How a bite is formed What a correct bite looks like Types Definition of a bite Possible consequences Methods of correction
Teeth bite is the relative arrangement of the dentition when the jaws are completely closed.
The formation of the dental system begins in intrauterine development. By the 11th week, the fetus has jaw stripes. Almost all children are born with malocclusion. The lower jaw is moved back. Dentists call this phenomenon retrognathia. When a baby actively sucks, the muscles are trained. By 6-8 months with breastfeeding, and a little later, with artificial feeding, the lower jaw takes the correct position. For bottle-fed children, it is necessary to monitor the position of the body and the hole in the nipple. If the formula does not flow from the bottle, you have to make an effort to get it, the child’s tongue and jaw muscles receive sufficient stress and malocclusions can be avoided.
Stages of bite formation
The first stage is completed by the time teeth erupt. Then it is formed:
- Temporary bite
Period: from 6 months to 3 years
. Teeth are actively growing, their relationship in the jaw is changing. When all the teeth have erupted, the stage of a formed temporary bite begins. It lasts until the moment when baby teeth begin to be replaced by permanent ones. The number of teeth is 20. Their location is influenced by the child’s habits: thumb sucking, sucking a corner of a bedspread, long-term use of a pacifier. Most causes of pathologies appear at this age.
- Replaceable (mixed)
Period: 6-14 years
. The active growth of permanent teeth increases the bite and promotes changes in the position of the jaw relative to each other. The jaws are in the process of formation. This is the ideal time for orthodontic treatment.
- Constant
Once all the baby teeth have fallen out, the bite becomes permanent. Number of teeth 28-32. With the appearance of fangs, the bite increases again.
The final formation of the jaws is completed by the age of 21, but the movement of teeth continues throughout life. The teeth are worn down by the friction of the side parts, because of this their position in the jaw changes, although we do not notice it. Dentists call this process mesial movement.
Reviews
The formation of a permanent bite is a complex multi-stage process, the correctness of which is determined by many factors.
Its anomalies distort not only external aesthetics, but also complicate the work of many internal organs and their systems.
Orthodontic dentistry today offers several options for solving this problem for each patient.
You can share interesting and important information on this topic and express your opinion on the effectiveness of a particular treatment method by leaving a comment on this article.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter.
Tags permanent bite bite
Did you like the article? stay tuned
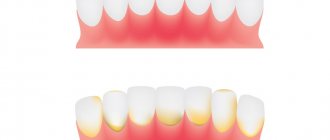
What does a correct teeth bite look like?
Physiological (correct) occlusion in humans is characterized by:
- adequate form of dentition. The top one looks like a semi-ellipse, the bottom one resembles a parabola;
- the upper incisors overlap the lower ones by ⅓ of the height;
- there is contact between all teeth;
- the lower teeth are vertical, the upper teeth are inclined;
- each tooth, except 4, has 2 antagonists (one opposite);
- the correct bite in the diagram is marked by the symmetry of the incisors;
- chewing teeth are in contact with each other.
Correct bite in adults has its own variations. All of them are considered a variant of the norm:
- Orthognathic
. The upper teeth slightly overlap the lower teeth, and all molars and premolars occlude. - Straight
. The upper teeth do not overlap the lower ones, but join with them. The lateral teeth meet well. - Physiological progeny
. The lower teeth protrude beyond the upper teeth, but contact is maintained. The lateral teeth close together without gaps. - Biprognathic
. The incisors of both jaws are inclined forward, with intact contact.
Row shape
A correct bite has the following characteristics:
- symmetrical contours of the lower facial region;
- dense (without gaps) arrangement of all incisors;
- symmetry in relation to each other of the frontal units of the jaws;
- overlapping the upper elements by 1/3 of the crowns of the mandibular incisors;
- increased in size (length and width) of the upper jaw arch.
These parameters indicate that the load during chewing is correctly distributed between the elements in the dentition.
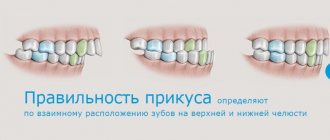
In orthodontics, there are 4 types of bites that do not require correction of the jaw position:
- Orthognathic. Aesthetically it is considered perfect, but in practice it is extremely rare.
All elements of the frontal region of the upper jaw only slightly overlap the mandibular units. This type of bite is optimal for complete swallowing and chewing of food. - Progenic. The lower elements are slightly moved forward relative to the upper ones. Such a bite is borderline between deviation and normal.
- Straight . When the incisors of each jaw have closure with cutting edges. With this ratio, the enamel is quickly erased.
- Bioprognathic. Externally, the characteristics are very similar to the orthognathic one, but with a slight difference - the units of both jaws have a slight forward tilt.
Other types of occlusion in dentistry
There are 3 large groups of bites.
