Those who are planning to remove “eights”, known as wisdom teeth, are probably aware of the possible complications during and after the procedure. Today we will talk about how to stop being afraid and give recommendations after wisdom tooth removal that will help you recover quickly.
One of the most common questions after the procedure is: how to relieve swelling after wisdom tooth removal? It is not always possible to remove it quickly - the degree and nature of swelling is individual. Let's understand the nuances of the procedure to understand that swelling and some discomfort for 3-5 days is nothing to worry about.
Teeth and inflamed lymph nodes: what is the relationship? Symptoms of pathology, causes, treatment methods
When inflammation of the lymph nodes occurs after tooth extraction, not everyone is ready for such a turn of events. People who have not gone through the extraction procedure (removal) are even less likely to expect an inflammatory process in this important system for the body. However, this phenomenon is not uncommon. At the same time, doctors often find a connection in it with teeth. Let's look at the nuances of this difficult topic together.
After dental treatment, the gums became inflamed
The cause of inflammation is a developing purulent process (abscess). A new growth may appear in the form of a white ball on the gum. These problems should not be cultivated. You should immediately seek qualified medical help. The development of cysts on tooth roots is not just “some natural process.” This is inflammation, leading to the dissolution of bone tissue, inflammatory processes have a serious impact on the entire immune system, lymph nodes, etc. Therefore, if after treatment of a tooth the lymph node becomes inflamed, then this is a symptom with which you need to go back to the dentist . You yourself can diagnose the process of inflammation of the tooth root, you will be able to evaluate all the accompanying symptoms, but not a single patient will be able to provide treatment corresponding to the severity of the disease on his own. Leaving the source of inflammation, suppressing acute symptoms somehow with everyday methods, is the wrong way of treatment, which keeps all the problems inside. If you feel discomfort or inflammation after treatment, you should visit a dentist. Treatment of inflammation at the very beginning is easier than treatment of a purulent abscess
The gums near the wisdom tooth are inflamed
Painful eruption of wisdom teeth is normal. Usually, the growth of wisdom teeth is always painful. The painful eruption of the “eights” is caused by the absence of their predecessor milk teeth. However, these teeth, rudimentally inherited by man from his previous rounds of evolution, can erupt with great difficulty. Sometimes surgery is necessary. If the gums around a wisdom tooth are inflamed, then there is no reason to be alarmed. The growth of wisdom teeth is long-term and can last for several years, periodically causing redness and inflammation of the gums. Discomfort can only be relieved by time: the tooth will erupt and everything will pass.
But the difficulties that occur during the eruption of wisdom teeth will require you to come to the dentist for a consultation. If the painful process upsets and worries you, then go for a consultation. Difficulties may occur during the eruption of wisdom teeth. A dentist with good experience will instantly either remove your doubts and reassure you, or provide dental assistance. Rinsing daily may be sufficient to prevent inflammation.
Signs that require a visit to the dentist during wisdom teeth eruption are as follows:
- Temperature increase;
- Pain when swallowing;
- Swelling of the submandibular lymph nodes;
If after the removal of a wisdom tooth the temperature remains between 37 or 38, you must consult a dentist again.
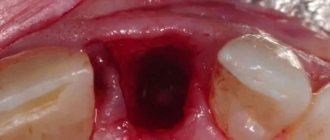
Abscess after wisdom tooth removal
Soft tissues, the site of tooth extraction, deeper tissues - all these places are susceptible to infection and the development of an inflammatory process. A developing abscess can be a source of not only pain, but also a full-fledged, severe purulent abscess. You should not hesitate, with this question, you should immediately consult a doctor!
To relieve inflammation after tooth extraction, proper treatment is necessary.
- Patients are prescribed antibiotics
- Strict adherence to daily hygiene
- In difficult cases, surgical procedures are performed within the walls of the dental clinic to open the abscess.
The eruption of wisdom teeth can be difficult, cause inflammation of the gums and require medical care within the walls of a dental clinic
Inflammation under the crown of the tooth
Crowns installed under metal-ceramic prostheses are associated with grinding down the tooth and depulping it. The destruction of teeth under the crown cannot be determined in a timely manner because such teeth are devoid of nerves. Often in such cases, when removing crowns, there are completely rotten teeth underneath, which need to be urgently removed.
Therefore, any pain under the crown is a symptom that helps us save our tooth. You can’t wait and hesitate - go to the dentist immediately!
