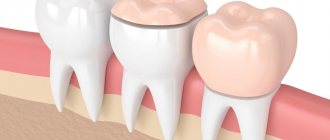
There are certain criteria by which the correct bite in children is assessed. Thus, it is considered normal when the upper row of teeth overlaps the lower row by about 1/3. Malocclusion in a child is any disturbance in the occlusion of the upper and lower rows of teeth, which is fixed when the jaws are completely closed.
Considering defects in tooth growth as a cosmetic problem is fundamentally wrong. In this article we will talk not only about the types of pathologies in children, but also about their complications, treatment methods at different ages and methods of prevention.
Physiological bite
A bite is a type of closure of the upper and lower teeth with each other (occlusion). Normally it should be like this:
- the dental arch of the lower jaw is located behind the anterior one;
- the upper dentition overlaps the lower one by no more than 1/3;
- the central axes of the lower and upper jaws coincide with each other;
- The upper and lower chewing teeth are in contact with each other by their biting surfaces.
There are no gaps, no crowding of teeth - this is the ideal type, which orthodontists call orthognathic.
Formation occurs in stages:
- From birth to 6 months. From the moment the first incisors erupt, the period of a temporary set of teeth—deciduous teeth—begins.
- From 6 months to 3 years. This stage is characterized by rapid growth of the child's jaw bones. By the end of this period, on average, 8 incisors and molars and 4 canines have erupted.
- From 6 to 12 years. There is a gradual replacement of the milk kit with a permanent one. When a child has both primary and permanent teeth, it is called a mixed dentition.
- From 12 to 15 years. The final stages of formation. The final development of the skull occurs under the influence of sex hormones during puberty.
Partial bracket system “2x4”
Metal bracket system 2x4
Ceramic bracket system 2x4
This system is specially designed for treating children aged 8-9 years. Braces are fixed only on the permanent incisors and first molars, which allows you to quickly correct the position of the front teeth and create space for the lateral group of teeth (which begin to change from temporary to permanent from the age of 9).
Pros of partial braces:
- the ability to correct the position of the front teeth even in the most difficult situations;
- speed of treatment (up to 8-10 months);
- the ability to choose the most invisible braces (ceramic).
An important factor during such treatment is maintaining careful oral hygiene using special toothbrushes and brushes.
Examples before and after treatment
Before treatment
After treatment
Before treatment
After treatment
Types of violations
Orthodontists distinguish several types in which unsatisfactory occlusion is observed. There are such malocclusions:
- Distal. The lower jaw is shifted forward, the face takes on an overly surprised or perplexed expression.
- Mesial. The mandibular bone is significantly shifted forward relative to the upper one or the upper one is underdeveloped (has a reduced size).
- Cross . The closure occurs like scissors - the teeth in certain areas close in the opposite ratio.
- Deep. The upper dentition completely covers the antagonists.
- Open . In some areas there is no occlusion; even when the jaws are completely closed, a gap remains.
General overview
Occlusion is a medical term used to describe the relationship of the dentition. As part of the diagnostic measures, the orthodontist analyzes the general condition of the masticatory ligaments and muscles, assesses the correct functioning of the temporomandibular joint, as well as the position of the units during tight clench of the jaws. The final characteristic is determined by the clinical picture, which allows one to classify the current development and determine the need for treatment.
Causes
The reasons why children develop malocclusion can be of two types: congenital and acquired.
Congenital ones include:
- Hereditary factor. If one or both parents have similar problems, the child is likely to inherit them.
- Difficult pregnancy. Various diseases of the mother, taking heavy medications, severe gestosis can lead to disruption of the formation of the alveolar processes.
- Mother's bad habits. Excessive alcohol consumption, smoking, drugs, and inhalation of toxic substances can cause various disruptions in the development of the dentofacial apparatus.
- Injuries during childbirth. This includes various fractures during passage through the birth canal
Purchased:
- Bad habits. Sucking fingers and other objects, and lip sucking often cause orthodontic disorders.
- Sucking a pacifier. Prolonged pacifier sucking and bottle feeding.
- Diseases of the musculoskeletal system. The dentofacial apparatus is part of this system, so its pathologies negatively affect the development of the dentition.
