How does a tooth rot?
Recognizing that dental tissue is susceptible to rotting is not so difficult. There are a number of pronounced symptoms that indicate this:
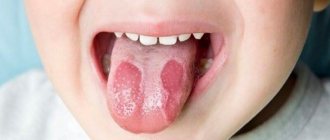
- A bad odor appears from the mouth.
- The color of the tooth does not change for the better; it begins to darken.
- Holes appear on the tooth. When food, cold or hot liquids get into them, acute, sometimes unbearable pain is observed.
- In the most advanced cases, loosening of the unit is observed.
If you experience at least one of the above signs, you need to urgently go to the dentist, otherwise you may lose a tooth. Remember that having a rotten tooth is not only an aesthetic drawback. This can lead to other health problems.
How to identify rotten tooth roots and rotten teeth
Why are rotten teeth dangerous? First of all, unpleasant sensations. It is discomfort that serves as a signal of problems with dental health. The following symptoms should alert you:
- rapid formation of plaque on enamel;
- unpleasant putrid odor from the mouth;
- painful reaction to hot or cold, to sweet foods;
- pain or even mobility of teeth when chewing;
- stains on tooth enamel - yellow, brown, black;
- swelling of the gums in the area of the decayed neck of the tooth;
- purulent discharge;
- constantly increasing pain.
At the same time, the patient should not be reassured by the disappearance of pain and discomfort due to rotten teeth. The inflammatory processes did not stop or reverse. The absence of pain only indicates that the root of the tooth has begun to rot.
Why is this happening?
The main reason for this problem is poor hygiene, lack of timely dental treatment and neglect of preventive dental examinations. In 90% of cases, it is these factors that cause tooth decay. There are also indirect reasons that can affect this process:
- Having bad habits, especially smoking.
- Hereditary predisposition.
- Bad ecology.
- Poor nutrition.
- Concomitant diseases of the oral cavity.
- Poor quality drinking water.
Tooth root caries - treat or remove?
Just a few years ago, the answer to the question “Is it possible to cure tooth root caries?” would be definitely negative. The diagnosis suggested mandatory removal. However, today the situation has changed - modern drugs and methods for treating root caries make it possible not only to save the tooth, but also to prevent the disease.
However, if more than half of the root is damaged, removal will still have to be considered. Although even here there is a possibility that the tooth itself can be saved. The main methods of treatment that allow you to save a tooth in the presence of root caries: resection (removal of the affected root apex), amputation (removal of one part of a multi-rooted tooth), coronoradicular separation (separation of roots in the presence of caries in the branching area), hemisection (removal of the damaged part of the root together with an adjacent crown). The final decision as to whether the tooth can be saved is made by the attending physician based on diagnosis.
What could be the consequences?
Complications and consequences can be disappointing. Losing a tooth is not the worst thing that a rotten tooth can lead to. An abundant accumulation of pathogenic microorganisms often provokes problems with the body and disrupts the functioning of internal organs. Let's consider a number of the most common manifestations:
- Blood poisoning.
- Inflammation of the meninges.
- Constant headaches.
- Sleep disturbance.
- Problems with the gastrointestinal tract.
- Lack or significant decrease in appetite.
- Damage to adjacent teeth.
Treatment of tooth root caries
The main problem in treating tooth root caries is gaining access to the lesion. Therefore, the stages of treatment proceed according to the following scenario.
- Retraction is the lowering of the gum edge using special threads.
- Elimination of overgrown gum tissue.
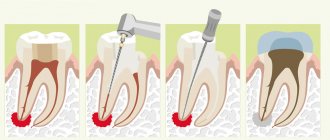
- Direct treatment of caries. If it is possible to diagnose a patient with root caries in the spot stage, then treatment will be reduced to a fluoride remineralization procedure and the prescription of a course of calcium-containing medications. The advantage is that the cement tissue of the tooth is much more susceptible to remineralizing therapy, and thanks to this property, treatment and restoration of the tissue occurs quite quickly. If the disease has managed to lead to a defect in hard tissues, drilling and filling of root caries will be required.
- Installation of an inlay or crown (relevant if the tooth is more than half destroyed).
Treatment of tooth root caries should be carried out by a specialist with extensive experience and high qualifications, since the procedure, due to the close proximity of the vessels, requires especially careful manipulation of instruments. During treatment, special drugs are used that minimize the risk of further damage. To make sure that all infected areas have been removed, a caries indicator is used - a special substance that is used to fill the cleaned cavity. To fill root caries, materials are used that protect the tooth from secondary caries under the filling.
So, after contacting the doctor, the following algorithm will follow:
- X-rays must be taken to determine the condition of the tooth root.
- The doctor examines the coronal part of the unit and assesses the situation.
- Construction of a treatment plan. The patient should be explained in detail about the clinical picture and methods of its treatment.
- Be sure to carry out comprehensive hygienic treatment of the oral cavity in order to thoroughly remove plaque and tartar.
- If the root is in normal condition and has no deviations, the canals are cleaned, the tooth is polished and filled. In some cases, depulpation, that is, removal of the nerve, may be required. This procedure is necessary if pulpitis is observed against the background of advanced caries.