Gum inflammation can be caused by other diseases
Inflammation of the gums during periodontal disease and gingivitis is the main symptom of the disease. Periodontal disease is an inflammation that specifically affects the periodontal tissues, leading to subsidence of the gums and a decrease in the volume of bone tissue. Periodontitis, Gingivitis - all these gum diseases require treatment and monitoring. Unlike painful inflammation of the gums of the tooth root, gingivitis in the presence of gum inflammation does not cause such obvious pain. The disease gingivitis occurs with possible bleeding, redness of the gums, and ulceration of the mucous membrane.
Any inflammation of the gums, accompanied by pain, swollen lymph nodes, bad breath, bleeding, requires treatment
Why does the inflammatory process occur?
As you know, the lymphatic system is a very important component of our body. It prevents various pathogens from entering the blood and internal organs, but it itself is often the first to take the blow due to decreased immunity. Many people know that swollen lymph nodes are often the first signal that a person has some kind of disease in the body. They usually swell shortly before the first symptoms of the disease appear. Their increase may indicate a sore throat, HIV, syphilis, tonsillitis, lupus, measles, scarlet fever, arthritis and many other pathologies.
This is interesting! Scientists have found that in the human body there are more than 400 lymph nodes (they are located in small groups) and about 2 liters of lymph that passes through them. The greatest concentration is on the neck and head, under the jaw and chin, under the arms and in the groin. Each group is responsible for the well-being and protection of nearby organs.
However, not everyone knows that inflammation in this important system for the body often occurs due to dental pathologies. This means that the infection gets there from a nearby area, in this case, from the oral cavity, where a large number of different bacteria live. Naturally, staphylococci, streptococci and other harmful as well as beneficial bacteria are constantly present in the mouth, and this is normal. But the problem arises only if microbes multiply rapidly and pathogenic microflora begins to predominate. Why is this happening? Read on.
Main dental problems leading to pathology
- abundant accumulation of bacterial plaque on and under the gums,
- gingivitis and periodontitis,
- advanced caries, pulpitis, periodontitis,
- purulent-inflammatory processes: flux, fistula, abscess, festering cyst and granuloma, osteomyelitis, phlegmon,
- damage to the oral mucosa by stomatitis, especially in acute and recurrent [1] varieties caused by the herpes virus or Candida fungus,
- glossitis of the tongue,
- poorly installed, old fillings and crowns under which inflammation has developed,
- long-term lack of sanitation of the oral cavity: during the sanitation process, the doctor applies a set of measures aimed at eliminating all dental pathologies.
This is interesting! The submandibular lymph nodes are responsible for the condition of the nose, throat, teeth and ears. If they are the ones that become inflamed, then you need to look for pathology in the listed organs, and to eliminate the problem, contact a dentist (in 60% of cases, dental pathologies are detected) or an ENT doctor.
Treatment and prevention of alveolitis
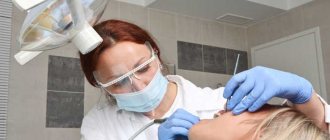
Treatment of alveolitis is carried out by a dentist; self-medication is unacceptable. Firstly, you may make a mistake with the diagnosis, as a result all manipulations will be ineffective. Secondly, traditional methods are not enough, and for professional ones you do not have enough experience and equipment.
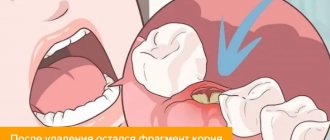
How is treatment carried out at the clinic? The doctor numbs the wound, cleans it, and puts a tampon with medicine. If foreign bodies (shards of tooth, root, pieces of food) prevent the socket from healing, the dentist removes them. You may need to take antibiotics, undergo physical therapy, baths with medications, and follow a diet during healing (excluding hard, hot foods from the diet). In advanced cases, additional operations are required. Traditional methods are acceptable with the permission of a doctor. For example, rinses with sage, chamomile, burdock and others. These solutions can accelerate tissue healing and alleviate the patient's condition.
What measures exist to prevent inflammation? In the first days, do not eat hard or too hot foods, and do not rinse your mouth. These actions help flush out the clot, which can cause inflammation. If tooth extraction is not an emergency, it is advisable to take care of the treatment of caries and other oral diseases in advance. Give up bad habits during healing: alcohol thins the blood, which prevents the formation of a clot, tobacco increases the risk of infection of the hole. If your gums hurt on the first day after tooth extraction, you can simply take a painkiller.
Two days after tooth extraction, the pain has not subsided, it has intensified, and its character has changed, which means that you should definitely consult a doctor! Alveolitis does not go away on its own; it can only lead to unpleasant consequences and complicate further treatment. Monitor the condition of your teeth especially carefully if there were other diseases of the oral cavity or the body as a whole at the time of removal. Doctors at Comfort Dentistry give recommendations for further care after tooth extraction. They tell you how to treat gums after tooth extraction, and in what cases to contact a dentist. If you doubt the correctness of self-diagnosis, you can call us and consult with a specialist.
