What it is
If a person does not treat the tooth in a timely manner, the crown is destroyed. And sometimes this leads to the need for additional support to restore the tooth. A pin is used here if the roots are suitable for prosthetics. Thus, the dentition is not deformed and the jaw structure is preserved.
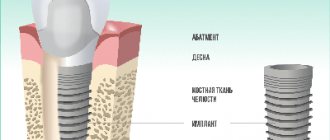
A pin is a structure that is fixed in the root canal. To install it, you need to meet certain conditions - 2 mm thickness of the root walls, it is possible to unseal the canal, completely seal it and give it the desired shape.
Sale of pins for fixing membranes throughout Russia
In our online store you can buy different models of pins, paper or titanium pins and devices for storing and installing them (pin holders, multi-section boxes) in St. Petersburg, Moscow and other cities.
We cooperate with foreign and domestic companies that produce high-quality consumables and instruments for orthodontics. Medical pins comply with international quality standards, certificates and other documents are provided.
Order dental instruments by filling out a special form: indicate the address, the name of the clinic or your name, the number of pins and other materials. For your convenience, we offer the “One-Click Purchase” option: select a product, provide a phone number or email address. Our employees will call or write to you to discuss the time, collection address, payment method.
We offer to buy pins at prices from manufacturers, with pleasant promotions and discounts. If necessary, we give installments of up to 6 months to pay for the goods. Find out more about the terms of cooperation from our managers.
Application in dentistry
A pin is used quite often in dentistry to restore a tooth that has been damaged. But using a pin also:
- build up a tooth;
- prosthetics are used when it is not possible to attach a fixed prosthesis to neighboring teeth;
- reinforce the tooth where the pulp was removed;
- for splinting teeth in case of periodontal diseases;
- to perform replantation surgery.
Types of pins and their differences
Before installing a structure, dentists often ask patients what type of post they are interested in. There are 2 types of rods, the difference being the material used in manufacturing. The first type is anchor, and the second is fiberglass.
The first to appear were anchor ones. They are made of metal material and have a small thread. Such a rod provides a high-quality restoration, but may be noticeable after the crown is installed.
Fiberglass installations have a more attractive appearance. They are invisible after all restoration procedures, and therefore are considered more modern.
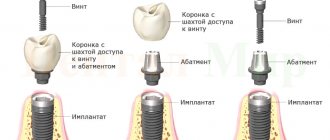
The classification of pins also depends on the method of securing them. If the anchor ones need to be screwed into the expanded channel using a special device, then the fiberglass ones are installed after loading into a special compound. This is a dental cement-fixer. It holds the rod inside and prevents further tooth decay.
Installation of a dental post
Several procedures are performed here:
- A treatment regimen is determined. The doctor tells how the pin will be installed, what material is best suited for the patient;
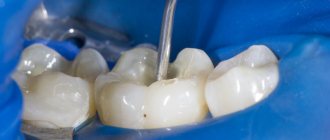
- The tooth is being prepared. It is processed and the filling, if any, is removed. In the case of a pin made of fiberglass or carbon fiber, the excess material is trimmed off. The rod is then fixed inside the canal using a composite;
- When the pin is fixed, the cement has hardened, and the part of the tooth that is the crown is restored. If the pin is on the front tooth, then you need to carry out artistic restoration so that it acquires a natural shade.
In what cases is it recommended to install pins?
Indications for the use of anchor pins are tooth destruction of varying degrees of complexity: from simple chips to almost completely lost volume of the tooth surface. Pins are installed when:
- destruction of the crown of the front tooth. The incisors and canines bear a huge load when biting; the corner or cutting edge of the tooth often breaks off;
- the destructive consequences of caries, when the enamel surface is severely damaged and holes appear in the chewing elements;
- consequences of injury, when one or more teeth have lost their integrity.
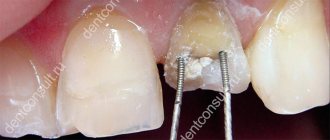
A prerequisite for the use of a titanium pin is an acceptable layer of dentin between the root and the gum. When the bone tissue is thinning, reliable fixation of the metal rod is impossible, so bone augmentation may be recommended. During extension, the membrane is also fixed with miniature titanium pins.
