necessary, begin treatment for caries and periodontitis in order to prevent the development of chronic diseases.
It is also advisable to be treated by experienced, qualified dentists, since poor-quality services can also lead to the formation of a fistula. After the intervention, you need to monitor your well-being to prevent the development of a fistula.
Prognosis and possible complications
If the fistula is detected and treated in a timely manner, the prognosis is favorable. If you follow all the specialist’s recommendations, within a week the resulting wound will completely heal and heal.
If proper treatment is not carried out, the following consequences are possible:
- abscess formation;
- phlegmon;
- osteomyelitis;
- tooth loss.
Preventive measures
- regular teeth cleaning;
- carrying out professional hygiene in the dental office;
- preventive examinations by a dentist every six months;
- daily consumption of fruits and vegetables.
Diagnosis of an abscess
The dental clinic conducts a comprehensive examination of the abscess, which includes:
- Collection of medical history. Complaints of persistent localized pain or swelling. Increased discomfort when biting. The cause of decreased immunity and the presence of common diseases are determined.
- Visual inspection. The doctor determines how swollen and reddened the gums are, the tissue at the root of the tooth, and the gingival margin. Periodontal pockets are probed.
- Pulp vitality test (PVT). With an apical abscess, the nerve fibers of the dental pulp are damaged, but with a periodontal abscess, the pulp is viable.
- Physical diagnostics. On palpation, the lump is soft and fluctuates when pressed (fluctuation). Severe sensitivity and sharp pain when percussing (tapping on the tooth). The mobility of units is determined.
- Radiography. X-ray images show the source of infection - a dark cavity in the periodontal pockets and swelling of the soft tissue. The affected pulp looks like an empty tooth socket.
- Other clinical tests. A bacterial culture is taken to identify the type of pathogen (infection), and the analysis determines the body’s immune response. The clinic selects material and checks:
- General blood analysis. With an abscess, an increased level of leukocytes is observed.
- Analysis of urine. The presence of protein and red blood cells indicates an inflammatory process.
Eruption of wisdom teeth: inflammation and consequences
The figure eight on the lower jaw begins to create problems from the moment of eruption, when the crown rests closely on the adjacent tooth or is tightly covered with a hood. When the hood becomes inflamed, favorable conditions are created under it for the proliferation of pathological microorganisms, and the gums are involved in the process. This manifests itself as pain during chewing or when accidentally biting the mucous membrane. It happens that a wisdom tooth partially erupts, and one or more tubercles rest against the hood, injuring it. In this case, the inflammation of the gums near the wisdom tooth will have to be treated by removing the hood or the tooth itself. If the figure eight is healthy and does not interfere with the adjacent tooth during eruption, then the dentist makes an incision in the hood so that the tooth can erupt calmly.
How to treat inflammation of the hood and gums near the wisdom tooth at home? To do this, you will need to regularly rinse, rinse the mouth with antiseptic solutions and take analgesic and anti-inflammatory drugs for pain relief: Nimesil, Ketanov, Ibuprofen. If the hood is inflamed, you can rinse your mouth with weak solutions of the antiseptic Chlorhexidine, soda and saline solutions.