- Causes
- Signs of pathology
- Classification of pathology
- What complications can there be?
- Treatment and correction of distal bite
Distal bite is a pathology in which the occlusion (closing) of the upper and lower jaws is disrupted. In this case, the teeth of the upper jaw protrude much forward relative to the lower jaw. Another name for the anomaly is prognathia. It has a negative effect on appearance, causes consequences in the form of disruption of the digestive system, and psychological problems.
If a distal bite is diagnosed, correction is faster and easier in childhood. Correction in adults is also possible, but it requires a lot of effort and time.
Signs
This orthodontic pathology has many symptoms. Some of them are visible to the naked eye, while others can only be noticed by a specialist.
Main symptoms:
- The upper incisors protrude forward, so the occlusion (closing) in this area is broken or completely absent. If the problem is very severe, a sagittal gap is formed - a vertical gap between the upper and lower incisors. This clinical picture is called diocclusion and can take traumatic forms if the cutting edge of the lower teeth rests on the hard palate. In this case, the mucous membrane of the oral cavity is chronically injured.
- A deep incisal overlap is possible - complete overlap of the lower dentition with the upper, which is observed in a number of cases.
- “Bird profile” is a group of specific characteristics expressed in a retracted profile with reduced lip thickness. The double chin may become larger, especially in overweight patients. The lower third of the face is reduced, and the upper lip protrudes forward. In the presence of a sagittal fissure, the mental fold stands out sharply. The facial expression becomes surprised or dissatisfied.
- Posture changes - the head is tilted forward, the back is slouched, scoliosis, a skewed pelvis, and flat feet are possible.
A protruding upper jaw is the most noticeable symptom of a distal bite.
The symptoms of a distal bite increase with age, so it is better to carry out treatment as early as possible: then it takes less time and does not allow concomitant disorders to worsen. In adults, the list of symptoms is usually more extensive.
Final correction of the bite after removal of the Herbst appliance
After removing the Herbst appliance, the orthodontist usually prescribes wearing orthodontic elastics to achieve more correct and dense interdental contacts.
The myofunctional therapist selects a set of exercises aimed at strengthening the correct functioning of the masticatory muscles and maintaining the lower jaw in a new position.
Commentary by myofunctional therapist T.B. Zukor: “When I prescribe exercises to adult patients, I often hear that there is not enough time to complete them. But the stability of a corrected bite depends on proper muscle function! Nobody wants their teeth to become crooked again, and their jaw to go back, because so much effort has been spent. The exercises are not complicated and do not require special sportswear, location or preparation. Do exercises while driving, standing in a traffic jam, when taking a shower, watching TV - any 5-10 minutes will make a significant contribution to your health!”
Throughout the entire orthodontic treatment, the osteopath relieves excess tension in the muscles and joints and helps to quickly adapt to the new bite.
Causes
There are several reasons for the formation of distal occlusion:
- Heredity . This symptom is dominant, so the appearance of the problem in children whose parents had this pathology is very likely.
- Difficult pregnancy . The appearance of this type of bite can be caused by illness of the mother during any trimester, toxicosis, or the use of heavy medications or narcotic drugs during this period.
- Artificial feeding . In this case, sucking occurs with less load on the facial muscles, which provokes improper formation of the facial part of the skull.
- Nasal breathing disorder . Chronic ENT diseases lead to constant open-mouth breathing. Because of this, a high hard palate develops, the upper jaw narrows and extends forward.
- Bad habits . Sucking of fingers, the inner surface of the cheeks, and tongue lead to changes in the facial bones and bite. Frequent tongue pressure on the teeth can also cause them to move. In children, this leads to the appearance of a persistent anomaly much faster, since the formation of the dentofacial apparatus is in the active phase.
- Poor posture . Violation of the vertical axis of the body causes changes in the jaw bones.
- Early loss of primary incisors . This may be a consequence of deep caries or injury. The premolars then move closer to the center, and there is little space left for the permanent molars, so they move forward.
- Absence of lower canines . The load on the lower dentition decreases, and the growth of the lower jaw slows down.
- Rickets and disorders of the structure of the musculoskeletal system.
What is distal bite (occlusion)
This is a pathology in which the upper jaw is not located at the same level as the lower jaw, but is significantly pushed forward, as a result of which the teeth close incorrectly, with displacement. And not only the front ones, but also the lateral ones, which creates a block that prevents the healthy development of all incisors.
