Full text of the article:
Working with diseases of the internal organs is especially difficult because they cannot be seen. Previously, doctors had to treat patients literally “blindly,” since it was possible to examine a person’s internal organs only during surgery. Nowadays, doctors don’t have to pick up a scalpel; various types of scans help make a diagnosis. However, patients are wary of this type of examination. This is due to the high cost of some procedures and the fear of radiation. Let's try to figure out what the features of certain scans are and when to resort to them.
X-ray
The oldest and most common method of visualizing the human body. X-rays are used everywhere, from surgery to dentistry. The method is simple and clear: a person is irradiated with special rays that easily pass through soft tissues and linger in hard ones. Thanks to this principle, an image is transmitted to a photographic film or sensor located on the side opposite the ray source, and radiography or fluoroscopy is available to the doctor.
Main advantages
such an examination: speed and cost. Almost all hospitals are equipped with X-ray machines; the procedure is quick and inexpensive.
Main disadvantages:
exposure and image quality. When performing radiography, the patient is irradiated, and the picture is two-dimensional. The doctor can hardly see the internal organs individually, since their shadows overlap each other. It is also impossible to see the cartilage tissue and brain in detail. The cartilage practically does not block the rays, the brain is securely closed by the skull. X-rays are not suitable for their examination.
It will be most effective to carry out radiography for damage to bones, joints and teeth.
Are X-rays dangerous?
X-rays are a type of electromagnetic wave. They are emitted by electrons, which, having greatly accelerated, hit a dense material. X-ray waves are not something created artificially by man, they are natural radiation that reaches the Earth with the rays of the Sun. Every person daily experiences the effects of X-ray and even radioactive radiation in minimal doses.
Yes, scientists classify X-rays as carcinogens, that is, factors that increase the risk of cancer. However, if X-rays are used correctly, the risks are negligible and are not comparable to the benefits that X-rays bring.
It is better to take an x-ray if this is helpful. Making a diagnosis and choosing the best treatment option outweighs the very small risk of having an x-ray.
X-ray is a safe diagnostic method because:
- The level of radiation in X-ray machines is strictly dosed. During the study, the patient receives a safe dose.
- Doctors prescribe a study only if it is necessary, if without it it is impossible to establish a correct diagnosis and prescribe effective treatment.
- Certain periods of time are maintained between x-rays. No doctor will order a test for you every day.
- Modern devices provide a lower level of radiation compared to older models; the body receives a minimal dose.
- If the doctor finds contraindications for you, they will not prescribe an x-ray. Doctors always weigh potential benefits against potential risks.
Fluorography
Another type of examination that all residents of our country regularly undergo. Fluorography was “invented” almost a hundred years ago. This is a kind of accelerated radiography. Scientists proposed photographing a screen with an image obtained from radiography. This made the procedure faster and more widespread. Screening tests began to be administered to everyone in order to detect latent pulmonary tuberculosis.
Main plus
The procedure is fast,
the main disadvantage
is the image quality. The patient also receives a dose of radiation, and the doctor has a rather blurry picture, so fluorography is recommended to be supplemented with questionnaires and laboratory tests for the presence of tuberculosis.
Expert opinions
Ilya Gipp, Ph.D., Head of MRI-guided therapy:
— Many of these devices can be used for treatment. For example, a special installation is attached to an MRI machine. It focuses ultrasound waves inside the body, increasing the temperature in a targeted manner, and burns out tumors - for example, uterine fibroids.
