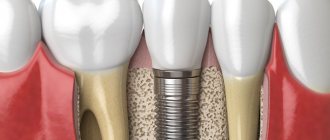
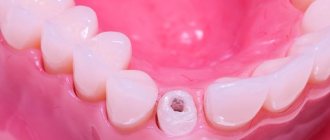
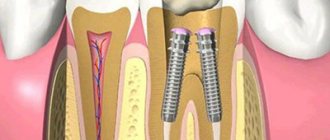
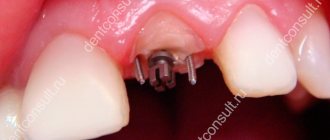
The anchor pin gets its name from the German word anker - anchor. In dentistry, this is an individually sized rod that is inserted into the root canal when restoring a severely damaged tooth. It acts as a support and actually replaces a weak or damaged root. The dentist later installs a filling or microprosthesis on the product.
An intracanal anchor pin is a ready-made structure that the dentist can place during treatment. Thus, restoration from the moment of removal of necrotic tissue to the return of its original appearance takes one visit to the doctor. If the damage is significant, an additional session may be required.
Pin in a tooth - what is it?
Phrases from the series “putting a tooth on a pin,” “building a tooth on a pin,” or “tooth under a pin” sound quite scary for many patients. However, in reality, restoring a tooth with a pin will help avoid its removal, and the design itself does not cause any discomfort. A dental pin is placed into the root canal. The device performs a supporting function and helps to optimally distribute the load on the tooth. Since a pin is placed in the root of the tooth, a number of therapeutic and endodontic procedures must be carried out before starting treatment.
Indications for installing a pin in a tooth
- Serious damage to the coronal part. A tooth without a post has a higher risk of destruction after treatment if more than 50% of its visible part is initially damaged.
- Repeated dental treatment due to secondary caries or destruction of tooth tissue due to other reasons.
- The need for additional supporting and fixing elements for installing a crown.
- When preparing the abutment tooth for fixing the prosthesis.
- For the treatment of advanced forms of periodontitis and periodontal disease. Pins are installed on loose teeth for subsequent splinting.
- During tooth replantation (in rare cases).
Contraindications to the procedure are related to the condition of the tooth (severe damage, too thin walls), anatomical features and pathologies of the root canal structure, as well as concomitant diseases (caries, acute periodontitis, cyst, granuloma, abscess, mental disorders) and body conditions (pregnancy) .
General overview
Elements of the dentition are large in size and can withstand high loads, so they must be stable, otherwise they are subject to serious damage. When restoring severely damaged teeth, the filling or crown simply will not hold.
The retainer is a special design that acts as a support for installing a crown or filling. Its active use in dentistry is due to the possibility of obtaining good results at low cost.
There are several types of retainers in dentistry. The anchor type is used to completely restore a unit in case of severe destruction.
The only drawback of this restoration method is that for a quality installation, the roots must be in good condition.
The principle of restoration is that the rod is installed in the root, then covered with a crown or photopolymer materials.
This method allows you to restore not only the appearance of the organ, but also ensure its full functions. Externally, the restored element is no different from an anatomical organ.
Dental pins - what are they?
Today, doctors have a wide selection of dental pins, varying in shape, material and area of application.
Dental pin materials
- Metal.
The most popular options: titanium, brass, palladium and precious alloys. - Metal-free.
They are made from gutta-percha, ceramics, fiberglass and carbon fiber.
Forms
- screw
- cylindrical
- conical
- combined
Recovery methods
- pins for tooth crown
- tooth filling on a pin
Mounting methods
- Active.
Threaded pins are screwed into the root canal, thereby achieving a tighter fixation. However, there is a risk of perforation of the canal walls. - Passive.
A more gentle (but less reliable) method of fastening. The pin is placed inside the root canal and fixed using a special compound.
Types of dental pins
Gutta-percha
Filling dental canals with gutta-percha pins allows you to achieve predictable results, since the entire root canal cavity is filled. However, the gutta-percha pin cannot perform a full support function.
Metal pins in teeth (anchors)
Most types of anchor pins are made of metal, threaded, and installed using the active method. An anchor pin in a tooth is a classic option that is most often used for fixing crowns (a crown on a tooth on a pin). There are also modern analogues: these pins have a smooth surface and are made of ceramic, but some experts no longer call these products anchors.
Fiberglass
Fiberglass teeth pins are sufficiently strong, elastic and safe. They are almost transparent, so they are actively used to restore teeth in the smile area. The front tooth on a fiberglass post looks quite aesthetically pleasing, since the material does not stain over time and is generally quite durable.
Carbon fiber
Another type of modern and popular pins, which are as similar as possible to the structure of dental tissues. They are very durable, help to optimally distribute the load and prevent root fractures.