If a tooth hurts after installation, what should you do?
When a damaged tooth is restored, tissue may be destroyed. Therefore, sometimes the patient feels that the treated tooth hurts. If there was no pain before the procedure, and the tooth has been depulped for a long time, then the pain may arise due to the fact that the canal was entered too deeply. Then it is worth taking an x-ray to determine the cause of the pain.
It happens that pain occurs due to an allergy to a certain material. It can also manifest itself as deterioration of the condition, hyperemia, stomatitis.
general characteristics
A parapulpal pin is a dental rod made of a stainless metal alloy with a polymer coating.
The diameter of the structure is in the range of 0.3 - 1 mm, length - 5 mm. The number of implanted pins is determined by the type of dental elements and the degree of damage. Restoring anterior units involves installing a pin on each corner of the crown. In lateral teeth, the number of parapulpal pins corresponds to the number of missing humps. The distance between products is 5 mm.
The pin is implanted not into the tooth cavity, but into the dentin. Pulp tissues are not affected. The product acts as a basis for the prosthesis, securely fixing it in place and reinforcing the filling.
Kinds:
- Cementable - fixed with a cement composition in a wide passage.
- Friction - implanted into a canal of smaller diameter than the pin.
- Screw-in – screwed into the created channel.
- Combined - use two methods of fixation.
Flaws
With the help of pins, you can restore even a tooth that is almost completely destroyed. But there are certain disadvantages of this design and its application:
- if there are errors in the manufacture of the pin, the tooth may then deteriorate faster and complications may arise;
- If it is necessary to remove the pin, then all materials are removed from the roots. After all, the pin is locked tightly;
- an allergy to the material can provoke a reaction in the body;
- Since the walls of the tooth are subjected to stress, they become thinner. And this destroys the tooth and does not allow it to be restored.
Stump inlays
They are a classic example of the fact that everything new is well forgotten old. They were used back in the days when the Soviet dentist could not even think about anchor pins. True, the technology for their production left much to be desired. As a result, after the fall of the Iron Curtain, the appearance of anchor pins created a real sensation among dentists and inlays were forgotten for a while.
But a few years later, when they encountered the first complications, many doctors almost completely abandoned the pins and returned to inlays. By that time, high-precision casting technology “came” to us from Germany, ashless plastics and ashless pins appeared, which, unlike previously used wax, do not deform and allow the production of a stump insert of any length and shape.
Contraindications for installation
Contraindications for the use of pins are related to how damaged the walls and roots are, how thick the walls of the tooth are, how long the canals are, how obstructed they are, and whether there is inflamed, damaged periodontitis tissue. Also, the structure cannot be installed if there are granulomas, cysts, caries, or other diseases.
Before placing a pin, a specialist must examine the tooth that was damaged, clean the canals, and take an x-ray. If the length of the root is less than the height of the dental crown, then such a procedure cannot be performed. The walls must be 2 mm thick, otherwise the load on the tooth will be very large, as a result of which it will simply begin to collapse. In addition, the tooth root must have good stability.
How to choose the right fiberglass pins
During a dental appointment, a practicing doctor quite often has to deal with significant destruction of the tooth crown. This raises the question: how to restore such a tooth?
Very often, not only the future fate of one tooth, but also the effectiveness and service life of a particular orthopedic structure depends on the strength and reliability of the restoration, which significantly increases the doctor’s responsibility for the quality of the work performed.
Unfortunately, it has not been established precisely at what minimum volume of preserved tissue it is necessary to use pins. The decision made is based primarily on the doctor’s personal experience and intuition. It is obvious that decisions are sometimes made that are not entirely justified.
Previously, it was widely believed that after endodontic treatment, tooth weakening occurs, which manifests itself in an increased risk of root fracture. As a result, a myth appeared: “The intracanal pin increases the strength of the root of a tooth weakened as a result of endodontic treatment.” However, it is not. It is an undeniable fact that intracanal pins are used only for the purpose of creating reliable retention of a future restoration.
In addition, the use of pins helps protect the apical region and root canal from bacterial contamination due to possible microleakage.
Some authors (Chilikin V., 2007) pointed out the need to use intracanal pins only when one wall is preserved or in the complete absence of tooth walls.
