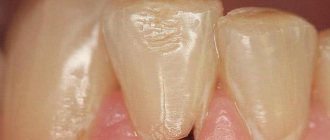
Chewing teeth include premolars and molars. They are located at the end of the dentition, have a bumpy surface and take on the main load in the process of chewing food. Dentists note that these teeth are susceptible to caries. This is due to their complex structure and inaccessibility during cleaning.
Are your chewing teeth decayed? See your dentist to prevent further loss. A specialist will examine the oral cavity and tell you whether the teeth can be restored. Today, even severely damaged teeth are restored. If molars cannot be restored, they can be removed and implants placed.
Mechanism of caries development
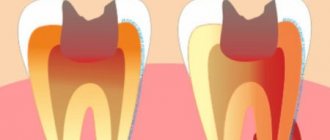
Caries is a dental pathology that destroys the structure of the tooth. It develops when a large number of cariogenic bacteria create a lot of organic acid in the mouth. It penetrates the structure of enamel and dentin, softens them, which leads to carious lesions. The more bacteria and the acid they produce, the more active dental caries develops.
In this article
- Mechanism of caries development
- Why is it important to stop tooth decay?
- Can dental caries be prevented?
- Fissure sealing is a way to prevent or slow down caries in a child
- How to stop caries?
- How can you stop caries at the spot stage?
- Features of caries in elderly patients: how to slow it down
- Conclusion
This pathology affects people of different ages. In recent years, experts have noted a trend towards an increase in morbidity among children. According to statistics, by the age of seven, approximately 85% of children’s teeth are affected by caries, and among the adult population this dental disease ranks first in prevalence.
How is cervical caries diagnosed?
If the carious lesion is localized on the visible part of the tooth, the doctor makes a diagnosis after an external examination. But to confirm it, a special test is performed using a dye solution. It is applied to the enamel and left for 3-4 minutes. The affected area turns blue. After a few hours, the dye is completely washed out of the mouth.
The doctor may also prescribe an x-ray to assess the nature of the spread of caries, the depth of the carious cavity, the condition of the nerve endings, etc. Based on the results of the examination, a treatment method is selected. It is determined, first of all, by the stage of the disease.
Why is it important to stop tooth decay?
Any disease is easier to prevent than to treat. And dental caries is no exception. There are many reasons why it is important to stop the progression of tooth decay as early as possible.
- It is easier to treat teeth at an early stage.
The peculiarity of caries is that it develops gradually and relatively slowly. At an early stage, it looks like a small chalky stain on the enamel and is very easy to treat. The damaged area of the tooth is covered with special gels and solutions that restore the mineral composition of the enamel, or treated with an infiltration composition - it seals the enamel pores. The main thing is that caries can be treated at an early stage without preparing the carious cavity. It is quick, painless, simple and allows you to preserve the integrity of the tooth.
- Treatment in later stages is painful.
If the further spread of caries is not stopped, it will penetrate into the deeper tissues of the tooth, which will lead to the formation of a cavity and sometimes damage to the pulp. Such caries is treated with drilling, cleaning, filling - such procedures are unpleasant and painful, and therefore require anesthesia.
- With untreated caries, there is a risk of severe destruction or complete loss of the tooth.
In such cases, crowns or implants will have to be installed, which involves large financial costs. In addition, an artificial tooth does not have the same strength as a real one, and its useful life is limited.
- Carious teeth are a source of infection.
Teeth affected by caries are a source of chronic infection in the body. The deeper the process spreads, the greater the risk of infection of other organs and tissues.
- Bad teeth lead to digestive problems.
Teeth support the chewing process. With caries, they become less durable, cease to cope well with the chewing function, which is fraught with digestive disorders and can lead to gastrointestinal diseases.
- Aesthetics are compromised.
Teeth are not only health, but also beauty. Teeth affected by caries darken, holes form in them, the smile loses its attractiveness, which is reflected in a person’s appearance.
- Complex caries is more expensive to treat.
Dental treatment is not cheap. Moreover, the more serious the problem, the more expensive it will cost. Therefore, stopping caries at an early stage is much more profitable from a financial point of view.
Why is it necessary to restore teeth?
If a chewing tooth has collapsed, you should consult a doctor as soon as possible. Loss of a dental unit leads to:
- to displacement of adjacent teeth,
- uneven distribution of chewing load,
- various diseases of the gastrointestinal tract,
- development of complexes and decreased self-esteem.
When you smile, decayed teeth may not be visible, but it is important to remember that they are breeding grounds for bacteria. They cause bad breath and pain when eating cold or hot food.
Can dental caries be prevented?
The fact that about 90% of the world's inhabitants have caries does not mean that this pathology cannot be prevented. An integrated approach to preventive measures will significantly reduce the risk of dental caries.
