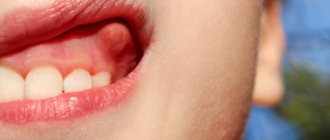
We often receive calls from concerned parents who don’t know what to do: their child has a lump on his gum. It doesn’t look very nice, the baby feels pain and other symptoms. It is best in such situations to immediately come to the clinic. The doctor will quickly diagnose and solve the problem. If there is a lump or a purulent abscess of the gum, under no circumstances should you self-medicate!
In itself, such a bump is not news. In children with baby teeth, such inflammation occurs quite often for various reasons. We'll talk about them later, but for now let's figure out what a lump is.
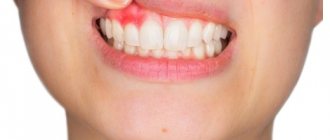
A convex formation indicates the presence of a focus of inflammation. A purulent infection is activated under the surface of the gum and an active process is underway. This is accompanied by symptoms such as:
- bad breath,
- pain while eating and brushing teeth,
- bitter taste in mouth
- discharge of pus, blood,
- deterioration of the general condition of the body.
Different causes of purulent gum abscess are characterized by a certain set of unpleasant sensations. In this case, the child may not immediately notice the bump. He may also ignore the symptoms or simply hide them from his parents. Your task is to ensure that your baby always brushes his teeth on time and eats well.
There is a lump with pus on the gum - what to do?
If a lump does appear on the gum, you should consult a doctor. In an advanced stage, when discomfort becomes obvious, you should not hesitate with treatment. You will not be able to remove the lump on your own using herbal rinses.
Most often, a neoplasm noticed at the wrong time above a baby tooth causes fear in parents. It seems like something very serious is going on. And sometimes this is true, so do not hesitate to contact the clinic.
The problem can occur anywhere on the gum, mainly above the chewing teeth. The abscess may be red-blue or white-yellow, depending on the cause of its appearance. In any case, you cannot open the abscess yourself, apply ointment, apply compresses, and try in every possible way to cure the gum on your own. This is very dangerous: the infection can spread even further and deeper. It is important to continue your normal oral hygiene routine even if brushing your teeth is uncomfortable.
Why does a lump appear on a child’s gum?
The formation of a growth on a child’s gum can be caused by:
- advanced stage of caries;
- inflammation of gum tissue;
- mechanical trauma to the jaw;
- teething.
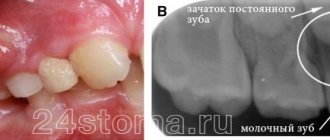
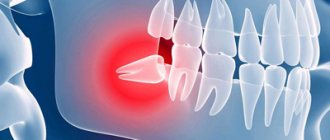
The most common reason for the formation of a “pimple” on a child’s gum is carious infection. In the absence of professional treatment, there is a risk of suppuration near the apex of the root. The pus requires release and begins to collect under the mucous membrane near the diseased tooth. This forms a cyst (flux), which looks like a white dot on a child’s gum.
Infants and children of the second year of life may also develop “cysts,” but white bumps on the gums of a child of this age are associated with teething. They occur infrequently, but can greatly bother the baby until the teeth come out completely.
Reasons for the formation of bumps on the gums
The reason for the appearance of lump-shaped inflammation is that an infection gets into the gum tissue. It accumulates and is localized in one place under the mucosa. Pus forms there and infectious processes are activated. Often, a purulent gum abscess quickly increases in size, covering a large area.
Causes of infection in the gum tissue:
- deep caries,
- poor oral hygiene,
- teething,
- injuries to teeth, jaw or gums,
- poor quality treatment
- weakened immunity,
- braces that limit oral hygiene.
New growths above a baby tooth and bumps during eruption often go away on their own after the tooth appears on the surface. However, if such a problem occurs, it is still recommended to show the tumor to a dentist to eliminate risks.
If a lump appears on the gum, you should not try to diagnose its nature yourself. When it comes to children's health, it is better to make an appointment for an examination once again, even if the last one took place just a month ago.
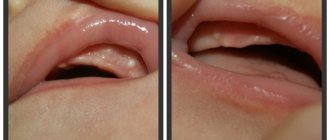
Teething cyst
Bumps on the gums that appear during the eruption of milk or permanent teeth (usually at 5-6 years old or much less often at 7-8 years old) have a major difference from abscesses - they are not inflammatory in nature and are only a reaction of soft tissues to the advancement of the dental crown .