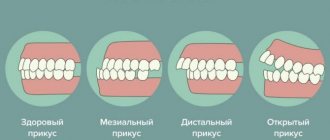
- Normal
(physiological). These bites have several variations, but the teeth are closed, the jaws are in the correct position, and the teeth are symmetrical along the incisors. - Anomalous
. Congenital defects caused by harmful effects on the fetus during pregnancy or genetic disorders - Pathological
. Defects acquired after teething as a result of disease, missing units, or displacement of teeth.
In life, the last two concepts are often mixed and replace each other. Based on the relationship between teeth and jaws, the following types of bite are distinguished:
Deep
The upper teeth cover the upper ones by more than ⅓. The contact between the teeth is broken. This leads to impaired chewing function, abnormal enlargement of the upper jaw, and disruption of the anatomical structure of the face. The second name for this defect is traumatic. As a result of pathology, the functioning of the temporomandibular joint is often disrupted, the mucous membranes are injured, and the enamel is pathologically erased. This is the most common pathology.
Open
The teeth do not close completely. The defect can be frontal or lateral. This pathology is characterized by impaired diction, chewing, and swallowing. Mouth breathing is observed, hence drying out of the mucous membrane and frequent caries.
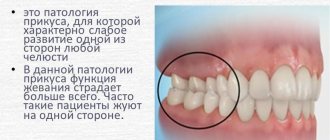
Distal
With this defect, the upper jaw is strongly pushed forward. The front teeth do not occlude, and the occlusion of the rear teeth is broken. Characterized by problems with breathing, chewing, and swallowing. Patients complain of joint pain, frequent caries, and periodontal disease.
Mesial
When the lower jaw is pushed forward, they speak of progeny or mesial occlusion. This jaw bite pathology is accompanied by diastemas (large gaps between the front teeth) or trema (gaps between any teeth). Often patients have crooked lower teeth, they are crowded, and there is increased deposit of tartar.
Crossbite
Some units overlap each other. Difficult to treat, surgical intervention is often used. It is characterized by facial deformation, speech defects, disruption of chewing function and the functioning of the TMJ. Patients complain of constant biting of the cheeks and tongue.
All pathological forms of bites in orthodontics are recommended for correction with removable (for baby teeth) and non-removable structures (braces), and aligners.
Correction Methods
In children, pathology is corrected much easier and faster than in adults. This is explained by the fact that with a deciduous bite, the bone structure is not yet fully formed and can be easily corrected.
It is for this reason that children under 6 years of age undergo correction using gentle methods - they are offered to wear orthopedic devices, vestibular plates and perform myogymnastics.
To correct the bite in adults, complex therapy is carried out, including wearing orthodontic devices (removable or fixed), and even surgical procedures.
The choice of treatment method depends on a number of factors:
- The patient's ability to properly and regularly care for the orthodontic appliance. Not all people are ready and have the opportunity to care for structures every day, so a specialist offers them an easy-to-care product, for example, mouthguards.
- Defect complexity. Minor deviations can be easily corrected with trays or plates. Complex defects are corrected with braces or surgery.
- Patient's age. Anomalies of a fully formed bite take much longer and are more difficult to correct.
- Conditions of the oral cavity. In addition to the fact that the doctor has to treat the abnormal bite, he needs to carry out a number of manipulations, namely, to cure carious units, existing inflammation, etc.
- The patient's financial condition. Dentistry today can offer effective methods and devices that are low cost.
- Social status of a person. Patients who lead an active lifestyle are usually offered removable designs with minimal wearing time. Those of them who, due to their professional activities, communicate a lot, are offered less noticeable products.
Types of devices
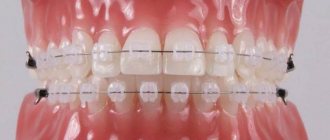
Braces
The design consists of small brackets connected to each other by an arc. Each bracket is fixed to the teeth with dental glue, and the pressure on each unit of the row is controlled using an arc.
Braces are considered an effective device that is customized for each patient. They help fix defects of any complexity.
The duration of the correction course is from 6 months. up to 2 years.
Orthodontic appliances
These are alternative designs to braces that eliminate bite defects:
- Aligners. Their wearing is justified only for minor anomalies.
For example, when units are crowded or some of them are displaced. To obtain the required result, the device must be worn for 20-22 hours. The total duration of treatment depends on the severity of the pathology and can reach up to two years. - Trainers. Special design made of transparent plastic.
The correction takes place in 2 stages. Initially, the patient wears an elastic product, and then it is replaced with a more elastic and durable one. Typically, wearing them is recommended to combat bad habits, correct pronunciation and normalize respiratory function. The approximate duration of treatment is 1 year.
Surgery
It is carried out only when other methods of correcting the bite do not produce any effect.
Indications for intervention are the following conditions:
- pathology accompanied by problems with chewing and speech functions;
- dysplasia (underdevelopment) of the chin;
- severe facial distortion;
- defects of a genetic nature;
- serious maxillofacial injuries.
