Clasps or hooks on dentures: classification, what they are and how they are used
Article navigation
- What is it and what is it used for
- Classification
- Requirements
- Manufacturing
- Common clasp designs
- How to remove dentures
- Complications
- Alternatives
- Price
Question for a specialist
To fix removable dentures, dentists use various fasteners. One of the most common types is clasps or the most common hooks. Next, we will tell you in more detail about the types of clasps in orthopedic dentistry, about their purpose and structure, what functions they perform, and what requirements must be met when using them.
What types of clasps are there?
There are 3 types in total, of which 2 main ones:
- holding;
- support-holding
(3rd type - support clasp, used as an auxiliary clasp together with the support-retaining one)
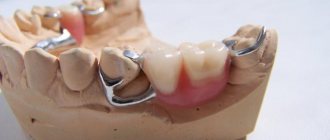
(The figure shows an example of a support clasp)
Retaining clasps are needed only to hold the denture in the mouth. They are used in plate prostheses.
Support-retaining clasps, unlike support clasps, transfer part of the chewing load to the tooth.
A prosthesis with this type of clasp is called semi-physiological . Such dentures are more comfortable and easier to get used to. (Read more in our article)
What is it and what is it used for
What is a clasp in dentistry? In German, klammer is a clamp, frame, bracket. In dentures, a clasp for removable dentures is an element of a partial denture, with the help of which the structure is attached to the abutment tooth and held on it. The simplest clasp looks like a small hook (that’s why such dentures are called “hooked”), but there are elements of more complex shapes. They are designed to fix and stabilize the prosthetic base - that is, the orthopedic structure must remain stable both at rest and during talking or chewing, during the process of swallowing food.
What does a clasp consist of? The design includes the following parts or elements - shoulders or rings, body and process, and in some cases the occlusal pad. Let's take a closer look at the structure of its components:
- shoulders or shoulder: this is an elastic part that covers the supporting tooth on the sides of the crown (instead of a shoulder there may be a ring) and is pressed against its gingival part, the shoulder itself smoothly passes into the body,
- the body is the connecting element between the shoulder and the process,
- the process is immersed in an acrylic base or attached to the arch of a clasp prosthesis,
- The occlusal pad is located on the chewing part of the crown between the tubercles of molars and premolars: it is a supporting element that helps to correctly distribute the chewing load. The pad is smoothly connected to the body,
- frontal overlay: the purpose is the same as the occlusal overlay, but it is placed on the front teeth (usually on the lingual side of the row, so as to be invisible from the side).
In turn, the shoulder is also divided into elements - the supporting and holding parts. The supporting one makes up approximately 70% of the length of the entire shoulder, and the holding one makes up the remaining 30%. The thickness of the clasp is on average 0.25-0.5 mm.
Ney's clasp system
This is one of the best artificial structures of its kind. The Ney system clasp has an important advantage - there is no need to use crowns. Therefore, a healthy tooth is not injured during grinding; when chewing food, the load is distributed to the chewing teeth. The denture is fixed with several fasteners, each of which is located in a specific place to hold the product in one position.
The advantages of this product are:
- reliability;
- elasticity;
- practicality;
- long operating period.
Classification and varieties
There are many types of classification of clasps - by function, shape, material of manufacture, method of connection with the prosthetic base, location of contact, degree of crown coverage, manufacturing methods. Let's look at each classification group in more detail.
By purpose or function
- retaining clasps: used in orthodontics (occlusion correction) and orthopedics (dental prosthetics). They have only 1 function - holding the plate or removable denture on the supporting crowns. When chewing, the entire load goes to the prosthetic base and gums, which can rub, resulting in pain and stomatitis. Another method of application is fixation of rubber dam (latex film for dental treatment),
- supporting-retaining (with an occlusal pad, for example): also options are also used in orthodontic and orthopedic treatment. However, they have 2 functions - holding and support. When chewing, the load will be distributed, among other things, to the supporting teeth, their ligaments and the adjacent bone (periodontal tissue). In this case, the mucous membranes “suffer” less.
Experts note that the division into retaining and support-retaining is conditional. Because retaining hooks also transfer part of the load to the periodontium. But in this case, the distribution of pressure is incorrect, so negative consequences often appear - injuries, loosening of teeth, loss of gums.
By shape
The following types of clasps are distinguished by shape:
- flat,
- tape,
- semicircular,
- round.
Don't know what type of prosthetics to choose?
We will help in the selection, advise where to read more information and compare types of prosthetics.
