Malocclusion is a common pathology that begins at an early age. Its symptoms are quite easy to notice, because tooth displacement is visible to the naked eye. Although children's malocclusion can be corrected at any age, neglected problems can greatly affect a person's life. It is necessary to establish as quickly as possible what disorder the child is suffering from and promptly correct it.
Typically, surgery is not required to correct most malocclusions early in life. At the same time, installing braces for a child is a rather controversial decision, because they can cause a lot of inconvenience, not counting individual contraindications such as metal intolerance. There are several alternatives that we will look at in this article.
Stages of bite formation in children
The process of developing a child’s bite can be divided into several important stages.
Each of them is characterized by changes in the structure of the jaw and has factors that influence the formation of pathology. Stages of bite development in children:
- Elementary.
From birth to six months of the child. The first teeth begin to erupt towards the end of the period. The cause of pathology at this stage is a genetic predisposition or improper latching of the nipple during breastfeeding. - The process of formation of the bite of primary teeth.
Lasts until the age of three; as a rule, by the end of the period, all 20 baby teeth are in their position. At this age, the presence of gaps between the teeth is acceptable, but twisting, too close a fit, and growth in an uncharacteristic plane are considered as deviations from the norm. In addition to the above reasons, the most common factor in the development of pathology is bad habits: thumb sucking, pacifiers, toys or eating disorders. The child's diet should include a sufficient amount of solid food. - Preparation for the development of permanent dentition.
The stage continues until the appearance of the first permanent teeth. With proper oral care, no external changes are observed during this period. Bad habits can cause malocclusion. It is necessary to ensure that the child does not chew hard objects: pencils, thick books, furniture, since baby teeth are very soft and easily deformed. - Changing the temporary bite to a permanent one.
The most critical stage. It is during this period that serious pathologies begin to manifest themselves as unpleasant changes: torsion, improper growth of teeth, discrepancy between the size of the jaw and the volume of bone units, etc. On average, this period lasts up to 12 years. Factors in the development of anomalies are physiological characteristics or untimely replacement of teeth. - Formation of a permanent bite.
The teeth complete their growth and occupy a certain position in the jaw.
You can start correcting your bite from the early stages. There are several hardware and manual methods for this. Treatment with braces begins after a permanent bite has formed.
Early treatment: orthodontic plates and trainers.
- Plates for straightening teeth are familiar to most people for a simple reason: they have been actively used for many decades. They have many types and design options. The most classic ones are plates with screws, which are used to stimulate the growth of the upper (and sometimes lower) jaw. In addition, the plates can be equipped with additional elements: arcs, pushers, and so on. Their goal is to correct the position of individual teeth, but, unfortunately, the accuracy of work comparable to the work of braces is almost impossible to achieve with their help. Therefore, often, plates cannot be the only treatment. The plates should be worn around the clock, removing them only during hygiene to remove food debris.
A plate with a screw for the lower jaw.
- Elastic positioners : trainers, LM-activators, Myobrace and other functional devices are designed to activate jaw growth and eliminate bad habits. In addition, some types of trainers, for example, the Myobrace brand, have cells for teeth (helps teeth erupt correctly, in case of not very pronounced anomalies). Since elastopositioners are double-jawed devices, they cannot be worn around the clock. The wearing scheme is as follows: mandatory evening wear for 2-3 hours (for example, while watching cartoons, etc.) + mandatory night wear.
LM activator
- The functional group includes the Frenkl apparatus and its modification: the Persin apparatus. Perhaps one of the most famous “name” devices. There are 3 main types to correct different anomalies. The principle of operation is similar to elastopositioners: changing muscle balance and stimulating the growth of the upper or lower jaw. The wearing pattern is similar and the effectiveness is comparable to trainers. The difference is that the Frenkl apparatus and its modifications are made of hard plastic and are much less comfortable to wear. In addition, it requires a high level of skill from the technician and physician to properly manufacture and fit it in the oral cavity. Today, elastopositioners are preferable to use precisely for these reasons.
