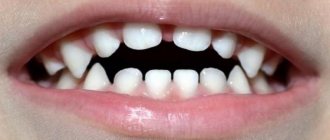
Erosion of tooth enamel is a serious dental disease of a non-carious nature, manifested in the gradual abrasion of dental tissue. The disease can appear not only in adults, but also in children, although baby teeth are affected much less frequently. The difficulty in treating erosion lies in the fact that people suffering from erosive lesions of the teeth perceive it solely as an external defect, and are in no hurry to go to the dental office. Features of the disease, methods of its diagnosis, treatment and prevention will be discussed in detail in this article.
Stages and features of treatment of tooth enamel erosion
Treatment of this disease is a rather long and complex process, the success of which often depends on the stage of its development. Based on this, appropriate treatment methods are selected.
Based on the intensity and depth of the lesion, the following stages of the disease are distinguished:
- Initial. Not visually detectable. The top layer is affected.
- Average. The disease becomes visually noticeable, there is a pronounced whitish tint, and all layers of enamel are susceptible to destruction.
- Heavy. The entire enamel is affected, the upper layer of dentin is involved.
It is important to understand that this pathology does not appear immediately, but gradually destroys the enamel and leads to serious consequences.
The disease can be identified by a number of symptoms:
- loss of the original shine of the enamel;
- change in tooth color;
- tooth sensitivity, pain when exposed to hot/cold food. This is explained by the appearance of a cavity in the affected area, which reacts to thermal changes and causes a corresponding painful reaction;
- the contours of the teeth are unnaturally transparent in appearance.
If such symptoms occur, you should make an appointment with the dentist.
How to detect the disease in time
Erosion on the enamel should be treated immediately. The disease can progress very quickly and within a few months completely destroy not only the surface of the tooth, but also the dentin, leaving the pulp exposed.
There are three main stages of pathology.
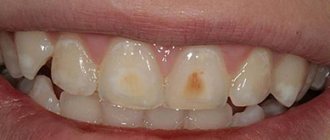
- First. This is the initial stage, during which it is difficult to independently detect signs of dental damage. During examination, the dentist may detect a loss of shine and a change in the shade of the enamel.
- Second. At the middle stage, more pronounced signs already appear indicating increased sensitivity of the enamel: reaction to food (salty/sweet, hot/cold, spicy, etc.). Pigmentation becomes obvious.
- Third. It is considered a deep and advanced stage. Part of the enamel may be completely missing. Dentin is exposed. Brown or yellow spots are visible on the preserved surface of the tooth.
The disease is also classified according to the nature of its course. There are two forms: active and stable. In the active form, the disease progresses quickly with a characteristic change in the color and structure of the enamel. The stable form is characterized by the absence of symptoms and restoration of enamel using the body’s resources.
Factors and stages of disease development
In fact, there are quite a few reasons that provoke enamel erosion.
However, it is possible to identify the main factors that affect the condition of teeth:
- disorders of the thyroid gland;
- abuse of foods with high acidity;
- uneven distribution of load during chewing (for example, chewing on one side / missing several teeth)
- teeth grinding (so-called bruxism);
- somatic diseases of the internal organs of the digestive tract (gastritis, toxicosis during pregnancy, bulimia causes a change in the composition of saliva, increasing its acidity);
- improperly formed bite;
- use of medications (antibiotics, hormonal, antiviral drugs, medicines, etc.);
- mechanical injuries, chips that violate the integrity of the enamel;
- use of low quality toothpastes, tooth powder or frequent use of whitening agents;
- working in production and being in an environment with harmful working conditions (inhalation of chemicals and dust by mouth);
- ecological situation.
Enamel erosion is most often detected in people who do not carefully observe the rules of personal oral hygiene. To avoid the development of this disease, it is recommended to visit a dental hygienist (2 times a year), who will perform comprehensive professional teeth cleaning.
Causes of erosion and consequences of pathology
Erosion of tooth enamel is a type of non-carious lesion. The first signs of the disease are the appearance of small, slightly protruding areas on the surface of the teeth; the course at the initial stage is without obvious symptoms. However, over time, the enamel’s sensitivity to temperature factors increases, the spots gradually darken, unpleasant and even painful sensations appear, and hard tissues begin to wear out very quickly.
Important! At the moment, the reasons for the development of pathology are not precisely known!
However, experts name a number of factors that can provoke the appearance of erosion. Among them:
- disturbances in the functioning of the endocrine system;
- causing mechanical damage (including the use of home methods for whitening tooth enamel, hygiene with a hard brush, abuse (constant use) of dental veneers with abrasive particles, etc.)
- exposure to certain chemicals (eg, vinegar, sour drinks, citrus fruits);
- uneven chewing load (standard reasons - malocclusion, loss of a unit of dentition without timely restoration);
- constant interaction with chemicals, contact with mineral or metal dust (usually associated with professional activities).
- long-term use of potent pharmaceutical drugs.
By delaying contacting the dentist, you risk waiting until the damaged top layer leads to dentin damage.
Diagnostics
This disease can be diagnosed during a dental examination. The dentist detects the location of the erosive focus by thoroughly drying the tooth surface with a stream of air and lubricating it with 5% iodine tincture. The area of enamel affected by the disease becomes brownish in color.
Erosion differs from other pathological processes in its contours, localization, smooth surface and is usually located closer to the base of the root.