Kirill Shalyaev, director of the largest Dutch manufacturer of medical equipment:
- What seemed impossible yesterday is reality today. Previously, during CT scans, a drug was administered to slow down the heart. The newest CT scanners make 4 rotations per second, so there is no need to slow down the heart.
| What radiation doses do we receive* | ||
| Action | Dose in mSv** | Over what period of time will we receive this radiation in nature? |
| X-ray of a hand | 0,001 | Less than 1 day |
| X-ray of a hand using the very first machine in 1896. | 1,5 | 5 months |
| Fluorography | 0,06 | 30 days |
| Mammography | 0,6 | 2 months |
| Mammography with MicroDose characteristic | 0,03 | 3 days |
| Whole body CT scan | 10 | 3 years |
| Live in a brick or concrete house for a year | 0,08 | 40 days |
| Annual norm from all natural radiation sources | 2,4 | 1 year |
| Dose received by liquidators of the Chernobyl accident | 200 | 60 years |
| Acute radiation sickness | 1000 | 300 years |
| Epicenter of a nuclear explosion, death on the spot | 50 000 | 15 thousand years |
| *According to Philips **Microsievert (mSv) is a unit of measurement of ionizing radiation. One sievert is the amount of energy absorbed by a kilogram of biological tissue. | ||
Mammography
A separate type of radiography designed to diagnose breast diseases, which is why women undergo mammography. There is no consensus on the recommended age for the procedure. Mammography helps ensure the absence of a malignant tumor with an accuracy of 89%. It is believed that women should be screened regularly starting at age 39, although some cancer societies recommend screening at a younger age.
Mammography is prescribed to diagnose breast cancer, the procedure is quick
, this is a plus, but the patient
is irradiated
, and the risk of an incorrect diagnosis remains, this is a minus. Mammography can be digital or film; digital mammography provides a clearer image.
Computed tomography (CT)
Computed tomography is also carried out on the principle of radiography, but as a result the doctor receives not a flat two-dimensional picture, but a three-dimensional image. This is achieved by simultaneously taking a large number of images, which are assembled into a single image. CT scanner sensors are highly sensitive and distinguish a huge number of shades, so the doctor can examine in detail all the bones and organs of the patient. The image quality can be further improved by injecting the patient with a special substance, the so-called “contrast”. The contrast helps to distinguish healthy tissues from altered ones and detect abnormal structures in the body, and also makes it possible to study the condition of blood vessels in detail. CT with contrast is not prescribed in every case; often a simple computed tomography is sufficient.
CT scan is done quickly
, with its help to screen for lung cancer. You can also use computed tomography directly during surgery.
Disadvantages of CT
can be considered a high radiation dose to the patient. Therefore, CT is not prescribed to pregnant women, children and overweight patients (more than 200 kilograms).
In what cases is it necessary to take an x-ray? What diseases does it help diagnose?
X-ray examination is one of the most commonly used imaging methods. It is used to diagnose a wide variety of diseases in various fields of medicine.
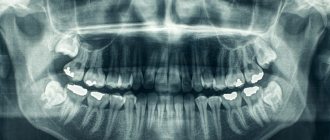
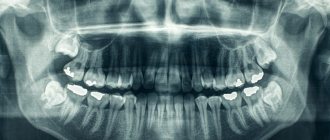
When a person who has been injured arrives at the emergency room, the first thing the doctor will do is order an x-ray. The study helps to determine whether bones and joints have been damaged and to distinguish fractures and dislocations from less serious injuries. Traumatologists use radiography to check how correctly the bone fragments were reduced (compared), whether they were installed correctly, and whether the pins, screws and other metal structures were displaced.
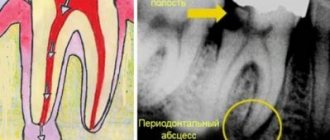
X-rays help dentists assess the condition of the tooth root and the tissues that surround it and the jaw bones. ENT doctors use X-rays to evaluate the condition of the paranasal sinuses. Chest X-ray plays an important role in diagnosing pathologies of the heart and lungs.
X-rays are often used to diagnose spinal diseases. It helps to identify anomalies and injuries (fractures, subluxations) of the vertebrae, assess the condition of posture, intervertebral discs, diagnose scoliosis, osteochondrosis and other diseases. This is an indispensable diagnostic method in the work of neurologists and orthopedists.
Soft tissues are not as visible on x-rays as bones. But they can be “painted” using special radiopaque solutions. X-ray with contrast is used to study blood vessels, organs of the digestive system, bronchi, kidneys and bladder.
