Teething rarely occurs without complications. When the figure eight appears on the gum surface, inflammatory processes develop. The pathology in medicine is called pericoronitis, or wisdom tooth hood. The disease is treated in two ways: medication and surgery. Untimely therapeutic measures can lead to the development of an abscess or flux in the oral cavity, which can lead to further blood infection and death. It is necessary to consider the main symptoms of pericoronitis, the causes of its occurrence and methods of elimination at home and in the dental clinic.
What is pericoronitis
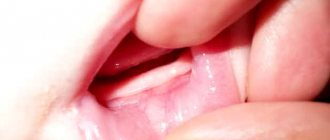
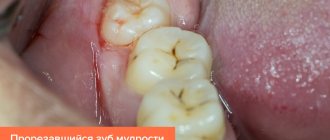
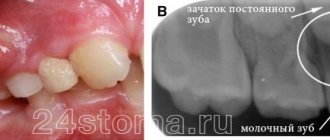
Dentists refer to wisdom teeth as eights or last (third) molars. They can grow at any age, and their absence in the oral cavity is considered normal. The main feature of the elements during growth is the formation of a hood over the crown. The hood is represented by soft gum tissue that hangs over the problem unit.
Food particles and bacteria gradually become lodged under the gums, causing inflammation and bad breath. The condition also leads to difficulty chewing food and the proliferation of pathogenic flora in the mouth. The hood interferes with the normal eruption of the last molar.
Difficult eruption manifests itself in a clear clinical picture: the patient develops severe swelling of the face and body temperature rises. Such signs are a reason to immediately contact a dentist, and then a surgeon for urgent assistance.
Inflammation from the hood gradually spreads to the bone tissue of the tooth and jaw. The hood delays the timely cleansing of the oral cavity from bacteria and food debris. The main symptoms of the pathological condition: pain when chewing and swallowing food, swelling of the gums and cheeks, disruption of the full functioning of the dentofacial apparatus.
How to understand that you need to remove the figure eight hood
- Doctors insist on surgical treatment if:
- pus accumulates between the molar and gum;
- the pain is so severe that it is even difficult for a person to talk;
- signs of acute gingivitis appear, surrounding tissues are included in the pathological process;
- pain radiates to the temple, neck, lymph nodes;
- body temperature often rises.
All these symptoms indicate that the inflammation is very strong and measures need to be taken as soon as possible to eliminate it.
Causes of inflammation
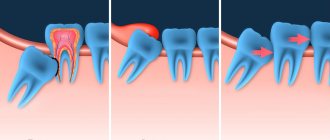
The first eight begins to erupt in a person from 18 to 25 years of age, less often at a later age. The main reasons for the problematic appearance of the last element on the gum surface is the lack of space in the dentition due to the reduction in the size of the jaw of a modern person. Another reason for the appearance of pericoronitis is the retraction of the unit.
Retraction is the incomplete emergence of a tooth to the surface.
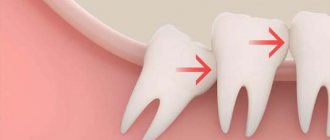
If the growth is abnormal, the third molar compresses the sevens and causes their premature destruction. In some cases, wisdom teeth rest against the soft tissues of the cheek, which also leads to inflammatory processes in the mouth and sore gums.
A wisdom tooth hood can occur due to uneven growth of the figure eight. Inflammation usually develops under the retreated part of the crown. The unpleasant symptoms will go away on their own after the remaining part of the tooth appears on the surface of the gum. Trouble-free growth of a unit is possible only if there are no obstacles in its path.
Symptoms
The hood of a wisdom tooth makes itself felt only a few days after formation due to the fact that food debris accumulates under it. Bacteria multiply more actively in a favorable environment, which ultimately leads to the appearance of symptoms of pericoronitis. Saliva does not penetrate under the hood, and this interferes with the normalization of the microflora under the gum.
