Causes of pain in the face and head
Headaches that radiate to the face can have different origins. In some cases it is primary (migraine, cluster pain, tension headache), in others it is one of the symptoms of diseases of the nervous system, musculoskeletal system, heart and blood vessels. It is important to take into account the exact localization of painful sensations, their nature and intensity, and the conditions of occurrence.
Trigeminal neuralgia
The trigeminal nerve is a paired nerve and represents the fifth pair of cranial nerves. In the temporal region it is divided into 3 main branches: the ophthalmic, maxillary and mandibular nerves. They provide facial skin sensitivity, motor activity of the facial and masticatory muscles. When the trigeminal nerve becomes inflamed or damaged, an acute headache begins, which spreads along the nerve fibers. It is so intense that during the period of exacerbation of trigeminal neuralgia, patients cannot touch their face, eat food, turn or tilt their head.
The cause of neuralgia is inflammation of the nerve or its mechanical damage. There are also several factors that can contribute to the development of acute pain:
- viral respiratory diseases, as well as herpes virus infection;
- neoplasms in the cerebellopontine region of the brain;
- dental diseases, including stomatitis, periodontitis and others;
- acute purulent inflammation of the paranasal sinuses (sinusitis);
- atherosclerosis is a disease in which arterial blood flow deteriorates and the supply of oxygen to brain tissue decreases;
- bruises, injuries in the facial area, which are accompanied by damage to nerve fibers.
Headache with trigeminal neuralgia can spread to any part of the face. It is sharp, throbbing, and can be confused with pain caused by dental problems. In some patients, the disease is chronic and worsens at regular intervals. More often this happens in the winter and in the off-season - inflammatory reactions are caused by a sharp drop in temperature and the effect of a viral infection. During an attack, additional symptoms are also felt: increased lacrimation in response to bright lighting, cold weather and decreased sensitivity of the facial skin, involuntary contractions of the facial and masticatory muscles.
In most cases, treatment of trigeminal neuralgia is carried out with medication. The doctor prescribes antibiotics, antiviral and anti-inflammatory drugs. To make you feel better, you will need painkillers. Some patients require surgery to destroy the trigeminal nerve root or remove pathological formations that exert mechanical pressure on the nerve. Physiotherapy is also useful as treatment and rehabilitation.
Cluster pain
Main article: Cluster headaches
Cluster headaches are the least common type. They are characterized by a very high degree of intensity and do not have an exact cause. An attack consists of a series of pain sensations in the area of the projection of the brain onto the human skull. It is so acute that the person cannot continue to carry out daily tasks during this time, and conventional over-the-counter analgesics are ineffective.
Cluster headaches have several features:
- first appears in adulthood, most often from 20 to 30 years;
- has no warning symptoms, begins abruptly, at any time of the day;
- extends only to one half of the head;
- accompanied by deterioration of vision, constriction of the pupil, increased heart rate, redness of the skin;
- the period lasts from several days to several months - during this time the patient experiences on average 1-3 headache attacks per day, often at the same time.
Cluster pain is more common in women . There is no hereditary predisposition, since the disease in most cases is found in only one family member. After the end of the exacerbation period, a long-term remission is observed. It can last up to 3 years, during which the pain does not bother the patient. A seasonal course of the disease is also possible if it appears only at certain times of the year.
Migraine
Main article: Chronic migraine
Migraine is one of the types of primary headaches. It is often one-sided and affects only one half of the head. Painful sensations can be of varying degrees of intensity, but most often acute. The exact cause of migraine is unknown. It often develops in response to factors such as changes in weather and atmospheric pressure, stress and emotional tension, intense physical activity, disruption of the daily routine, as well as smoking and frequent alcohol consumption, poor diet, and hormonal changes.
Migraine is a one-sided headache. There are several theories of its origin - doctors explain its appearance by vascular, nervous, and hormonal disorders. Migraine can occur in different ways, but the classic form includes several stages:
- The initial stage is prodromal. It begins a few days before a headache attack. During this period, a person’s mood often changes, irritability and fatigue appear, concentration and performance deteriorate. This symptom complex does not occur in all patients, but its appearance accurately indicates the onset of migraine.
- Aura (Main article: Migraine with aura) is the period several hours before an acute headache. It is typical for migraine, but also does not necessarily occur. Its cause is considered to be spasmodic contraction of brain vessels and deterioration of its blood supply. The aura is manifested by increased sensitivity to sunlight, the appearance of bright circles and dark spots before the eyes, as well as hearing impairment and severe fatigue.