However, in our opinion, it is necessary to take into account the thickness of the remaining walls of the tooth. It should be at least 1.5-2 mm. If all the walls of the tooth are preserved, but their thickness is insignificant, it is necessary to use intracanal pins. In addition, the preserved rim of the tooth root with a height of at least 2 mm, represented by healthy tissue, is of great importance.
We often hear from our orthopedic dentist colleagues that fractures often occur in the crown of teeth restored with fiberglass pins and covered with artificial crowns. This situation can indeed occur when using low-quality fiberglass pins. But this never happens when working with high quality pins.
Studies by Mannoci and Ferrari found a 9% root fracture rate following cast restorations during the first 4 years and 0% following fiberglass pin restorations over the same period.
Considering the above, in our practice we widely use Rebilda Post fiberglass pins (VOCO, Germany), using an example of which we will tell you what characteristics you need to pay attention to when choosing intra-canal pins.
Firstly, the pins must have a double-taper design - a smaller diameter in the apical third and a larger diameter in the coronal part, i.e., have a cylindrical-conical shape that is as close as possible to the anatomical structure of the root canal (Fig. 1).
Rice. 1. Design of fiberglass pins “Rebilda Post” and pins from Russian manufacturers.
This provides a preparation that preserves tooth structure compared to the preparation required by parallel wall post systems (Manhart J., 2009).
Secondly, it is very important that the pin is radiopaque and clearly contoured in the root canal during radiovisiography. Due to the presence of a special processed filler in Rebilda Post, the pins have high radiopacity.
Thirdly, unlike pins produced by other companies, the translucency of Rebilda Post is close to tooth dentin (27.2% and 28.1%, respectively).
Fourth, the more filler in the post compared to epoxy resin, the more durable and fracture resistant the post will be. It is also important to choose the right material for fixing the fiberglass pins.
Currently, dual-curing composite materials are most often used to fix pins. The components of their adhesive system enter into physical and chemical interaction with root dentin and composite materials [2]. But these cements are not ideal for fixation, because they have disadvantages:
- the use of bond increases the operating time;
- they are sensitive to surface cleanliness. In addition, to obtain a strong bond, it is important that the material for fixation and the material used to restore the coronal part of the tooth have the same composition. When using dual-cure composite cements and composite materials, the formation of a strong bond between them is questionable.
Therefore, we give preference to special materials - reinforced dual-curing and low-viscosity composites (core materials), for example, Rebilda DC. The peculiarity of this material is that it can be used both for fixing pins and for restoring the destroyed coronal part of the tooth. "Rebilda DC" has a composite consistency of increased fluidity, which allows you to fill all undercuts. The thickness of the permissible applied layer is 4 mm.
CLINICAL CASE
Patient M., 53 years old, came to the dental clinic to prepare for orthopedic treatment. After consulting an orthopedic doctor, it was decided to carry out repeated endodontic treatment of tooth 3.3.
Subsequently, it was planned to install a fiberglass pin, and then make a metal-ceramic crown for tooth 3.3.
To restore the coronal part of the tooth and fix the fiberglass pins, the Rebilda Post system (Rebilda Post, VOCO, Germany) was chosen, which includes Rebilda Post fiberglass pins, calibration drills, a low-viscosity dual-curing composite Rebilda DC, and an adhesive system. Futurabond DC." Using this system, it is possible to fix a fiberglass pin and restore the tooth stump in a matter of minutes.
After applying the rubber dam and the initial passage of the Largo Peeso-Reamer channel, the final configuration of the channel was created using a calibration drill corresponding to the diameter of the selected pin, and the pin was fitted in the channel (Fig. 2).
Rice. 2. Creation of the final root canal configuration using a calibration drill.
The Rebuild Post set includes three sizes of pins. Each pin size corresponds to a calibration drill included in the kit. Due to the good cutting ability of these drills, the additional use of other tools is not required (Fig. 3).
Rice. 3. Calibration drill versus reamer.
In addition, the calibration drill is longer than similar instruments from other manufacturers, which allows free passage of the root canal of teeth even with a high clinical crown (Fig. 4).
Rice. 4. Tooth 3.3 after processing the canal with a calibration drill.