Frenkl's apparatus.
- Double-jaw devices to activate the growth and advancement of the lower jaw. This group includes a twin-block and a Twicare device. Used for distal occlusion (Class 2 according to Angle). They can be used in adults: in this case, the lower jaw does not grow, but only moves to a more anterior position. But in some cases, this is what is needed, since the posterior position of the lower jaw is a fairly common phenomenon.
Twin block device diagram.
- Device for rapid palatal expansion . It has many names: expander, Derichsweiler apparatus and others. There are many modifications, but the essence and active part (screw) is the same. Used to correct narrowing of the upper jaw. It is a non-removable device. Can also be used in adults, but only in combination with surgical support. It has a screw similar to the screw of conventional plates for expanding the upper jaw, only more powerful, as well as a more durable design. The screw is tightened much more often, and accordingly, expansion occurs quickly (due to the divergence of the median palatal suture) - in children it is quite mobile, and in adults it is mobilized surgically. Often, to reduce the lateral inclination of teeth, support is used on microimplants installed in the palate. There are many opinions at what age the use of a palatal expander is justified: most orthodontists believe that the optimal age is 13-14 years, but sometimes the device is placed on six-year-old children based on milk teeth and good results are achieved.
Derichsweiler apparatus
- There are a great variety of different nominal devices, differing in both design and principle of operation. Many of them have long been outdated, many are quite functional, but have more convenient/effective/easy-to-use analogues, some are still relevant today. The main thing is that your orthodontist clearly understands why he is prescribing this or that device.
Quadhelix is a device for expanding the palate.
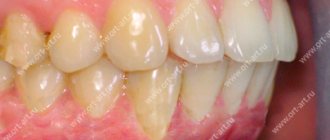
Signs of malocclusion
For timely detection of maxillofacial defects, it is necessary to regularly examine the baby’s oral cavity. Here are a few signs by which you can identify a malocclusion in a child:
- obvious displacement of the lower jaw outward or inward;
- crooked, uneven teeth;
- vestibular or lingual growth of teeth - in front or behind the main row;
- diastema - spaces between the incisors;
- strong overlap of the lower teeth with the upper ones;
- non-closure of the upper and lower incisors with a formed bite;
- half-open mouth, replacement of nasal breathing;
- speech defects.
Signs of malocclusion
In addition to the visible signs, if you look closely, you can notice abrasion of the enamel on the front or back teeth, and gum injuries. The child complains of tension in the jaw muscles, difficulty chewing or swallowing food, and headache. These signs will help you understand that your child has a malocclusion and seek advice from an orthodontist.
Treatment prices
The cost of correcting an open bite directly depends on the complexity of the defect. The total cost includes inspection and consultation with a specialist, payment for the procedure for installing a correction device, as well as the purchase of the structure itself. If surgical intervention is required for bite therapy, the price will be higher.
It is better to find out more about how much such bite treatment will cost directly in the clinic.
The iOrtho clinic network provides high-quality services for correcting malocclusion with Invisalign aligners, sign up for a consultation now!
Types of malocclusion
The curvature of the teeth does not always mean a pathology of the bite, which is understood as the closing of the jaws, ensuring the full, unhindered functioning of the masticatory apparatus.
Among the types of malocclusion in children are:
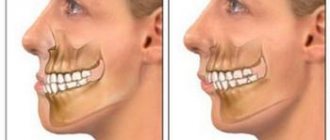
- Prognathia – distal occlusion.
This is a common reason for visiting an orthodontist in early childhood. The muscles of the lower jaw are not yet sufficiently developed, so outwardly it seems that the upper row of teeth protrudes strongly forward compared to the lower one. With the introduction of hard foods into the diet: hard fruits and vegetables, the problem may disappear without medical intervention. - Progenia – mesial occlusion.
At an early age, this pathology is usually caused by genetic characteristics or improper latching of the nipple during feeding. The sooner the pathology is identified and treatment is prescribed, the fewer negative consequences the child will receive. - Deep bite.