Teething and enlarged lymph nodes
The problem is typical mainly for children whose first milk units are being cut. Babies have a weak immune system, and during this period it weakens even more, since the body is under a serious load. Often, teething itself is very difficult, accompanied by alarming symptoms (moodiness, cough, fever, runny nose) and even the addition of bacterial and viral infections.
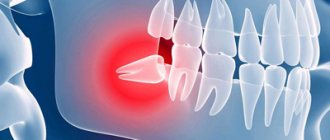
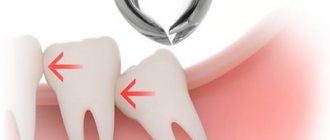
This pathology does not always escape adults. For example, when a wisdom tooth is cut and the submandibular lymph node increases in size, this is a fairly common occurrence. The third molars pass through the jawbone, and this process takes a long time, plus it is often associated with disturbances. “Sages” can compress and touch the branches of the trigeminal nerve, rest against neighboring elements of the row and destroy them. Their eruption may be accompanied by a decrease in immunity and an increase in body temperature, to which all the defense systems of our body react very sensitively.
Sometimes growth pathologies of the “eights” lead to the development of a purulent-inflammatory process such as pericoronitis. The problem arises when a kind of hood forms between the gum and the not fully erupted “figure eight”, where bacteria and food debris get trapped.
On a note! If your wisdom tooth hurts and the lymph node is swollen, then the symptoms may indicate damage to the third molar by caries, pulpitis, or periodontitis. If the cheek is also swollen, then, most likely, gumboil has developed.
Why does the problem occur after tooth extraction?
Let us list the main reasons why nodes become swollen after tooth extraction.
1. The body's reaction to surgery
It is not uncommon for a lymph node in the neck or under the jaw to slightly increase in size immediately after tooth extraction. Some experts believe that after surgery such a reaction is quite natural, because the body has activated all its forces in order to quickly cope with the physiological trauma inflicted on it.
If you have removed a wisdom tooth and then felt an enlarged lymph node in your neck, then you should not panic ahead of time. Procedures for extracting “eights” are always complex, large-scale and quite traumatic. Therefore, after them, a non-infectious inflammatory process almost always occurs, accompanied by a number of characteristic symptoms: increased body temperature, pain, limited jaw mobility and the inability to open the mouth wide, general weakness.
The procedure was carried out against the background of a purulent-inflammatory process
Typically, patients come for extraction (removal) if there are advanced dental diseases in the mouth that cannot be restored. Often the operation is performed urgently, against the background of an acute inflammatory process. Therefore, enlarged lymph nodes after tooth extraction with periodontitis, gumboil, fistula, cyst, granuloma are a common story. After all, the inflammatory process in this case had already been going on for some time. And it does not go away immediately after eliminating the problematic element; you still have to fight it by taking antibiotics and other medications, lotions, antiseptic rinses, and physiotherapy.
Extraction complications occurred
If several days have passed after tooth extraction, and you notice that the lymph node under the jaw hurts and is inflamed, this may indicate the development of the following complications of extraction:
- alveolitis: this is where it all begins. This is an inflammation of the socket that occurs due to a medical error or due to a violation of the postoperative regimen on the part of the patient. Actually, the complications that we will list below appear because the patient develops alveolitis, or tries to cure the disease on his own and does not seek medical help,
- flux, abscess, phlegmon, osteomyelitis.
The main reasons for the appearance of alveolitis after tooth extraction
Tooth extraction is a surgical procedure that is accompanied by the formation of a wound. A blood clot forms in it, protecting it from the penetration of microorganisms. Inflammation of the tooth socket after extraction occurs due to disruption of the process of formation or displacement of a blood clot. The most common causes of pathology:
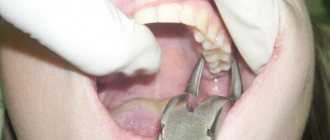
- Difficult extraction. The more traumatic the operation, the more the tissue’s ability to regenerate decreases and the likelihood of infection increases.
- Wisdom tooth removal. The structure of the root system of third molars is complex, so their extraction is always traumatic. In addition, the bone in the figure eight area has increased density and is less vascularized compared to other areas, which also creates conditions for the formation of a dry socket.
- Concomitant somatic diseases of the patient (diabetes mellitus, immunodeficiency states).
- History of pericoronitis (inflammation of the soft tissues around the tooth).
- The presence of foci of infection in the mouth before surgery. Penetrating into the wound with saliva, pathogenic flora causes alveolitis.
