Root cysts or gingival granulomas are a common problem today. Neglect of regular examinations, hygiene rules, the development of caries or periodontitis contribute to the development of cystic formations. The disease affects all segments of the population, regardless of gender and age. In fact, it does not matter on which jaw a radicular cyst occurs, because the process of appearance, treatment, and consequences develop according to the same scenario. To eliminate pathology, there are a number of new techniques that can completely eliminate the disease with a guarantee of no relapses.
Radicular cyst as a disease
Cyst translated from Greek means “cavity”, “bubble”. In medicine, this bladder is often filled with blood, organic fluid or purulent exudate. The outer layer of the cystic component consists of soft connective tissue, and the cavity itself is filled with epithelium. Diagnosis of a radicular cyst is carried out specifically in the upper segments of the jaw bone. Detection of its signs in the lower jaw is quite rare. At the very beginning, the disease occurs in a latent stage and does not manifest itself in any way. If detection occurs, it is usually through an X-ray of a completely different dental area. Based on size, dentists distinguish two groups of cysts:
cystogranuloma (about 0.5 cm); cyst (more than 1 cm).
Radicular cysts of the jaws (lower or upper) are cavity neoplasms in the periapical dental area with cystic fluid, formed as a result of the inflammatory process of the periapical (root) part of the tooth. There are main forms of the disease:
acute process; chronic form.
Prolonged growth of the cyst can lead to gradual perforation or thinning of the jaw bone, which increases the risk of jaw fracture in the affected segment. A radicular cyst often requires surgical treatment, so if unpleasant symptoms are detected, a visit to the doctor is urgent.
How does education appear?
Exacerbations of granulomatous periodontitis lead to disruption of circulation in the area of the granuloma, after which fibroblasts accumulate, producing collagen and creating a fibrous membrane. During remission of the inflammatory process, epithelial cells develop, which replace the granulation tissue with the epithelial membrane. This process leads to the development of cystogranuloma, subsequently - perihilar cyst.
If the necessary actions are not taken, there is a risk that the radicular cyst will continue to grow under the periosteum, resulting in a defect that is visible from the bones only with an x-ray.
Etiology and provoking factors
The appearance of a cystic component is the body’s response to the inflammatory process in the tooth. Cysts form in patients with a long course of carious destruction, when the lesion reaches the root part of the tooth. But there are other diseases or conditions that can serve as a trigger for the formation of cavity formations:
chronic periodontitis; severe pulpitis; trauma to the tooth and gums: previous illness of an infectious nature; chronic stomatitis; inflammation of the maxillary sinuses; abnormal bite; catarrhal otitis; diseases with a pronounced decrease in immunity; complication during the eruption of wisdom teeth.
A radicular cyst of the maxillary bone is most often formed under the influence of a long-term untreated carious tooth. Sometimes the cause of the appearance of a radicular cyst in the upper jaw is unprofessional treatment of caries, violation of canal filling technology, or lack of competence of a specialist in the treatment of chronic forms of periodontitis. Lack of treatment for a radicular cyst can lead to serious complications not only from the maxillofacial anatomical zone, but also from all organs and systems of the body as a whole.
Symptoms of a dental cyst
It is practically impossible to recognize the disease at the stage of its inception. The epicenter of development is located deep in the tissues, so it is quite difficult to immediately make a diagnosis. The inflammatory process makes itself felt when external signs or pain symptoms appear:
- darkening of the enamel, redness of the gums;
- pain when biting, pressing;
- itching sensation near the gums;
- discomfort when chewing;
- the appearance of a tugging, sharp piercing pain in the area of the tumor.
During this period of time it is difficult to determine what is happening where. It seems to the patient that this or that tooth hurts - he may mistakenly indicate a healthy one, but in fact, “dead” cells accumulate, and the inflammatory process enters the next stage of development. A purulent formation is formed: the skin is stretched under the pressure of an enlarged, rapidly growing bladder. As the amount of pus increases, the blister grows in size, exceeding 1 cm in diameter. At this stage, the patient’s sensations and appearance make it possible to visually diagnose a dental cyst:
- swelling of the gums, face;
- severe aching pain;
- elevated temperature;
- lack of appetite, malaise;
- statement of the fact of pain in the lymph nodes, their enlargement;
- headache if a cyst appears in the maxillary sinus.
The problem cannot be ignored. The formation of a purulent capsule does not go unnoticed. The process must be kept under control to avoid side effects. We recommend that you consult a specialist when the first, even the slightest, signs of the disease appear. Timely medical care from a dentist helps save the tooth; its results have a positive effect and cause a cosmetic effect.