Ultrasound examination (ultrasound)
X-ray is not the only way to “look inside” the human body; another technology is ultrasound. Some animals, such as bats, use sound waves to orient themselves in space. People have also learned to use waves to solve some problems, including in medicine. A picture of the internal organs can be obtained by sending a sound wave into the human body and monitoring its return. The computer helps process the results and present them in the form of a three-dimensional picture.
The main advantage of this research method is safety.
. Ultrasound can be performed even on pregnant women; in addition, ultrasound devices are mobile and can easily be placed in the patient’s room to monitor the condition of organs and blood flow in real time.
However, ultrasound cannot provide a high-definition image, so the use of this method of research is limited, for example, gastrointestinal diseases cannot be diagnosed using ultrasound.
Who doesn't use X-rays?
- First of all, radiography is contraindicated during pregnancy, since X-rays can cause unwanted mutations in the cells of the embryo. The degree of risk depends on the stage of pregnancy. Sometimes doctors still make an exception and prescribe a test for a pregnant woman.
- X-rays are not performed in patients who are in serious condition, if there is serious bleeding or damage to the chest with depressurization of the pleural cavity.
- The solutions used for X-ray contrast studies contain iodine. It causes allergic reactions in some people. If the patient is allergic to iodine, contrast should not be administered.
- X-ray contrast studies are contraindicated in certain diseases of the thyroid gland, severe pathologies of the kidneys and liver, active tuberculosis, and decompensated diabetes mellitus.
Sign up for an x-ray at the medical office. To make an appointment, call +7 (495) 120-08-07 . If you are scheduled for an X-ray of the lumbosacral region, read about preparing for the study.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
The principle of MRI is based on the property of atomic nuclei to respond to a strong magnetic field. The calculation is based on the reaction of hydrogen nuclei, of which there are many in the composition of water molecules, and the human body, as is known, consists of 60% water. When entering a magnetic field, the nuclei of atoms are oriented along it; they can be excited and the energy that they will give off when the influence weakens can be recorded, i.e. “relaxation”. Computer analysis allows you to convert the information received and determine the location, density and structure of tissues in the body.
MRI allows you to “see” cartilage, soft tissue and the human brain without causing harmful effects
, so the procedure can be performed by anyone and as many times as desired.
However, the examination takes a long time
, and closed-type tomographs can cause attacks of claustrophobia. True, there are open-type devices. MRI procedures should not be performed on people who have electrical devices (such as pacemakers) or metal implants implanted in their bodies.
MRI will be effective in studying tumors, brain and vascular abnormalities.
Scintigraphy, SPECT, PET
Perhaps these are one of the rarest procedures on our list. These examination methods are based on radiation diagnostics, but it is used in reverse. The patient is not irradiated from the outside, but a special radioactive drug is injected into him to make him “glow from the inside.” First, scientists invented and tested scintigraphy. With its help, it was possible to obtain two-dimensional images. Then research went further and single photon emission computed tomography ( SPECT)
), followed by positron emission tomography (
PET
). The difference between these methods is rather technical; they use different radiopharmaceuticals and different types of detectors that record radiation from the patient’s body.
The question arises: “Why such difficulties?” The fact is that thanks to these procedures, you can see formations in the pictures that are not visible in pictures obtained by external irradiation. Metastases and tumors can appear inside bones or organs and remain silent for a long time. The radiopharmaceutical is injected into the body and accumulates in the tissues, which allows it to “illuminate” certain areas.
Main disadvantage
of this examination method is the cost. The radiopharmaceutical is developed individually for each patient; in addition, the patient receives radiation exposure, and the procedure itself is more complex than those we described earlier. However, in some cases it cannot be avoided, for example, in cases of oncological and neurological diseases, diagnosis of heart and thyroid diseases.
Hybrid Imaging Techniques
Probably, science would not be science if it did not constantly move forward and try to create something new from the old. So, doctors began to combine different scanning methods to obtain even more detailed and high-quality images. PET and SPECT are combined with CT, MRI complements PET. Such experiments are not cheap, but can sometimes help make decisions about further treatment for the patient.