- Impaired nasal breathing due to anatomical features or diseases.
- Other diseases. Most often these are pathologies such as diabetes mellitus or central nervous system dysfunction.
- Improper diet – lack of solid food in the daily menu.
- Premature tooth loss due to injury or lack of dental treatment.
Preventing the development of malocclusion in children
The success of orthodontic treatment depends on a number of factors. One of the most important is early diagnosis and timely treatment. In addition, in most cases there is a real opportunity to prevent disturbances in the development of the dentofacial apparatus.
Orthodontists at the Amel Dental dental clinic recommend following the following preventive measures:
- During pregnancy, carefully monitor the health of the expectant mother;
- observe the technique and duration of breastfeeding;
- eliminate in a timely manner the causes of defects (for example, plastic surgery of a shortened frenulum of the tongue, lips);
- use only orthodontic pacifiers and bottle nipples; after 1-1.5 years, wean the child off these devices;
- monitor the condition of the ENT organs, the baby’s nasal breathing, ensure prevention and timely treatment of otolaryngological diseases;
- monitor the condition of the oral cavity, regularly visit the dentist, treat caries of baby teeth in a timely manner;
- engage in physical exercises with the child to develop correct posture, make sure that the child does not slouch;
- master with your child and regularly perform myogymnastics.
Malocclusion in a child is a problem that, in addition to cosmetic defects, carries the danger of diseases of various organs and systems in the child’s body, so it is very important not to miss the moment and correct mistakes in time. If you suspect your baby has problems, you should definitely make an appointment with an orthodontist. Even if the child’s teeth are growing normally and there are no visible deviations, he needs to visit the dentist every 3 months in order to ensure timely dental treatment if necessary.
How to determine
In order to identify a malocclusion in your child, you can focus on a number of signs that not only specialists, but also parents can see. The main ones:
- asymmetry of the face from the front (between the right and left halves, especially in the area of the nasolabial triangle and chin);
- extra or missing teeth;
- untimely teething or change of dental sets;
- crowded dentition;
- excessive tension of the chin and lips during swallowing;
- frequent snoring or grinding in sleep;
- constantly slightly open mouth in the absence of nasal congestion;
- poor posture;
- frequent injuries to the tongue or cheeks.
Complex.
It implies a set of corrective techniques to achieve a better result.
Myotherapy and surgery are used infrequently. In the first case, the method is limited by the patient’s age and is used for children 3-5 years old, when the emphasis is on the proper development of masticatory and facial muscles. Surgical techniques are indicated for extremely serious pathologies - when other methods have not helped, and the lack of correction is fraught with serious health consequences.
Most often, orthodontists use an integrated approach - a combination or alternation of hardware techniques.
Diagnostics
Even if parents carefully monitor all the signs of malocclusion in their child, they will not notice them at the initial stage. This can only be done effectively by a dentist, to whom the boy or girl should be taken for preventive examinations every six months. This period is enough for the bite to begin to change, but not to deform significantly. Such examinations can begin at the age of two.
If problems are detected, the dentist will refer the patient for a consultation with a pediatric orthopedist. A visit to an otolaryngologist, speech therapist, or periodontist may also be necessary.
Comprehensive diagnostics may include the following components:
- panoramic image (orthopantomogram);
- X-ray of the skull in a lateral projection (teleroentgenogram);
- photo of the face in front and profile;
- making a model of the dentition based on a cast;
- computed tomography of the temporomandibular joint;
- myography of facial muscles.
All data obtained will allow us to determine the size of the problem and develop a treatment regimen.
Bite pathologies are present in approximately 80% of the world's population. For some people, incorrect alignment of the dentition causes serious functional (difficulty in chewing, pain when opening the mouth, clicking in the temporomandibular joint) and aesthetic disorders, while for others the problem is less pronounced. In any case, an incorrect bite not only contributes to the disruption of the beauty of a smile, but also has a detrimental effect on health. Incorrect position of the teeth triggers a restructuring of the musculoskeletal system, slowly adapting muscles and ligaments to the changed “comfortable” position of the dentofacial apparatus. In addition, bite pathologies in most cases disrupt the processes of chewing food, so patients with dental anomalies often experience problems with the gastrointestinal tract.
