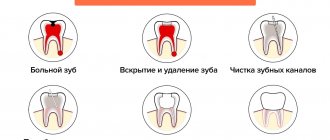
Tooth root granuloma (apical granuloma) is a formation around the apex of the tooth root, consisting of granulation tissue. It is a type of chronic periodontitis – its granulomatous form. Without proper treatment, the disease can cause dangerous complications.
Timely implementation of preventive measures will help prevent the development of the disease or diagnose it at the initial stages of development. This will help you get by with conservative treatment methods and avoid serious surgical interventions.
Causes of the disease
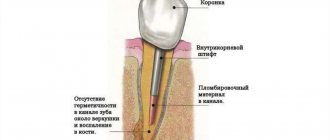
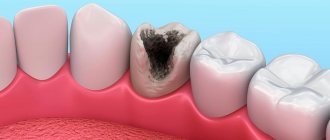
The main cause of apical granuloma is chronic pulpitis, when bacteria penetrate the periodontium through the root canals and periodontitis develops. Gradually, the inflamed tissues around the apex of the tooth root grow, and a cavity appears filled not only with granulation tissue, but also with purulent contents. The size of the granuloma reaches 0.5 cm, the bone tissue at the site of its formation is resorbed. Without treatment, the neoplasm becomes covered with a capsule, the granuloma turns into cystogranuloma (average size 0.5-0.8 cm), and later a cyst forms (its size can reach more than 1 cm).
Also, the reasons for the development of apical granuloma are:
- periodontal injuries;
- tooth root cracks;
- incorrect application of arsenic to the tooth cavity during the treatment of pulpitis;
- non-compliance by the dentist with the technique of filling root canals after removal of the dental nerve.
What is the difference between a dental cyst and a granuloma?
Many patients in dental clinics confuse cysts and dental granulomas, while these two pathological processes are significantly different. Seeing the difference is important because the diagnosis affects how the problem is addressed. Thus, treatment of tooth root granuloma is often conservative, but getting rid of the cyst can only be done through surgery - it is excised or removed along with the affected unit. So, how is a granuloma different from a cyst?
- Firstly, by its structure and structure. The first does not have a cavity and is a continuous formation of granulations, while the second is a capsule that is filled with pathological contents;
- Secondly, its size. Cysts are always larger than granulomas: they often reach one centimeter in diameter;
- Thirdly, symptoms. Granuloma is more prone to exacerbation, the development of pain symptoms and exacerbations than a cyst. But if the latter reaches a large size, the unit becomes mobile, which is not observed with granulomas;
- Fourthly, in the condition of the surrounding tissues. With cysts, the mucous membrane does not look inflamed and does not change its color, but the bone tissue, as the process progresses, becomes more pliable and decreases in volume. With granuloma, the mucous membrane reddens and swells, the formation of a fistula is possible, but the bone tissue is almost not affected.
On an x-ray, the cyst has clear contours and boundaries, which cannot be said about the granuloma, which looks like a darkened round shape.
Symptoms of granuloma
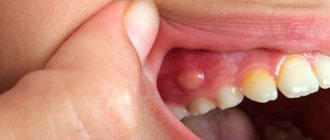
Often the chronic granulomatous form of periodontitis is asymptomatic; sometimes patients complain of minor pain when biting and discomfort in the area of the diseased tooth. When granuloma grows, the following symptoms occur:
- swelling and redness of the gums:
- darkening of the affected tooth;
- increased toothache, its bursting nature;
- sharp sharp pain in the tooth in the morning, immediately after waking up;
- discharge of pus from the subgingival space;
- development of periostitis - inflammation of the periosteum (patients call it gumboil): the gums swell greatly, the swelling spreads to the lips and cheek; toothache radiates to the ear, temporal region, eye; a fistula tract may appear through which pus is released;
- increase in body temperature to 38°C and above;
- headache;
- feeling that the tooth has grown and become taller when biting;
- general weakness.
Factors contributing to the manifestation of symptoms of the disease:
- a sharp change in climatic conditions (weather change, moving to an area with a different climate);
- stress;
- hypothermia of the body;
- previous colds;
- physical stress.
Diagnosis of granuloma
During a routine examination, there are no signs of granuloma development. The affected tooth may not have a cavity or may have been treated previously, but without signs of any abnormalities. When tapping on the tooth, patients do not feel anything; slight sensitivity is possible; The doctor may be alerted by a painful bulge on the gum along the projection of the granuloma. In this case, the patient must be referred for an X-ray examination.