Parents often confuse it with the distal one, however, with a deep bite, the lower jaw does not go back, but seems to sink inside. The upper front incisors overlap the lower ones by more than half. Obvious signs of pathology are speech defects and soft tissue injuries. - Crossbite.
It appears at the stage of replacement of milk teeth with molars. In this case, on the one hand, the upper jaw overlaps the lower jaw, on the other, the lower teeth come to the fore. - Open bite.
With this malocclusion pathology, there is a noticeable lack of closure between the teeth of the upper and lower rows. Most often, this disorder affects the incisors, but it also occurs on the posterior premolars and molars.
Types of Malocclusions
Malocclusions in children are diagnosed during annual examinations. It is important not to waste time and immediately begin preventive or therapeutic treatment.
Diagnostics
In addition to a visual examination, the orthodontist can measure the gap and assess the degree of open bite for further treatment. There is a possibility of direction for more in-depth research that will give a complete picture:
- teleroentgenogram;
- orthopantomogram;
- taking impressions.
Often a specialist sees the presence of a combination of disocclusions: distal open bite, mesial.
To collect information about the patient and the progress of the correction, before and after photos are taken.
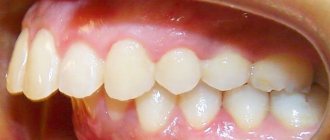
Photos of children with pathological bite
In the presented images you can see the child’s malocclusion. The photo shows various pathologies that are often found in patients with baby or molar teeth. Detailed photographs of children with malocclusion captured in the photo during an orthodontic consultation will help parents in self-diagnosis of the pathology. However, the doctor chooses the effective therapy regimen.
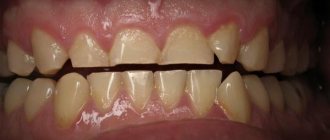
Photo of a girl with an incorrect open bite
Photo of a child with an incorrect deep bite
Photo of a boy with an incorrect deep distal bite
The boy has an open bite
The girl has a deep distal bite
What is an open bite
Open bite - incomplete closure of the frontal row of teeth or lateral sections. A vertical gap is formed, which causes not only an aesthetic problem, but also functional disorders. Quite often, this type of pathology can be combined with another form of occlusion, and it is necessary to treat a distal or mesial open bite.
How to correct a child's bite
No matter how severe the pathology, the earlier treatment is started, the easier it is to achieve an effective result. To correct violations, there are three ways to correct bite in children:
- traditional – installation of braces;
- alternative (without braces) – mouth guards, plates, physiotherapy;
- cardinal – surgical intervention.
Until the final stage of permanent bite formation, only alternative methods are used, but is it possible to correct a child’s malocclusion with their help?
Removable orthodontic plates
Orthodontic plates
are structures consisting of a polymer jaw-expanding base and metal arches that serve to fix the plate and align the front row of teeth.
Removable orthodontic plate
These devices are made individually, based on casts of the jaw of a small patient. To adjust the load, the devices are equipped with screws and expanders. At an appointment with a doctor, the child’s parents will learn how to perform this procedure on their own, which will save time on visits to the orthodontist.
Plates for correcting malocclusion in children are designed to be worn constantly, but the removable structures are removed during meals or hygiene procedures.
Trainers for teeth
Trainers
To correct malocclusion in children, they are mouth guards made of dense silicone.
Trainer for correcting the bite
The trainer performs several functions:
- Self-corrects minor pathologies.
- Prevents further development of malocclusion and prevents complications.
- Helps get rid of bad habits that have caused crooked teeth.
Mouth guards for correcting malocclusion in children fix both jaws simultaneously in the correct position. But when using them, it is impossible to lead a normal lifestyle: talking, eating. Therefore, mouthguards are worn while the child is sleeping and for several hours during the day.
The process of correcting a bite with trainers is long and requires patience from the child and parents.
It has been noticed that in children who regularly use trainers before installing braces, the effect of therapy occurs faster.
Myotherapy
Myogymnastics
in orthodontics, it is a set of exercises to relax or develop individual facial muscles.