- Inadequate sanitation of the alveoli. After removal, careful curettage of the wound is necessary to remove fragments of bone tissue, roots, pieces of filling, and granulations. Foreign fragments disrupt healing and lead to alveolitis.
- Exceeding the dose of anesthetic. Leads to a narrowing of the lumen of the capillaries, the development of local ischemia, which disrupts the filling of the hole with blood.
- Mechanical damage to the clot. Failure to follow the doctor’s recommendations during the postoperative period (rinsing the mouth, carelessly brushing teeth, etc.).
- Impaired hemostasis. Due to poor blood clotting, a clot does not form.
Alveolitis can be provoked by smoking, taking hormonal contraception, and insufficient oral hygiene. Age plays a certain role in the development of alveolitis after tooth extraction: the older the patient, the greater the likelihood of developing pathology. This is due to a slowdown in metabolic processes and a decrease in the regenerative ability of tissue cells.
Signs of pathology
If there is no pathology and the person is healthy, then the lymph nodes are quite difficult to palpate. But if there are problems in the body, their condition changes. At first, the inflamed areas only swell slightly and increase in size, which becomes noticeable upon palpation. The pathology is not accompanied by any other signs at the initial stages.
If, due to dental problems or after tooth extraction, the lymph node hurts, then it means that the person has started the underlying disease, against which he may have developed lymphadenitis. What is this? This is just inflammation of the lymph nodes. Let us list the symptoms of the pathology.
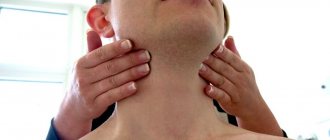
- Swelling and enlargement of the areas under the jaw, chin and neck. When you feel them, you can find lumps and even lumps. In rare cases, the lymph node behind the ear may also increase in size, for example, if there are eruption pathologies or complications arise after the removal of a wisdom tooth.
- Discomfort when opening the mouth, chewing and swallowing food, when swallowing saliva and drinking liquids (soups, drinks). Pain when pressing on inflamed and enlarged areas. In later stages of the disease, pain can spread to the neck, head, and radiate to the jaw and throat.
- Increased body temperature. The more the disease progresses, the higher the temperature. The thermometer can reach 40°C.
- The appearance of general malaise and weakness, chills, insomnia.
Symptoms of alveolitis of the socket
Alveolitis goes through several stages of development, each of which has its own clinical picture:
| Stage | Description |
| Serous inflammation | The first clinical symptoms appear the next day or after 3 - 4 days after surgery. Non-purulent inflammation is manifested by the appearance of episodic pain and swelling of the soft tissues around the alveoli. |
| Purulent alveolitis | If measures were not taken at the previous stage, a purulent process develops within a few days. The pain becomes constant, radiating to the auricle, jaw, and neighboring teeth. The infection spreads to nearby lymph nodes, causing them to enlarge. A gray-green coating appears inside the hole. The temperature rises. |
| Purulent-necrotic stage | The pain intensifies and becomes throbbing. A putrid odor appears from the mouth. Progression leads to disruption of microcirculation, ischemia, and the development of necrosis. The patient’s health deteriorates significantly, and signs of intoxication appear. |
| Hypertrophic tissue change | Lack of medical intervention within 14 days leads to chronicity of the process. Soreness and swelling become less pronounced. Soft tissues grow and fill the hole. When pressure is applied to the granulation, pus is released. The mucous membrane is swollen, bluish in color. |
If left untreated, alveolitis has an unfavorable outcome. The main complications after alveolitis:
- phlegmon (extensive purulent inflammation);
- acute periostitis (inflammatory process of the periosteum);
- osteomyelitis (purulent-necrotic inflammation of the jaw bone);
- sepsis (purulent-septic blood disease).
Dangerous consequences of pathology
If you do not promptly treat the underlying problem that caused the swelling and enlargement of the lymph node, then, as mentioned above, you will develop lymphadenitis.
Usually, the submandibular form of the disease occurs first, but in the absence of therapeutic measures, the infection descends lower, and then the cervical type of pathology develops. That is, the lymph nodes in the neck become inflamed, which poses a serious threat to life and health. For those who do not consult a doctor on time, the body may become severely intoxicated.
From the acute form, the disease passes into the chronic stage, and pus begins to accumulate in the tissues. When the pathology is neglected, there is a risk of developing phlegmon [2], thrombosis, the formation of malignant tumors, as well as a purulent abscess, the contents of which can at any time break into nearby organs, spread through the hematopoietic system, reach the bronchi and respiratory tract, and cause sepsis.