- The immediate attack of headache lasts several hours, but in some patients it may not stop for up to several days. It is acute, one-sided, and intensifies in the presence of external stimuli (bright light, loud sounds). Painful sensations are concentrated in one half of the head and can spread to the face and neck. Symptoms such as lacrimation, nausea and vomiting, and dizziness are also typical.
- Resolution stage – lasts 1–2 days. Some patients feel better immediately after the headache ends, but resolution may be slow. Symptoms include weakness, decreased alertness, and increased sensitivity to bright lights and loud noises.
According to statistics, migraines are more common in middle-aged women. To treat it, a set of medications is prescribed that help reduce pain and shorten its duration. If attacks occur frequently and do not stop for 3–5 days or more, hospital treatment may be necessary. The procedures are aimed at preventing complications: dehydration, cerebral edema, seizures, heart attack and stroke.
Somatogenic facial pain
Pain in the face and head can be somatogenic (secondary), that is, associated with diseases of other organs and systems. They are less intense than cluster pain, migraine and facial neuralgia, but also affect performance and can cause complications. Common causes of pain in the face are dental diseases, inflammation of the paranasal sinuses, and ophthalmological problems.
- Toothache – often spreads to the scalp, skin, muscles and nerves of the face. It is often associated with inflammatory processes and dental caries. Symptoms such as pain in the jaw joints, pain when chewing, or eating cold or hot food and drinks also occur. To make you feel better, consultation with a dentist, medication, and, if necessary, surgery are recommended.
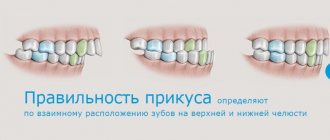
- Joint pain is another type of somatogenic pain. They are often triggered by arthritis or arthrosis of the temporomandibular joint, its deformation or injury. In addition, soreness may be a sign of a malocclusion, tooth loss, or discomfort when wearing dentures.
- Inflammation of the paranasal sinuses is a group of dangerous diseases. The sinuses (sinuses) are cavities formed by the bones of the skull. Normally, they are empty, filled with air and necessary for proper breathing. Their inflammation is accompanied by the appearance of aseptic or purulent contents, an increase in body temperature, a sharp deterioration in health and nasal congestion. The most common type of sinusitis is sinusitis. It develops as a result of hypothermia, the proliferation of a viral, bacterial or fungal infection, head injuries and bruises.
- Eye diseases also cause headaches. When diagnosing pain, glaucoma may be detected - increased intraocular pressure. This is a dangerous condition that requires immediate treatment. Increased pressure causes compression of blood vessels and nerves, and over time can lead to poor vision and even complete blindness.
If a patient complains of pain in the face and head, a comprehensive examination is prescribed. The scheme will include general diagnostics, as well as consultations with specialized specialists: ophthalmologist, otolaryngologist, dentist and others.
Other reasons
Soreness is a symptom of a number of disorders that do not necessarily indicate dangerous diseases. Headaches can occur periodically in a healthy person, and then go away on their own or after taking painkillers. Doctors identify a number of reasons that can cause deterioration in health:
- stress, nervous tension;
- sleep disturbances caused by insomnia, moving to regions with a different time zone, irregular schedules, or working at night;
- poor nutrition, an abundance of fatty foods, flour products, spices and sweets in the diet;
- intense physical activity;
- sudden changes in weather, temperature or atmospheric pressure;
- hormonal changes.
Doctors recommend calling for a full examination if headaches continue for several days or more. Also dangerous are acute pains that affect performance and are accompanied by additional symptoms: nausea, vomiting, impaired coordination of movement, and memory impairment.
Diagnostics
Pain when opening the mouth requires, first of all, diagnosis; only an experienced doctor can make a correct diagnosis. There may be several reasons for this pathology, and the doctor’s task is to correctly diagnose the disease, since the treatment method will depend on this. During the consultation, the doctor examines the patient and finds out, the patient’s posture is also assessed, and how difficult the functions of swallowing, chewing and breathing are.
During the examination, the doctor will also pay attention to the location of the pain, whether it manifests itself on one side or is bilateral. Based on the results, an additional examination will be prescribed: x-rays, manual functional analysis and other procedures.