Clinical picture
The development of the cystic component can develop for about several years and does not manifest itself symptomatically. If unexpressed but unpleasant signs of a cyst appear, treatment should be carried out immediately, since treatment of the tumor after its significant growth will be quite difficult. As the cyst grows, it puts strong pressure on the surrounding connective tissue, so its growth is rapid. In the photographs, the cyst looks like a small spherical formation. The main manifestations are:
the appearance of severe throbbing pain; swelling and redness of the gums in the affected area; feeling of tooth mobility; feeling of fullness in the apical space; bad breath: prolonged persistence of low-grade body temperature.
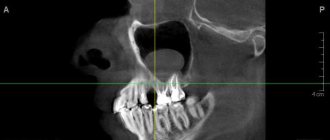
An early cyst can be diagnosed by X-ray examination, and later stages of development are detected by visual examination of the patient’s oral cavity. Usually the suspicion of the presence of a cystic cavity is justified.
The main differences between granuloma and cyst
Indicators and signs for comparative analysis Granuloma Cyst External signs, structure Solid formation covered with connective tissue. Reddish color Cavity with liquid or pus, covered with stretched skin, transparent, dirty-white in color Overall dimensions, diameter of the abscess 40 – 80 mm 90 –300 mm Result of X-ray studies There are no contours of the tumor The image shows a clear border of the round capsule Clinical course of the disease Tooth stable and stands motionless in its place The tooth becomes mobile The condition of the gums and other periodontal soft tissues, lymph nodes Swelling appears in the oral cavity, and redness of the mucous membrane occurs. The effect on bone tissue is insignificant. The cyst develops locally, the inflammation is not transmitted to the mucous membrane. The tumor causes a negative effect by reducing the development of bone tissue, “corroding” it, so the picture shows the process when hard bone tissue decreases
Diagnostic methods
After the patient contacts the dentist, a planned additional examination is prescribed, which will help identify the dental cyst in the upper jaw from other maxillofacial tumors and pathological changes. Among the main ones it is worth highlighting the following:
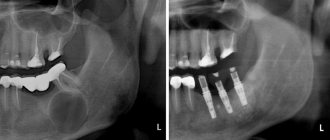
X-ray examination. On an x-ray, the cyst appears as a small oval or spherical shadow with clear outlines. The shadow is located at the top of the tooth root closer to its side. The periodontal gap is not displayed on the image, but significant destruction of the bone structure in the affected area is detected. Electroodontometry. The method is used when it is impossible to differentiate a radicular cyst on an x-ray. The excitability threshold of the affected tooth varies from 90 to 120 μA. Such indicators correspond to necrotic development of the pulp. Puncture. A puncture with a thick needle is performed to reliably exclude the malignancy of the cystic component. The contents of the cyst are sent for cytological examination.
A radicular cyst of the lower jaw bone is almost no different from the flow in the upper segments of the jaw. Often a radicular cyst is similar to osteoblastoma, but the main difference between a cyst is the absence of a cellular structure and the presence of clear contours of shadows in the projection image. Differential diagnosis allows you to reliably identify the disease and treat it according to accepted medical tactics.
Types of dental cysts
A molar cyst is distinguished by several characteristics:
- depending on the reasons for the appearance;
- according to location.
Distributing according to the reasons that provoke the appearance of a dental cyst, the following varieties are distinguished:
- A keratocyst appears on the lower jaw. Older people are susceptible to the disease. It can turn into a malignant form - it grows deeply into the body and destroys the bone.
- Odontogenic or radicular dental cyst is the most common type. After periapical inflammation and necrosis of the pulp, a granuloma of the dental root is formed in the upper part. The size of the purulent focus ranges from 3 mm to 3 cm. The process does not affect bone tissue and does not provoke tooth displacement.
- A cyst that forms at the site of teething is a retention cyst. It appears during the period of replacement of milk teeth with molars. A purulent fistula with bloody contents looks like a dark blue abscess. Education is formed if the process of eruption is slow. The purulent contents of the abscess should be opened and cleaned out.
- A calcifying odontogenic tumor occurs in the area of the support of the lower jaw. Experts do not have a consensus on the reasons for its formation - they have not yet been fully studied.
- A residual formation with pus occurs after tooth extraction as a result of careless work by the doctor. If a piece of root or a fragment of a tooth remains in the wound, a granuloma forms.
- A follicular cyst forms in place of soft tissues that resist the eruption of a new tooth. A cyst grows around a tooth hidden by the gum, enlarges and can spread to other teeth. The result of the development of a cyst can be tilting, tooth displacement or root resorption.