What to do if your wisdom tooth is cutting out and your gums hurt
The development of dental disorders is indicated by:
- swelling of the gums;
- pain when swallowing saliva;
- putrid odor from the mouth;
- temperature increase;
- dizziness;
- swelling of the face.
What to do if one or more symptoms of pericoronitis appear? The listed signs are a reason for a visit to the dental clinic. Lack of timely treatment threatens the development of infectious complications. The pathological process often spreads to the masticatory muscles. In this condition, even minor movements of the jaw will be accompanied by pain.
The infection spreads through numerous vessels in the oral cavity to neighboring systems and organs. Because of this, with pericoronitis, an exacerbation of chronic pathologies is observed. In such a situation, drug treatment will not bring the desired results: surgical intervention will be necessary.
Drug treatment
If, with swelling of the gums and cheeks, the patient cannot see a doctor immediately, then he should resort to emergency measures. It will not be possible to completely stop the inflammatory process at home, so a visit to the doctor will be mandatory.
Before visiting the dentist, you need to rinse your mouth with furatsilin solution every 2-3 hours. For this purpose, other pharmacological agents with an antiseptic effect can be used - Chlorhexidine, Miramistin, Rotocan. And you can also use traditional medicine to rinse your mouth, for example, tea leaves or tincture of crushed garlic.
The list of other alternative medicine used to prevent complications of pericoronitis includes:
- baths based on sea salt and soda: 1 tsp. each dry ingredient is dissolved in 200 ml of warm water;
- treating the wisdom tooth hood with saline solution.
To relieve the symptoms of itching and discomfort, gels with an anesthetic effect are used: Lidocaine, Kamistad, Cholisal.
You should not open or cut off the inflamed area of the gum on your own. A similar procedure must be performed by a surgeon taking into account all antiseptic rules. Only in this case will it be possible to avoid more dangerous infectious consequences.
Complications and care after surgery
Care
After the procedure, patients are advised to avoid cold and hot foods or drinks for several hours. For quick and painless healing it is recommended:
- rinse your mouth with cool antiseptics: potassium permanganate solution, Chlorhexidine, Miramistin, Stomatidine or Rivanol;
- apply cold to the operated area;
- take painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs: Nimesil, Nurofen, Sedalgin, Solpadein, Tempalgin, Ketanov, Baralgin.
In case of purulent processes, antimicrobial therapy is additionally prescribed and antibiotics are prescribed - Metronidazole in combination with Clindomycin, Lincomycin, or medications based on Norfloxacin, Ciprofloxain or Ofloxacin.
Warm compresses and rinses are categorically unacceptable, because in warmth bacteria multiply and inflammation worsens!
It is important to maintain oral hygiene and use a brush with toothpaste every time after eating. The operation area must be carefully avoided. If the pain is too severe, it is recommended to rinse your mouth with toothpaste diluted in water.
Possible complications
With correctly performed excision and high-quality postoperative care, there are no complications. However, if bacteria enter the wound, the inflammation continues to progress. A hood again forms over the erupting crown, and it is recommended to remove the “eight”.
Surgery
The essence of the intervention is to excise the hood over the wisdom tooth and fill the wound with antiseptic agents that will prevent the infection from spreading into the deeper layers of the gum. The surgeon will not prescribe surgery if there are pronounced purulent processes in the gums, since there is a high risk of infection of nearby tissues.
In case of purulent inflammation, the surgeon makes an incision in the gums in order to quickly rid the patient of necrotic masses. After the intervention, the patient will be prescribed antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs. In rare cases, the surgeon immediately suggests wisdom tooth removal.
Removing part of the gum involves excision of inflamed tissue. Thanks to this, the infectious focus is removed, which causes the active proliferation of bacterial flora in the mouth. The operation is characterized by low trauma, except in cases where it is necessary to remove a large volume of affected tissue.
The operation is performed by a doctor under local anesthesia. For anesthesia, Lidocaine or Ultracaine is usually used; Novocaine is used only in rare cases, for example, when an incision in the gum is necessary, rather than removal of the inflamed area. Minor discomfort may appear 30–40 minutes after surgery, so you should immediately take a pain reliever when you get home.