- Regular teeth cleaning.
Oral hygiene comes first in importance in the development of caries. Cariogenic bacteria live in dental plaque and feed on food debris. If you brush your teeth, as doctors recommend, twice a day for at least 2-3 minutes, following the basic rules of brushing, you can protect your teeth from caries.
- Use of additional hygiene products.
Using dental floss and irrigator, along with a brush and paste, helps improve the quality of oral care and reduce the risk of dental caries. The floss is needed to clear the interdental spaces of partially stuck food. This helps prevent contact caries developing on the lateral surfaces of the teeth. Using a powerful water jet, the irrigator cleans not only the interdental spaces, but also periodontal pockets, the space under crowns, dentures and other hard-to-reach areas.
- Strengthening the immune system.
A weakened immune system cannot resist the destructive effects of bacteria. Therefore, in order to prevent the development of dental caries, it is important to strengthen the immune system. An integrated approach may include hardening, proper nutrition, a healthy lifestyle, and taking vitamin supplements as prescribed by a doctor.
- A balanced diet rich in vitamins and microelements.
To prevent or slow down the development of caries, it is necessary to adjust nutrition in several areas. Reduce your consumption of simple carbohydrates - sugary foods and drinks, baked goods, fast food. Reduce the number of snacks and stop eating sweets at night. Make sure your diet includes plenty of foods rich in phosphorus, calcium, fluoride, and vitamin D. There should also be plenty of solid vegetables and fruits, which naturally cleanse your teeth of food debris and plaque.
Why do baby teeth rot?
As in adults, in children, caries and subsequent tooth decay is caused by the decomposition of food debris stuck between them. A child’s mouth contains a huge number of microorganisms, because children love sweet, sour, salty foods and foods with strong “chemical” tastes. During their life, microorganisms produce acid, which destroys enamel.
Add to this process the deteriorating environment, a small amount of mineral salts in the water and not very thorough children's dental care. It is not surprising that according to statistics, every second child today, already at the age of 3, suffers from caries and rotting of baby teeth.
The most common external causes of rotten teeth in children include:
- insufficient brushing of teeth or lack of oral hygiene;
- improper unbalanced diet - lack of vitamins, minerals, excessive consumption of sweets and soda;
- drinking water with low fluoride content;
- heredity;
- mechanical damage to tooth enamel;
- unfavorable environmental conditions in the region or area of residence of the child.
Rotten teeth in children are often caused by internal causes, which include:
- Chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Prematurity. In babies who were born prematurely, the enamel of the tooth buds is not sufficiently developed. Weak teeth are more susceptible to various negative factors.
- Pathologies of the endocrine system that cause changes in hormonal balance in the body.
- Liver diseases.
Various streptococcal infections, leukemia, anemia, cancer, diabetes, scarlet fever, and chickenpox also have a detrimental effect on dentin. Hard tissue is affected from the inside, and retrograde caries appears. A child’s teeth also often begin to rot after taking tetracyclines and antihistamines.
Teeth often begin to deteriorate even during the period of weakened immunity of the baby. Due to prolonged stress, poor nutrition, and illness, the child’s immune defense decreases, and the teeth immediately react to any adverse factors.
Fissure sealing is a way to prevent or slow down caries in a child
Caries in a child can be stopped by fissure sealing. Fissures are the natural grooves and grooves on the chewing surface of the teeth. The anatomical features of their structure are such that food debris is easily retained in the fissures, and the process of enamel mineralization is slower than in other areas of the teeth.
To prevent dental caries (most often in children, but the method is also applicable for adults), fissures are sealed. The essence of the method is that natural grooves are covered with special dental sealants containing calcium and fluoride. Sealants seal the tooth, preventing the impact of cariogenic factors on it, and the mineral components included in the composition nourish the dental tissues.
The main indication for sealing is deep fissures that are difficult to clean during daily oral hygiene.
It is optimal for a child to seal the grooves on the teeth six months after teething. At about 6-8 years old, the child’s permanent teeth begin to be sealed - first the first molars, closer to 10 years - the premolars, and by the age of 12-13 - the second molars.
Sealing is not carried out if caries has already formed in the fissures - like a stain or a cavity in the tooth.
The sealing procedure can be invasive or non-invasive; the technology is selected by the doctor individually for each patient. If the fissure is clearly visible, it is sealed using a non-invasive method: the tooth is cleaned of plaque, treated with a special gel that ensures reliable fixation of the filling, sealant is applied and illuminated with a lamp. For narrow and deep fissures, the bottom and walls of which are difficult to see to ensure the absence of caries, the dentist chooses an invasive sealing method.