Determination of dental occlusion
Often problems with bite are obvious, but it also happens that everything looks normal on the outside, but there is a problem. Therefore, it is better to entrust the determination of the bite to the dentist. They use special methods to determine correct or incorrect bite and prescribe treatment.
Diagnostics include:
- Clinical examination
The orthodontist collects anamnesis, conducts a general examination and examines the oral cavity and nasopharynx. They examine breathing, speech formation, swallowing, chewing, biting.
- X-ray examination
A panoramic X-ray or CT scan allows you to identify skeletal abnormalities, see the exact location of the teeth, the condition of the roots, and bone tissue.
- Biometric test
The doctor examines the jaws, takes and records all measurements.
- Functional test
Examination in a stationary position, while talking, opening the mouth in the lateral and frontal projection.
It is impossible to put the jaw back in place on your own, but the sooner the intervention begins, the better the result. It is very difficult to restore the correct position of teeth after 25 years; it is better to do this while the bite is forming.
Price
The cost of the entire course of correction depends on the complexity of the defect and the technique used to correct it.
The price for placing braces often reaches 140 thousand rubles. The exact figure depends on the material from which the device is made. The average cost of products looks like this:
- metal - from 4 thousand rubles;
- ceramics - from 30 thousand rubles;
- sapphire - from 50 thousand rubles.
The price is also affected by the type of braces:
- self-regulating - from 45 thousand rubles;
- lingual - more than 110 thousand rubles.
Cost of placement of other corrective devices:
- aligners - from 45 thousand rubles;
- kapov - about 60 thousand rubles;
- trainers - from 5 thousand rubles.
The cost of surgical intervention starts from 50 thousand rubles. and also depends on the complexity of the problem and its extent.
Important! The final cost will depend on the pricing policy of the dental clinic, its status, location, qualifications of the specialist and the volume of preliminary procedures that are always carried out before the start of treatment.
Consequences
The influence of bite on the condition of the dental system and the entire body is enormous.
Bite pathologies lead to:
- Loss of teeth. Uneven chewing load leads to cracks and chips. Bacteria penetrate through the damaged enamel layer, affecting periodontal tissue. Periodontitis develops. Teeth become loose and fall out. The risk of caries in such cases is higher than in people without defects.
- Disorders of the temporomandibular joint (TMJ). It begins to click, hurt, and in severe cases, dislocation is possible.
- Due to crowded teeth, plaque and tartar quickly form, which provokes gingivitis and periodontitis.
- Insufficient contact between teeth leads to food being poorly chewed. As a result, problems arise with the gastrointestinal tract.
- Oral, impaired breathing causes diseases of the respiratory system.
- The position of the jaws affects posture. An abnormal movement of the jaw forward shifts the center of gravity, the position of the neck changes, the chest collapses, and the person begins to stoop. Muscle tone is impaired and back pain begins.
- An incorrect bite distorts facial features and disrupts its symmetry.
Anomalies of the jaws affect the psychological state. The person withdraws into himself and avoids company. Depressive states are common.
Orthodontic treatment restores physical and emotional balance and helps improve self-esteem.
Prevention measures
In order for the formation of the bite to proceed correctly, you need to adhere to the following recommendations:
- Eat a balanced and healthy diet, constantly supplementing your daily diet with vitamins and important microelements.
- Eliminate bad habits.
- Treat dental diseases in a timely manner.
- Regularly engage in the prevention of conditions caused by calcium deficiency or impaired calcium metabolism.
- Take good care of your oral cavity every day.
The video provides additional information on the topic of the article.
Other pathologies
The formation of a pathological permanent bite can occur due to a large number of reasons.
Dentists identify the main factors influencing the condition of teeth during their formation:
- disturbances during the formation of the rudiments of milk or permanent teeth due to a lack of calcium in the body of a pregnant woman or child;
- heredity;
- pathologies of intrauterine development or chronic diseases;
- presence of bad habits , for example, prolonged sucking of a pacifier or fingers, biting nails, resting the chin on the palms of the hands;
- mechanical injury to the jaw.
Experts in the field of orthodontics note that the formation of an abnormal permanent bite causes not only disturbances in the aesthetics of the appearance of the oral cavity, but also numerous functional disorders .
The most common of them are the following diseases:
- disturbances in the functioning of the digestive system as a result of inadequate chewing of food;
- inflammation of the gum tissue due to injury;
- pathological abrasion of the enamel due to the incorrect relationship of the opposite elements of the jaw rows;
- loosening of teeth , characteristic in cases of uneven distribution of chewing load;
- breathing and diction problems.
In the absence of timely treatment, acquired diseases will progress, leading to new severe consequences for the body.
What is Costen's syndrome and the symptoms accompanying the pathology.
From this publication you will learn how the pacifier affects your child’s bite.
Here https://orto-info.ru/zubocheliustnye-anomalii/chelyustey/krivaya-ne-prigovor.html all the most important things about methods for correcting a crooked jaw.