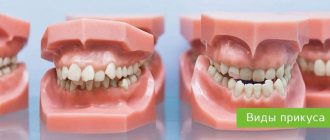
Occlusion is the relative position of the teeth relative to each other. In dentistry, this concept is called central occlusion, in which the dentition, when closing the jaws, has the maximum number of points of contact. There are different types of dental occlusion in humans; their types are usually divided into two main groups - correct (physiological) and incorrect (pathological).
The classification of types of occlusion includes several types of correct and incorrect occlusions. Most of them can be determined visually, by functional and morphological characteristics: the structure and symmetry of the dentition, the nature of the closure of the teeth, the usefulness of the function of the dental system. To accurately determine the nature of occlusion in orthodontics, various methods are used; one of the simplest and most effective is measuring the height and type of bite using a face bow, a tool that records the movements of the jaws relative to each other.
Check your bite
There are a number of objective parameters by which the correct, or in other words physiological, bite is determined:
- When closing, the teeth of the upper jaw come into contact with the lower teeth of the same name. The ideal arrangement of teeth is one in which the upper incisors overlap the lower ones by 1/3.
- clear contact of the chewing teeth: molars and premolars,
- no interdental spaces,
- the vertical axis of symmetry of the face passes exactly between the central incisors,
- no problems with diction, chewing and swallowing.
All types of occlusion in dentistry are divided into abnormal and physiological, and within these groups there is a more detailed classification.
What factors influence malocclusion? Is there any way to avoid the problem?
Typically, the bite develops in people between infancy and about 17 years of age. It may be incorrect due to the following reasons:
- genetic predisposition;
- bad childhood habits: pacifier sucking, bottle feeding, finger sucking;
- problems with the spine that have not been corrected;
- chronic ENT diseases (for example, adenoiditis);
- calcium deficiency, as a result of which bone tissue is not formed correctly.
It is important! If a child breathes predominantly through his mouth during sleep, play, or in a calm state, this is one of the signals of problems, which may include an incorrect bite. The faster occlusion pathologies are corrected, the less likely it is that not only dental problems will occur, but also ENT diseases.
Types of correct bite
Let's consider the physiological types of occlusion and their features:
- orthognathic bite - an ideal in which the same 1/3 overlap is observed, which was mentioned above;
- straight - there is no overlap, as in the previous version: the upper and lower incisors are in contact with the cutting edges. This increases the risk of tooth wear, but from the point of view of orthodontics, this case refers to the types of correct bite;
- biprognathic - all incisors are slightly inclined towards the lips, the dentition is pushed forward, but there are no occlusion disorders;
- progenic – the lower jaw is slightly protruded. The closure is tight.
These types of dentition bites do not affect either aesthetics or functionality and are therefore considered the norm.
Straight bite
Direct or orthogenic bite is distinguished as a separate type, since it is not a pathology, but is not the norm either. Experts have differing opinions on this matter. In direct occlusion, the upper incisors close tightly over the lower ones. This type is characterized by the following characteristics:
- absence of visual imbalances;
- no gaps between dental rows;
- general aesthetic appearance of the smile;
- there are no jaw elements protruding forward.
This smile looks almost perfect and can be considered a standard. But constant contact of the upper and lower incisors provokes a number of problems, in particular, intense wear of the teeth, and therefore the height of the crowns decreases.
Other problems of orthogenic occlusion are considered to be an increased risk of caries, dysfunction of the temporomandibular joint, and bruxism.
It is not always possible to determine the type of occlusion only by visual signs. Sometimes only a specialist can identify deviations from the norm. But in any case, occlusion anomalies must be corrected so that they do not lead to more serious consequences.
Incorrect or abnormal bite
The bite is considered incorrect when there are anomalies in the location of the teeth and occlusion disorders, as a result of which the functions of the dentofacial system are disrupted. All types of malocclusion, to a greater or lesser extent, lead to the destruction and loss of teeth, disorders of the TMJ (temporomandibular joint), as well as facial asymmetry. The consequences of an abnormal bite are discussed in more detail below. Orthodontic treatment in this case is necessary not so much for aesthetics, but for maintaining health.
Causes of pathological bite
Factors that provoke improper closure of teeth can be divided into congenital and acquired.
Congenital malocclusion is caused by a genetic mutation, hereditary predisposition or pathology of intrauterine development of the fetus. Such anomalies are more difficult to correct and are often an indication for surgical intervention.
