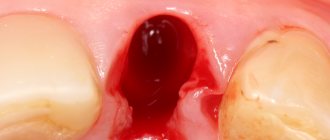
Modern hand instruments, when used correctly, provide excellent results for both the doctor and the patient. It should be noted that some of these results can only be achieved using hand tools, not rotary power tools. The shape of the preparation dictates the specific circumstances in which hand instruments must be used, while the accessibility of the preparation may require different conditions.
Hand-held cutting tools are made from two main materials, carbon steel or stainless steel.
In addition, some of them have carbide inserts that add hardness to the cutting edges. Carbon steel is harder than stainless steel, but is susceptible to corrosion if not protected. Stainless steel retains its shine in most cases, but loses its edge sharpness much more quickly than carbon steel. The latter, despite its hardness and wear resistance, is brittle and cannot be used in all tools.
Other alloys containing nickel, cobalt or chromium are also used, but dental preparation instruments are not typically made from such alloys.
Dentistry instruments for orthopedics, which are used in all areas of dentistry
In general, there are only three such basic large tools:
- Mirror
- Probe
- Tweezers
Large instruments are used during the examination and treatment phase by all dentists.
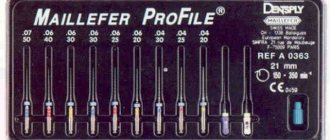
Among the small instruments, burs are used in all areas of dentistry - they are used to grind hard tooth tissues.
Based on material, burs can be divided into the following groups:
- Steel, designed to operate at up to 10 thousand revolutions per minute, they are used for processing dentin - the inner tissue of the tooth.
- Carbide - for them the operating speed is higher, up to 30 thousand revolutions. However, they are also used for processing dentin, but also for sawing metal structures.
- Diamond-coated burs are basically burs for a turbine tip, as well as carbide burs, which allow you to work at speeds of up to 30 thousand revolutions. They are used for grinding enamel – the outer tissue of the tooth and for sharpening ceramics.
The bur consists of a shank - a smooth part that is fixed into the tip, which gives it rotation, and a head - it is on it that there is cutting or diamond coating for grinding fabrics.
The influence of the price of instruments on the price of dental services
Let's be honest, many of the patients of dental clinics are frightened at the sight of new and modern dental equipment, believing that dental treatment in such an institution will cost much more.
How does the average private dentistry patient think? The management may try to return the huge amount of money invested in a private dental clinic as soon as possible, so the prices here will be unreasonably high! But in practice, given competition, regulations and rules, many dentists make concessions, trying to find the so-called “golden mean”.
Speaking of Yulistom, management is constantly searching and monitoring promotions for dental equipment and materials.
They are purchased directly from manufacturers, bypassing stores with the appropriate specialization. It is thanks to this that patients of dental clinics near the Zvezdnaya and Pionerskaya metro stations in St. Petersburg are offered affordable prices for healthy teeth! And don’t let modern dental equipment scare you, it in no way affects the fixed prices of dental services (price list at the link). Moscow metro station Zvezdnaya, Danube Avenue, 23
You can also divide burs according to the shape of the working part:
- Globular
- Cone and reverse cone
- Cylindrical
- Disc-shaped
- Olive
- Spiked
- Wheel-shaped, etc.
Burs come in sizes from size 1 to 11, where the first size bur will have a diameter of 1 mm, and size 11 will have a diameter of 2.5 mm.
There are also burs for faster tissue removal - these are usually marked in black and green, the average speed of tissue removal is marked in blue and red, and for very slow removal, essentially polishing and finishing - in white and yellow.
There is also a separate subspecies that is as close as possible to burs - this is a cutter for a straight tip. The burr is used in the dentist's office to adjust removable dentures. The cutter has a large head with notches and is used primarily by orthopedic dentists.
Basic methods of orthodontic treatment
Without knowing what exactly the patient came with, it is impossible to say what the orthodontist will do , because the methods of influence primarily depend on the problem and defects in the dentition. Sometimes you can get by with minimal interventions, in other cases you need to involve a dental surgeon.
The most popular methods of dental orthodontism are myotherapy or myogymnastics, hardware treatment and surgical intervention. It is rare that these methods are used in their “pure” form; usually the doctor combines them, forming the course of treatment necessary for a particular patient.
Myotherapy
Myotherapy is one of the ways to strengthen the muscles of the maxillofacial area, thanks to which the formation of anomalies in childhood can be avoided. Based on theoretical calculations about orthodontic treatment, we can conclude that this is the safest and least effective method. Therefore, myogymnastics is almost never prescribed separately.
During classes, the child needs to perform two types of exercises:
- dynamic, when the muscles of the face and jaw sometimes tense and then relax;
- static, forcing the organs to be in tension all the time.
Considering that the exercises must be systematic, classes require adult supervision. Also, it is the parent or teacher who checks that the tasks are completed correctly, because the child may forget or not understand the doctor. The specialist selects tasks, then teaches the adult the exercises, then the adult checks the child.
