3404
Not all people have a sparkling, beautiful smile, as there are many factors that can affect aesthetics. One of the conditions for healthy teeth and the entire oral cavity as a whole is correct bite.
In particular, orthognathic occlusion, which is the subject of today’s article, falls into this category.
What is orthognathy
Translated from Greek, “gnathos” means jaw, and “ortho” means straight or regular.
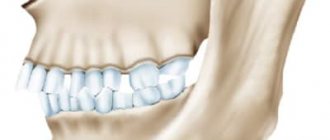
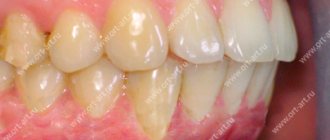
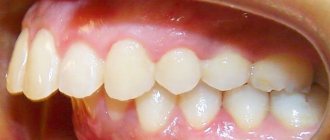
In dentistry, orthognathic is a physiologically correct bite. Its main feature is a slight overlap (up to 1/3 of the crown height) of the lower teeth with the upper ones. This occlusion is considered the most advantageous from an anatomical and physiological point of view (which we will talk about later). Other characteristics of correct occlusion include straight teeth and tight grip of the incisors (there are no gaps between them).
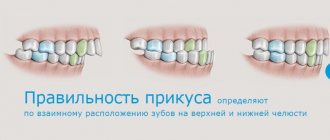
Orthognathic bite: how to determine
The surest way to determine the type of occlusion is to consult a dentist for an examination. Orthognathic bite has the following features, which can be determined independently:
- The upper teeth overlap the lower teeth by 1/3 (or less) of the crown height. This is the basis of a physiological bite. It is important to note that if the closure is direct (when the edges of the upper teeth directly meet the edges of the lower teeth), then this is a type of pathological bite, although such a smile looks very aesthetically pleasing. With such closure, the teeth quickly wear out and are destroyed.
- One upper tooth meets the two lower ones.
- Middle line. Many people mistakenly believe that the middle of the upper jaw should coincide with the middle of the lower jaw. In fact, it is important that the midlines of the upper jaw and face coincide.
- You do not feel any functional impairment. The processes of chewing and swallowing are not accompanied by discomfort and pain. If clicking or crunching is felt, this indicates dysfunction of the temporomandibular joint (TMJ). This symptom is often observed with pathological bites.
- Correct facial proportions. This is an indirect characteristic for physiological occlusion. There are cases when pathological closure of teeth does not affect the symmetry of the face. There are also opposite cases when those with a correct bite have an asymmetrical face. An individual approach and correct diagnosis by a doctor are important here.
What does an orthognathic bite look like?
Orthognathia: benefits
- Uniform load on teeth . This protects hard tissues from premature destruction.
- No speech impediment . With pathological occlusions, a violation of diction is often observed, since some sounds are difficult for a person to hear.
- No strain on the digestive organs . With an incorrect bite, a person chews food poorly. Relatively large pieces of food enter the stomach, which impairs digestion.
- Effective oral hygiene . The correct shape of teeth is the key to good hygiene. In this case, the risk of developing caries, periodontitis and other dental diseases is significantly reduced.
- Successful dental treatment . People with malocclusion experience difficulties with prosthetics, implantation and other types of dental treatment. Often, before the main treatment, the doctor prescribes bite correction.
- Aesthetic benefits . In most cases, an orthognathic bite provides a beautiful smile and facial symmetry.
How does a correct bite develop?
You need to monitor your bite from early childhood. Pay attention to the position of the tongue, the position of the teeth and the development of the child’s jaw. Let's consider the main stages of bite formation in children of different ages.
- 0-6 months . During this period, the foundation for the closure of the dentition is laid. If the child is fed correctly (so that the masticatory muscles experience the proper level of load), then the dental arches and jaws develop harmoniously (if there are no hereditary or congenital anomalies of the dental system).
- 6 months . The first milk teeth appear, the tongue rests on the roof of the mouth.
- Up to 3 years . Closer to 3 years of age, baby teeth are formed. At this age, the child’s dentofacial arches are fully functioning, he is able to chew food normally and speak.
- 4 years . From this age, the milk bite gradually loses its position.
- 6 years . Permanent teeth appear in place of the lost milk teeth. An overlap of the lower teeth with the upper teeth is formed (no more than 1/3 of the height of the crown). If the child had gaps between the teeth in the primary dentition (tremas or diastemas), then by the time the permanent dentition is formed, these defects disappear.
- 15 years . In adolescents, the formation of dentition ends. The overlap of the upper teeth with the lower ones should remain at 1/3 of the height of the crown.
Do I need to prepare for orthognathic surgery?
The preparatory period can last more than one week. As mentioned above, orthognathic surgery is completely predictable. Therefore, at the first stage, the specialist decides what results should be after treatment:
✔
determines the necessary future parameters;
✔
finds the maximum possible number of closures between opposing teeth;
✔
monitors how the results of the operation will affect the patient’s appearance.
In most cases, when preparing for surgery, surgeons use special 3D modeling tools for the result. Thanks to the software, a template is obtained and the paths that will lead to the expected effect of orthognathic treatment are found.
Then orthodontic treatment with braces or aligners begins. This can take from several months to a year and a half. Once the dentition is aligned, orthognathic surgery can begin.
Orthognathic intervention takes 4-6 hours. Then the patient remains in the clinic for another 3-4 days under the supervision of the attending physician. Afterwards you can return home, and after 3 weeks you can go back to work.