Consultation with an orthopedic doctor in Moscow clinics is free! Call now or request a call
Working hours: from 9:00 to 21:00 - seven days a week
According to the method of connection with the prosthesis base
The connection can be of the following types:
- stable, i.e. rigid: the hook, through which pressure is distributed on the crown, is fixedly attached to the prosthetic base. There is almost no load on the gums and alveolar ridge,
- springy or semi-labile: a distinctive feature is the presence of a long body that is capable of springing. Here, only part of the chewing load is applied to the crown, and the rest is absorbed due to the “lever effect”,
- articular or labile: due to the presence of a hinge (or joint), almost all the pressure from the prosthesis goes not to the support, but to the gum and alveolar ridge.
At the location of contact
Based on their location or location, these elements are divided into types such as:
- dental: adjacent to the crowns, most often made of metal,
- pelota or gingival: they are wide extensions of an acrylic base, fixed only on the gums,
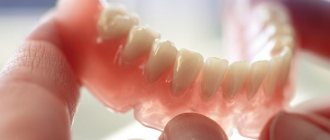
- dentogingival: simultaneously in contact with the gums and supporting crowns. For example, immediate dentures or “butterflies” have these – what the clasps on a denture look like is shown in the photo.
According to the degree of coverage of dental crowns
- one-armed and two-armed,
- ring-shaped (also called “changeover”),
- double,
- multi-link clasp: is a frontal overlay (it was discussed at the beginning of the article) on the lingual surface of the front teeth - most often placed on the lower ones. Externally, a multi-link one looks like either a horizontal plate with processes or several united half rings. Helps stabilize an entire group of teeth.
According to the material of manufacture
Classification according to materials of manufacture includes such types of clasps as:
- from base metals: for example, from medical steel, nickel, cobalt alloys with chromium and iron, titanium alloys,
- from noble metals: platinum, gold, palladium,
- from synthetic polymers, resins: plastic, acrylic, nylon, acetal.
By manufacturing method
- bent clasps: for production, wire is used, which is bent in accordance with individual bite parameters. Such elements are more elastic or resilient, but fit less accurately to the crowns,
- cast: the manufacturing technique of casting also involves the use of metal. Cast metal clasps are less elastic, but more accurately replicate the anatomical parameters of the crown, i.e. fit tighter
- made using cold or hot polymerization: gingival ones are made from a synthetic polymer (acrylic, nylon, etc.), usually simultaneously with the manufacture of the prosthetic base.
Swenson and Jackson design
The clasp used on canines is called the Swenson design. This design creates the correct load on the supporting teeth. This is very important during their mobility. The disadvantage of the design is that there must be a gap between the molar and premolar to secure the anterior shoulder.
A reversible clasp is a type of Jackson support-retaining device. The product has 2 branches and bodies. The structure is made by cast and bent method in the shape of a loop.
Requirements for hook placement
Denture clasps must be selected in accordance with all of the following requirements:
- the fixation will be the same on all supporting teeth,
- rotation or overturning of the prosthesis is excluded,
- do not overestimate the bite in the presence of occlusal pads,
- do not lead to injury to the teeth (including those of the opposite or antagonistic teeth) when closing the jaws and chewing,
- do not greatly reduce the aesthetics of a smile: metal ones located in the “smile zone” are highly noticeable from the outside, while synthetic ones are less noticeable. But the latter quickly stretch and break more often,
- the supporting teeth do not have pathological mobility,
- crowns of correct anatomical shape and sufficient height (5 mm or more).
You also need to take into account the position of the boundary line - this is the line that divides the crown into supporting and retaining parts. This parameter is determined using a parallelometer device. So, for example, on the lower teeth, the upper part of the clasp (occlusal pad and top of the shoulder) is located above the boundary line, and the lower part of the shoulder falls below the line. On the upper jaw, everything is, accordingly, the opposite.
Side effects from clasps
Denture clasps can cause:
- To the abrasion of the tooth enamel itself due to constant load and micro-movements.
- This leads to a significant deterioration in the hygienic condition of the mouth due to the fact that the clasp is a separate structure and various food debris can accumulate under it. As a result, carious processes begin to develop very quickly. And this destroys the supporting teeth.
- Clasps can cause teeth to become very loose. This happens due to the movements of the prosthesis in a horizontal position. As a result, there is a functional overload of the teeth, which serve as support.
Sources used:
- Kurlyandsky V. Yu. Orthopedic dentistry. — 4th, corrected. - M.: Medicine, 1977.
- Eden SE; Kerr WJS; Brown J. (2002). "A clinical trial of light cure acrylic resin for orthodontic use." Journal of Orthodontics.
- Earls, Stephanie (22 February 2014). "Re-enactor brings George Washington to life." The Washington Times.
