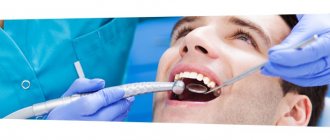
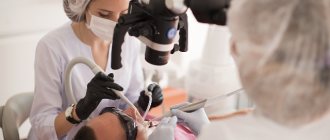
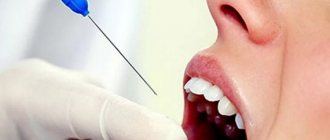
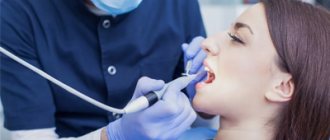
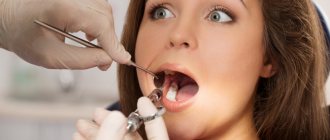
- We use modern equipment. We use a microscope to accurately assess the condition of the canals and treatment, as well as a laser for better cleaning of cavities.
- We preserve living tissues We use endo-tips, which, in combination with a microscope, allow us to remove only affected tissues.
- We use nanostructured filling materials. Materials enriched with minerals prevent the re-development of diseases.
- We provide extended warranties and are responsible for the work done. Long-term guarantees even for therapeutic treatment and 3 years of free service for disease prevention.
Regardless of the treatment method, Smile-at-Once specialists use gentle techniques that allow you to remove the dental nerve with minimal damage to living tissue. Without a nerve, a tooth can last for several decades and can also be used as a support for a prosthesis.
In our clinic, in a number of situations, a microscope is used to treat pulpitis - due to the presence of special magnifying glasses, the doctor is able to better examine the condition of the tissues inside the tooth and carry out better cleaning of the canals, especially narrow and curved ones. This ensures that there are no pockets of inflammation under the filling, which can lead to destruction of the tooth from the inside and the spread of infection to the tissue around the tooth root.
Why do you need temporary dental filling in a nutshell?
Endodontic treatment or root canal treatment, a complex procedure that consists of instrumental and medicinal treatment of the canals, their temporary filling and permanent obturation
The goal of any endodontic treatment is to prevent the development of inflammatory processes and complications after pulpitis and periodontitis.
After providing access to the root canals, removing the inflamed or necrotic pulp and treating the tooth canals, Novodent+ doctors often temporarily (for 2-3 weeks) fill the canals with various medications. The purpose of this temporary filling is to sterilize the entire root canal system. Temporary filling materials have a pronounced antimicrobial effect. This stage of endodontic treatment is optional; it is used for acute and chronic periodontitis, abscess, and sometimes in the treatment of pulpitis in multi-rooted teeth.
The final stage of endodontic dental treatment is permanent obturation of the root canal (or canals, there may be several of them). And only after permanent filling do doctors begin to restore the tooth. After each stage of root canal treatment, a temporary filling is placed on the tooth, which protects the tooth from infection from the oral cavity and provides comfort to the patient between appointments with the doctor.
| Why do you have to re-treat dental canals? |
Tooth hurts after filling
If your tooth hurts after a filling for just a few days, then don’t panic! Provided that the pain is not severe, does not arise on its own, but from external factors (during meals, as a reaction to hot/cold), such pain can last up to two weeks. This depends on the individual tissue’s ability to regenerate after the intervention.
The most common reasons that are responsible for toothache after filling:
- Traumatic pain (overheating of the tooth): When preparing a tooth for filling, there is a chance that the tooth's pulp may experience a sudden shock, and this may be the reason why the tooth hurts after filling. If such toothache persists, then, most likely, you will have to treat the root canals.
- Referred pain: The nerves of nearby teeth may carry signals from the nerves of the filled tooth. That is, teeth that were not involved in the treatment process may also hurt.