Professional diagnostic measures
When a lymph node becomes inflamed, you should not hesitate to see a doctor. It is better to start by visiting a dentist, who will examine the oral cavity and send you for an x-ray to obtain information about the presence or absence of hidden processes and dental pathologies.
Additionally, the patient may need the help of other specialists: an ENT doctor, a therapist, an infectious disease specialist. Be prepared that for a detailed diagnosis you may be referred for urine and blood tests (usually they reveal an increased number of leukocytes), bacterial culture, and ultrasound.
Measures to eliminate the problem
Dental treatment
In order for the lymph nodes to return to normal, it is first necessary to get rid of the main problem that caused their enlargement and inflammation. Depending on the pathology, the dentist can perform the following manipulations:
- cleaning teeth from plaque and tartar,
- treatment and filling of root canals,
- surgical opening and drainage of ulcers (with flux, abscess),
- cleaning the socket (for alveolitis),
- tooth-preserving operations: cystectomy and cystotomy, resection of the root apex for cysts and granulomas,
- replacement of unsuitable fillings and crowns.
After treatment of dental pathologies, the lymph nodes do not disappear immediately. Swelling may persist for the next 7-10 days. In order for the patient’s condition to normalize faster, he is additionally prescribed physiotherapy (for example, UHF therapy) and prescribed medicinal support.
“I once had a tooth removed with periodontitis on the lower jaw. A few days after this, I noticed that the lymph node was a little swollen and painful. I didn’t want to go to the dentist again, I hoped that it would go away on its own. Then the hole healed safely, but the swelling under the jaw sometimes appeared again. In general, I started this case, and when more frightening symptoms appeared, I ran to the doctors. I was told that there was pus inside the lymph nodes and it needed to be cut out. There was no choice, I had surgery, then took antibiotics. Now I regret that I didn’t go to the clinic right away...”
S. Tsareva, review from gidpozubam.ru
Drug therapy
The doctor will prescribe medications to take at home. In case of inflammation of the lymph nodes, as well as in advanced dental diseases, a course of antibiotic therapy is prescribed for 7-10 days. The patient is also recommended ointments for applying external lotions and applications to the affected areas. Additionally, immunostimulants and multivitamin preparations are prescribed, which must include vitamin C to boost immunity.
Symptomatic treatment is also prescribed. For fever, antipyretics are taken, and for pain, painkillers are taken.
How long does it take for gums to heal after tooth extraction?
It’s best to start with the fact that wisdom teeth can grow on the lower and upper jaws. Next, you need to take into account the location of the tooth: whether it stands straight or crooked, and how it is located in relation to the tooth next to it.
Most often, they are not very functional - they practically do not participate in chewing food, since they are too deep in the jaw. For this reason, they are quite difficult to clean. Ordinary home hygiene does not give wisdom teeth the necessary cleaning, so caries often occur on them. It also affects neighboring teeth.
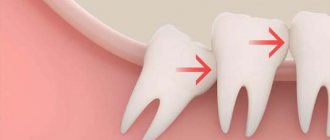
This doesn't always happen. There are cases when “eights” perform their functions normally, stand straight and do not interfere in any way. Then you don't need to delete them. But more often there are situations when these teeth interfere - they injure the gums, provoke caries, hurt, and interfere with the installation of braces.
Let's look further to understand how long it takes for gums to heal after tooth extraction. Now we need to determine why it is taking longer than usual.
One of the popular problems is the horizontal position of the lower wisdom teeth. Due to problems with bite or formation of molars, they can take an initially incorrect position and grow under the gum. Such teeth are called impacted, that is, unerupted.
Sometimes this does not create problems - the tooth is quietly under the gum, does not become inflamed and does not bother the person. But the opposite also happens - it suddenly begins to partially erupt, becomes inflamed, aches and hurts. In this case, removal is most often prescribed. The fact is that it is technically impossible to cure such a tooth: it is hidden under the gum. And since its location is obviously incorrect, it puts pressure on the adjacent tooth and in all respects causes discomfort. Therefore, it can be safely removed on the recommendation of a doctor.
Obviously, this is not the easiest task, which is why recovery after tooth extraction takes a little longer than usual.
The procedure for such a complex removal takes place with virtually no discomfort for the patient. A good pain reliever will ensure that you don't feel anything. Removing an impacted tooth, like the “eight” on the upper jaw, causes mainly psychological discomfort. The teeth sit firmly in the jaw and are far away, so the doctor takes noticeable efforts to remove them. This is why swelling and swelling occur after tooth extraction.
After the tooth is extracted, the doctor will put sutures on the gums (if an impacted tooth was removed) and place a sponge or tampon with a special agent in the hole.