According to statistics, every third person suffers from pathologies of bones and joints. One of the first places is occupied by diseases of the jaw joints. The problem is that in the early stages of the development of the disease, symptoms may be absent or mildly expressed, and increased tissue wear is characteristic. However, therapy must be started as early as possible, which will speed up recovery and also prevent complications.
X-rays of the jaw allow timely detection of many diseases of the temporomandibular joint. Therefore, when the first symptoms of such ailments appear, you must contact a medical center for an x-ray.
When is a jaw x-ray taken?
Tell the patient exactly whether he needs and can have x-rays of his jaws
, should his attending physician. General indications for such a diagnostic procedure are:
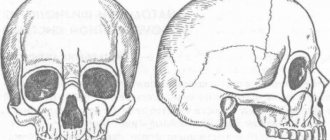
- Suspicion of jaw development abnormalities (in childhood or adulthood). These may be congenital clefts of the hard/soft palate, impaired growth and proper development, or malocclusion.
- Suspicion of infectious-inflammatory and specific pathologies. These include osteomyelitis, periostitis, syphilis, actinomycosis, tuberculosis or necrosis of the jaw bone.
- To identify various acquired defects resulting from injury or removal of oncological formations.
- Suspicion of the presence of a false joint.
- Suspicion of a benign or malignant neoplasm.
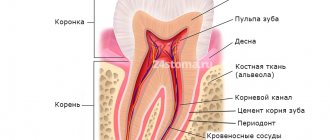
What can you see in the photographs?
The following can be seen on x-rays of the upper and lower jaws:
- defects - cracks, fractures, presence or absence of bone fragments;
- pathological changes in bone tissue - areas of tissue thinning, compaction, thickening or thinning of the cortical plate;
- areas of necrosis - sequestra;
- sclerotic process;
- various periosteal layers, osteophytes (bone growths);
- tumor-like neoplasms.
Diagnosis of pathologies using x-rays of the jaw
If you have symptoms indicating dysfunction of the temporomandibular joint, you must contact a diagnostic center for research. You can make an appointment for an x-ray in our clinic, where modern equipment is used to ensure the safety of the procedure for patients.
Pathologies can be diagnosed using x-rays:
- traumatic arthritis;
- neuralgia;
- purulent arthritis;
- rheumatoid arthritis;
- osteoarthritis;
- osteomyelitis;
- temporomandibular joint dysfunction syndrome;
- injuries of bone and joint tissues.
The technique provides high information content, which allows the doctor to make a correct diagnosis in a timely manner, prevent further development of pathologies and the occurrence of complications. In addition to X-rays, the doctor may prescribe a computed tomography scan, which will allow you to most accurately diagnose the disease and identify the causes of disorders in the temporomandibular joint.
How is the procedure performed?
X-ray of the jaw of an adult or child is a simple procedure. It can be done in different projections in order to better examine the structure of the bone tissue and make an accurate diagnosis.
X-ray of the lower jaw
To obtain general information about the condition of the lower jaw, an X-ray is taken in a direct projection. It allows for primary diagnosis of inflammatory, oncological and traumatic diseases. The patient is positioned as follows: lying on his stomach, face down, resting the tip of his nose and forehead on the cassette. The X-ray machine sensor is installed at the occipital protuberance.
A lateral view of the lower jaw is taken to assess the condition of the body, ramus and teeth of the desired side. The patient lies on his side, with his cheek on the cassette located at a slight angle.
To diagnose diseases of the lower jaw, images are also taken in the axial projection. The patient takes a position lying on his stomach, stretching his head forward with his chin as much as possible. At the same time, it is pressed against the cassette by the front surface of the neck and lower jaw.
X-ray of the upper jaw
To assess the condition of the bone tissue of the upper jaw and the chin area of the lower jaw, a nasomental placement is performed. To do this, the patient lies on his stomach, face down, resting the tip of his nose and chin on the cassette. The sensor is installed perpendicular to the cassette, 2 pictures are taken - with the mouth open and closed.
When is an x-ray required?
It is necessary to contact the clinic for an x-ray in the following cases:
- It is difficult to open your mouth after waking up; symptoms may disappear during the day;
- pain when chewing solid food, often manifests itself on one side;
- crunching, clicking of the jaw joints;
- pain in the ear area, especially when chewing;
- redness, swelling in the area of the temporomandibular joint.
These phenomena indicate the presence of disturbances in the functioning of the temporomandibular joint. In addition to these, fever, lack of appetite, and weakness may also occur.
In these cases, you must contact your dentist, who will order an x-ray. Based on the results of the study, the doctor will develop a treatment strategy. Timely diagnosis will help to make a correct diagnosis, as well as speed up the patient’s recovery process. An important advantage of x-rays is the ability to detect various pathologies, disorders of bone tissue and joints.
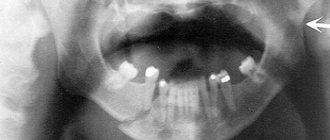
Panoramic shot of the jaw
A panoramic X-ray, or orthopantomogram, displays the entire upper and lower jaw in a direct projection. In such a picture you can see almost all the anatomical features of the patient’s dental system, all kinds of neoplasms, defects, fractures of tooth roots, and so on. An orthopantomogram allows you to identify the following pathologies:
- damage to tooth roots by caries;
- hidden carious cavities;
- cysts, granulomas, tumors;
- pathological changes in the roots and peri-root space.