Granuloma is often discovered accidentally when taking x-rays during treatment of caries and root canals in adjacent teeth. In the photograph, an apical granuloma appears as a dark spot at the tip of the tooth root.
Our doctors are always ready to help and cure granuloma.
| Pankratieva Alesya Georgievna. Practicing dentist of the first qualification category. More than 15 years in the profession. Founder of the Family Dentist clinic, Member of the Belarusian Dental Association. View profile | Bobkova Irina Leonidovna. Practicing dentist of the highest qualification category. More than 20 years in the profession. Assistant professor. Co-author of a patent for a method of treating periodontitis. View profile |
Feedback from our patient:
Thank you very much for your attentive attitude towards patients. Quality services. I have been discussing at the Family Dentist for a long time and the doctors always have a good mood and a smile on their face. I will recommend your dentistry to my friends and acquaintances.
With respect, Gameza N.A.
| Do not leave the source of infection untreated - sign up for the Family Dentist clinic. The sooner you start treatment, the cheaper and easier it will be. | Call to make an appointment +375 29 604-61-61 |
Treatment of granuloma
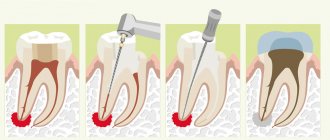
Treatment of granuloma can be therapeutic (conservative) and surgical; the choice of treatment method depends on the degree of development of the disease.
Conservative treatment
It is carried out at an early stage of granuloma development, when its size is small. Stages of conservative treatment:
- Opening the tooth cavity to access the root canals using a drill. Anesthesia is applied.
- Working with channels. If they were sealed, they will be unsealed. If the canals have not been previously filled, depulpation is performed - removal of the nerve of the tooth, followed by instrumental treatment of the canals.
- Root canal treatment using medications. In order to eliminate the source of inflammation, the root canals are washed several times with antiseptic solutions.
- Removal of medicinal substances beyond the root apex using the instrumental method. This is done to speed up the resorption of the granuloma.
- Filling the canals with temporary material and installing a temporary filling. Paste for temporary filling has an antiseptic effect.
- Repeating points 4 and 5. Rinsing the root canals and replacing the medication behind the apex is carried out several times until the granuloma is completely reabsorbed.
- Ingestion of antibacterial drugs. The use of antibiotics and sulfonamides helps get rid of pathogenic microflora at the apex of the tooth root. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are also prescribed to eliminate pain: ketorolac, nimesulide, ibuprofen.
- X-ray control. Allows you to evaluate the effectiveness of therapy.
- Root canal filling. If the granuloma is successfully treated, the root canals are filled with permanent materials.
- Placing a permanent filling.
Conservative treatment of granuloma is long-term and can last about six months. After placing a permanent filling, it is necessary to periodically carry out control radiography of the tooth.
Depophoresis
Depophoresis is a new method of conservative treatment of root canals, with which you can get rid of apical granuloma. Its essence lies in the treatment of the canals of a pulpless tooth with copper-calcium hydroxide ions using a special apparatus. An aqueous suspension of copper-calcium hydroxide has high antibacterial properties and can stimulate the formation of bone tissue.
After cleaning the root canals, a medicinal substance is injected into them, and under the influence of a weak current, electroiontophoresis of copper-calcium hydroxide occurs. As a result of the procedure, microbes are destroyed, unremoved remains of the dental nerve are destroyed, and the inflammatory process stops.
The advantages of the method are the possibility of its use on teeth with curved root canals and ensuring complete sterility of the treated canals. The course of depophoresis consists of three procedures with weekly breaks, but the doctor can adjust these periods.
According to statistics, the percentage of successful treatment of granuloma with therapeutic methods is about 80%; if conservative treatment is ineffective, surgical methods are resorted to.
Surgical methods for treating granuloma
Surgical treatment is used not only if therapeutic treatment is ineffective, but also in advanced cases, when the granuloma has reached a large size and threatening symptoms have appeared: increased body temperature, swelling of the gums and cheeks, purulent discharge from the gums.
Previously, surgery for apical granuloma consisted of tooth extraction. Modern surgical methods make it possible to save a tooth or part of it, but this is impossible in the following cases:
- the cause of the disease was a cracked tooth as a result of some trauma;
- severe tooth decay due to untimely treatment;
- lack of patency of root canals.
The following surgical treatment methods can be used:
- Opening the gums to drain pus. A drainage tube is installed in the wound, the purpose of which is to prevent the wound from healing and facilitate the removal of pus.
- Cystectomy – removal of the granuloma along with the damaged apex of the tooth root (resection of the apex). The removed tooth tissues are replaced with artificial ones, and a permanent filling is placed.