The importance of physiological occlusion
Physiological occlusion is important for health for the following reasons:
- the bone tissue of the skull elements develops harmoniously;
- uniform load on teeth and joints;
- no negative effects on the digestive or respiratory system;
- correct facial proportions, lack of psychological discomfort in this regard;
- beautiful smile;
- good oral hygiene.
Anatomy and physiology of the dental system
When it comes to occlusion, not only the location of the teeth is important, but also the functions of the remaining elements of the dental system. These are the upper and lower jaws, jaw joints and muscles that ensure the process of chewing and swallowing.
The greatest load on the teeth occurs when chewing. It is important that at this moment the load is evenly distributed on the surface of the teeth. This way hard tissues will retain their strength and structure longer. Otherwise, the teeth will quickly wear out. This threatens with caries, wedge-shaped defect, gum disease and final tooth destruction.
Under the physiological norm, the position of the jaws should be parallel. The lower jaw resembles a parabolic arch, and the upper jaw is a semi-oval. The coordinated functioning of the jaw joints is also important - without discomfort, clicks and crunches.
When is treatment needed?
As a rule, no treatment is required for orthognathic occlusion. But there are also some anomalous processes when correction may still be necessary. For example:
- The incisors are too large in relation to the rest of the dentition.
- Unevenly positioned dental units in relation to the rest in the row. This situation spoils the smile and causes psychological discomfort to the person.
- Traumatic injuries to the jaw.
Each specific clinical case has its own characteristics and the final decision on the need for therapy is made by the orthodontist.
What are the problems with orthognathic occlusion?
Orthognathia does not guarantee the absence of dental problems. Even with a physiologically correct bite, various defects are possible. These include:
- crowded teeth;
- diastema and trema - gaps between teeth;
- edentia (absence of one or more teeth);
- speech defect;
- other violations.
Important. Under no circumstances should you neglect such defects in your primary bite. Many parents believe that baby teeth are not that important because they will soon fall out. This is a big misconception, since the health of permanent teeth largely depends on the condition of baby teeth. Therefore, if you want your orthognathic bite to be preserved in the future, then take care of your teeth from early childhood.
Preventing Changes
Over time, the correct arrangement of dental units during orthognathia may change. Therefore, even in adults, you should monitor the safety of your bite. Possible reasons for changes:
- Periodontal diseases.
- Loss of teeth (due to caries, age-related changes, injuries).
- Improper breathing (oral breathing). It occurs due to frequent or chronic ENT pathologies.
To preserve your bite, such problems must be corrected immediately. Expert recommendations:
- daily proper oral hygiene;
- surgical restoration of teeth after their removal;
- timely treatment of ENT diseases.
Correct bite: how to maintain
Pathological bites are formed due to hereditary or external factors. If we cannot influence genes, then we can change our lifestyle. To avoid malocclusion, we recommend adhering to the following rules:
- Wean your child off bad habits - thumb sucking, cheek biting, excessive use of the pacifier.
- Provide normal nutrition - introduce solid food in a timely manner so that the jaw experiences normal load.
- Treat respiratory diseases. The child should breathe through his nose. Mouth breathing is one of the risk factors for the formation of a pathological bite.
- Treat dental diseases in a timely manner.
- Visit your dentist regularly for preventative checkups.
- Use an orthopedic pillow while sleeping.
FAQ
Why is correct bite important?
Correct bite means a reduced risk of not only dental, but also other diseases. With pathological occlusion, the load on the teeth is uneven, which leads to accelerated wear of some teeth.
In addition, malocclusion is an additional burden on the digestive system and respiratory organs. Finally, there is psychological discomfort due to facial disproportion.
Can the bite be incorrect if the teeth are straight?
Yes. The straight bite mentioned above can be formed with straight teeth. Therefore, the ideal shape of the teeth can also be observed in pathological occlusions that require orthodontic correction. In addition to straight teeth, straight teeth can also be observed in deep, distal or open bites.
Correct jaw anatomy - what is it?
The main sign of a physiologically correct jaw is its shape. The lower jaw resembles a parabola, while the upper jaw resembles a semi-oval. This is how the teeth are located on the corresponding jaws.
Both jaws should be symmetrical along an imaginary vertical line that runs between the central upper teeth.
What is the correct tongue position?
The entire tongue (both tip and back) should touch the roof of the mouth.
How to recognize an abnormal bite?
Above we looked at the criteria for correct bite. Therefore, deviations from these signs can be considered incorrect occlusion. At the same time, you cannot make diagnoses yourself. Consult a doctor who will accurately determine the type of bite. Let us remind you that among pathological bites the following are distinguished:
- distal – the upper teeth hang excessively over the lower teeth;
- mesial – the lower jaw protrudes strongly forward;
- deep – the upper teeth overlap the lower teeth by more than half;
- open – the presence of a sagittal gap between the teeth;
- cross – displacement of one jaw relative to the other (displacement towards the teeth, molars and premolars);
- straight - the closure of the lower edges of the upper and lower teeth during occlusion.
Diagnostics
The correctness of the bite is determined by the orthodontist at the appointment. Such a specialist is available in any dental clinic - both for children and for adults.
He determines the correct position of the teeth and also selects a method for correcting it. Already during the initial examination, large gaps between bone formations, their crowding, extra teeth or knocking them out of the general row are noticeable.
For more accurate diagnosis, X-ray equipment is used. Such an image allows you to clearly determine the distance between the teeth, the location of the jaws relative to each other, the presence or absence of large gaps between bone formations. Also, an x-ray will show how best to correct the bite in the presence of pathologies.