Myotherapy in orthodontics
The method serves as both a primary and an auxiliary method of occlusion correction. For each type of pathology there is its own set of exercises. The first lessons are carried out under the supervision of an orthodontist; as soon as the child learns to do gymnastics correctly, he continues to work at home independently or with his parents.
Conditions for performing exercises to correct bite in children:
- Systematicity and regularity.
- Sufficient application of force without jerking or pressure. The muscles feel resistance, but are not overloaded.
- Cyclicality. Exercises are performed in several approaches to achieve good results.
- Gradual increase in load and intensity.
Myotherapy is especially effective in correcting occlusion in combination with physiotherapy: electrophoresis, vibration massage, ultrasound, vacuum therapy, massage.
Alternative methods can correct mild pathologies of malocclusion in early childhood or slow down the development of complications and wait until the formation of the jaw is completed to begin basic treatment.
Braces
Braces
– the main way to correct uneven teeth and malocclusion in children from 12–16 years old and adults of any age.
Braces for correcting bite
They are a system of clasps fixed on the outer or inner surface of the teeth and a steel arch stretched between them.
Under the pressure of the arch, the teeth are aligned and placed in the correct position. With the help of braces, it is possible to correct almost all malocclusion pathologies. Treatment takes from 6 to 18 months and ends with the acquisition of a beautiful, even smile.
Care and hygiene rules
One of the advantages of aligners is their ease of care. To keep them clean and effective throughout the correction, follow these simple rules:
- aligners must be worn up to 22 hours a day, depending on the orthodontist's indications, removing them only for eating or oral hygiene;
- The aligner must be cleaned regularly by rinsing the inner surface with warm running water and brushing with a toothbrush;
- You should avoid too hot water so that the polymer does not deform due to temperature changes.
Aligners do not require special solutions. If you remove them, then put them in a special clean and sealed box, protected from dust and moisture.
Oral hygiene when wearing aligners also remains the same - brush, paste, mouth rinse solutions and dental floss. The latter is also suitable for effectively removing food particles.
Let us note the contraindications under which aligners cannot be installed:
- periodontal disease. Like other methods of orthodontic treatment, aligners are not prescribed for periodontal disease due to the high risk of losing teeth due to destruction of periodontal tissue;
- severe deformation of the jaw. Aligners work well for minor malocclusions. However, serious defects require surgery;
- in the presence of impacted teeth. Often this problem occurs with molars that do not erupt and remain in the gum or even in the jaw bone. Having an aligner can interfere with their development and lead to problems in the future;
- if 4 or more teeth have been lost.
In other cases, aligners are equally effective for all ages - from children to adults.
Expert of the article you are reading:
Pokrovskaya Natalya Sergeevna
Head of the Department of Orthodontics
Specialization: Invisalign bite correction, neuromuscular diagnostics, pediatric orthodontics.
Free consultation
Treatment of malocclusion in children of different ages
Anomalies in jaw development and tooth growth cannot be ignored. Early childhood is not a reason to refuse correction. The orthodontist will help you choose the most effective treatment method. The use of alternative therapy methods can completely restore jaw function or prevent the occurrence of health-threatening complications.
Let's look at how malocclusion is treated in children of different ages.
Children under one year old
At this age, parents' actions should be aimed at preventing the development of jaw pathologies. Effective measures include:
- maintaining the correct position of the head during feeding, it does not tilt back, the chin is not pressed against the baby’s chest, make sure that the nipple is grasped correctly;
- the use of orthodontic pacifiers that imitate the female nipple and promote the correct position of the jaws when sucking;
- preventing the development of bad habits;
- introduction of solid food into the diet with the appearance of the first teeth;
- adequate consumption by mother and child of foods containing fluoride and calcium or vitamin supplements designed specifically for nursing women;
- preventive examination at the dentist.
Most often, malocclusion in a child of the first year of life develops due to the use of a low-quality pacifier, so the choice of this accessory is very important.