- Milward, P.; Katechia, D.; Morgan, M. Z. (November 2013). "Knowledge of removable partial denture wearers on denture hygiene". British Dental Journal.
How is production carried out?
Manufacturing is carried out in a dental laboratory by a dental technician. First, the model of the prosthesis and materials are determined. As a rule, both metal wire and cast hooks are bent using special pliers, pliers and round nose pliers. Then the clasp is included in the base and the entire structure is tried on the patient; if necessary, the product is modified. During the manufacturing process, it is important to comply with the requirements for the manufacture of the shoulder and the implementation of the contact process. Thus, the shoulder should not overload the supporting tooth, but should adhere to the crown at the maximum number of points. The metal is well polished so that the hook does not injure the enamel and does not become a place where plaque accumulates. As for the process, it is bent with round nose pliers and notches are made for better connection with the base.
Design features
Retaining type clasps consist of the following elements:
- The shoulder performs the function of holding the clasp on the tooth surface. This element ensures the spring properties of the structure and the transfer of pressure to the support unit. The shoulder should not have sharp protrusions to avoid injury to the gum tissue and cheek.
- The body is an element of the product placed on the surface of the tooth and connecting the shoulder and the process of the clasp.
- The process performs the function of fixing the fastening in the prosthetic structure. Placed under the plastic components of the hook.
In support-retaining clasps, in addition to the shoulder and body, there is an occlusal pad that prevents tooth displacement when pressure occurs on it, and an anchor part - an element connecting the clasp to the metal base.
Common clasp designs
- Ney's system: there are 5 types of clasps - Acker, Roach, combined (from Acker and Roach designs), single-arm reverse action, single-arm ring. This system was developed in 1949 with the participation of dentists and engineers. It includes both already known fastenings (modified) and new ones,
- developed by Acker: a supporting-retaining element with a rigid connection, consisting of 2 arms, an occlusal pad and a body. One of the oldest and most famous varieties, which first appeared in 1926,
- Roach: a support-retaining device with an occlusal pad and a spring (elastic) connection, which is easy to distinguish from others - its two arms look like the letter “T”. Because of this similarity, the hook is called “split”. Made from cobalt-chromium and gold-platinum alloys,
- Bonneville: Also known as the “six-arm” because it consists of 4 arms and 2 occlusal pads. Fixes 2 teeth at once,
- Jackson: includes 2 branches and 2 bodies, made of wire,
- Adams: one of the most versatile and effective types, suitable for both free-standing teeth and those included in segments,
- arrow-shaped Schwartz clasp: consists of 1 or 2 links, can also be multi-link. It is made of elastic wire and fits well into the interdental spaces.
%akc72%
Lock type 3, 4 and 5
Type 3 fasteners combine Acker and Roach fasteners. One shoulder has a T-shape, the second is located next to the chewing area. Clamp 3 is recommended to be used when the dividing line is uneven.
Type 4 latch is called reverse-acting. It is used when small molars and canines are inclined, as well as when there is low support.
Type 5 fasteners are also called single-arm ring fasteners. It is recommended to use it if single teeth are positioned obliquely. The body is supported and completely surrounds the tooth. The main disadvantage is the fragile retention of the prosthesis, therefore discomfort may occur when chewing solid food.
Complications that may arise due to clasps
Negative consequences or complications associated with prosthesis attachments can occur for various reasons. These include low-quality materials, errors at the manufacturing or installation stage, and non-compliance with operating rules. You may also be allergic to metal or synthetic materials. In patients who already have dentures made of other metals in their mouths, galvanosis often occurs - the sensation of an electrical impulse. Often chips and cracks appear in the enamel, gums bleed and recede, and the necks of the teeth are exposed.
If oral hygiene is unsatisfactory, pieces of food become trapped under the hooks, plaque and tartar form. This provokes caries, periodontitis, causes an unpleasant odor and generally worsens the aesthetics of a smile.
Caring for clasp dentures
A dental patient gets used to the prosthesis in about two days. At the initial stage, problems with diction may arise, but this goes away after getting used to it and some exercises. There may also be problems when eating - pain and control of food intake at the initial stage. It is better to exclude hard and sticky foods from the diet while adapting to the prosthesis. It is also not recommended to remove the denture at night, as this will allow the oral cavity to quickly adapt to the changes.
Cleaning and rinsing of the prosthesis is performed twice a day with special products prescribed by the attending physician. Storage of the prosthesis excludes water; it is simply placed in a special container.
If the prosthesis is damaged, you must contact a dental clinic or dental laboratory, where work on the repair of clasp dentures is carried out. Sometimes restoration of the prosthesis takes several hours - with prompt treatment. Most often, clinics provide guarantees for the installation and for the prosthesis itself, so repairs can be free.
