Correction of bite in children is carried out in several ways. The likelihood of a favorable outcome increases if parents noticed the anomaly in time and showed the child to a specialist. Treatment is selected depending on the type of pathology and the reasons for its formation. It is better to start it before the final period of bite formation (growth of molars) begins.
Pediatric dentistry is required from the appearance of the first teeth. The child should undergo the first examination by a pediatric orthodontist at the age of two, since during this period baby teeth are formed. The next visit to a specialist is necessary at the age of mixed dentition, which corresponds to the child’s seven to nine years of age. Upon reaching the age of fifteen, visits to the dentist-orthodontist should become annual.
Types of dental malocclusion in children
- Distal bite.
The lower jaw is posterior to the upper jaw
- Mesial bite.
Does the child have an incorrect bite, does the lower jaw protrude forward? This kind of bite is called mesial. In this poetic form, we can give a brief description of another common type of jaw disproportion, when the lower jaw is much more developed than the upper.
- Cross or scissor bite.
A less common, but very unpleasant dental anomaly. With a crossbite in a certain place, the jaws close in the opposite relationship - they close in reverse, which is why the dentition resembles scissors.
- Deep bite.
A very common type of malocclusion in children and adults, when the upper teeth cover the lower teeth by more than half.
- Open bite.
One of the most complex anomalies, causing physical and psychological discomfort to the child. The upper and lower rows of teeth cannot meet completely, causing a noticeable gap to form between them.
Above we described what a child’s malocclusion looks like in various manifestations, but we should also briefly talk about the correct one, which can be perceived as a kind of guideline. The ideal bite is considered orthognathic. It is distinguished by an absolutely even dentition without gaps, curvature or crowding, when the upper teeth cover the lower ones by one third. There are several types of correct bite, but if your child has dental defects, this almost always indicates problems.
Correction
With a distal bite, the development of the apical points of the alveolar and basal arches of the upper jaw is restrained, and the growth of the child’s lower jaw is activated. For this purpose, during the period of loss of baby teeth, the following devices can be used:
- Andresen activator
- Engle's arc apparatus
- Ainsworth arc apparatus
- Herbst arc apparatus
- functional Frenkel apparatus of the first or second type
Removable plates are placed on the teeth, and a vestibular retraction arch helps reduce tremors. Also, the goal of treatment is to give the desired direction to the growth of the maxillofacial bones. To do this, a facebow is installed outside, which the child wears at home; there is no need to wear it to school.
How to determine malocclusion in a child?
“How can you tell if a child has a malocclusion?” - This is a question many parents ask. It is important to understand that only an experienced pediatric orthodontist can make an accurate diagnosis here, so we strongly advise you to undergo regular preventive examinations with this specialist from a very early age until the complete replacement of baby teeth with molars. If the baby teeth are located too closely together, this can also become an additional complication when the molars erupt (the latter take up more space because they are larger). In the case of a small child (under 3 years old), it is difficult to be guided by purely visual principles and determine by eye whether the bite is correct or incorrect. Be that as it may, there are a number of signs that directly or indirectly indicate that the child has prerequisites for orthodontic anomalies.
Improper breathing
The child's mouth is constantly in a half-open position, he does not breathe through his nose (of course, if there are no colds).
Snore
If your baby constantly snores in his sleep, this may also be one of the consequences of the development of malocclusion.
Jaw formation
Pay attention to how the child's jaws are formed. Ideally, there should be no noticeable disproportion between the top and bottom. Additionally, if a child continually pushes their lower jaw forward, this is considered a clear sign of pediatric bite problems.
Postural disorders
If your child has postural and spinal problems, this may affect the development of malocclusions.
Prognosis and prevention
The most effective results in correcting malocclusion are achieved during the mixed or primary dentition. If you choose the right treatment method, it is possible to achieve high-quality jaw alignment in adulthood, but it will take more time.
The formation of the bite in infancy plays an important role. It is important to monitor the correctness of breastfeeding, the position of the child during sleep, and prevent the formation of bad oral habits. Timely treatment of disorders that slow down or impair the growth of jaw bones and dental correction is also required.
Causes of malocclusion in children
The causes of malocclusion in children can vary, and most of them are difficult to address without orthodontic treatment. Below you can see a list of the key reasons for the occurrence of such anomalies in a child.
Genetics.
If you are wondering why your child has an incorrect bite, look at yourself first. Genetic predisposition is the most obvious and common cause of malocclusion in a child. If one or both parents have pronounced anomalies, then with a very high degree of probability their children will inherit them.
Bad habits.
Children often chew and put into their mouths literally everything they can get their hands on. Often such cravings provoke a violation of the formation and development of teeth. Malocclusion in a child from a pacifier is also quite common.
Breathing problems.
Children with nasal breathing disorders are much more likely to suffer from malocclusion, as experts say.