Children from 1 to 2 years old
There are often questions from worried parents on the Internet: “My child is one year old, it seems that he has the wrong bite, what should I do?” First of all, if you suspect the development of pathology, you need to show the baby to a specialist. He will determine whether the feature is an age-related norm or a complication.
Malocclusion in a 1-year-old child occurs as a result of dysfunction of sucking (and then chewing). At such an early age, hardware correction methods are not yet available, so physiotherapy and the use of orthodontic pacifiers, which return the jaw to its normal position, are most often prescribed.
To correct malocclusion in a child 2 years of age and older, Hintz plates are used, which are similar in shape to a pacifier, but instead of a pacifier, a flap is placed in the mouth and clamped between the teeth. The longer the device is used, the faster the bite is corrected and bad habits are eliminated.
Children from 3 to 5 years old
Malocclusion in a 3-year-old child is corrected with special caps for correcting the position of the jaw, which are worn at night. You can also continue therapy using Hintz plates.
Another accessible method at this age is myogymnastics. A three-year-old child can easily cope with the exercises.
From 4 years of age it is allowed to use LM activators under the supervision of an orthodontist. And malocclusion in a 5-year-old child is corrected with the help of trainers and orthodontic plates.
The first thing to do when malocclusion is detected is to show the child to a qualified orthodontist.
Children from 6 to 14 years old
Malocclusion in a 6-year-old child should cause the greatest concern for parents, since when baby teeth are replaced, this pathology will certainly affect the growth of permanent bone units.
Therefore, careful adherence to the dentist's recommendations is necessary. At this age, all alternative methods are available; the doctor will select the most effective one.
Defect correction
Correction is carried out using conservative and surgical methods.
Conservative therapy
For hardware correction, removable and non-removable correction devices are used.
These include the following devices:
For correction use:
- vestibular shields - used to wean the baby from sucking fingers and other objects;
- Trainers are used to correct minor anomalies and align the positions of individual units in the dental arch;
- correction plates are plates made of plastic and metal, used to correct anomalies during tooth replacement, they are self-regulating devices;
- aligners are silicone molds made of silicone that give a physiological bend to the dental arch.
- braces are a non-removable orthodontic structure for correcting the most complex dental defects and anomalies;
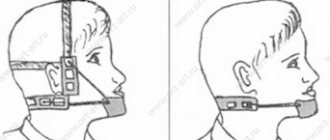
- extraoral devices – used to correct severe anomalies when braces cannot be installed.
Devices for correcting malocclusion and the position of individual teeth are selected based on the severity of the defect and age. Is it possible to correct the bite using only conservative methods? In most cases, the use of these devices is sufficient.
Surgical treatment
I use surgical techniques only in the most difficult situations, when the use of conservative methods has not eliminated the defect. They are used only in adolescence and in adults only in cases of serious deformities of the facial skeleton.
Indications for this are:
- gross facial asymmetry;
- gross anomalies of occlusion;
- underdevelopment of the chin.
After the operation, long-term rehabilitation is carried out for at least five months.
Causes of malocclusion
Many factors influence jaw development. Among the main reasons for the formation of malocclusion in children are:
- heredity;
- incorrect position during breastfeeding, incorrect grip of the nipple or bottle nipple;
- bad habits;
- physiological features, for example, a narrow jaw;
- late transition to solid food;
- ENT diseases;
- metabolic disorders, lack of microelements;
- incorrect posture;
- intrauterine developmental pathologies;
- early loss of baby teeth or delayed loss of teeth;
- accompanying illnesses.
The habit of thumb sucking can cause malocclusion.
Before starting treatment, you need to make sure that the factor that caused the pathology no longer has an effect.
Correcting a child’s malocclusion without eliminating the cause is ineffective.
Short frenulum of the tongue, upper and lower lips
- A short frenulum of the tongue is, in most cases, a hereditary problem that leads to problems with sucking, diction, and in complex cases, over time leads to recession (loss) of the gums on the lingual side of the lower dentition. Often the best option is frenuloplasty at an early age (often before one year), in which case speech therapy problems will not arise. The procedure itself takes several tens of seconds, since the frenulum has neither blood vessels nor nerve endings. Therefore, if a pathology is detected by doctors or parents, plastic surgery is performed at any age, including immediately after birth.