- A lateral periodontal cyst looks like a small formation, most often found on the lateral part of the root.
Depending on the location of the purulent tumor, there are:
- A cyst is formed on a tooth root. Three location options: basal, inter-root or peri-root zones. When a purulent capsule forms, the disease manifests itself well.
- The purulent focus is located in the maxillary sinus. Making a diagnosis is extremely complicated - you cannot do without an image of a certain area. In the advanced phase, the cyst provokes the appearance of sinusitis.
- At the initial stage, a cyst on the gum is asymptomatic. At the moment of filling with purulent contents, the bubble begins to grow rapidly. In treatment, medications are used, and they are also fought by puncturing the capsule, treating with saline solution and cleaning until complete healing.
- The formation of a cyst under the tooth crown occurs after unsuccessful disinfection during its installation after treatment. As a result of a loose fit, food debris gets under the crown, rots and creates a favorable environment for cyst growth. To treat it, you need to remove the crown.
- A cyst on the front teeth has practically no room for development and localization. It comes out at the initial stage of development.
- A wisdom tooth cyst forms at the site of a long-erupting “figure eight.” As a treatment for this category of teeth, a proven effective method is recommended - removal of the cyst and wisdom tooth together.
Treatment process
Treatment of cysts can be therapeutic (conservative) or surgical. The treatment method is determined by the doctor after a visual examination of the oral cavity and the results of diagnostic studies.
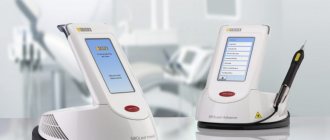
Laser treatment
Laser beam treatment is gaining increasing popularity in dentistry. Under the influence of a laser, a tumor can be removed completely painlessly, without the risk of infection. In addition, the laser completely disinfects the affected channels and ensures rapid recovery. The laser treatment algorithm looks like this:
opening and expansion of dental canals; introduction of a laser beam into the canals: disinfection and removal of the cystic component.
The only disadvantages of the method are the relative high cost and the need for special high-precision equipment. Laser treatment also involves following the doctor’s recommendations immediately after the procedure (rinsing with an antiseptic and abstaining from food for up to 5 hours).
Conservative treatment
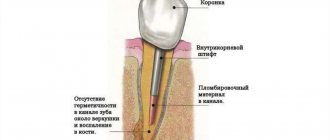
Therapy for a cystically altered tooth root requires disinfection, tooth cleaning and filling. An alternative treatment method is the introduction of a therapeutic suspension containing copper and calcium, followed by exposure of the tooth to low-power electrical discharges. The main indications for drug therapy are:
absence of fillings on root canals; poor filling in the root canals (not along the entire length); The size of the cyst barely reaches 8 mm.
In treatment, special drugs are used that negatively affect the cyst capsule and its contents. After which, the purulent exudate is completely removed, and instead of it, dental paste is injected into the cyst cavity to restore the bone structure. The manipulations are completed by filling the canal and crown. Cases of relapse of the disease are possible.
Operative method
Surgical treatment is carried out in some cases, since in 80% of cases a radicular cyst is an advanced process. The main indications for surgical intervention are:
presence of a pin in the root canal; early prosthetics of the causative tooth; the size of the cyst exceeds 8–8.5 mm; gum swelling and pain.
Until recently, the cystic component was removed along with the tooth. Alternative methods of surgical treatment are now being used to preserve the natural tooth. A tooth is removed only when the roots of the tooth have become part of a cystic structure or have been destroyed to the very root as a result of disease.
Main methods of surgical treatment:
| Cystectomy. | It is a complex but most effective method of cyst removal. The cavity is completely removed along with the damaged part of the root and the membrane. Indications for surgery are the rapid development of a tumor in the upper jaw to large sizes. |
| Cystotomy. | The procedure involves removing the anterior wall of the cystic cavity. The operation is performed in case of severe destruction of the bone floor of the nose, palatine plate, or with a large cyst. Cystotomy has the longest recovery period. |
| Hemisection. | The simplest method involves removing not only the cyst, but also part of the tooth root, the tooth itself or part of its crown. |
The postoperative period can take a long time. For the entire recovery period, antiseptic rinses are required, and sometimes antibiotics are required. You should not take aspirin, as it provokes bleeding. Recovery takes about a day, and swelling and slight soreness persist for several more days. If unpleasant symptoms persist or their intensity increases, it is important to immediately consult a doctor.
Traditional methods of treatment
Separately, it is worth mentioning the possibility of treating a tumor of the apical part of the upper jaw tooth with traditional healing recipes. Infusions of herbs, compresses and various poultices are good when the patient is in the postoperative period. Herbal treatment for tooth root cysts helps only as a local disinfectant along with traditional treatment methods. There are main herbs that heal gums faster:
Oak bark; pharmaceutical camomile; swampy cudweed; plantain and others.