An individual and comprehensive approach is the priority of the Orto-Artel clinic. Therefore, to establish the root cause of the problem and its further solution, consultations with specialists such as:
- osteopath;
- neurologist;
- kinesiologist;
- psychologist.
The joint efforts of dentists and general specialists will make it possible to make the correct diagnosis.
If your jaw hurts when chewing or opening your mouth, then in most cases, the pain is a sign of inflammation. Therefore, often, when ear pain or tinnitus is detected, it is associated with purely “ear” problems. And with pain localized in the area of the temporomandibular joint, doctors who do not have adequate experience in diagnosing and treating TMJ dysfunctions usually make a standard diagnosis - “arthritis of the temporomandibular joint.”
The diagnosis of arthritis in medicine means inflammation of the joint, but this formulation does not include information about the specific causes of such inflammation. Therefore, making such a diagnosis is a very general formulation. It's a very general diagnosis. Non-binding. Does not reflect the root cause of inflammation. In fact, it is only a statement of the fact of inflammation in the joint.
But the causes of this inflammation can be very different, and accordingly, treatment, depending on the causes of inflammation, will differ significantly in different patients, even those who have common symptoms - pain in the jaw joint when opening the mouth. Or ear pain. Inflammation is the body's normal response to injury. And injury can be caused by various factors.
Diagnostics is the first and key step in treating pain in the jaw when opening the mouth. Do you want to know why it’s impossible to do without diagnostics?
In the case of joints, most often the injury will be mechanical. It occurs when the bones that form a given joint (in particular the head of the mandibular condyle) exceed their normal range of mobility. And they overstretch the joint capsule, ligaments and muscles associated with this joint. Every person has encountered this at least once in their life. Because this process has a well-known name - joint dislocation.
The dislocation may be acute. This is when it happens sharply and suddenly. In the case of the temporomandibular joint - with sudden opening of the mouth (for example, when yawning). Or due to a blow to the lower jaw area.
The dislocation can be chronic. This is when the bones that form a joint regularly (constantly, for a long time) exceed the amount of their normal mobility. In the case of TMJ, this happens when the bite is incorrect. Then each closure of the teeth will direct the lower jaw into the “wrong” position. And it is chronic injury that is more dangerous. Because, unlike an acute injury, a gradual stretching of the capsule and ligaments of the joint occurs, which camouflages (hides) the painful manifestations of the problem. After all, pain will occur in the later stages, when the process has already gone quite far, which often leads to untimely (belated) seeking medical help. Chronic injury is the cause of 90% of all TMJ problems. And it refers to functional problems (dysfunctions). When the daily, seemingly normal functioning of this joint leads to its gradual wear and tear and, ultimately, destruction.
The generally accepted traditional allopathic approach to the treatment of TMJ pathology with a banal (simplified) diagnosis of arthritis, and the resulting treatment (all this anti-inflammatory therapy, using pills, physiotherapy and other “traditional” methods) is erroneous and ineffective, since it does not eliminate the root cause of the problem .
Treatment in installments
The Orto-Artel clinic offers installments for the entire process of treating any disease. Personal conditions are considered on an individual basis.
Find out more
or call 8 (495) 128-11-74
In addition, I would like to note that pain in the jaw when opening the mouth is not always associated with problems in the TMJ (just as pain in the ear or tinnitus is not always associated directly with “ear” problems). Therefore, to differentiate the cause of the problem, to determine the true source of pain, consultation and assistance from a qualified specialist who understands these subtleties is necessary.
Diagnostic methods
For effective treatment, it is important to determine the exact cause of the headache and facial area. It is impossible to carry out diagnosis on your own, since it requires the use of precise equipment and laboratory tests. The complex may include the following activities:
- blood tests - prescribed to determine inflammatory processes, bacterial infections and various diseases of the heart and blood vessels;
- X-ray is one of the examination methods for suspected diseases of the teeth and temporomandibular joint;
- MRI, CT scan of the brain;
- ophthalmological examinations aimed at diagnosing vision and measuring intraocular pressure;
- assessment of the condition and conductivity of the vessels of the neck and head - carried out by radiography using a contrast agent.
The Clinical Brain Institute offers headache diagnostic programs. The set of measures is selected individually, based on the results of the inspection. To obtain accurate data, it is important to notify the doctor about all conditions for the occurrence of pain, their nature and intensity, and also undergo the prescribed examinations.