Misdiagnosis: If there is no correct diagnosis, then there is no correct treatment. This most often happens when the doctor neglects radiography. But there are also borderline cases when the doctor, trying to preserve your tooth as much as possible, uses the least invasive (traumatic) treatment. Sometimes it is worth it, but the result of treatment is not guaranteed (the patient is usually warned about this).
Each person is unique, and the body's response to treatment is always individual. Pain is a normal reaction to external intervention, although we try to minimize it.
Let's take a closer look.
Endodontic treatment, or root canal treatment , is a long-term procedure that involves removing non-viable nerves and pulp from the tooth. This treatment method is indispensable in dentistry and can significantly extend the life of the tooth in diseases such as pulpitis, periodontitis, etc.
For endodontic treatment, our clinic uses a dental microscope, which allows us to greatly enlarge the canals of the tooth and not treat blindly.
Indications and contraindications for tooth nerve removal
Indications for the procedure:
- pulpitis,
- periodontitis,
- cysts, granulomas,
- trauma leading to pulp damage,
- indications for orthopedic treatment.
Contraindications:
- viral hepatitis;
- high temperature, especially with ARVI;
- cardiovascular diseases;
- leukemia,
- HIV,
- stomatitis;
- mental illness, epilepsy;
- tuberculosis.
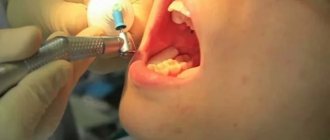
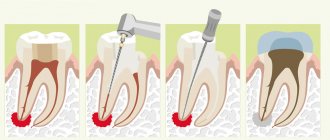
Stages of root canal treatment
Endodontic treatment is carried out in several stages, namely:
- Professional oral hygiene.
- Providing access to the channel.
- Removal of nerves and pulp.
- Mechanical and medicinal treatment of root canals.
- Temporary tooth filling.
- Permanent tooth filling and restoration of its shape.
If the essence and purpose of almost all stages are more or less clear, then not everyone knows why temporary tooth filling is necessary during endodontic treatment.
Further in the article we will tell you why temporary filling is performed, why a temporary filling is placed after root canal filling, what indications for this procedure exist and why a tooth may hurt after temporary filling.
Treatment without nerve removal
After making sure that the pulp is not infected, the dentist will not remove the dental nerve. In this case, treatment is carried out according to the following scheme:
- The patient is given an anesthetic injection, after making sure that he is not allergic to anesthesia.
- Using a drill, the tooth is prepared and all affected, necrotic tissue is removed.
- Next, the doctor carries out medicinal treatment of the tooth with antiseptic drugs.
- Thoroughly dry the prepared cavity with an air stream.
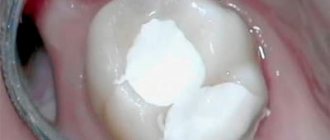
- A therapeutic or insulating pad with eugenol, calcium hydroxide or other substances is installed at the bottom of the cavity. This is the most important stage in the treatment of deep caries, because the lining protects the pulp from pressure and other negative influences from the filling, and also has an antimicrobial effect and stimulates the growth of the dentinal layer between the bottom of the cavity and the pulp. Installation of a gasket for deep caries is carried out in 95% of cases, although if the walls and bottom are sufficiently thick, the doctor may decide to fill the tooth without a therapeutic gasket
- The next step is installing the seal. Fillings made from light-curing composites are considered one of the most reliable and durable. This material is applied layer by layer to the tooth and each layer is illuminated with an ultraviolet lamp. Light fillings almost do not sag, have high strength and good aesthetic characteristics, therefore, when treating deep caries, it is recommended to use just such a filling material.
- At the last stage of treatment, the filling is aligned to the bite, polished and ground smooth, giving the tooth a natural anatomical shape.
If the dentist suspects infection of the pulp due to deep caries, he will not immediately place a permanent filling. After dissection and removal of the affected tissue, he will apply medication and install a temporary filling. If toothache does not appear within four days, then there is no pulpitis, and the doctor will replace the temporary filling with a permanent one. If increasing pain appears during this time, the patient probably has pulpitis. In this case, pulp inflammation is treated using the optimal method, and only after that the tooth is covered with a permanent filling.