Acquired factors can manifest their effects both in infancy and in adulthood. Thus, the main reasons for the development of malocclusion starting from early childhood are:
- birth trauma of the skull;
- improper latching on the breast when feeding;
- long-term breastfeeding or bottle feeding;
- chronic diseases of the endocrine and respiratory systems;
- lack of essential microelements in the diet, unbalanced nutrition;
- previous rickets;
- bad habits – finger or foreign objects (pencil) in the mouth;
- early tooth extraction, jaw injuries.
With age, factors such as errors in prosthetics, gum disease, the absence of most teeth, and pathologies of the motor joint of the jaw are added.
Types of malocclusion
The following types of malocclusion in adults are distinguished:
- distal bite
– the upper jaw protrudes forward. The upper incisors can be inclined forward, towards the lips, or backward, into the oral cavity. Often there is no contact between the front teeth of the upper and lower jaws, a sagittal gap and disocclusion (lack of closure) are formed. This type of dental malocclusion is visually manifested in a beveled profile and an upper lip hanging over the lower lip; a “double chin” may form;
- mesial bite
– the lower jaw protrudes forward. Here, a sagittal gap may also be observed and there may be no occlusion, or there may be only a slight overlap of the upper teeth with the lower ones. External signs of mesial occlusion are a protruding lower jaw and a massive chin; the lower lip is usually enlarged;
- deep bite
– the lower incisors are hidden by the upper ones by 50% or more. Depending on the stage, with a deep bite in adults, occlusion may be completely absent and inflammation of the tissues of the upper palate may develop due to injury to the lower teeth. With a deep bite, the so-called gummy smile is common, the lower third of the face looks inharmoniously small, and the chin is sloping;
- open bite
– when the jaws close, there is no contact between the upper and lower teeth. This type of bite causes significant impairment of chewing and speech functions; the facial muscles are usually overstrained and the lower part of the face is elongated;
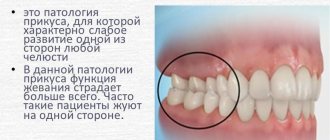
- crossbite
– vertical asymmetry of the jaws; When closing, an intersection of the dentition is observed. It develops when one of the jaws is underdeveloped and leads to noticeable asymmetry of the face.
The above types of dental malocclusions can be supplemented with dystopia - a malocclusion in which one or more teeth are positioned incorrectly, out of place.
Varieties and characteristics
When talking about what types of dental occlusion there are in adults in dentistry, there are two basic categories. In the first case, we are talking about correct occlusion, characterized by a harmonious relationship, natural facial contours, proportional shapes and symmetry of the midline and the junction of the frontal incisors. Such an anatomical structure not only ensures the aesthetics of a smile, but also allows you to fully realize the main tasks of the jaw region, which include food processing, as well as respiratory and speech functions. In turn, incorrect development is accompanied by more or less pronounced anomalies, often causing both physical and psychological discomfort to patients.
Physiological types of occlusion
Not only defective, but also natural conditions are subject to orthodontic classification. The ratio is divided into three varieties, the membership of which is determined by the indications of visual and hardware diagnostics.
Orthognathic
It is considered a reference because it provides optimal conditions necessary for the implementation of functional tasks. It is characterized by the overlap of the lower row with the upper by about a third of the height of the incisors, close contact when closing, as well as the absence of spaces and interdental gaps.
Biprognathic
A bite, the distinctive feature of which is the presence of a slight vestibular inclination, with a vector oriented towards the vestibule of the oral cavity. In this case, the frontal units retain points of contact, and the canines of the maxillary region are covered with antagonists for several millimeters.
Straight
It is diagnosed in cases when the cutting edges of the anterior incisors, which form the visible area of the smile, contact each other when closing, while the occlusion of the chewing molars remains correct. Eliminates the presence of empty areas, trema and diastemas, as well as signs of crowding.
The meaning of correct bite
The human body is a complex biological system in which each element affects the overall condition. Correct occlusal closure not only ensures the implementation of basic functionality, but also eliminates side effects such as joint pathologies, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, as well as heart and blood vessels. The asymmetrical position of the jaws leads to incorrect redistribution of the load, which ultimately forces the muscles to readjust, causing a change in posture, causing pain and dizziness.
When is the tooth relationship considered incorrect?
Factors indicating abnormal development include:
- Lack of contact between antagonists.
- Diction defects.
- Problems with chewing food.
- Distortion of facial features.
- Deformation of the jaws.
- The occurrence of pain syndrome.