After cleaning the tooth, the fissures are opened with a drill and their condition is assessed. In the absence of carious lesions, further sealing is carried out similarly to the non-invasive method. Fissure sealing is one of the most effective ways to prevent caries in chewing teeth.
Advantages of treating tooth root caries in our clinic
Working with affected subgingival areas of the tooth requires special practical skills. At Kariesu.net clinics, patients with complex dental diseases are treated by experienced specialists. The doctor considers each case individually. Explains in detail to the patient the essence of the identified pathology, informs about the features of the upcoming treatment. The main principle of our dentists’ work is minimal invasive intervention. Specialists try to preserve healthy tissue and the tooth itself.
Our clinics use traditional and new treatment technologies. Modern filling materials are used. An exceptionally polite and understanding attitude towards patients is practiced. Make an appointment with our doctor by phone or through the online form.
How can you stop caries at the spot stage?
The first stage, in which only a small light spot forms on the enamel, is the most favorable from the point of view of treatment prognosis. At an early stage of caries, it is possible to cure it without painkilling injections, preparation of the carious cavity, or filling.
How to stop caries is decided by the dentist in each specific case, but today there are several possible non-invasive methods.
- Remineralization of enamel.
Caries begins when tooth enamel loses minerals, loses its strength and cannot effectively protect the deep tissues of the tooth from the acid produced by bacteria. Remineralizing therapy is aimed at restoring the balanced composition of the enamel, strengthening its structure, and returning its strength and protective characteristics. The essence of the method is that the dentist alternately applies compositions containing phosphorus, calcium and other useful substances to the cleaned tooth surface. Another way is to attach special trays with remineralizing gel to the teeth.
- Fluoridation.
Using this method, you can increase the strength of enamel, its resistance to acid, eliminate microdamage, and reduce the pain reaction to cold/hot. Saturation of dental tissues with fluoride ions helps to achieve this effect. A simple or deep fluoridation procedure is possible. In the first case, the dentist uses fluoride varnishes or fluoride gels. They are applied to the teeth using trays or cover the surface of the enamel with a brush. In deep fluoridation, compounds are used to seal tooth enamel. The teeth are first cleaned, dried, isolated from saliva, deep fluoride is applied to them, dried again, and then treated with copper-calcium hydroxide. With this method, a fluoride-containing substance penetrates deeply into the pores of tooth enamel and helps preserve calcium.
- Infiltration method.
Another method will stop the development of caries at the spot stage without drilling and filling, and will prevent the formation of a carious cavity. First, the dentist treats the carious stain with a special etching composition; the next step is to apply a liquid composition to the cleaned, washed and dried surface to seal the pores of the tooth. The infiltration method helps stop the spread of the carious process, since the acid produced by bacteria cannot penetrate the sealed pores of the enamel and continue the destructive process. The method is completely safe, painless and suitable even for children over three years old. This treatment is usually not performed on a younger child, because during the procedure you need to sit still for about 20 minutes, which is not possible for small children.
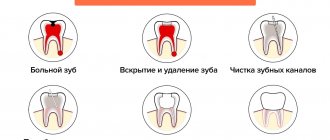
In addition to the listed methods, ozone therapy and laser therapy are used today, which also help stop the carious process without tooth preparation. If a hole has already formed, then the only way to stop caries is surgical treatment. Using a drill, the doctor removes the affected tissue, prepares the cavity for filling and installs the filling there layer by layer, returning the tooth to its natural anatomical shape.
Is it possible not to fill and not drill?
The leading expert of the Australian research group, Wendell Evans, believes that filling is an optional procedure: previously it was believed that when caries appears, you need to immediately drill a hole and install a filling to prevent further tooth destruction; however, tooth decay actually does not spread as quickly as dentists believe. On average, it may take from 4 to 8 years for caries to move from the initial stage of enamel destruction to the destruction of inner dentin.
According to scientists, it is necessary to drill in the case when there is already a hole in the tooth, i.e. its cavity is visible. Before this, local use of dental protective varnish is recommended - it will help in the early stages of caries development to slow down, or even completely prevent its development.
Dental research offers a variety of methods to prevent dental caries. For example, many years of research by dentist Wenyan Shi from the University of California made it possible to positively answer the question: is it possible to stop carious lesions with a simple rinse?
Late last year, Dr. Shi introduced a new mouthwash to American patients that almost completely destroys harmful streptococcal bacteria. These bacteria are the main cause of dental caries. They contribute to the formation of plaque on teeth, which in turn can also cause gum disease and erode enamel.
The new mouthwash contains special antimicrobial peptides that only affect bacteria that cause caries. This approach differs significantly from the action of various antibiotics, which kill all bacteria, both harmful and beneficial. Also, the use of such peptides makes it possible to develop a kind of protection against the formation of new plaque and tartar.