Attention!
To restore teeth, pin inlays are also used - these are solid structures made of metal alloys or ceramics, the base of which is installed in the root canals, and the stump imitates part of the crown.
Product and installation cost
Prices for installation of an anchor pin depend on the type of material. Standards are also taken into account - the design is made according to a template or to an individual order. The cost also depends on the clinic where the procedure is performed.
On average, a standard option in dentistry costs:
- titanium rod – 500-600 rubles;
- titanium structure with installation - approximately 850 rubles;
- damask crown – 1200 rubles;
- metal-ceramic crown – 9500 rubles;
- extension procedure – 2000 rubles.
The rod has low cost, long service life and strength. Before installation, the clinical picture, the condition of the root itself and contraindications are assessed.
How is a pin inserted into a tooth?
Installing a pin into the root of a tooth is a rather labor-intensive process, including diagnosis and preliminary treatment of canals. Further actions depend on the treatment method. The first option is to place a pin and build up the tooth using composite materials. The second option, a tooth prosthesis on a pin, involves installing a crown. Dental prosthetics with a pin is not performed. The role of the prosthesis is performed by the crown, and the pin is only an additional supporting element. Finally, the extended tooth on the pin is polished and brought into proper condition. In the case of a crown, the doctor makes sure that the prosthetics was successful.
Prices
| The doctor's consultation | |
| Titanium | From 1,250 ₽ |
| Fiberglass | From 3,000 ₽ |
Expert of the article you are reading: Svetlana Viktorovna Derevyakina Chief physician, doctor of the highest qualification category, therapist, periodontist, leading specialist of the NovaDent network
28 years
Clinical experience
Petrovsko-Razumovskaya
Verkhniye Likhobory
st. Dubninskaya, 27, building 1
+7
Free consultation with this specialist
Titanium pin in tooth
The pins located in the tooth canals can be made of titanium, but they should not be confused with implants. Dental pins belong to endodontics and partly to orthopedics, while implantation is a separate area. When a titanium pin is placed in an extracted tooth, the product is called an “implant.” This is an artificial root that is implanted in place of a lost tooth. Theoretically, a dental implant can be called a titanium post (which many people often do), but compared to classic posts, it performs a completely different function. The advantages of implantation today are undeniable: if a natural tooth is lost, it is the implant that can best restore its functionality and aesthetics.
Reviews
People's opinions regarding the use of anchor pins are striking in their diversity. Among the negative ones, there are reviews from people whose tooth with an anchor has been functioning normally for 10 years, sometimes more.
But professional specialists are skeptical about this type of structure, considering them outdated.
For readers who have had experience using anchor pins, we invite you to share it and write your reviews in the comments to this article.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter.
Tags anchor pins tooth extension pins
Did you like the article? stay tuned
Previous article
Modern methods of dental restoration in aesthetic dentistry
Next article
Learn in detail about all the nuances of dental treatment under a microscope
What to do if a tooth with a pin hurts?
Painful sensations may well occur after installation of the pin, since surrounding tissues were affected during the treatment process. Often, unpleasant sensations occur after depulpation, especially with the use of arsenic. A tooth without a nerve and a pin should not hurt, since it is dead. If a tooth hurts after installing a pin and these sensations do not go away for several days, there is a risk that the treatment was carried out with errors and complications arose. In this case, you should consult a doctor as soon as possible.
Proper care
Like any dental structure, such a pin requires careful care. It is recommended to avoid solid foods and not use toothpicks for 14 days. This significantly reduces the risk of damage to the restored tooth.
In addition, it is necessary to carefully monitor oral hygiene and use soft toothbrushes (they reduce the degree of damage to the gums when brushing). It is recommended to regularly visit the dentist and provide timely treatment for dental diseases.
Is it worth putting a pin in a tooth?
Like all dental treatment methods, pins have their drawbacks. This list is small, but these nuances must be kept in mind before agreeing to treatment.
- Allergic reactions to metal alloys are possible.
- Even with ideal treatment, a tooth with a pin will be more vulnerable than a healthy tooth. Its service life is shortened and the tooth becomes more fragile.
- The risk of root fracture increases (especially when using classic anchor pins).
On the other hand, this technique allows you to save a tooth in almost hopeless conditions.
When installing a structure fails
It is not always possible for a specialist to install an anchor pin - there are a number of contraindications to its use. In addition to the fact that the clinical picture must meet the above requirements (2-3 mm of dental tissue above the gum level and at least 2 mm of root thickness), the patient should not have the following problems: chronic inflammatory processes in the soft tissues of the oral cavity, canal obstruction, neoplasms in the root area. Contraindications also include blood clotting disorders and disruptions in the functioning of the nervous system.
It is not possible to use with severely damaged teeth.