Incorrect bite leads to a large number of problems in the oral cavity. Inflammatory periodontal diseases, the appearance of increased tooth sensitivity, abrasion, chipped restorations - all this can occur if the teeth occupy an incorrect position in the dental arch.
To correct imperfections in your smile and straighten your teeth, contact orthodontist Irina Butorina.
What kind of bite should a person have?
Occlusion is the nature of the juxtaposition of the dentition during the habitual closure of the jaws.
There are physiological and pathological types of occlusion. Physiological:
- Orthognathic is the most correct bite, in which there are close contacts between the teeth and dentition, as well as 1/3 of the crowns overlap the lower dentition with the upper one.
- Progenic – a bite in which the lower jaw is slightly pushed forward.
- Straight bite - a bite in which the teeth of the upper and lower jaws touch the cutting edges and cusps in the usual occlusion.
- Biprognathic - a bite characterized by an inclination of the crowns of the teeth towards the vestibule of the mouth.
Physiological types of occlusion are not capable of leading to disturbances in the dental system, therefore they are considered as a variant of the norm.
Pathological:
- Deep – a type of bite in which the upper teeth overlap the lower teeth by more than 1/3 of the crown;
- Crossbite – a bite in which the upper teeth overlap the lower teeth in one segment, and vice versa in the other.
- Open bite – characterized by non-occlusion of the teeth in the position of central occlusion.
- Distal – a bite characterized by a large upper jaw.
- Mesial - a bite in which the lower jaw moves forward.
Pathological types of bite can cause serious disturbances in the functioning of the masticatory apparatus, as well as spoil the aesthetics of a smile.
Is it possible to determine the type of bite yourself? In most cases, this is very difficult to do, so it is better to consult a qualified orthodontist.
Butorina Irina Aleksandrovna is an orthodontist with more than 14 years of experience. The doctor has more than 1000 grateful reviews from patients who have already entrusted the specialist with transforming their smile!
Causes of dental deformities
Dental deformations are violations of the location of teeth in the dental arch, which lead to improper distribution of chewing pressure and worsening oral health.
The main causes of dental deformation in childhood are:
- Hereditary predisposition. In some cases, if parents have an incorrect bite, it is genetically passed on to the child.
- Using the wrong pacifiers and nipples for feeding. The feeding hole of the bottle should be at the bottom so that the baby can keep his tongue in a natural position while sucking. Pacifiers should be very thin at the base so that the baby's teeth are in a closed position.
- Using pacifiers after one year/Breastfeeding after one year. Prolonged sucking can lead to the formation of an infantile type of swallowing. In this case, the tongue “gets used” to resting on the teeth and gradually pushing them out.
- Poor oral hygiene. The accumulation of large amounts of plaque in the oral cavity contributes to the formation of caries. In childhood, all carious processes develop rapidly, so they very quickly turn into complicated forms. Unfortunately, some forms of complicated caries cannot be cured conservatively, so teeth have to be removed long before the physiological change. Early removal of baby teeth can lead to crowding of permanent teeth.
- Caries of milk teeth. If the caries of a temporary tooth is not treated in time, the infection can spread to the permanent tooth. This will manifest itself as a change in the shape, shade or size of the permanent tooth.
- Mouth breathing.
- Diseases of the ENT organs.
- Bad habits (finger sucking, holding foreign objects in the mouth, biting cheeks and lips, etc.).
- Postponed rickets.
- Diseases of the nervous system.
- Mother's illnesses during pregnancy.
The main causes of dental deformation in adulthood:
- Bad habits (biting a pen, biting a thread, etc.).
- Traumatic injuries.
- Long-term absence of one or more teeth in the oral cavity.
- Increased tooth wear.
- Impaired bone density.
- Diseases of periodontal tissues.
- Eruption of wisdom teeth.
What are crooked teeth?
For most people, crooked teeth are teeth of irregular shape, size, or those that are very different in position in the dentition.
But the curvature of teeth can be different. There are three main groups of deformations: dental anomalies, dentition anomalies, and dentition relationship anomalies. The first group includes individual teeth that differ in shape, size or shade from the rest of the dentition. The second group includes deformations formed during the eruption of several teeth at once, which violate the aesthetics of the entire dentition. The third group is deformations that occurred at the level of the jaws and entail their incorrect closure. Bite pathologies can appear at any age, so the process involves both permanent and temporary teeth.