The presence of even one of these signs is considered sufficient grounds for diagnosis. Practice shows that the earlier deviations are detected, the easier it is for the patient to eliminate them. Dental specialists use modern methods and technologies to determine the specifics of existing bite defects and draw up an optimal treatment plan that takes into account individual indications and recommendations.
Consequences of malocclusion
All types of malocclusion cause a complex of problems, both dental and more general:
- the development of caries and gingivitis is caused by ineffective oral hygiene. Even with regular and thorough brushing of teeth, due to malocclusion, hard-to-reach areas remain where food debris accumulates and bacteria multiply;
- accelerated tooth decay, abrasion and chipping of enamel - caused by uneven load on the teeth;
- disorders of the gastrointestinal tract that occur due to insufficient chewing of food;
- diseases of the respiratory system due to improper development of the dental system;
- problems with the TMJ, causing pain in the head, ears, back, overstrain of the facial muscles, bruxism, poor posture, etc.;
- violations of facial aesthetics: asymmetry, nasolabial folds, sagging skin of the chin and neck - these and other defects caused by malocclusion can be effectively corrected only with the coordinated work of a cosmetologist and an orthodontist.
Need some advice?
Enter your phone number and we will give you a free consultation
I want a consultation
*By making an appointment you consent to the processing of your data
What to do in case of malocclusion, and how to correct it in adults?
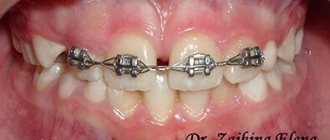
In modern dentistry, various designs are used, with the help of which even significant violations can be eliminated. Various braces systems restore the correct position of the dentition. In this case, treatment takes place according to an individually developed plan.
As a result, the external defect in the facial structure and the physiological disorder disappear - this normalizes the load on the teeth during the process of chewing food.
Correction can and should be carried out even in adulthood. The orthodontist will select an option that causes minimal discomfort and ensures the most effective restoration of normal occlusion.
How does the bite change when teeth are missing?
Injuries, advanced caries and other pathologies can lead to premature tooth loss. Their absence provokes not only a deterioration in chewing function, but also a significant malocclusion.
As a result, the functioning of the temporomandibular joints is disrupted, the skin of the face loses its tone and becomes covered with wrinkles.
If the bite is disturbed in the absence of an incisor, the load on the adjacent teeth increases, this can lead to their displacement with significant visual deviations.
In addition, due to the increased load, the risk of losing adjacent teeth and additional problems with biting hard foods increases. Visually, the lips begin to collapse, the nasolabial fold becomes deeper, and the corners of the mouth droop.
All this visually makes a person older
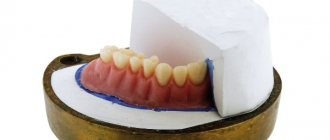
The bite in the absence of chewing teeth is also quickly disturbed: the cheeks visually sink, the skin tone is disturbed, and over time, atrophy and thinning of the bone tissue occurs. The solution to the problem of complete absence of teeth will be only comprehensive prosthetics with restoration of the entire dentition.
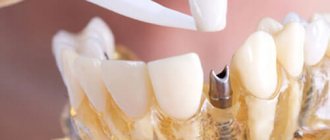
If only a few teeth are missing in the jaw, you can choose the appropriate prosthetic option - this is the installation of removable and fixed dentures, as well as modern implants implanted into bone tissue.
What does malocclusion affect?
Defects in the dental system negatively affect the condition of the entire organism - this has been repeatedly confirmed by scientists during observations and research.
Malocclusions affect both the appearance and functionality of the dentition, and the psychological state of a person. Defects in appearance provoke psychological complexes and self-doubt; they can become an obstacle to finding a partner and self-development.
We can list only a few facts about how dental occlusion affects a person’s appearance and health:
- Faster wear of enamel due to improper distribution of chewing load. This leads to increased sensitivity of the teeth, pain when exposed to heat and cold, exposure of the necks of the teeth and their premature loss.
- Pathologies of the temporomandibular joints. Their improper functioning can cause constant headaches and decreased performance.
- Aesthetic defects. It is easy to see what an incorrect bite affects : the proportions of the face are sharply distorted, wrinkles appear, and the smile is distorted.
- Functional disorders. Chewing function suffers; insufficient chewing of food provokes gastrointestinal diseases.
- Speech defects. She may become unintelligible, leading to communication difficulties and decreased self-esteem. Distortion of facial expressions is also possible.
- Breathing disorders. As a result, various pathologies of the nasopharynx and trachea may occur.
What else affects the bite of a person’s teeth?