- If the rotting process is observed at the root, then the only option is to remove the damaged unit and further prosthetics.
Do I need to remove rotten teeth?
If a tooth root or crown is completely rotted, it cannot be restored. Such a tooth cannot be left in the jaw so that its purulent contents do not spread to the surrounding tissues. If there is rot in the root canals, it is not possible to make artificial crowns, since they will not be able to fix on the destroyed tissues. Therefore, in advanced situations, dentists prescribe the removal of a rotten tooth, and this operation cannot be refused. After removal, a course of antibiotics may be prescribed.
To prevent your teeth from rotting, you need to regularly monitor their condition. To maintain dental health, you need to adhere to a nutritious diet and maintain oral hygiene, as well as promptly treat any dental and internal diseases. Purulent processes are extremely dangerous, therefore, if the carious process has reached an advanced stage, you should not refuse to remove the diseased tooth.
How to prevent trouble
It is much easier to prevent this situation than to solve it. Preventive measures are extremely simple. Just follow a few important tips:
- Make it a rule to go to the dentist every six months for preventive examinations.
- At least once a year you should get rid of tartar and accumulated plaque (this is done in the dentist’s office).
- Hygienic measures must be carried out efficiently and regularly (at least twice a day).
- Nutrition should be complete and varied so that the body does not experience a deficiency of beneficial microelements.
- Try to drink only filtered water.
- Stop smoking as soon as possible.
- Carry out dental treatment in a timely manner.
Content
- Causes of tooth decay
- Signs
- Dental diagnostics
- Methods of dental treatment
Pathological changes in teeth restored with crowns are an extremely unpleasant situation and, moreover, dangerous for the health of the entire body. With the correct use of a well-made and installed crown, the likelihood of such problems occurring is minimized. However, cases of tooth decay under crowns still occur. It is important to recognize the problem in time and seek help from a doctor.
PROMOTION
Zirconium crowns and bridges
RUB 12,500
What types of this pathology exist?
Depending on the origin, the classification of periodontitis includes:
- an infectious form that develops mainly as a complication of caries, and then pulpitis;
- traumatic periodontitis is a consequence of a strong external impact on the tooth with its damage.
According to the type of clinical course, pathology is divided into:
1. Acute form with rapid development of symptoms. It, in turn, is divided into a serous subtype - with periodically changing pain intensity; and purulent - with purulent discharge, constant severe pain, tooth mobility and a high risk of irreversible loss.
2. Chronic periodontitis of the tooth, which progresses rather slowly and sometimes has no clinical manifestations at all. This form of the disease is divided into three subtypes:
- fibrous variant - the initial stage of the disease, which is often detected by chance - on radiography for other reasons;
- granulating periodontitis - the next stage with swelling of the soft tissues of the gums, the appearance of purulent discharge, as well as constant pain;
- granulomatous periodontitis, in which purulent cysts are already formed in the thickness of the gum tissue, requiring immediate surgical removal.
The types of the disease are also divided according to the location of the inflammatory process. If the apex of the tooth root is affected, it is apical periodontitis, which in most cases becomes a complication of pulpitis. And when periodontal inflammation occurs in other parts of the tooth, a marginal form develops - its appearance is most often caused by injuries.
Treatment
Before developing a therapeutic program, you need to conduct an examination and establish what caused the disease. If treatment is prescribed without establishing an accurate diagnosis, it will provide temporary relief.
- First, the dentist examines the oral cavity using palpation.
- The patient is then sent for radiographic diagnosis. An x-ray must be taken when a rotten wisdom tooth is discovered, because this area is difficult to see visually.
- An important step is to identify the area of decay with infected lesions of the periodontal tissues.
- If necessary, the patient is recommended to undergo instrumental diagnostic methods.
- To determine the type of pathogen, a smear is taken.
After analyzing the information received, the doctor draws up a therapeutic plan. Treatment, removal, or prosthetics may be prescribed. The conservative method is used in the initial stage of the disease. It consists of an antiseptic treatment to kill pathogenic bacteria. Rotocan, Miramistin, Chlorhexidine may be prescribed. To treat periodontal tissues, periodontology suggests using gel products that are applied to the gums. The painful area is treated with Kamistad, Solcoveril, Dentol, Pansoral.
Soft and hard deposits are removed, the canals are cleaned according to indications, followed by filling. Dentists resort to fluoridation of enamel to strengthen its tissue. The dentist recommends that the patient use mouth rinses, which speeds up healing. The doctor explains the importance of following the rules of care for the chewing organs and oral mucosa.
Do I need to remove rotten teeth?
If a tooth has rotted down to the gum, its root cannot be treated; as a rule, extraction is used. But only the dentist can decide on removal. Surgical operations are performed with complete irreversible destruction of tissue. Before making such a decision, the doctor should definitely consider the possibility of a composite restoration. Only when this is not possible and preservation methods are useless is extraction performed. This is an extreme measure, a radical technology. When the wound has healed, an implant is implanted or prosthetics are performed. This event must be carried out without fail, otherwise healthy masticatory organs will gradually begin to shift and become loose. This will disrupt your bite, change your facial expression, and make your smile unattractive.