After treatment of deep caries in a tooth with preserved pulp, moderate pain may be felt, which occurs when chewing and normally goes away after a couple of days. If the pain persists longer and intensifies, you should definitely consult a dentist.
Temporary filling
Why a temporary filling is placed after root canal filling is a common question.
Root canal treatment is quite lengthy and often requires several visits to the dentist. Protection of open root canals from external flora at the time of treatment is one of the main indications why a temporary filling is placed after filling the canals. In addition, filling a tooth with a temporary filling is also carried out for therapeutic purposes - the material for such filling can be various medications (antibacterial, corticosteroid, antiseptic, antifungal pastes for filling).
The following reasons can be identified why a temporary filling is placed after canal filling:
- Root canal cleaning.
- Their disinfection - based on various observations, filling a tooth with a temporary filling can destroy up to 97% of bacteria.
- Preventing the development of the inflammatory process.
- Activation of regenerative processes in periodontium.
Thus, the main task of temporary filling is to prevent the development of complications and protect open canals during endodontic treatment.
Filling canals with hot gutta-percha
Dentists and manufacturers of dental equipment are constantly improving technologies for passing through canals, their disinfection and filling.
In the NORD DENTAL clinic, for filling complex canals, the method of vertical condensation (compaction) of hot gutta-percha is used using equipment from the German company VDW GmbH.
Today this is the most effective technology for “sealed” channels of complex shapes.
Come to the NORD DENTAL clinic for quality dental treatment.
Why do you need a temporary filling?
Temporary filling of root canals is an optional step in endodontic treatment. Indications for its implementation are various conditions and diseases, which we will discuss below.
For therapeutic purposes, temporary canal filling can last for several weeks, but usually the temporary filling is replaced with a permanent one at the next visit to the dentist. The main tasks performed by temporary filling of root canals are their complete disinfection, treatment of the pulp, if appropriate, elimination and prevention of inflammatory processes, monitoring the effectiveness of root canal treatment (the paste that is used during temporary filling is visualized on x-ray).
Drugs placed under a sealed barrier
The service life of the temporary plug initially depends on the drug put into it:
- Arsenic is used to kill the nerve in the tooth for subsequent depulpation. For this purpose, a number of other toxic substances are used, which help not only to painlessly remove the nerve, but also to subject the entire pulp tissue to necrosis;
- To treat periodontitis or pulpitis, antiseptics or antibiotics are used to relieve inflammation. Such a filling is usually worn for about 20 days until the infection is completely suppressed.
How long do you need to wear a filling?
You can wear a temporary filling for a period of one day to six months. The maximum validity period of Vinoxol, the strongest and most durable of them, is exactly 6 months. However, such fillings are placed quite rarely, and in general their shelf life depends on their original purpose.
If medicine was placed under the cork, the period will be from 3 to 20 days. In general, the timing of removing the temporary barrier depends entirely on the treating dentist.
Important! You should not wear a temporary filling in your mouth for a longer period than recommended by your doctor, even if it is in perfect order.
Description of pulpitis
Those who are not good at dentistry do not even realize that there is a main nerve in the tooth. Its inflammation is called pulpitis. This is a very complex disease, the symptoms of which are almost impossible to miss. At risk are people who have advanced caries with extensive carious cavities. As a rule, the first signs are observed after consuming too hot, cold foods or drinks. The nerve begins to react sharply to aggressive substances, which causes severe pain in the tooth, body temperature often rises and a general loss of strength. If you immediately go to the doctor and begin treating pulpitis, the intensity of the inflammatory process can be quickly reduced. If you try to solve the problem at home for a long time with the help of painkillers and improvised means, you may waste time and the only way will be to completely remove the nerve.