Despite the safety and effectiveness of this product, experts do not cancel traditional teeth brushing, since the likelihood of streptococci counteracting such peptides still remains. To further study this problem, dentist Wenyan Shi has already received a grant.
It is quite possible that such rinses will soon be recommended by dentists in Volgograd and Volzhsky. In the meantime, American patients have the opportunity to taste the peptides by purchasing special anti-caries lozenges.
Do not delay visiting the dentist; timely plaque removal and professional teeth cleaning will allow you to postpone the appearance of caries for a long time, which means the danger of tooth loss!
Features of caries in elderly patients: how to slow it down
Elderly people are considered to be over 60 years of age. Caries in the elderly develops under the influence of the same cariogenic factors as in younger people, but there are some peculiarities.
A study conducted in a Swiss clinic showed that in patients aged 50-94 years, a quarter of the remaining teeth were affected by caries.
One of the characteristic features of caries in the elderly is its localization in the neck of the tooth. Often in older people, carious lesions do not spread deep into, but along the surface of the tooth enamel. Many people wear dentures, and the teeth in contact with them are often affected by caries. A large percentage of defects are recurrent and chronic caries.
As you age, the risk of tooth root caries increases, which some doctors call the main problem in treating the teeth of older people.
Effective measures to prevent caries in the elderly are:
- professional oral hygiene twice a year;
- brushing your teeth twice a day using a toothbrush, toothpaste and floss;
- use of saliva thinners;
- deep fluoridation of dental tissues.
This set of preventive measures helps reduce the risk of developing caries in the elderly by more than half.
Stages of cervical caries
Cervical caries develops according to the same scenario as other types of this disease, but much faster. Let us describe the stages of development of root caries:
- Initial (white spot stage). It is asymptomatic. A demineralized area of enamel forms in or under the gum area. It looks like a white or chalky spot. Gradually it begins to fade, but this is difficult to notice with the naked eye, especially if the pathology is localized on the back surface of the tooth or on the molars and premolars. If it starts under the gum, then it can only be detected using hardware diagnostics.
- Superficial. The carious spot becomes larger and acquires a yellowish or brownish tint. Destructive processes begin on the tooth surface. At this stage, the pathological focus has not yet spread to hard tissue. The patient may experience discomfort when eating sweet foods. It disappears immediately after the stimulus is removed. Often people attribute this symptom to increased sensitivity of the gums.
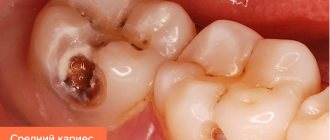
- Average. Damage to hard tissues is observed. A person experiences severe discomfort when eating sweet, sour, cold or hot foods. Possible pain. These signs disappear as soon as you brush your teeth.
- Deep. The last stage is an advanced form of the disease. Deep damage to dentin occurs. The pathological process involves the tooth root and pulp. The tooth may split into several parts or break in the neck area. The patient almost constantly experiences pain, which painkillers do not help eliminate.
Treatment for caries can vary depending on the degree of damage to the tooth. The method is selected individually after diagnosis.
How to treat cervical caries on the front teeth
Cervical caries of the anterior teeth causes the most discomfort. Firstly, it develops and progresses faster than on molars and premolars. Secondly, the front teeth fall into the smile zone, so a cosmetic defect also occurs. Treatment is carried out according to the usual scheme, but the material for the filling is selected more carefully. It should not differ in color from the rest of the tooth, otherwise it will look unaesthetic. The cost of such a filling is significantly higher than the standard one.
How to treat initial cervical caries
At the white spot stage, caries can be treated using therapeutic procedures. It is necessary to restore the enamel structure by saturating it with minerals. First, the dentist will clean the affected tooth from plaque and tartar, and then apply a solution containing fluoride, magnesium, phosphorus and calcium to it. Under the influence of the active components, the enamel is remineralized and the pathological process is blocked. The patient is also prescribed mouth rinses with an antiseptic solution and toothpaste with fluoride.
How to treat superficial caries
If the carious area has managed to destroy the enamel, but has not penetrated into the hard tissues, remineralization is carried out, as in the first stage. The dentist grinds the affected area of the tooth, removes damaged tissue and applies a solution to the enamel to restore it. Several procedures may be required - 5-10 sessions. Throughout the treatment, the patient uses medicated toothpaste.
Treatment of cervical caries at the middle stage
As a rule, people consult a doctor when root caries has reached the third stage. At this stage, tooth filling is required. The doctor removes the affected tissue, carries out antiseptic treatment of the carious cavity and fills it with filling material. The procedure is performed under local anesthesia.