It arises and develops as a result of one, several or a whole group of interrelated factors (discussed in detail below), which entails other anomalies, most often diastema. Over time, it also causes weakening of the chewing muscles, respiratory problems and other complications that are dangerous to the body.
Varieties
Orthodontists distinguish two types of distal occlusion:
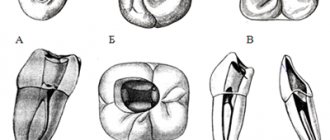
- The first is due to upper macrognathia. The upper molars have a fan-shaped arrangement, they are narrowed at the base, and sometimes twisted in relation to the central axis. The lateral sections of the dental system are narrowed compared to the norm.
- The second is in most cases accompanied by lower micrognathia. The central incisors of the lower jaw are oriented towards the palate, that is, they are inclined towards the inside of the oral cavity. In this case, the lateral incisors are deviated towards the lips. The lower lip appears thickened.
Signs of both forms may be present simultaneously.
Types of closure according to Engle's second class
Diagnostics
Correct and detailed diagnosis of distal occlusion is very important, since the root cause of the disease must be dealt with in order to achieve a lasting effect. The orthodontist must understand what caused the changes - irregularities in the shape of the jaw, structural changes in bone tissue, incorrect orientation of the teeth, or the complex influence of these reasons.
At the first stage, a visual examination is carried out with a comparison of the parameters of the facial part of the skull. To confirm the diagnosis, the patient is referred to a number of diagnostic procedures:
- teleradiography in the lateral plane - helps to determine violations of size, proportions and identify displacement of the jaws;
- computed tomography – helps to study the temporomandibular joint and masticatory muscles;
- electromyography – allows you to evaluate the conductivity of muscle tissue;
- rheography – identifies areas with insufficient blood supply.
Sometimes a diagnostic plaster model of the jaws is made in order to be able to make accurate measurements of all parameters of the patient’s dentofacial apparatus.
How to care for braces?
Caring for braces requires care and discipline. We talked about it in more detail in a separate article. After installing braces, the doctor will tell you how to live now. We will indicate the most important things.
- Always have brushes and a single-tuft brush on hand.
- Add a waterpik to your arsenal.
- If you are not sure that you have brushed your teeth well, use an indicator tablet. After brushing your teeth, the tablet must be dissolved in your mouth. The areas where plaque remains will turn blue. These areas need to be cleaned again.
- Avoid very hot and very cold drinks. Braces, like enamel, do not like sudden temperature changes.
- To prevent braces from coming off, follow a diet. Eliminate nuts, toffees, seeds, and flour from your diet. Apples and other hard fruits should not be bitten off, but cut into small pieces and placed on the chewing teeth.
Treatment
This complex anomaly is removed by various methods. In most cases, complex treatment is required, combining several techniques.
In childhood, with primary or replacement teeth, treatment of distal occlusion is faster. In adults, it will take more time, but the orthodontist will not be able to give an accurate forecast of the duration of the course, since the speed of recovery processes is individual for each patient. Estimated dates:
- 1-1.5 years for children;
- several years for adults, at least 3-4 years.
In children
For patients with a distal anomaly who have primary teeth, wearing vestibular plates and bite formers is prescribed:
- orthodontic plates are removable plates that can be used only for the lower, only for the upper, or for two rows of teeth at once;
- Basharova’s bite former – can be equipped with a screw for expansion or a bite device; at the age of up to 8 years it gives quick results.
These methods lead to normal jaw size, normalize breathing and swallowing, and also reduce pressure on the outer side of the cheeks and on the incisal edge of the dentition.
In children after 8-10 years of age, with a replaceable set of teeth, functional guidance equipment is used. The following models are most often used:
- Bionator;
- Twin Block;
- articular orthosis;
- Herbst apparatus;
- Frenkel function regulator;
- Andresen-Goipl activator;
- Persin apparatus.
In childhood, myogymnastics shows excellent results. For children under four years of age, it may be the only treatment method, and it will be quite sufficient for complete correction. After four years, it is usually used in complex therapy, but significantly reduces the course time.
For teenagers, special crowns are often prescribed for the lower teeth, which normalize the natural position of the chewing muscles. Orthodontic structures based on cervical traction are rarely used. They look cumbersome and cause significant discomfort, so they are prescribed only in cases where other methods cannot be used for various reasons.