Signs of an eruption cyst
Such formations form quite rarely and can appear both on the upper gum and in the area of the lower teeth. Non-inflammatory bumps do not cause any discomfort to the child and are detected only during examination of the oral cavity. Only sometimes infants may experience excessive salivation.
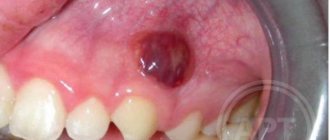
2-3 weeks before the tooth appears, a transparent or blue lump forms on the mucous membrane of the gum, which has a soft consistency and does not hurt when pressed. If the developing cyst affects a small blood vessel, then hemorrhage into its cavity is possible. She turns black. At the moment of eruption of the dental crown, such a lump is imperceptibly opened or gradually dissolves without a trace. The general condition of the children does not change in any way.
Treatment
This type of dental cyst does not require treatment. Sometimes, if such a lump appears in the area of the front teeth and causes cosmetic discomfort to the child, then it is possible to open it in the sterile conditions of a dental office.
Memo to parents
Even though baby eruption cysts are not dangerous and do not cause any complications, there are some things you should be aware of:
- It is strictly forbidden to open the cones yourself, since non-sterile objects can introduce infection into the gum tissue and cause the development of inflammatory reactions.
- It is extremely rare, but eruption cysts can fester. If, against the background of complete well-being, the baby begins to complain of pain in the gums, fever, and the lump itself becomes red and swollen, then you should immediately seek the advice of a dentist.
Purulent bumps and cysts during teething are not a sign of pathology in the development of the dental system. In both cases, it is important to maintain proper oral hygiene, periodically examine the mucous membranes and, if necessary, visit the dentist.
Treatment of abscesses and abscesses in a child
Depending on the nature and cause of the abscess, the doctor will choose the appropriate method of treating the lump on the gum. Most often this is:
- opening and cleaning of pus;
- treatment of caries or removal of a tooth if it is severely damaged and cannot be restored.
In this case, an abscess over a baby tooth can often be eliminated only with the removal of the tooth itself. This is an undesirable process, but it may turn out that it is impossible to fix the problem in any other way.
When treating ulcers in children, the doctor is always guided by the fact that soon the milk teeth will be replaced by molars. The formation of a cyst or abscess over a baby tooth can affect the future molar, so sometimes the decision to remove a tooth is actually advisable.
After the procedure, the child is prescribed antiseptics for home use.
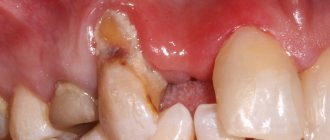
What does a fistula on the gum look like?
It is possible that the inflammation will not be so acute, and the result will be a breakthrough of pus into the oral cavity - a fistula on the gum that looks like a lump or an abscess in a child.
Symptoms:
- possible complaints of pain in the mouth;
- body temperature is often within normal limits;
- redness of a small area of the gum;
- fistula in the gum area - looks like a light or yellow lump due to the accumulation of pus.
What to do? The situation does not require immediate consultation with a doctor, but it is necessary to see him at least within 1-2 days, since a fistula is also evidence of an inflammatory process. Don't delay visiting the dentist. The fact that the fistula has broken through does not mean that the inflammatory process has stopped. The doctor must clean the canal and prescribe adequate treatment.
Please note that the child may not complain of pain in the mouth. You may not track the onset of the disease, but detect the fistula already at the healing stage. Even if this is the case, it’s worth seeing a doctor - he will determine the reason why the canal became inflamed and recommend what measures to take to prevent this from happening again.
Causes of an abscess on the gums of a child
Flux or fistula with the release of pus always indicates an inflammatory process. The reasons may be:
- Periodontitis is a complication of caries in which the tissues surrounding the tooth become inflamed. At the same time, granular red tissue grows, which can replace healthy gum cells. In childhood, a tendency to periodontitis is observed more often. Inflammation can begin due to viral infections, stress, and hypothermia. This is the most common reason for the formation of fistulas on the gums or gumboils in children.