The Faberge dental laboratory in St. Petersburg provides dental services. We are ready to provide all the information you are interested in about our production, the technologies used and the specialists. With us you will receive first-class products of any kind.
What alternatives exist
An alternative to clasp fixation are attachments (clasps) and telescopic crowns. All of these options are used for removable dentures. Dentists note that orthopedic structures on attachments are fixed better, and they themselves are completely invisible from the outside. As for telescopic crowns, this is also a very good option, but it is considered the most difficult to manufacture.
“Mom wore a clasp denture for several years. It seemed convenient, but outwardly the metal hooks on the teeth stood out. Well, she began to smile less, of course, because of this. Then the prosthesis had to be changed, and the doctor persuaded me to use attachments. “He turned out to be much better in beauty, from the outside he looks like his own teeth and no hooks are visible.”
Lina O., review from the website stomatology.rf
If we consider the best option for prosthetics in principle, then here the first place is firmly held by dentures fixed on implants - fixed or conditionally removable. They have many advantages - strong, reliable and durable fastening, highest aesthetics, comfort when chewing (they feel like your “native” teeth).
Read on the topic: conditionally removable dentures on implants - how they are attached and how they differ from others.
Useful tips
How to get used to dentures? At the beginning of wearing, many feel pain and scratches appear. You need to make sure that the structure is put on correctly. If this does not help, then you need to visit the dentist.
Pain often appears during chewing, so it is recommended to abstain for a while from solid foods that cause discomfort. Gradually, you need to switch to your usual diet, since chewing load is an important point in getting used to the prosthesis.
How to get used to dentures if you are worried about dry mouth or increased salivation? In this case, it is advised to drink enough water in small sips throughout the day.
The use of special fixing gels and ointments will help to securely secure the structure and prevent the formation of abrasions and wounds. Although the formation of chafing at the initial stage of addiction is considered normal. This process can last 3 months. At this time, the formation of the prosthetic bed occurs. To prevent chafing, you need to:
- clean your denture regularly;
- have the product adjusted by a doctor;
- rinse your mouth after eating.
Often, long-term addiction occurs as a result of an incorrectly selected or ill-fitting product.
To find out how much dentures cost in each specific case, you need to consult a dentist. The reliability of their fastening and the aesthetics of a smile depend on an element such as a clasp. Therefore, you need to choose it responsibly and seriously.
How much does prosthetics cost?
The cost of prostheses with hook fixation is the lowest in the segment. For example, a “butterfly” prosthesis can cost from 6,500 rubles, a removable acrylic one from 15 thousand rubles. Much here depends on the length of the orthopedic structure, the type and material of the fastening, the number of clasps, and the base material.
1Glen P. McGeevey Partial Dentures, 2006.
Your questions and answers
QUESTION Hello, tell me, which prosthesis with clasps is better to install? Irina T.
ANSWER Hello, Irina. The choice of prosthesis will depend on the condition and number of supporting teeth, as well as the capabilities of the clinic and the patient’s preferences. With clasps you can make a removable partial denture, acrylic, Acry-free, nylon, acetal, or clasp denture. Better reliability and more compact sizes are found in classic clasp frames, as well as in their modern metal-free counterparts Quattro Ti (“Quadrotti”).
Author: Chernov A. R. (Thank you for your help in writing the article and the information provided)
Clasps in dentistry classification
Clasps secure dentures. The shape of the structure directly depends on the functions performed (support, retention).
When choosing a design, special attention should be paid to two areas. The devices should create a secure fit for the prosthesis while the person chews and talks. The fastener should have minimal impact on the mucous membrane of the supporting teeth.
Boundary line
The location of the boundary line is of great importance when choosing the type of clasps to be installed.
There are 5 options for its placement:
- The boundary line originates from the contact point of the row element on the side where the pathology is located and descends to the center of the proximal region of the adjacent tooth. In this case, the use of clasps with long holding arms is effective.
- The equator line is located in the center of the approximal surface and is directed towards the contact point of the adjacent tooth along the lingual or buccal side. The situation requires the use of support and retention mechanisms.
- The boundary line is placed diagonally on the surface of the supporting element - from the chewing area in the defect area to the neck of the element on the reverse side. Experts prefer to use Ney clasps for this pathology.
- The boundary line is located low, the equator passes in the area of the tooth neck . To fix the prosthetic structure, the use of support clasps is required.
- A high location of the equator occurs in cases of increased tooth abrasion. To restore their functionality and appearance, artificial crowns are required.