If a crooked tooth scratches the inner surface of the cheek, over time this leads to inflammation and serious pathologies. Tooth enamel suffers from constant increased exposure, resulting in chips and other damage.
Methods for eliminating malocclusions
Orthodontic treatment using modern methods can eliminate even very serious disorders. The only exception is a declining bite: such a disorder occurs as a result of the natural grinding of teeth throughout life.
In this case, various prosthetic options are used to correct the irregularities, including the installation of new dental crowns made of durable materials or veneers.
The most common option is to correct the bite with braces in adults or use aligners. Special designs are made according to a personally developed model. The doctor determines the sequence of correction of the disorder and draws up an individual treatment plan.
Another option is to treat the bite with aligners made of transparent material. It lasts longer, but allows you to minimize discomfort.
, the orthodontist will conduct a full examination and determine all the causes of the violations. If it is possible to correct the bite without braces , he will prescribe appropriate therapy.
However, orthodontic structures remain the most in demand.
In the most difficult cases, surgery is required. Make an appointment with a specialist to find out exactly about the condition of your bite and get effective treatment.
Types of bite correction
Orthodontic and surgical types of bite correction depend on the nature of the pathology. In case of skeletal abnormalities, surgical intervention is necessary to correct the bite. In other cases, with dental anomalies, only orthodontic treatment is sufficient. In our clinic, we use aligners for this - invisible mouth guards that allow you to correct all types of dental bites in a person of any age. The technology allows you to achieve a guaranteed result within a predetermined period, and even before the start of treatment you will see what your smile will look like after the bite is corrected.
How to correct an overbite
Orthodontic treatment is carried out at different ages, but it is easier and faster in children. For adults, it takes longer to correct abnormal teeth alignment. The milk bite is also subject to correction. Although it will be replaced over time, permanent teeth grow in the place of their predecessors. Modern methods of bite correction are safe. They cause the patient only minor discomfort.
The doctor carefully studies the problem, assesses the condition of the oral cavity (if necessary, it is sanitized) and develops a treatment regimen. One of the following designs can be used in the process:
- Bracket systems. There are different types. They differ in aesthetic qualities, installation methods and prices. Such orthodontic structures will help correct almost any disorder.
- A mouthguard is a polymer product made from an individual impression. Easily removable, which is necessary for eating and brushing teeth.
- Records. The most effective designs for correcting primary malocclusion. They can also be given to adults, but this will not be the main treatment.
In complex cases (congenital pathologies), surgical intervention is required. Sometimes auxiliary techniques are used. Treatment of tooth wear in a “reducing bite,” in which dental tissue wears down with age, is carried out through prosthetics with crowns or veneers.
Remember! Correcting your bite is not only about getting a beautiful smile, but also a significant contribution to your health. Entrust the solution to your problem to a specialist. He knows how to check the bite for abnormalities. If they are identified, the correction will be carried out competently.
general information
In dentistry, types of occlusion refer to the position of the teeth in the mouth when the jaws meet. This contact is called occlusion. Central occlusion is when the teeth meet at most points, the head of the mandible is at the base of the articular tubercle, and the middle of the face should correspond to the passing line between the main incisors.
Normal (physiological) types of occlusion include:
- straight;
- orthognathic;
- biprognathic;
- progenic.
Each of them has its own characteristics. Violations can be determined at home. An exemplary closure is considered to be the option when the upper row of teeth overlaps the lower ones by no more than a third. The contact itself is tight. In addition, the shape and size of the teeth are taken into account. The upper jaw is characterized by a slight inclination towards the lips, and the lower jaw - towards the tongue.
Stages of formation
In order to understand what pathological bites are, you need to understand what factors provoke their appearance. Formation occurs from the moment of birth and lasts until adolescence (approximately 16 years).
It all starts with the appearance of the first incisors. The bite is determined after the replacement of milk teeth with molars. It is influenced by external factors and heredity. The most common reason is prolonged sucking of the nipple or objects that replace it. It is best to breastfeed the baby and wean it after one year.
The baby's sleep should be calm, breathing should be through the nasal cavity, and the mouth should be closed. Problems can arise due to cleft lip and palate (in the common sense, such a defect is called a “cleft palate”), adenoids, and so on. All this must be treated immediately and the situation must not be allowed to worsen. Sometimes the eruption of molars is delayed, and this causes the row to shift. As a result, an incorrect bite is formed.
Orthodontics is a branch of dentistry that deals with the comprehensive study of dental anomalies. It is this doctor who is able to determine the type of bite and prescribe corrective measures.