The earlier the pathology is diagnosed, the more successful its treatment will be.
Why you can't ignore the problem
If the problem is not recognized in time and treatment is not started, very serious complications are possible, namely:
- distribution of dark spots over the entire surface of the tooth;
- violation of the uniformity of enamel color (up to the transparency of the cutting edge);
- increased abrasion of enamel, accelerated wear of teeth;
- increased sensitivity to temperature influences, the appearance of painful sensations.
When the lesion spreads to the dentin, rapid destruction of the hard tissues of the tooth occurs, as a result - the development of various dental diseases
The widest risk group by age is people of middle age, but the pathology is often found in children.
Therapeutic measures
Treatment of erosion consists of a combination of the following methods:
- Remineralizing. A set of measures that includes applying a drug with a high calcium content to the lesions. Usually 3-5 procedures are prescribed. To consolidate the positive effect, fluoride varnish is applied to the damaged surface.
- Physiotherapeutic treatment. Calcium electrophoresis, which promotes the restoration of tooth tissue.
- Restoration. In case of severe tooth damage, the dentist recommends the use of veneers and crowns to hide the cosmetic defect and protect the tooth from further destruction.
- General therapy. Medications, vitamin therapy, and enrichment of the body with essential microelements are prescribed.
- Tooth polishing and whitening. Polishing is carried out using a special paste or powder, and bleaching and covering the eroded areas with fluorine-containing varnish will help restore the former whiteness.
Visible changes indicate the effectiveness of the treatment. The lesions begin to lighten and decrease in size.
Erosion on baby teeth
In children, the most common cause of the development of non-carious lesions is excessive consumption of liquids high in sugar and acids (milk and juice). Therefore, if the baby refuses to fall asleep without a bottle, it is better to pour regular water into it. It is also important to take care of oral hygiene: regularly cleaning them from bacterial plaque will help prevent the development of erosion on baby teeth.
Other problems that lead to erosion in children are crowded teeth and malocclusions.
Carefully monitor the condition of the tooth enamel in children, contact your dentist immediately when the first signs of the disease appear!
Prevention
To prevent the formation of erosive lesions, the following preventive measures must be taken:
- reduce consumption of foods/drinks containing large amounts of acids;
- brush your teeth with a paste enriched with fluoride and calcium;
- avoid drinking too hot/cold drinks;
- After each meal, normalize the acid balance, or use sugar-free chewing gum;
- follow the rules for brushing your teeth: start from the back surface, spend at least 2 minutes brushing your teeth, and do not put too much pressure on the brush;
- When purchasing, give preference to brushes that have medium-hard bristles;
- if it is not possible to brush your teeth after each meal, then it is advisable to rinse your mouth with water at room temperature;
- drink acidic drinks through a straw;
- after a diet that consisted of acid-containing foods, it is better to refrain from brushing your teeth for one to two hours;
- For preventive purposes, visit the dentist’s office once every six months.
Following these simple rules will help reduce the risk of developing such an insidious disease as tooth enamel erosion.
How is the treatment carried out?
Erosion of enamel can be detected by a dentist during a preventive examination; this most often occurs at the initial stage during regular visits to a specialist, or it can be diagnosed after a patient complains.
If indicated, the dentist may refer you to an endocrinologist or gastroenterologist for consultation. For successful treatment, it is important to correctly identify the provoking factor and draw up an individual plan for complex therapy.
Damaged tooth enamel cannot be restored naturally. If treated in a timely manner, the dentist must take measures to block the process of tooth decay. After treatment is completed, teeth are restored to restore their appearance.
Where can you find a qualified dentist in Ivanteevka?
High-quality dental care is provided by specialists from the Sanident clinic. We are one of the largest clinics providing our services in Shchelkovo and in the urban district of Ivanteevka. We have the most modern equipment, employ only professionals with extensive experience, who use progressive methods of dental treatment and provide competent advice. We regularly hold various promotions and discounts for our patients.
The activities of our clinic are aimed at creating maximum comfort for our patients, minimizing pain and discomfort. You can make an appointment with a specialist by calling the number listed on the official website of dentistry.
You can receive the necessary dental services at the following addresses:
- Ivanteevka, st. Novoselki, 4;
- Shchelkovo, st. Central, no. 80.
How to protect tooth enamel from reflux?
What to do if doctors suggest that your problems, for example, enamel erosion, are most likely associated with reflux disease.
The logical answer is to be friends with the dentist and gastroenterologist and follow all their recommendations.
But there are simple and logical measures that can also help.
It is necessary to reduce the consumption of sour foods , especially fruit juices and other drinks, sour candies. Let’s not aggravate aggression with acid from the inside and aggression from the outside.
It is necessary to increase the amount of saliva so that it better neutralizes stomach acid.
This can be done by drinking enough liquids (not soda!) throughout the day.
A great way to increase saliva production is by chewing sugar-free gum .
Saliva decreases during sleep, especially if you sleep in a hot room with dry air. In this case, a humidifier will help.
You may not produce enough saliva due to a condition called xerostomia .
Xerostomia may be associated with advanced age .
It may appear due to certain medications that you take for various reasons - you will understand this by studying the list of side effects according to the annotations.
It's a shame that the drugs used to treat GERD sometimes also reduce the amount of saliva.
Xerostomia can also be a sign of chronic diseases .
Dentists know the list of these diseases and they can refer you for additional examination
The next part will be about dental plaque.
1, total, today