Temporary teeth Often temporary teeth erupt with some curvature, but gradually take the correct position in the jaw. This feature is associated with intensive growth and development of the jaw bones in childhood. Unfortunately, in some cases, temporary occlusion is subject to the following defects: crowding of teeth, delayed eruption, early tooth loss, open bite, etc. All this can be avoided if you consult an orthodontist in time. The first visit for the purpose of prevention can be made at the age of 2 years.
Permanent teeth The eruption of permanent teeth largely depends on the condition of the temporary occlusion. In order to correct the condition of permanent occlusion in a timely manner, it is important to consult an orthodontist for a consultation.
Do I need to correct crooked teeth?
It is necessary to correct uneven teeth for the following reasons:
- An incorrect bite creates a functional overload on certain groups of teeth, which entails their rapid destruction;
- Deformations of the dentition lead to disruption of the normal functioning of the temporomandibular joint, hypertonicity of the masticatory muscles and overload of periodontal tissues;
- Crooked teeth are more susceptible to caries than others, and they are difficult to treat due to their incorrect position in the dental arch;
- An incorrect bite can cause problems in the gastrointestinal tract and respiratory system.
Orthodontist Irina Aleksandrovna Butorina will help correct the position of the teeth. You can make an appointment with a specialist by calling 8 926 203 32 32.
Up to what age is correction possible?
Many people believe that bite correction can only be done in childhood.
This opinion is not entirely correct. Modern orthodontics allows you to correct the condition of the dentofacial apparatus at any age, so there is no longer a time period for acquiring a beautiful smile! However, it should be understood that different age groups require completely different approaches to treatment. For example, in children, orthodontic treatment is faster and easier, since the dentofacial apparatus is at the stage of formation. Adult patients require longer treatment because their jaws have finished growing.
Overview of correction methods
You can correct crooked teeth using the following methods:
- Removable/fixed orthodontic structures (braces, aligners, plates, mouth guards, trainers, etc.);
- Surgery;
- Restoration of dental defects.
But how not to make a mistake when choosing a treatment method?
The orthodontist chooses methods for correcting malocclusion individually in each case. The choice depends on the patient’s age, as well as the growth characteristics of the components of the dentofacial apparatus. For example, in childhood, the facial part of the skeleton has not yet completed its growth, so all stages of orthodontic treatment should be aimed at stimulating the correct development of the jaws. For these purposes, the orthodontist may prescribe wearing special removable or non-removable structures, as well as performing certain exercises to strengthen the muscles of the oral cavity.
The teenage period is characterized not only by hormonal changes in the body, but also by a change in bite. Jaw growth continues, so it is important to properly influence the structures of the maxillofacial apparatus. During this period, plates can be fixed to temporary teeth, and braces can be placed on permanent teeth.
Gradually, jaw growth stops. This usually happens by age 21. The condition of a permanently formed bite can be corrected with the help of braces, aligners or surgical operations (in more complex cases). Sometimes for effective treatment it is necessary to combine surgery with wearing an orthodontic appliance.
For minor tooth curvatures that do not cause functional impairment, orthodontic treatment can be avoided. In this case, it is necessary to restore the tooth using veneers, crowns or filling material.
How long does it take to straighten teeth?
Only a specialist can establish specific terms for orthodontic treatment after examining the oral cavity and carrying out diagnostic measures. On average, the duration of therapy with an orthodontist lasts from one to three years.
Prevention of crooked teeth
It is important to prevent the appearance of crooked teeth from a very early age. Parents should follow the following recommendations:
- Visit an orthodontist for preventive examinations from the age of 2-3 years at least once a year.
- Avoid pacifiers/pacifiers/breastfeeding if the child is over a year old. For up to a year, use only orthodontic pacifiers and pacifiers.
- Perform lip and tongue frenuloplasty in a timely manner on the recommendation of an orthodontist and pediatrician.
- Attend preventive dental examinations, as well as professional oral hygiene procedures at least once every six months.
- Treat caries and its complications in a timely manner.
- Eliminate bad habits (chewing a pen, biting threads, etc.).