Preparing for a panoramic dental photograph
The procedure does not require special preparation. You can consume drinks, food and medicine - this will not affect the x-ray in any way. Immediately before the procedure, metal jewelry must be removed from the body. It is not recommended to drink alcohol.
When visiting a dentist, you must take panoramic and x-ray photographs from the last few years, as well as a medical history. With their help, the doctor will be able to track visible changes in the patient’s health status or compare treatment results.
X-ray radiation poses a possible risk to pregnant women. According to some studies, it can negatively affect the intrauterine development of the fetus. Pregnant women should tell their dentist about their pregnancy. In this case, carrying out OPTG depends on the ratio of possible risks and benefits.
Decoding the results
An x-ray of an adult's jaw is usually interpreted by a radiologist.
Other specialists may also be involved in this work: dentist, facial surgeon, otolaryngologist. Specific pathologies of the upper and lower jaws have certain radiological features:
- Chronic osteomyelitis. Depending on the type of disease, the images may show foci of resorption of various shapes with a shadow of necrotic masses inside. In more severe cases, communication of the sequestra with the oral cavity is visualized.
- Acute osteomyelitis. When examining the image, you can see areas of bone tissue resorption that do not have clear boundaries.
- Fractures or cracks in the jaw bones. This pathology reveals itself by the fact that thin, elongated shadows are quite clearly visible in the photographs. In such cases, it is important not only to identify the fracture, but also to see the bone fragments, if any, and to understand how much they are displaced.
- Chronic periostitis. In the image with such a pathology, periosteal thickenings will be visible. If the disease has become severe, areas of ossification of the periosteum and new bone tissue along the edge of the jaw are visualized.
X-ray of the lower and upper jaw of an adult: what does it show?
X-ray examination is a method for diagnosing the upper and lower jaws, which makes it possible to detect pathological foci, their shapes, sizes and depth of tissue damage.
An X-ray is taken in the following cases:
- Differentiation of diseases;
- For preventive purposes, which allows timely detection of the disease;
- Treatment quality checks;
- Determining the position of teeth in the dentition;
- Before orthopedic, orthodontic, therapeutic treatment;
- Tissue structure assessments;
- Before implantation;
- Exclusion of contraindications before treatment;
- If pathology in the sinuses is suspected.
X-rays in dentistry have virtually no contraindications. The only contraindication is the presence of bleeding.
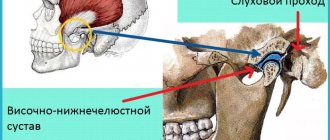
X-ray TMJ
X-ray TMJ
X-ray of the TMJ is performed to identify pathologies of hard structures in this area. This scanning method is non-invasive and does not cause pain or discomfort. Radiation exposure is minimal and safe for humans. After the diagnosis, a conclusion is drawn up with a description of the area and conclusions about the condition of the joint. The essence of radiography of the temporomandibular zone With the help of modern X-ray machines, you can obtain images on electronic media, which are highly informative and clear. This method is most relevant when diagnosing joint diseases. This study is often prescribed if jaw mobility has decreased or pain has appeared in this area. A specialist can give a referral for examination if there is facial asymmetry, extraneous sounds appear when moving the jaw, or headache. X-rays show the effects of the area after surgery, conservative treatment or injury. A scan is required before surgery. X-ray placement of the TMJ does not take much time. To obtain clear and reliable images, the patient only needs to fix the oral cavity in a closed and open position in turn. If there is a suspicion of serious diseases such as tumors, an additional illuminating substance is injected. Checking is often required when a tooth is damaged, when baby teeth are replaced with permanent ones, if there are symptoms of oncology, or when blood flow is impaired. Scanning is required when planning the installation of implants, in case of pathological abrasion of teeth. To avoid serious complications and identify abnormalities in the early stages, it is recommended to carry out diagnosis at the first symptoms of the disease. Algorithm of the procedure No complex preparation is required before the examination. Diagnosis can be difficult if the patient cannot take a stationary position and suffers from involuntary movements of the head and limbs. If necessary, a contrast agent is administered in advance. It is completely eliminated from the body after 1-2 days and, in the absence of contraindications, does not harm health. The procedure is prescribed for pain, swelling, and clicking in the joint. It is possible to identify layers, stones in the submandibular gland, evaluate the relationship of the jaws, the correctness of the closure of the teeth, their relationship, and the development of atrophic processes. The ratio of the articular head to the glenoid cavity is assessed. X-rays in dentistry An instrumental examination is required, since not in all cases the doctor can fully assess the picture of the disease or check the condition of the teeth and joints. Scanning allows you to identify hidden pathologies and make a correct diagnosis. X-rays may be prescribed for preventive purposes in order to identify dangerous diseases in the early stages. An X-ray examination allows you to evaluate the root canal, the condition of the filling and crown, the quality of its installation, detect carious lesions, and monitor the filling of the canals. The condition of the tooth tissue is determined. Research is required for joint diseases and planning prosthetics and implantation. To find out the cost of performing an x-ray of the jaw joint and jaw, contact our specialists at Ortolaym. We will help you calculate the cost of diagnosis and treatment.
Indications
- Diagnosis of jaw injuries (fracture or dislocation)
- Diagnosis of congenital malformations or malocclusions
- Diagnosis of infectious bone lesions such as tuberculosis, syphilis, osteomyelitis or necrosis
- Detection of pseudarthrosis or arthritis of the joint
- Diagnosis of jaw bone tumors (benign and malignant).
- Finding out the causes of swelling and pain in the jaw area
- Periodontitis
- Cystic formations
- Dental pathology, including wisdom teeth
- Sinusitis