The average cost for a service in paid clinics is from 2,500 rubles, depending on the complexity of the operation, the volume of surgical work and the need for sutures. In provincial cities, the cost of the procedure can be several times lower. At the clinic at your place of residence, the procedure will be performed free of charge upon presentation of your passport and insurance policy.
Stages of the procedure for the treatment of pericoronitis of the third molar:
- Performing an injection with an anesthetic.
- Excision of the overhanging part of the gum 15 minutes after the injection. The surgeon performs the procedure using a scalpel, less often using a laser.
- Treatment of the wound resulting from excision.
- Placement of iodoform turunda on the site where the soft tissue was excised.
After the intervention, the surgeon gives a referral to the patient for a re-examination. And the specialist also advises the patient regarding behavior during the recovery period.
Advanced dental clinics recommend laser excision of the problem area of the gum to patients. This method of intervention will prevent excessive bleeding and minimize the risk of complications. Unfortunately, only a rare dental clinic in Russia can boast of innovative equipment.
Procedure
The standard treatment is surgical excision of the hood. In case of serous inflammation, the hood is excised using a scalpel or medical scissors. If there is pus, the doctor dissects the mucous hood and allows the exudate to drain.
This procedure is quite simple to perform, it is performed under local anesthesia and takes about a quarter of an hour. The tooth is numbed using effective anesthetics and a carpule syringe. After the operation, the wound is washed with antiseptics and antimicrobial agents. The doctor uses a cotton swab to stop the bleeding.
Features of the recovery period
After removal of pericoronitis, the surgeon prescribes to the patient:
- rinsing the mouth with Chlorhexidine solution (up to 4 times a day);
- taking antibacterial agents (not in every case);
- use of painkillers (up to 5 days).
How long will your gums hurt after the intervention? Full recovery of the patient occurs 4–5 days after the procedure. Rehabilitation after traumatic types of surgery takes up to 7 days. If a week after surgery there is severe pain in the operated area or swelling of the soft tissues, you should contact a surgeon to evaluate the previous treatment.
Special gels sold in pharmacies will help you cope with inflammation faster: Cholisal, Kamistad. They accelerate the healing of damaged mucous membranes.
The turundum with iodine solution is removed from the socket 24 hours after the operation. It is advisable that the procedure be carried out by a surgeon, but removing the napkin at home is also acceptable; the iodoform turundum remaining in the socket will later become a source for the spread of infection.
Before removing the napkin, you must wash your hands with soap. After the home procedure, the wound is treated with 3% hydrogen peroxide. Repeated formation is a reason for another operation, during which the doctor will decide on the advisability of leaving the wisdom tooth in the oral cavity. Recurrent pericoronitis is an indication for eliminating the problem unit. There are other indications for wisdom tooth extraction.
Surgical intervention: removal of the dental hood
The following techniques are used in dental practice:
- Pericoronarotomy. The procedure is performed under local anesthesia. It involves removing the gingival hood in order to eliminate purulent exudate.
- Pericoronarectomy. A surgical intervention that involves complete excision of the overhanging tissue. With this technique, the lateral surfaces of the tooth may be exposed.
- Extirpation. Extraction of an element of the dentition by sawing and subsequent removal of the pocket and dental unit. The hood is removed from the tooth and all manipulations are performed under local anesthesia.
Dentists at the Alpha Dent clinic provide professional treatment of pericoronitis. They are ready to provide qualified assistance of any level of complexity, will help solve the problem, speed up recovery and shorten the rehabilitation period.
Indications for unit removal
The most effective method of treating gum inflammation above the third molar is to remove the latter. Before the procedure, the doctor will order an x-ray for the patient. The operation will be complicated if the figure eight has curved roots.
The list of situations in which the best way to solve the problem is to remove wisdom teeth includes:
- Insufficient length of the lower jaw. In this case, there will not be enough space to cut through the figure eight. In this case, extraction surgery is prescribed to prevent the remaining teeth from moving into an anatomically incorrect position. Timely intervention will prevent possible malocclusions.