- Gradually introduce solid foods into complementary foods.
- Learn to use a sippy cup.
- Starting from the first tooth, brush your teeth with a brush and toothpaste in the morning and evening. Hygiene products should be selected according to age.
- Rinse your mouth after every meal.
- Perform myogymnastics exercises (as recommended by the orthodontist).
- Treat diseases of the ENT organs in a timely manner.
- Follow a balanced diet, which will be dominated by fresh fruits and vegetables.
Conclusions. Expert advice
Bite defects can appear at any age for a huge number of reasons.
Currently, such imperfections can be eliminated if you consult an orthodontist in time. The specialist will draw up an individual treatment plan and restore the beauty and charm to your smile! An orthodontist in Moscow, Butorina Irina Aleksandrovna, has been correcting malocclusion for more than 14 years. The specialist has a large number of positive reviews from patients who have already entrusted their health to her!
You can make an appointment for a consultation with Irina Alexandrovna by calling 8, 8 926 203 32 32.
The specialist conducts consultations at the address: metro Botanical Garden, Lazorevy proezd 3, DentalArt Clinic
Treatment
Tactics and methods of treating malocclusion in a child depend on age and indications. The following common methods are distinguished:
- Myogymnastics. Very effective at an early age, up to 5-6 years. During this period, it can act as an independent means of therapy, and later – as an auxiliary one.
- Orthodontic plates. Removable devices that are successfully used from the age of three. They do not cause pain and can be used around the clock or only at night. Suitable for minor malocclusions only.
- Removable plates. They have a plastic base and metal arcs. They are used mainly after 10 years to regulate the growth of the jaw and correct the palate.
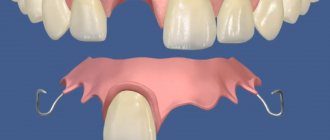
- Prostheses. They are installed in place of the missing tooth to prevent the displacement of other elements of the dentition.
- Trainers. Soft silicone mouth guards. Prescribed after 5 years for normal development of the jaw with a permanent set.
- LM activators. Used to eliminate bad habits and restore proper functions of the dental system.
- Braces. Fixed systems that create pressure on the dental arch, gradually bringing it to the desired state.
- Surgical correction. It is used in the most difficult cases when other methods are ineffective.
Often the treatment is complex, that is, several techniques are combined to achieve results.
The period of treatment is determined individually, but for the same child at an early age it takes less time than at an older age.
At what age can you start orthodontic treatment?
It is easier to solve bite problems or reduce the likelihood of them developing in children than in adults. This is due to lower bone density, which means the correction process requires less time.
The first consultation with an orthodontist should take place after all baby teeth have erupted (at 1-2 years). At this age, the doctor evaluates the correct development of the dental system and gives recommendations on how to avoid problems with bite in the future. If a child has bad habits, a gentle way to eliminate them using safe elastic vestibular plates may be recommended.
At the age of 4-6 years, treatment begins with removable and non-removable orthodontic appliances. There are no strict age restrictions for starting treatment - everything is determined by the discipline of the parents and the child. Removable devices must be worn strictly according to the doctor’s recommendations, otherwise the treatment will not bring the expected result.
Removable plates and trainers are used during the period of active jaw growth - on average, up to 12-13 years. In children over 14 years of age, after all permanent teeth have erupted, removable orthodontic appliances are ineffective due to the completion of the active growth phase and increased bone density. To correct the bite at this age, braces and transparent aligners are used.
Why are braces better than removable appliances?
Recently, parents are increasingly choosing braces instead of plates. Modern children live an active life - they attend clubs and sports clubs. With this rhythm, parents, who themselves usually work a lot, cannot control the child all the time. Children often forget to put on records and lose or break them. And in orthodontic treatment, regularity and continuity are important. If you do not wear the device for more than 1-2 weeks, it will not fit and you will have to make a new one. Each repair and replacement is subject to payment. As a result, treatment becomes unproductive and expensive.
The braces cannot be removed or lost, but they are quite difficult to remove. In addition, they do not need to be cleaned and washed separately; it is enough to use a brush and a special brush when brushing your teeth as usual.
The most important advantages of braces are the speed of alignment, the ability to correct complex pathologies and a more stable result.