Myogymnastics class in a children's group: warm-up
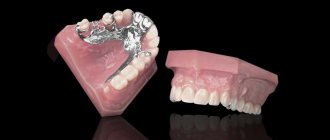
Hardware method
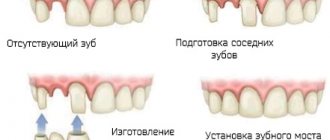
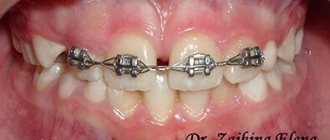
The frequency of use of the method clearly shows: an orthodontist is a doctor who treats with fixed and removable hardware systems. The most famous of them are braces, mouth guards and trainers, and plates. When installed, they act on individual teeth, causing them to slowly but surely move in the desired direction. As a result, all elements of the oral cavity occupy their intended position.
Treatment with devices has certain limitations. So, corrections are possible if:
- sufficient force is applied to the tooth, i.e. the equipment is assembled correctly and installed correctly;
- the device has a reliable support and is well fixed;
- there is a place in the dentition into which a stray element can fit;
- there are no obstacles in the path of the tooth being moved.
If these rules are not followed, the dental orthodontist corrects this , and then installs braces, plates or other devices. Sometimes it takes a lot of time to prepare, because it is necessary to remove excess teeth and wait for the restoration of the oral cavity.
Surgical method
If the diagnosis shows that the deformation of the development of the dental arches, jaws or malocclusion is too pronounced, it is necessary to resort to surgical methods. The most popular types of surgical intervention:
- exposure of the crown of an impacted tooth (i.e., removal of the upper gum tissue above a tooth that has not erupted correctly);
- rotation of the tooth around its axis, as a result of which the element falls into place in the dentition correctly;
- removal of individual teeth of irregular shape, extra teeth, as well as those that cannot be “fitted” into the jaw for some reason, etc.
In some situations, surgical intervention falls under the purview of what an orthodontist does . If the specialist cannot correct the situation on his own, he gives the person a referral to a dental surgeon.
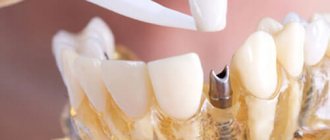
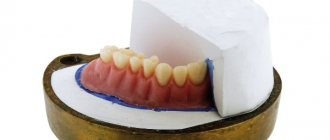
Dentistry orthopedics instruments
Specifically, orthopedics in dentistry sometimes uses specific tools - in particular, knives for processing casts and models of jaws, elevators and crown removers.
Knives for modeling casts and models.
Modeling knives are used to remove small parts of already hardened plaster or to cut off excess impression mass. They are also used directly during impression taking - sometimes the doctor needs to apply grooves to the impression or model the edges.
Wax knives, as the name suggests, are used for wax modeling. Such a knife will definitely have a handle made of a non-heating material because working with wax requires heating it. At one end of the modeling knife there is a small indentation for heating the wax.
Hardening and heat hardening
To achieve the best properties of carbon and stainless steel, they are subjected to two types of heat treatments: hardening and hardening. Heat treatment gives the alloy hardness, but at the same time makes it brittle, especially with a high carbon content. Thermal hardening reduces stress in the metal and increases its strength. These properties are optimized by manufacturers. Heat of hand-held cutting tools during use can destroy the original properties of the alloys from which they are made and render the tools unusable. Firing over a flame or improper sterilization can easily render a good instrument unusable.
Orthopedic crown remover
Typically, a crown remover is used when the crown is not held tightly or if some manipulations have already been carried out to remove it. The crown remover consists of a handle, a middle part represented by a rod with a groove for the working part, and, in fact, the working part.
If the structure is fixed well, then crown removers with a spring mechanism are used - in particular, Kopp's crown remover or, as dentists call it for short, cop. This type of crown remover, due to the spring, produces a single strong blow, which allows you to remove even a well-fixed crown. But at the same time, it is precisely due to the force when removing the structure that ceramics can become damaged and it will no longer be possible to fix it again.
To prevent the structure from chipping, there is another option - a manual crown remover, in which a weight is used instead of a spring - it is less powerful, but when used, there is a greater chance of keeping the structure intact.
Set of instruments for examining the oral cavity
Instruments for examining the oral cavity - a basic dental set - consists of a tray for instruments, a magnifying mirror, tweezers with a curved handle, with which the dentist performs all the necessary manipulations in the most inaccessible places, a metal probe with a straight and curved (angled) sharpened blade, thanks to in which the doctor accurately recognizes caries and determines the depth of the fissures.
A set of tools for examining the oral cavity also helps the doctor accurately determine the painful condition of the teeth, their mobility and other deviations in the functionality of the teeth, that is, it is the No. 1 assistant for carrying out the initial diagnosis of a wide variety of diseases of the dental system.