If you start treatment only with herbs and compresses, you may not only fail to help your body cope with the cyst, but also lead to complications in the form of rupture of the cystic contents. Purulent exudate quickly spreads through the bloodstream and carries all bacterial microflora to vital organs.
Treatment
Radicular cysts are treated through surgery—cystotomy or cystectomy.
Cystotomy is used in the case of a large cyst that affects the roots of several adjacent teeth and destroys the walls of the maxillary sinus. The operation involves cleaning out the cyst cavity through a small hole made from the mouth, nose or paranasal sinus. Upon completion, the surgeon disinfects the cavity and inserts a swab with iodoform there. A week later, the tampon is replaced with a new one, and this continues until the doctor is convinced that the inflammatory process has stopped.
Cystectomy is the removal of a cyst by separating the fibrous membrane of the formation from the surrounding tissue. The operation ends with tamponade of the cavity or bringing together the edges of the mucous membrane that have been damaged. Cystectomy is done for small cysts.
Postoperative recovery will be successful if the patient takes oral hygiene instructions seriously: use antiseptic rinses and brush teeth carefully. In case of increased body temperature, as well as intense and prolonged pain, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Complications and prevention
Complications after surgery are possible if you do not follow the doctor’s special recommendations. A frequent cause of complications is the lack of self-discipline in the patient. The main complications include:
tissue infection during surgery; generalized sepsis; abscess syndrome around the affected tooth.
Rarely, the cause of postoperative complications is considered to be a lack of professionalism on the part of the dentist. Before treatment, it is important to inquire about the quality of services provided and the rating of the dental clinic. Complications include damage to molars in the maxillary sinuses and sepsis. If not the entire volume of purulent exudate is removed from the cyst, then the emergence of a secondary source of infection occurs almost immediately. Pus quickly spreads throughout the body and leads to dysfunction of many organs and systems. With the high-tech development of dentistry today, cases of complications as a result of cyst treatment are isolated episodes.
Preventive actions
When carrying out high-quality prevention, the patient must follow simple rules:
Carrying out regular hygienic teeth cleaning; sanitation of the oral cavity once a year; dental examination - 2 times a year; timely response to unpleasant symptoms in the oral cavity.
Treatment of cysts today is carried out successfully in a number of cases, so before visiting the dentist it is important to collect as much information as possible about the clinic and the professionalism of the specialist. You should not delay treatment, since in advanced cases, surgery is often the only possible way to eliminate the pathology.
For quick post-operative recovery, it is important for the patient to observe a hygienic regime, carry out preventive rinses of the mouth with herbal decoctions (chamomile, celandine, string, propolis) and medications (Miramistin, Iodinol). The patient’s discipline and attention to their own health are the key to oral health and the ability to treat any problems in the early stages using the most gentle methods.
What to do with a dental cyst?
Features of the development of purulent inflammation of various forms and localizations show that the formation occurs at a slow pace. When pronounced symptoms appear, the cyst emerges on the surface of the mouth, gum or root, inflamed and filled with pus. Patients complain of severe malaise, “fever,” experience pain and discomfort when chewing food.
A decade ago, the only solution to getting rid of the problem was the ability to remove the source of pain. Modern equipment, special instruments, and medications (painkillers, anti-inflammatory drugs) make it possible to save a tooth by treating a serious tumor. Depending on the stage of development, surgical or therapeutic methods are used.
The latter option involves mechanical cleaning of the canals, careful processing and filling. The surgical procedure involves removing the damaged surface while preserving the tooth. The missing root tissue is replaced with a specific material. Complete removal is considered only in the case of a wisdom tooth or when damaged tissues occupy most of the tooth and root. An exceptional situation when there is no need to treat a dental cyst is if it appears next to a baby tooth and develops slowly, and there is only a short time left before replacing a molar one.
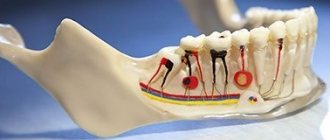
What are periapical tissues
To clarify the concept of a radicular or periapical cyst, it is necessary to clarify the features of its localization. The root of a tooth is the part of the tooth that is located in the jawbone, and the apex of the root is the end part, the narrowest and farthest from the crown of the tooth. The root has a root canal through which the nerves and vessels supplying the tooth pass.
Periapical tissues are all tissues surrounding the root of the tooth, located within the bone, that is, periodontium, root cementum and alveolar bone of the jaw.