- Hemisection - performed on multi-rooted teeth, consists of removing the granuloma along with one of the roots of the tooth and part of the tooth above it. After the operation, a crown is placed on the tooth.
During surgical treatment, antibacterial drugs and anti-inflammatory drugs are necessarily prescribed.
Causes of dental granuloma
The exact reasons for the formation of granuloma are not clear. Most often they occur against the background of other dental diseases:
- dental caries with pulp damage;
- periodontitis and periodontal disease;
- pulpitis;
- inflammation of the tissue under the crown;
- injury to the tooth or jaw.
Tooth granuloma does not begin overnight. For it to begin, a long-term inflammatory and infectious process is required with the gradual death of the pulp inside the tooth. Bacteria penetrate into the tooth canal and further into the bone and soft tissues surrounding the root. At the same time, a defense process is launched in the body, which consists of an attempt to limit the spread of infection. Infiltrative tissues are transformed into connective tissues. Thus, a dense membrane is formed around the source of inflammation, in which an infiltrate consisting of living and dead bacteria collects.
Granuloma is formed only in the presence of stress factors that are superimposed on the infectious and inflammatory process. These include hypothermia, severe fear, difficulties at work, and so on. Even moving from one climate zone to another can provoke the formation of hilar granuloma. It is these situations that provoke an exacerbation of the disease, in which unpleasant symptoms appear.
Laser treatment
A promising method of treating tooth root granuloma is laser therapy. The advantages of this method with timely initiation of treatment:
- non-contact impact on the source of inflammation;
- the laser ensures the sterility of the procedure;
- absence of stress and pain for the patient;
- short recovery period after treatment.
Before the procedure, the tooth cavity is opened and the root canals are cleaned. A laser light guide is inserted into the prepared channel and the granuloma is treated with laser radiation. Under its action, the granuloma evaporates, and at the same time, nearby tissues are disinfected.
Treatment at the Family Dentist clinic
We have a good reputation in Minsk, consultations are conducted by dental therapists with 16 years of experience , specializing in the treatment of dental canals. They trust us; more than 80% of patients brought family members and friends to the clinic. Every second patient has been with us for more than 6 years. We do radiovisiography on site in the office, working with four hands together with an assistant to reduce the time of unpleasant manipulations. The effectiveness of dental granuloma treatment is ensured by premium class equipment. Even with serious damage to the crown and root, we strive to preserve the dental unit.
Traditional methods and treatment at home
The use of traditional methods in the treatment of granuloma can lead to complications and irreparable consequences.
Under no circumstances should hot compresses be applied to the cheek on the side of the inflammation: this will accelerate the spread of pus. Even if you know the names of antibiotics used in the treatment of tooth root granuloma, you should not take them yourself. Treatment methods should only be chosen by a doctor.
The only thing that can be done while it is not possible to get an appointment with a doctor (for example, symptoms appeared late in the evening) is to take a Nurofen or Ketanov tablet to eliminate the pain.
You need to understand that the development of inflammation occurs inside the root canals and in the jaw, which cannot be reached by any folk remedies, and only the help of a specialist will help save the tooth.
Prevention
To avoid the development of cystogranuloma and its possible consequences, it is necessary to follow some preventive measures:
- examined twice a year to check for pathologies in the oral cavity and teeth and have them eliminated in a timely manner.
- Carefully monitor oral hygiene
- Change toothbrushes often .
- healthy .
It must be remembered that self-medication using traditional medicine recipes without a doctor’s recommendation can lead to serious consequences.
Complications
Untimely treatment of apical granuloma leads to the following consequences:
- Transformation of a granuloma into a cyst, the treatment of which is more difficult. The cyst can degenerate into a malignant neoplasm.
- Tooth loss. This leads to aesthetic discomfort, disruption of chewing and speech functions, and necessitates prosthetics.
- Due to the spread of infection through the bloodstream, there is a high risk of infectious myocarditis, an inflammatory lesion of the heart muscle.
- The development of pyelonephritis is an inflammation of the kidneys, which is also caused by the spread of infection from the focus at the apex of the tooth root.
- The threat of odontogenic sinusitis - inflammation of the maxillary sinuses due to infection from the root of the tooth.
- The development of osteomyelitis – purulent-necrotic inflammation of the jaw bone.
- The appearance of odontogenic subcutaneous granuloma is a change in the subcutaneous fat layer under the influence of microorganisms that have penetrated from the source of inflammation. As the disease progresses, fistulas appear on the skin of the buccal and submandibular areas, from which bloody-purulent discharge is observed for a long time, sometimes for several months.