To thoroughly seal the apical part of the canal, the depth of the space under the pin should be chosen in such a way that at least 4 mm of obturated root canal remains (Manhart J., 2009).
Preparing the pin for fixation is as follows: the pin is cleaned with alcohol and dried with air. Further, the doctor’s tactics depend on which pins are used - silanized or non-silanized. If the pin is not silanized, then silanization is carried out by applying to the surface a ceramic bond (Ceramic Bond), which is included in the kit specifically for this purpose, which is dried with air (Fig. 5).
Rice. 5. Silanization of the pin.
After this, the pin should not be touched by hand. Please note that the Rebilda Post pins are already silanized, i.e. coated with a layer of surfactant, so applying a ceramic bond to them is not necessary.
Disinfection of the intracanal space is carried out by irrigating it with a 3% sodium hypochlorite solution, rinsing with distilled water and drying with paper points.
Next, the intracanal space and hard tooth tissues are treated with self-etching dual polymerization adhesive “Futurabond DS” for 20 seconds and dried with a stream of air (Fig. 6).
Rice. 6. Application of Futurabond DC adhesive using microbrushes.
There is conflicting evidence on whether adhesive should be polymerized in the root canal or not. Some authors point out the need for polymerization of the adhesive before adding cement, while others note that photopolymerization of the adhesive in the canal does not need to be carried out in order to avoid the formation of nodules, which can lead to disruption of the pin. Using Futurabond DC, we do not polymerize it, since it itself polymerizes chemically within 3 minutes. Therefore, its incomplete polymerization in the depths of the root canal is excluded.
Let us remember that the light conductivity of fiberglass pins is not enough for photopolymerization of the light-curing material in the root canal. Therefore, posts should only be cemented to dual-cure materials and not to glass ionomer cements or other materials. In this clinical example, immediately after applying the adhesive, the dual-curing composite “Rebilda DC” was introduced into the space prepared for the pin and the pin was installed.
Photopolymerization was carried out for 40 seconds. Next, the coronal part of the tooth was restored with a second portion of the Rebilda DC material (Fig. 7).
Rice. 7. Restoration of the coronal part of tooth 3.3 using Rebuild DC.
After analyzing clinical situations, we came to the conclusion that many dental clinics purchase fiberglass pins and materials for their fixation at a lower price of dubious quality (pins with parallel walls, with a low content of glass fibers and a large volume of epoxy resin). As a result of this, a number of complications arise (fracture of the tooth crown, decementing of pins, etc.), all the blame for which lies with the doctors.
But they would be happy to use good materials, but they work with what employers buy.
We believe that only by using decent fiberglass pins and materials in our work can we create restorations that have an alternative service life to post-core inlays.
Thus, composite-reinforced glass fiber posts are a good choice due to their fast and easy application technique as well as their optical advantages (Bruder M., 2008). In addition, the use of fiberglass pins, composite cement for their fixation and a reinforced composite for restoring the core provides high strength of fixation, stability of the external structure of the restoration and restoration of the optimal structure of the lost hard tissues of the tooth (Terry DA, 3).
LITERATURE
- Manhart J. Composite fiber-reinforced endodontic pins // Endodontic practice. — 2009. — September. - pp. 17-21.
- Edelhoff D., Spiekermann H. All about modern root post systems // New in dentistry. - 2003. - No. 5. - P. 44-48.
Main advantages of titanium pin
Titanium pins have a number of advantages that make this dental product popular and effective:
- Complete chemical inertness. Titanium does not react with other substances; it is resistant to composite materials, which are necessary for high-quality prosthetics and fillings.
- Long-term use. A properly installed structure will serve its owner for at least 10 years without causing any inconvenience.
- High flexibility - makes it possible to adjust a titanium product to individual characteristics and sizes.
- Multifunctionality. Using a titanium post, you can restore the shape, integrity and functionality of the crown.
- High strength, which allows the support product to withstand the heaviest structures, such as bridges.
- Light weight significantly reduces the load on the dental canals and their tissues.
- Load uniformity. This property ensures the stability of the prosthetic structure as a whole.
- Availability. Thanks to the relatively low cost, most people can now afford to have their teeth restored.