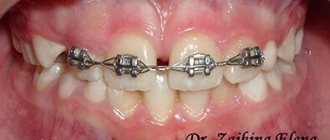
Braces are used only when the cause of distal deformation is tooth displacement, and not jaw structural or proportional disorders. They can install one system at a time, and if necessary, two at once.
Tooth extraction is indicated for cases of increased crowding caused by a lack of space in the jaw. Sometimes the reason for this is over-equipment, the presence of extra molars or premolars.
A small hard palate can be expanded using a non-removable Ainsworth or Frenkel apparatus. If the size of the mandibular bone is reduced, its growth can be stimulated with a palatal expander, a preorthodontic trainer, or a removable plate apparatus.
In adults
With a permanent set of teeth and a formed skull, the tactics for treating distal occlusion are different. They use two main directions:
- Masking a violation . The reason for such tactics remains, but its external manifestations are eliminated. Braces or retainers help correct the position of the teeth; one or two dental elements may be recommended to be removed so that there is no shortage of space in the dentition. These measures can significantly improve the profile of an adult patient.
- Correction using surgical techniques . It is used in more severe cases when disguise will not help. Palate plastic surgery is performed, which is performed under general anesthesia in the Department of Maxillofacial Surgery, followed by a rehabilitation process. Sometimes, in the second stage, surgery is needed to improve the shape of the chin.
Physiotherapy and massage are auxiliary measures. To fix the result obtained, in adulthood you will need to constantly maintain the effect with the help of myogymnastics and bite formers, which will need to be used for several hours a day, mainly at night.
Types of occlusion defects and methods of their correction
Scientists have calculated that only 40% of the planet's inhabitants are the happy owners of an ideal bite. All others have deviations from the norm to one degree or another. Defects can be critical when they have a negative impact on human health, and practically unnoticeable, not leading to moral or physical discomfort.
The picture below shows occlusion anomalies:
Modern orthodontics includes several methods for correcting malocclusion:
- using braces;
- through surgery;
- using myotherapy (physical exercises) and non-braces corrective devices.
Refusal of treatment
Faced with the need for long-term treatment, some patients or parents of children who need correction of distal occlusion doubt its advisability.
It should be understood that the visible disorder that is provoked by this pathology is a change in appearance. A small lower third of the face, a sloping chin, and protruding teeth will become more and more noticeable every year.
But refusal to treat distal occlusion does not end with aesthetic issues. Other related problems include:
- deterioration of diction and strengthening of articulation, aimed at compensating for speech deficiencies;
- poor-quality chewing of food, which can cause chronic deficiencies in the gastrointestinal tract;
- improper distribution of the load when chewing, which leads to abrasion of enamel, inflammation in the gums and periodontitis;
- clicks when opening and closing the mouth, which indicates pathologies of the temporomandibular joint, causing temporal pain and headaches;
- difficulties with prosthetics, reduced service life of crowns;
- progressive problems with the cervical spine.
Problems in case of refusal of treatment appear gradually, they worsen with age. Their occurrence is often not associated with distal occlusion and is treated for a long time by specialists in other areas of medicine, resulting in frequent relapses.
Promotions valid today:
White teeth in 45 minutes
Health as a Gift
Share the link:
- Click here to share content on Facebook. (Opens in a new window)
- Click to share on WhatsApp (Opens in new window)
pediatric dentistry, orthodontics, topic articles: Herbst apparatus, distal bite, bite correction, face bow, face mask, mesial bite, microimplants, palatal clasp, palatal expander
Prevention
Preventive measures in most cases can prevent the development of this pathology or slow down its progress. To do this, you should follow these recommendations:
- Children and adults should see a doctor at least once every six months to detect the initial stage of the disease. During this period, the correction will take much less time and will be carried out using gentle methods.
- Watch your posture.
- Prevent rickets or treat it promptly.
- Introduce natural breastfeeding and fight bad childhood habits.
- Ensure the constant presence of solid food in the diet.
- Avoid chronic ENT diseases or allergic conditions that cause nasal breathing problems.
Conclusions. Expert advice
The correct position of teeth is very important for a person. Bite abnormalities can cause improper development of the jaw, rapid wear of the enamel, and the development of dental diseases, which is why they have to be removed. If you do not pay attention to the problem, it begins to cause disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract, breathing problems, and ENT diseases. That is why it is important to diagnose the anomaly in a timely manner and begin treatment for malocclusion. Moreover, you can take care of your smile at any age; modern medicine allows you to do this!