- Odontogenic osteomyelitis is an inflammation of the tissues of the jaw bones. In children it develops especially quickly and is accompanied by high body temperature.
- A cyst in the tooth area is a painless formation, which is a capsule filled with liquid. Occurs due to disturbances in the development or eruption of teeth, if they are not treated correctly. A fistula forms when the cyst becomes inflamed, producing pus, and the pus ruptures.
- Odontogenic sinusitis is inflammation of the sinuses of the upper jaw due to dental diseases. It may also be accompanied by the formation of fistulas.
- Errors in dental treatment, for example, incomplete filling. In this case, an infection enters the canal, which causes inflammation and, as a result, the eruption of pus in the form of fistulas.
- Retention of teeth, i.e. impossibility of cutting through them. It is observed when breasts are removed too early. This condition is extremely rare and is usually associated with systemic disorders in the body, for example, rickets.
- Injuries to the tooth or gums, at the site of which inflammation may begin.
Treatment of gumboil or fistula in a child
Treatment of fistula directly depends on the cause of the disease. It is comprehensive and includes a number of measures to relieve inflammation and prevent new infections:
- Therapeutic measures include removing the filling, opening the canal, cleaning it and disinfecting it. The doctor may leave the canal open or place a temporary filling. He will also recommend applying for a permanent filling. These measures are justified if the tooth is permanent.
- If inflammation of the canal is observed in a baby tooth, the doctor will also open it and clean it. However, in some cases, he may recommend tooth extraction, since in the future inflammation can be recurrent, that is, periodic.
- Drug therapy. The dentist will prescribe antibiotics and also advise which solution is best to rinse the mouth. In some cases, doctors also prescribe antihistamines.
That is, a visit to the dentist if you find an abscess or lump on your child’s gum is mandatory. The inflammation will not go away on its own, it can only spread to other tissues - to the area of the buds of permanent teeth. Which will make the situation worse and may affect permanent teeth.
Home treatment for gumboil and fistula in a child
After the canal is cleared, the doctor will send you home. At home, you need to ensure that your child regularly rinses his mouth with antiseptic solutions. Rinsing reduces inflammation and helps clear the open canal of pus.
The doctor will determine which solutions are suitable for your child. He may also prescribe antibiotics if he thinks the inflammation is severe enough. Do not give your child medications unless prescribed by a specialist.
Is it possible to use traditional methods of treatment for fistulas and inflammations? In principle, herbal decoctions also have a wound-healing and slight antiseptic effect. However, it is better to also talk to your doctor about using them. Knowing the nuances of your situation, he will recommend the optimal remedy - effective and safe for your child.
Preventive measures for oral inflammation in children
To protect your child from unpleasant painful conditions, monitor his diet and pay attention to oral hygiene. Teach your child to brush their teeth correctly - on time and thoroughly. Come up with a home game that will help you remember that brushing your teeth is necessary.
Simple rules will help you maintain healthy teeth and gums:
- Do not allow children to chew hard and sharp toys or pencils.
- Bring your baby for a preventive examination to our clinic every 3-6 months.
- Create a nutritious diet with fruits and vegetables that you can chew and bite into.
- Avoid fast carbohydrates. Immediately after eating sweets, you should brush your teeth or rinse your mouth.
And remember: if a child develops a lump on his gum above a baby tooth, as well as any unusual symptoms, consult a doctor immediately.
A lump on an area of the gum where there is no tooth yet: what to do in this case?
A couple of weeks before the tooth erupts, a cyst may appear on the gum, looking like a lump filled with a clear or bluish liquid. Such bumps are by no means common: dentists do not consider such formations to be a pathology requiring treatment. In addition, such formations on the gums in no way indicate an inflammatory process.
According to statistics, a small percentage of children are affected by the appearance of such a cyst. The child may not even suspect that he has a lump in his mouth, because if he touches it, there is no pain. However, a dental examination is still necessary, because the inflammatory process may still begin, in which case intervention will be required. The presence of inflammation is indicated by such signs as increased body temperature, pain when touching the lump, and swelling of the mucous membrane.
Most parents do not like the fact that their child has a lump in his mouth: in this case, you can ask the dentist to make an incision under anesthesia, as a result of which the fluid inside the cyst will come out. As a rule, when part of the cyst is removed, the crown of the tooth about to erupt is visible.