Storing instruments in dentistry
At the moment, the most advanced method of storing sterile instruments is used - they are individually sterilized and stored in special Kraft bags sealed with heat sealing. These bags are combined: one side is paper, which makes it easy to open them during work, simply tearing the paper, and the other side is made of polyethylene, which allows you to seal the bags by melting the polyethylene with a special heat sealing machine. Such bags can be stored closed for up to 12 months, but if the bag has been opened, the instrument is processed, sealed in a new bag and sterilized again, even if it has not been used since opening.
What diseases does an orthodontist treat?
As already mentioned, an orthodontist deals with congenital, hereditary and acquired dental defects in childhood. This doctor does not work with injuries and does not set the jaw. Most often, an orthodontist is consulted with the following problems:
- facial asymmetry;
- improper growth of teeth;
- violation of chewing functions;
- abnormal position of teeth, etc.
After the examination, the doctor assesses the patient’s condition, studies the causes of the disease and selects a treatment method. Let's take a closer look at the classification of diseases that a doctor encounters.
Anomalies of teeth
Dental anomalies are various deviations of individual elements of the dentition. The following types of abnormal dental development are distinguished:
- violation of shape (spike-shaped, Hutchinson, Fournier, Pfluger teeth);
- non-standard size (micro- and macrodentia);
- too few or too many teeth (edentia, hypodontia, hyperdontia);
- problems with tissue structure (hypoplasia, hyperplasia);
- incorrect timing of appearance (premature or late);
- incorrect position of an individual tooth in the dentition (oral, vestibular, distal, mesial, infraposition, supraposition, rotation around the longitudinal axis, transposition);
- discoloration.
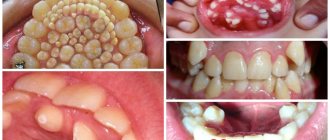
The picture below shows the most common anomalies of individual teeth.
The most common dental abnormalities
Anomalies of the dentition
The dentition can also have anomalies, which sometimes greatly disturb the patient and cause problems with nutrition and speech. The following are the problems faced by orthodontists:
- violation of the row shape;
- incorrect size towards narrowing/widening or lengthening/shortening;
- violation of the sequence of teeth;
- violation of the symmetry of the position of the teeth;
- violation of contacts between teeth (twisted or sparse position).
Malocclusions
Malocclusion is the most common problem that everyone hears. Sometimes patients even get the impression that orthodontics in dentistry deals exclusively with installing braces. Of course, this is not true, but bite correction is one of the most common problems, especially in childhood.
There are five types of malocclusion:
- distal, when the upper jaw is overdeveloped and protrudes forward, significantly affecting facial features;
- mesial, in which the lower jaw is already too developed;
- cross. Its owners have free space between their teeth, and they themselves are arranged “like scissors”;
- deep, in which the lower teeth are practically hidden under the upper ones;
- open, when there is no constant contact between the lower and upper teeth, it appears only in the area of the molars.
An incorrect bite, even if it is not very pronounced, is no less dangerous a problem than a tooth out of alignment or a violation of symmetry.
Malocclusion: main types
You will find detailed information on this topic in the article: All about the bite: what it is like, why it is important to monitor it and how to treat improperly grown teeth
Jaw anomalies
The jaws may also not be positioned quite correctly, is immediately visible to the orthodontist Examples of the most common pathologies:
- altered size (macrognathia or micrognathia), when one of the jaws has reached a much larger size in development than the other. It may be different: the jaws often remain small. The problem may be with only the upper or lower jaw or both;
- incorrect location relative to the base of the skull. There are asymmetric placement, prognathia (strong protrusion forward), retrognathia (movement of the jaw backward);
- abnormal relationship of the dental arches (distal or mesial occlusion, excessive overlap, non-standard occlusions.
The types of disorders of the dental system largely overlap, because, for example, it is impossible to consider the position of the teeth without taking into account the entire dentition. Therefore, if you understand who an orthodontist is in dentistry , then we can say that he is, first of all, a practitioner. He takes into account the characteristics of a particular patient and draws up a completely individual treatment plan.
When to contact an orthodontist
A child should learn who an orthodontist is before the age of 7. At this age, the permanent bite of the anterior incisors is still forming, so it is possible to stop some problems relatively painlessly. Most leaflets for parents contain the following recommendations for visiting a doctor:
- The child is one year old and parents have questions. What does an orthodontist do when the baby has no teeth yet? He examines whether the lips and those teeth that have already erupted are closing correctly;
- child is 3 years old. A visit is advisable, because at a young age, the prerequisites for incorrect development of teeth and jaws can be identified. Therefore, during such an appointment, the orthodontist always asks the parents whether the baby has bad habits, for example, sucking a pacifier, finger, tongue;
- the child has difficulty swallowing, chewing, and speech is not formed;
- you see that the child has changes in the position of the teeth or their closure.
Knowing what an orthodontist does , you can visit a specialist in advance to prevent problems in the development of the dentition and avoid their deterioration.