Treatment of headaches and facial pain
The treatment regimen for headaches and pain in the face is selected individually. It will include measures to eliminate the underlying disease, as well as to relieve symptoms. Based on the diagnostic results, the doctor may prescribe the following methods:
- drug treatment - may include anti-inflammatory and painkillers, antibiotics, drugs to improve cerebral circulation;
- physiotherapy – carried out to stimulate blood circulation and innervation in the face and head;
- diet for blood vessels - includes simple foods, with a minimum amount of fried foods, animal fats, fast food and spices;
- surgical intervention - most often prescribed for mechanical compression of nerves and blood vessels, in the presence of neoplasms and dental diseases, as well as for clearing the contents of the paranasal sinuses.
Doctors at the Clinical Institute of the Brain will select appropriate treatment tactics based on the results of a general examination. For most patients, it is enough to take medications, follow a diet and adjust their daily routine to improve their health. However, for some diseases surgical intervention is indicated.
Blepharospasm
The orbicularis oculi muscle surrounds the human eye socket on the face. Thanks to it, a person can close his eyelids and close his eyes. A condition in which involuntary contraction of this muscle occurs is called blepharospasm.
The main causes of blepharospasm:
- Facial paraspasm. This disease usually occurs in older people. It is believed to be caused by an imbalance between parts of the nervous system. Blepharospasm is one of the manifestations of facial paraspasm. The second possible manifestation is oromandibular dystonia - grimaces, trembling of the lower jaw, its involuntary movements. Sometimes blepharospasm is combined with oromandibular dystonia;
- Parkinson's disease;
- Multiple sclerosis;
- Meningitis, meningoencephalitis;
- Atherosclerosis of cerebral vessels, cerebrovascular accidents;
- Poisoning with toxic substances and certain medications;
- Inflammatory diseases of the eye (keratitis, conjunctivitis), nose, paranasal sinuses, teeth. As a result of the spread of the inflammatory process, the branches of the trigeminal nerve are irritated and reflex blepharospasm occurs.
Typically, a sick person begins to blink quickly, gradually the tension of the orbicularis muscle increases, and the eye narrows. At times, strong involuntary squinting occurs. Because of this, the eye cannot fully perform its functions and severe inconvenience occurs.
With such symptoms, you need to visit an ophthalmologist and neurologist. After the examination, the doctor may prescribe an electromyography or MRI of the head. It is important to identify the disease that led to the development of blepharospasm - this will help to correctly prescribe treatment.
Treatment
- Treatment of the underlying disease;
- Sedatives;
- Physiotherapy and reflexology.
- Drugs that improve cerebral blood flow and nervous system function;
- To reduce the tone of the orbicularis oculi muscle, a neurologist may prescribe botulinum therapy.
The greatest chances for a favorable outcome and complete restoration of impaired functions are in cases where proper treatment is started on time. If the first symptoms occur, do not delay visiting a doctor.
It is also worth remembering that sudden facial asymmetry is one of the symptoms of a stroke. This is a dangerous condition. It requires immediate hospitalization in a hospital.
Prevention methods
Timely prevention is the key to good health at any age. It is important to form the right habits that will have a positive effect on the health of the heart and blood vessels, teeth and other organs. Doctors recommend:
- eat right, get enough vitamins and microelements;
- give up bad habits - smoking and drinking alcohol affect the condition of blood vessels;
- normalize your daily routine and devote enough time to rest;
- carry out moderate physical activity to train the heart muscle.
At the Clinical Brain Institute you can undergo an accurate and high-quality diagnosis of headaches and pain in the face. There is modern equipment here that can be used to determine the causes of pain. Doctors will also select an effective treatment regimen for use at home or in the hospital of our center.
Prevention
The main preventive measure to prevent the manifestation of severe pain in the jaw is a timely visit to the doctor. If any minor deviations occur, you should immediately consult a specialist. Early identification of the cause of a pathology that begins to develop is the first step towards solving the problem.
The patient should already be alerted by the appearance of unpleasant sensations and discomfort in the form of:
- deterioration of jaw mobility;
- crunching while yawning or chewing food;
- pain when opening the mouth;
- noise or pain in the ears;
- frequent headaches;
- grinding or creaking of the jaw;
- painful sensations in the neck and back.
Such symptoms are a reason to undergo diagnostic measures and, after diagnosis, receive the necessary treatment.