- A short frenulum of the upper lip is a common anomaly (occurs in 10% of the population). Likewise, it can lead to problems with sucking, diction and gum recession in the future. Among other things, low attachment of the frenulum (normal attachment of the frenulum is 0.5 cm above the necks of the incisors) leads to the appearance of a gap between the central incisors - a diastema. In most cases, frenuloplasty is required. It is believed that the optimal age for this is about 7-8 years (after the eruption of the upper lateral incisors), but it can fluctuate. Before this age, interventions are not recommended for two reasons: the problem may disappear on its own (as the jaw grows and permanent teeth erupt, the frenulum may stretch and the place of its attachment may shift), secondly, plastic surgery of the frenulum at an early age can cause the correct development of the upper jaw and lead to malocclusion. Plastic surgery is not a traumatic procedure and is performed on an outpatient basis under local anesthesia.
Short frenulum of the upper lip, diastema, as a result.
- A short frenulum of the lower lip is less common and can also lead to problems with sucking and gum recession in the future. Treatment is similar to the previous anomaly at the age of 6-7 years (after the eruption of the 4 lower incisors).
Consequences
What complications can arise if a child’s malocclusion is not corrected? Possible consequences:
- tooth abrasion, premature wear, increased risk of caries;
- difficulty chewing causes gastrointestinal problems;
- mucosal injuries, gum inflammation, periodontal disease;
- increased load on the temporomandibular joint, pain, inflammation;
- breathing problems, ENT diseases;
- pinched nerves in the cervical spine;
- aesthetic facial defects, asymmetry;
- psychological problems;
- violation of diction.
Thus, malocclusion in children is dangerous for the development of diseases. It directly affects the emotional state of the individual, self-esteem, and self-confidence. If the bite is not corrected in time, physiological, psychological and aesthetic problems may develop.
Possible complications
Open vertical occlusion does not remain without consequences. The aesthetics of the face and smile suffer, difficulties develop in other functional departments:
- Digestion is disrupted due to problems with biting and chewing;
- the person has a lisp, and with a large gap, speech is slurred;
- The TMJ (temporomandibular joint) experiences difficulties, muscle tone decreases;
- the condition of the periodontium worsens (it experiences excessive load);
- the abrasion of the enamel of the teeth, on which all the work “falls”, increases, they are more loaded and experience increased pressure;
- Mouth breathing develops problems with the ENT organs and respiratory system.
Prevention
Prevention of the development of malocclusion in children begins at an early age. By following simple recommendations, you can avoid problems and maintain your baby’s beautiful smile.
Dentists' advice:
- Correct attachment to the breast or bottle. Usually a new mother will be helped with this by a pediatric nurse or a breastfeeding specialist.
- Prevent the development of bad habits, gradually abandon the pacifier when the first teeth appear.
- Supplement your diet with solid food in a timely manner.
- Keep your mouth clean.
- Perform gymnastics to develop facial muscles.
The effectiveness of preventive measures can be monitored by a local dentist, whose consultation is recommended for children at least once a year.
The health of a child’s teeth affects not only the appearance, but also the functioning of the entire body. Incorrect bite is the cause of serious illnesses. Therefore, it is important to identify pathologies in time and correct them using methods available for a given age.
How to determine
In order to identify a malocclusion in your child, you can focus on a number of signs that not only specialists, but also parents can see. The main ones:
- asymmetry of the face from the front (between the right and left halves, especially in the area of the nasolabial triangle and chin);
- extra or missing teeth;
- untimely teething or change of dental sets;
- crowded dentition;
- excessive tension of the chin and lips during swallowing;
- frequent snoring or grinding in sleep;
- constantly slightly open mouth in the absence of nasal congestion;
- poor posture;
- frequent injuries to the tongue or cheeks.