How to diagnose the disease
The decision on depulpation is made by the endodontist and he performs the procedure only after assessing the examination results.
A number of diagnostic measures are carried out, complementing each other:
- Sight image Allows you to determine in which tooth the nerve needs to be removed, because pain can radiate to neighboring ones, and a person cannot always accurately determine which tooth hurts. It makes it possible to assess the degree of development of the inflammatory process and see the structural features of the tooth.
- Computed tomography 3D image gives an idea of the condition of the tooth itself and the tissues surrounding it. Allows you to accurately determine the number and location of root canals. Identify possible root fractures, foci of inflammation at its apex, determine their location and size.
- Examination under a microscope Multiple magnification of the working field allows the endodontist to visually detect any changes in the tooth tissues - root caries, microcracks. Examine the anatomy of the tooth in all its detail and the smallest detail, identify the narrowest and hidden canals.
In what cases is tooth depulpation required?
Nerve removal or depulpation is an endodontic procedure to remove pulp from the root canal. The pulp (or, as patients say, the dental nerve) is a plexus of nerve fibers and small blood vessels that fills the tooth cavity - the pulp chamber and root canals. Responsible for nutrition of teeth, protects roots from infection.
Depulpation leads to the cessation of blood supply, making the tooth dead - dull and fragile. Therefore, it is advisable to keep the tooth alive. But sometimes it is necessary; removing a nerve when it is inflamed helps relieve a person from pain and save the tooth.
Indications for depulpation can be divided into 3 groups:
Pulp inflammation
The most common indication for nerve removal is pulpitis (or inflammation of the pulp). It develops as a result of advanced caries, when damage to the tooth enamel reaches the pulp chamber, exposure and inflammation of the nerve occurs. In most cases, a person feels unbearable pain and immediately goes to the clinic.
Less commonly, the process is asymptomatic and progresses to a more advanced stage - periodontitis, when the infection has already spread beyond the tooth root.
The reverse relationship is also possible - the infection penetrates through the root apex during inflammation of the tissues surrounding the tooth (retrograde pulpitis). In any case, the infected pulp must be disposed of to prevent complications.
Tooth injury
In the normal state, the nerve is completely isolated, but as a result of fractures and bruises, the dental pulp is exposed and becomes defenseless against microorganisms. Pathogenic bacteria enter the tooth cavity, causing inflammation. Traumatic pulpitis develops.
The second common cause of the traumatic form of the disease is errors in dental treatment. When removing deep caries, the dentist may damage the nerve or fail to place a special gasket under the filling. After treatment, such a tooth continues to hurt. Thermal damage to the nerve is also possible when preparing a tooth for a crown, when hard tissues overheat and the thermal effect is transferred to the pulp.
Preparation for prosthetics
Removal of the pulp before installing a crown is not always carried out; it is determined by the doctor taking into account the clinical picture of each case. If you decide to install a metal-ceramic crown with grinding down a large amount of tissue, it is advisable to remove the nerve. Grinding up to 2 mm is accompanied by the risk of pulp overheating, which causes inflammation under the crown.
For thin metal-free crowns, volume grinding is not required, and pulp removal is not necessary. A denture installed on a living tooth lasts much longer.
What is a nerve and how many are there in a tooth?
A tooth consists of several parts. Enamel is the top, most durable layer. It protects the underlying tissue - fairly dense but porous dentin. The infection slowly destroys it and spreads beyond the crown of the tooth, into the root canals. The first thing on the way is pulp. This is a neurovascular bundle consisting of a different number (from 1 to 3) of nerve endings and blood vessels. They are the ones who nourish the tooth, maintain its strong structure and vital functions. In addition, the pulp protects the connective tissues of the periodontium from infection and immediately reports it through pain and temperature sensitivity. When the nerve is removed, the tooth is left without nutrition and protection, and therefore becomes more fragile and susceptible to chipping. It is considered dead, although it retains its functionality.