- Inclination towards the third molar. The tilt can be observed towards the other elements or towards the cheek. An unremoved element will injure the mucous membranes of the cheeks or destroy the roots of a neighboring tooth.
Diagnostics
Any dentist can perform the diagnosis. To do this, you should study the symptoms and take an x-ray. Using the image, the doctor will see how the tooth is located, the condition of the bone tissue that surrounds it, as well as the condition of the periodontium. If the disease is chronic, then bone resorption is studied. Pericoronitis is treated by dentists in our dental center.
Features of wisdom tooth removal surgery
The operation to extract the problematic unit takes much longer than removing the hood of a wisdom tooth. The procedure is especially difficult for patients with a pathological fear of dental treatment. In difficult cases (improper location of roots, incomplete tooth eruption), tooth extraction in stationary conditions is indicated.
Complex operations and panic fear before the procedure may serve as an indication for performing the operation under general anesthesia. The procedure can also be prescribed to people with an increased gag reflex. This type of surgery does not last long and is painless for the patient.
Let's consider situations in which surgery to remove wisdom teeth is prohibited:
- Exacerbation of chronic diseases. In this case, it is necessary to wait for remission of the pathology in order to avoid complications after surgery.
- Pregnancy.
How is the operation performed?
The operation is performed under infiltrative or conduction anesthesia. The doctor performs preliminary irrigation of the gum tissue and pericoronal space to remove mucus, saliva, epithelial particles, and pieces of food. After this, he excises the hypertrophied mucosa. The mucous membrane can be removed with a scalpel, scissors, laser device, or through cryodestruction. A turunda of gauze is left in the wound, which is treated with an iodoform solution.
If the patient also has periostitis, the doctor additionally cuts the base of the pterygoid fold located at the bottom of the jaw. The doctor inserts a drain into the incision to sanitize the infection. The pain disappears 2-3 days after the procedure. The gum tissue heals completely within 7-10 days.
If the wisdom tooth is positioned correctly, it is left in place. If the cutting is incorrect, there is not enough space for the tooth in the row of alveoli, or there is significant destruction of the bone in the neck area, the doctor will prescribe an operation to remove the object of treatment from the dentition.
Possible consequences
Complications can arise even after simple excision of the gum located above the wisdom tooth. A common consequence is repeated inflammation. The problem arises due to non-compliance with antiseptic rules or insufficient removal of the gums above the wisdom tooth. Less commonly, consequences develop due to the anatomical features of the structure of the wisdom tooth.
If you refuse to visit a doctor, pericoronitis may become more complicated:
- development of a chronic inflammatory process in the oral cavity;
- injury to the mucous membranes of the cheek;
- thinning of the bone tissue of the jaw;
- development of osteomyelitis;
- inflammation of the submandibular lymph nodes;
- entry of pathogenic flora into the bloodstream;
- the formation of an abscess or phlegmon.
It is difficult to cope with inflammation of the wisdom tooth hood at home. The problem is caused by the growth of wisdom teeth and eruption. On their own, a person can only prevent the rapid development of infectious consequences. To do this, he needs to thoroughly brush his teeth and use special rinses after hygiene procedures. To better treat hard-to-reach areas of the oral cavity, threads or irrigators are used. In this case, a visit to the dentist will be necessary.
Why is excision done?
Pericoronitis is always associated with the formation of a gum hood. The tooth is cutting, but it is hampered by the gum tissue that is located on top. With this pathology, you can notice how the gum is swollen and hangs over the tooth, preventing the teeth from closing normally. To avoid complications, you should visit a doctor at the first signs of illness. The symptoms of the pathology are characterized by a gradual increase:
- sharp pain that radiates to the ear;
- difficulty chewing food due to loose rows of teeth;
- swelling of the gum tissues, changing their color to a darker one;
- inflammation of the lymph nodes located near the tooth;
- pus between the gum tissue and the tooth.