Problems with the musculoskeletal system.
The spine is the main “bearing structure” of our body, so it is not surprising that the functioning of the musculoskeletal system affects the dental system.
Other diseases.
The risk group (meaning malocclusion) also includes children with diabetes mellitus and central nervous system diseases.
Treatment of malocclusion in children
What to do if a child has an incorrect bite? Of course, start treatment immediately! Unlike adults, where malocclusions can only be corrected with braces or aligners (and in severe cases, surgery is often necessary), malocclusions in children are treated in a variety of ways. The technique depends on the age of the child and the specific clinical case. Below is a table showing possible treatment technologies for children of different age groups.
Malocclusion in a child under one year old
For very young children (up to 1 year), it is important to choose special orthodontic nipples for feeding, and also try to refuse pacifiers, which can negatively affect the development of teeth.
Malocclusion in a child aged 1–2 years
At this age, milk teeth begin to actively erupt, so the baby can already be taken to the orthodontist. When there is a potential malocclusion in a one-year-old child, special dental guards are often required to reduce the likelihood of developing malocclusions due to chewing habits.
Malocclusion in a child from 3 to 7 years old
By age 3, a child's primary teeth will usually have fully erupted, so correction of orthodontic problems can begin if necessary. At this age, to correct the bite, removable plates, trainers and LM activators are usually used, which are designed to straighten, expand or narrow the dentition, as well as improve diction.
Malocclusion in a child 8–9 years old
8 - 9 years are considered the borderline age when active replacement of primary teeth with molars occurs. It is important here that the process goes as smoothly and successfully as possible. To correct the dentition, the same trainers and plates can be used, as well as special orthodontic devices that ensure the correct interaction of the elements of the dental system, including muscles and soft tissues.
Malocclusion in a child 10–11 years old
At the age of 10, many children have a completely new set of teeth, so this age is considered the minimum acceptable age to start wearing braces. Today in orthodontics, aligners are also widely used - removable transparent aligners for correcting malocclusion.
Consequences of malocclusion in a child
Unfortunately, it is still not uncommon for parents to have no idea what the dangers of malocclusion in children are and are rather irresponsible about their dental health. Over time, the child develops malocclusions that carry with him into adulthood. In childhood, teeth are much more mobile and respond well to directed mechanical influence, while correcting a bite in an adult is a much more complex and lengthy process. Moreover, adults are much less likely to agree to treatment because of the associated inconveniences and restrictions, which over time leads to a number of complications and unpleasant consequences. An incorrect bite leads to disruption of the muscles and joints of the entire dental system, which causes characteristic clicks, spasms and pains that spread to adjacent areas and lead to migraines, hearing loss and other unpleasant manifestations. Improper functioning of the temporomandibular joint, in turn, often leads to apnea (sleep breathing disorder), which is an additional factor in the occurrence of cardiovascular diseases and leads to much more tragic consequences.
Why is malocclusion dangerous in children from a psychological point of view? If a child has serious abnormalities, this will certainly affect his self-esteem (especially in adolescence and adulthood). In the modern world, a smile is perceived as an integral part of the image of a healthy and successful person, so the issue of aesthetics in this case is also very important. As you can see, everything in our body is interconnected, so do not put off orthodontic treatment under any circumstances, especially since in childhood any problem is corrected easier and faster.
Symptoms
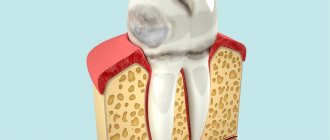
The list of characteristic signs is determined by the severity of the pathology. Thus, in the early stages, the only form of manifestation is the formation of small chips and cracks on the surface of the enamel, almost invisible to the naked eye. The cause of mechanical damage is the pressure of the elements of the lower row on the tissues of the palatal surface adjacent to the base of the upper teeth, as well as constant contact with the area of the cutting edge, whereas in normal condition the load is distributed evenly.
Untimely contact with an orthodontist is often due to the absence of pronounced symptoms that could cause the patient significant physical inconvenience. Manifestations characteristic of the middle stage include:
- Intensive abrasion of enamel from the lingual side of the upper incisors and the frontal covering of the mandibular elements, caused by constant contact, and leading to an aggravation of sensitivity in problem segments.
- Changes in facial contour, reflected in a decrease in the height of the lower third, as well as associated problems with diction and food processing.
- Development of TMJ dysfunction. Accompanied by extraneous sounds, painful sensations, and limited mobility.
- A noticeable deviation in the position of the lips, leading to impaired closure.
A severe degree is characterized by the diagnosis of pronounced anomalies of the skeletal structure, including a combination of macrognathia and microgenia, disturbing the proportions of the face (“bird-shaped”). The incisors constantly injure the palate, which causes chronic tissue inflammation, painful sensations when eating, as well as other negative consequences that require medical intervention.